Abstract
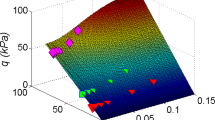
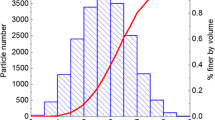
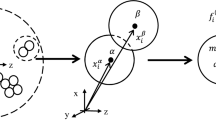
The quasi-solid-fluid phase transition of granular materials is closely related to the shear rate and solid concentration in addition to their intrinsic properties. The contact duration and the coordination number are two important temporal-spatial parameters to describe the granular interaction in phase transition. In this study, characteristics of the contact duration and the coordination number associated with the transition processes are determined using a 3D discrete element model under different shear rates and concentrations. The resulting macroscopic stress and strain-rate relations are discussed. The temporal and spatial parameters provide a linkage between the macroscopic constitutive law and interparticle micromechanics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Orpe, A. V., Khakhar, D. V., Solid-fluid transition in a granular shear flow, Physical Review Letters, 2004, 93(6): 068001.
Metcalfe, G., Tennakoon, S. G. K., Kondic, L. et al., Granular friction, Coulomb failure, and the fluid-solid transition for horizontally shaken granular materials, Physical Review E, 2002, 65: 031302.
Hartley, R. R., Behringer, R. P., Logarithmic rate dependence of force networks in sheared granular materials, Nature, 2003, 421: 928–931.
Zhang, D. Z., Rauenzahn, R. M., Stress relaxation in dense and slow granular flows, Journal of Rheology, 2000, 44(5): 1019–1041.
Miehe, C., Dettmar, J., A framework for micro-macro transitions in periodic particle aggregates of granular materials, Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 193: 225–256.
Goldenberg, C., Goldhirsch I., Force chains, microelasticity, and macroelasticity, Physical Review Letters, 2002, 89(8): 084302.
Sibert, L. E., Landry, J. W., Grest, G. S., Granular flow down a rough inclined plane: Transition between thin and thick piles, Physics of Fluids, 2003, 15(1): 1–10.
Mueggenburg, N. W., Behavior of granular materials under cyclic shear, Physical Review E, 2005, 71: 031301.
Wu, Q., Hu, M., Advances on dynamic modeling and experimental studies for granular flow, Advances in Mechanics (in Chinese), 2002, 32(2): 250–258.
Hou, M., Chen, W., Zhang, T. et al., Global nature of dilute-to-dense transition of granular flows in a 2D channel, Physical Review Letters, 2003, 91(20): 204301.
Shen, H. H., Sankaran, B., Internal length and time scales in a simple shear granular flow, Physical Review E, 2004, 70: 051308.
Xu, Y., Sun, Q., Zhang, L., Huang, W., Advances in discrete element methods for particulate materials, Advances in Mechanics (in Chinese), 2003, 33(2): 251–260.
Campbell, C., Granular shear flows at the elastic limit, Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2002, 465: 261–291.
Sun, G., Li, J., Gong, F. et al., Stochastic analysis of particle-fluid two-phase flows, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45(9): 806–810.
Tang, Z., Three-dimensional DEM theory and its application to impact mechanics, Science in China, Series E, 2001, 44(6): 561–571.
Ball, R. C., Blumenfeld, R., Stress field in granular systems: Loop forces and potential formation, Physical Review Letters, 2002, 88(11): 115505.
Babic, M., Shen, H. H., Shen, H. T., The stress tensor in granular shear flows of uniform, deformable disks at high solids concentrations, Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1990, 219: 81–118.
Zhang, D. Z., Rauenzahn, R. M., A viscoelstic model for dense granular flows, Journal of Rheology, 1997, 41(6): 1275–1298.
To, K., Lai, P. Y., Pak, H. K., Jamming of granular flow in a two-dimensional hopper, Physical Review Letter, 2001, 86(1): 71–74.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, S., Shen, H.H. Characteristics of temporalspatial parameters in quasisolid-fluid phase transition of granular materials. CHINESE SCI BULL 51, 646–654 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-0646-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-0646-y