Abstract
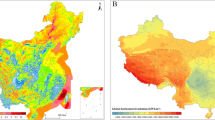
Impacts of climate warming on heating energy consumption and southern boundaries of severe cold and cold regions of China in the past 20 years are analyzed by using daily and monthly average temperature data from 590 weather stations in China and based on regulations of Heating Ventilation and Air Conditioning Design Rules (GB50019-2003) and Thermal Design Rules for Civil Building (GB50175-93) (China National Standard). The contribution of climate warming to coal saving for heating during cold seasons in major cities is calculated according to indices of coal consumption for heating in major cities during cold seasons defined in Energy Conservation Design Standard for New Heating Residential Buildings (JCJ26-95). Comparing with the period before 1980, southern boundaries of severe cold and cold regions shift toward north up to 2 degrees in latitude since the mid-1980s. Theoretically, climate warming could contribute to 5%–10% coal savings for heating since the mid-1980s in major cities, and even more since the mid-1990s.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Long W D. Sustainable development of China’s HVAC industry. J HV&AC (in Chinese), 1999, 29(3): 25–30
Yi Y H, Wang S W. Sudden global climate warming in the 1980s. Chin Sci Bull (in Chinese), 1992, 37(6): 528–531
Fu C B, Wang Q. The catastrophic phenomena in the long-term variation of South Asia summer monsoon and its synchronism with global rapid warming. Sci China Ser B (in Chinese), 1991, 21(6): 662–672
Ren G Y, Xu M Z, Chu Z Y, et al. Changes of surface air temperature in China during 1951–2004. Clim Environ Res (in Chinese), 2005, 10(4): 717–727
Chen L, Fang X M, Fang X Q, et al. Impacts of climate warming on heating climatic conditions and energy requirements over China in the past 20 years. J Nat Resour (in Chinese), 2006, 21(4): 590–597
China Academy of Building Research. Energy Conservation Design Standard for New Heating Residential Buildings (JCJ26-95) (in Chinese). Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 1996. 1–58
Ministry of Construction P R China. Code for Thermal Design of Civil Buildings (GB50176-93)(in Chinese). Beijing: China Planning Press, 1993. 5–7
Wei F Y, Cao H X, Wang L P. Climatic warming process during 1980s–1990s in China. J Appl Meteorol Sci (in Chinese), 2003, 14(1): 79–86
Zhou Z J. Changes of winter temperature and heating analysis in China. J Appl Meteorol Sci (in Chinese), 2000, 11(2): 251–252
Ministry of Construction P R China. Code for Design of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (GB50019-2003) (in Chinese). Beijing: China Planning Press, 2003. 25–35
Thom H C S. Seasonal degree-day statistics for the United States. Mon Wea Rev, 1952, 80(9): 143–147
Thom H C S. The rational relationship between heating degree days and temperature. Mon Wea Rev, 1954, 82(1): 1–6
Thom H C S. Normal degree-days above any base by the universal truncation coefficient. Mon Wea Rev, 1966, 94(7): 461–465
Durmayaz A, Kadıoǧlu M. Heating energy requirements and fuel consumptions in the biggest city centers of Turkey. Energy Conv Manag, 2003, 44: 1177–1192
Heller A J. Heat-load modelling for large systems. Appl Energy, 2002, 72: 371–387
Bulut H, Büyükalaca O, Yılmaz T. New outdoor heating design data for Turkey. Energy, 2003, 28: 1133–1150
Sarak H, Satman A. The degree-day method to estimate the residential heating natural gas consumption in Turkey: A case study. Energy, 2003, 28: 929–939
Büyükalaca O, Bulut H, Yılmaz T. Analysis of variable-base heating and cooling degree-days for Turkey. Appl Energy, 2001, 69: 269–283
Kadıoǧlu M, Sen Z. Degree-day formulations and application in Turkey. J Appl Meteorol, 1999, 38: 837–846
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by “Climate Change Research Project”, China Meteorological Administration (Grant No. CCSF2007-43)
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Fang, X. & Li, S. Impacts of climate warming on heating energy consumption and southern boundaries of severe cold and cold regions in China. CHINESE SCI BULL 52, 2854–2858 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-0386-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-0386-7