Abstract
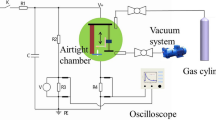
The effects of ambient atmospheres on the arc erosion behaviors of Ti3SiC2 cathodes were investigated at 5.5 kV in argon, nitrogen, air, and oxygen. The mass loss of the cathodes increased in the order of argon, nitrogen, air, and oxygen and the morphologies were measured by 3D laser scanning confocal microscope with a gradual blooming phenomenon. Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy were employed to detect the components of erosion regions. The erosion-chemical products mainly consisted of TiNx in nitrogen, TiNx, TiO2 and SiO2 in air, TiO2 and SiO2 in oxygen. The arc energy was responsible for the arc erosion characteristics in different atmospheres.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yanabu S, Zaima E. Power switching technology in Japan. In: 1st International Conference on Electric Power Equipment — Switching Technology, Xi’an, China, 2011. 1–6
Kesim M T, Yu H, Sun Y, et al. Corrosion, oxidation, erosion and performance of Ag/W-based circuit breaker contacts: A review. Corrosion Sci, 2018, 135: 12–34
Huang X C, Feng Y, Qian G, et al. Arc corrosion behavior of CuTi3AlC2 composites in air atmosphere. Sci China Technol Sci, 2017, 61: 551–557
Slade P G. Electrical contacts principles and applications. 2nd ed. New York: Taylor & Francis Group, 2014. 880–889
Hasegawa M, Imai K, Makimoto J, et al. An experimental study on operating characteristics of Ag, Pd and Cu contacts in argon atmosphere. In: Proceedings of the 49th IEEE Holm Conference on Electrical Contacts, DC, USA, 2003. 190–197
Xin C, Wu J, Bin L. Characteristic analysis of dc arc interrupting under hydrogen and air (in Chinese). Low Volt App, 2011, 10: 6–9
Ghorui S, Meher K C, Kar R, et al. Unique erosion features of hafnium cathode in atmospheric pressure arcs of air, nitrogen and oxygen. J Phys D-Appl Phys, 2016, 49: 295201
Grogg D, Schrank C. Impact of the gas environment on the electric arc. In: IEEE 62nd Holm Conference on Electrical Contacts (Holm), Horgen, CHE, 2016. 125–128
Barsoum M W. The Mn+1AXn phases: A new class of solids. Prog Solid State Chem, 2000, 28: 201–281
Zhang H, Su R, Shi L, et al. Structural changes of Ti3SiC2 induced by helium irradiation with different doses. Appl Surf Sci, 2018, 434: 1210–1216
Dmitruk A, Żak A, Naplocha K, et al. Development of pore-free TiAl-C MAX/Al-Si MMC composite materials manufactured by squeeze casting infiltration. Mater Charact, 2018, 146: 182–188
Barsoum M W, El-Raghy T. Synthesis and characterization of a remarkable ceramic: Ti3SiC2. J Am Ceramic Soc, 1996, 79: 1953–1956
Patel M K, Tallman D J, Valdez J A, et al. Effect of helium irradiation on Ti3AlC2 at 500°C. Scripta Mater, 2014, 77: 1–4
Tan Y, Luo H, Zhang H, et al. High-temperature electromagnetic interference shielding of layered Ti3AlC2 ceramics. Scripta Mater, 2017, 134: 47–51
Huang X, Feng Y, Qian G, et al. Influence of breakdown voltages on arc erosion of a Ti3AlC2 cathode in an air atmosphere. Ceramics Int, 2017, 43: 10601–10605
Zhang P, Ngai T L, Xie H, et al. Erosion behaviour of a Ti3SiC2 cathode under low-current vacuum arc. J Phys D-Appl Phys, 2013, 46: 395202
Huang X, Feng Y, Qian G, et al. Erosion behavior of Ti3AlC2 cathode under atmosphere air arc. J Alloys Compd, 2017, 727: 419–427
Kalin M. Influence of flash temperatures on the tribological behaviour in low-speed sliding: A review. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2004, 374: 390–397
Kubo S, Kato K. Effect of arc discharge on the wear rate and wear mode transition of a copper-impregnated metallized carbon contact strip sliding against a copper disk. Tribol Int, 1999, 32: 367–378
Xin C, Wu J, Liu B. Investigation of DC arc in hydrogen and air. In: 2nd International Conference on Electric Power Equipment — Switching Technology, Matsue, Japan, 2013
Wei H, Wu M, Dong Z, et al. Composition, microstructure and SERS properties of titanium nitride thin film prepared via nitridation of solgel derived titania thin films. J Raman Spectrosc, 2017, 48: 578–585
Kuznetsov M V, Zhuravlev J F, Gubanov V A. XPS analysis of adsorption of oxygen molecules on the surface of Ti and TiNx films in vacuum. J Electron Spectr Related Phenomena, 1992, 58: 169–176
Sprenger D, Bach H, Meisel W, et al. XPS study of leached glass surfaces. J Non-Crystalline Solids, 1990, 126: 111–129
Lange F, Schmelz H, KnÖzinger H. An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of oxides of arsenic supported on TiO2. J Electron Spectr Related Phenomena, 1991, 57: 307–315
Wei X, Yu D, Sun Z, et al. Arc characteristics and microstructure evolution of W-Cu contacts during the vacuum breakdown. Vacuum, 2014, 107: 83–89
Buchholt K, Ghandi R, Domeij M, et al. Ohmic contact properties of magnetron sputtered Ti3SiC2 on n- and p-type 4H-silicon carbide. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 98: 042108
Wenger C, Lukosius M, Costina I, et al. Investigation of atomic vapour deposited TiN/HfO2/SiO2 gate stacks for mosfet devices. Microelectron Eng, 2008, 85: 1762–1765
Sugimoto Y, Kajiwara M, Yamamoto K, et al. Dependences of effective work functions of TaN on HfO2 and SiO2 on post-metallization anneal. Thin Solid Films, 2008, 517: 204–206
Sohn S D, Kim S H, Kwak S K, et al. Defect-associated adsorption of monoethanolamine on TiO2(1 1 0): An alternative way to control the work function of oxide electrode. Appl Surf Sci, 2019, 467–468: 1213–1218
Xu J, Li S, Zeng Z, et al. Heat capacity, density, vapor pressure, and enthalpy of vaporization of isoamyl DL-lactate. J Chem Eng Data, 2019, 64: 3793–3798
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51871085, 51571078), and the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (Grant Nos. 1908085QE218, 1808085ME122).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Z., Feng, Y., Zhao, H. et al. Effects of different atmospheres on the arc erosion behaviors of Ti3SiC2 cathodes. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 64, 620–628 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-019-1552-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-019-1552-x