Abstract
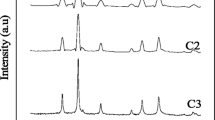
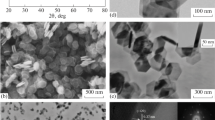
Monodispersed magnetite Fe3O4 and hematite α-Fe2O3 nanocrystals have been grown in co-solvents of alcohol and water. Either the shape or the size of the nanocrystals could be easily controlled. Both the phases and nanostructures have been characterized by powder X-ray diffraction patterns and electron microscopy. The magnetic and catalytic properties of these products were investigated and compared with each other. The obtained results clearly demonstrate that these iron oxide nanocrystals are soft ferromagnetic at room temperature and α-Fe2O3 has a more effective catalytic property on the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate than Fe3O4. Based on the experimental data, it is proposed that the magnetic and catalytic properties of these nanocrystals are dependent not only on the size and shape, but also on the surface structure of the nanocrystals. The nanoplates with significant anisotropic nanostructure demonstrate a highly enhanced performance as compared to nanoparticles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thompson DA, Best JS. The future of magnetic data storage technology. Ibm J Res Dev, 2000, 44: 311–322
Mitra S, Poizot P, Finke A, Tarascon JM. Growth and electrochemical characterization versus lithium of Fe3O4 electrodes made via electrodeposition. Adv Funct Mater, 2006, 16: 2281–2287
Zhou J, Song H, Chen X, Zhi L, Yang S, Huo J, Yang W. Carbon-encapsulated metal oxide hollow nanoparticles and metal oxide hollow nanoparticles: A general synthesis strategy and its application to lithium-ion batteries. Chem Mater, 2009, 21: 2935–2940
Hwang SO, Kim CH, Myung Y, Park SH, Park J, Kim J, Han CS, Kim JY. Synthesis of vertically aligned manganese-doped Fe3O4 nanowire arrays and their excellent room-temperature gas sensing ability. J Phys Chem C, 2008, 112: 13911–13916
Chen J, Xu L, Li W, Gou X. alpha-Fe2O3 nanotubes in gas sensor and lithium-ion battery applications. Adv Mater, 2005, 17: 582–586
Dobson J. Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Drug Dev Res, 2006, 67: 55–60
Alexiou C, Schmid RJ, Jurgons R, Kremer M, Wanner G, Bergemann C, Huenges E, Nawroth T, Arnold W, Parak FG. Targeting cancer cells: Magnetic nanoparticles as drug carriers. Eur Biophys J Biophy, 2006, 35: 446–450
Oswald P, Clement O, Chambon C, Schouman-Claeys E, Frija G. Liver positive enhancement after injection of superparamagnetic nanoparticles: Respective role of circulating and uptaken particles. Magn Reson Imaging, 1997, 15: 1025–1031
Wiltshire MCK, Pendry JB, Young IR, Larkman DJ. Microstructured magnetic materials for RF flux guides in magnetic resonance imaging. Science, 2001, 291: 849–851
Niu M, Huang F, Cui L, Huang P, Yu Y, Wang Y. Hydrothermal synthesis, structural characteristics and enhanced photocatalysis of SnO2/α-Fe2O3 semiconductor nanoheterostructures. ACS Nano, 2010, 4: 681–688
Liu Q, Cui Z, Ma Z, Bian S, Song W, Wan L. Morphology control of Fe2O3 nanocrystals and their application in catalysis. Nanotechnology, 2007, 18: 385605
Shaikh NS, Enthaler S, Junge K, Beller M. Iron-catalyzed enantioselective hydrosilylation of ketones. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2008, 47: 2497–2501
Zheng Y, Cheng Y, Wang Y, Bao F, Zhou L, Wei X, Zhang Y, Zheng Q. Quasicubic alpha-Fe2O3 nanoparticles with excellent catalytic performance. J Phys Chem B, 2006, 110: 3093–3097
Zhang L, Qiao S, Jin Y, Yang H, Budihartono S, Yan F, Wang X, Hao h, Lu G. Fabrication and size-selective bioseparation of magnetic silica nanospheres with highly ordered periodic mesostructure. Adv Funct Mater, 2008, 18: 3203–3212
Xu C, Sun S. Monodisperse magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Polym Int, 2007, 56: 821–826
Kim CY, Escuadro AA, Stair PC, Bedzyk MJ. Atomic-scale view of redox-induced reversible Changes to a metal-oxide catalytic surface: VOx/r-Fe2O3 (0001). J Phys Chem C, 2007, 111: 1874–1877
Morales MP, Veintemillas-Verdaguer S, Montero MI, Serna CJ, Roig A, Casas L, Martinez B, Sandiumenge F. Surface and internal spin canting in gamma-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Chem Mater, 1999, 11: 3058–3064
Tan Y, Zhuang Z, Peng Q, Li Y. Room-temperature soft magnetic iron oxide nanocrystals: Synthesis, characterization, and size-dependent magnetic properties. Chem Mater, 2008, 20: 5029–5034
Guardiaa P, Batlle-Brugala B, Rocab AG, Iglesiasa O, Moralesb MP, Sernab CJ, Labartaa A, Batlle X. Surfactant effects in magnetite nanoparticles of controlled size. J Magn Magn Mater, 2007, 316: e756–e759
Hyeon T, Lee SS, Park J, Chung Y, Na HB. Synthesis of highly crystalline and monodisperse maghemite nanocrystallites without a size-selection process. J Am Chem Soc, 2001, 123: 12798–12801
Wang W, Howe JY, Gu B. Structure and morphology evolution of hematite (alpha-Fe2O3) nanoparticles in forced hydrolysis of ferric chloride. J Phys Chem C, 2008, 112: 9203–9208
Liang X, Wang X, Zhuang J, Chen Y, Wang D, Li Y. Synthesis of nearly monodisperse iron oxide and oxyhydroxide nanocrystals. Adv Funct Mater, 2006, 16: 1805–1813
Chaudhari NK, Kim HC, Sonc D, Yu JS. Easy synthesis and characterization of single-crystalline hexagonal prism-shaped hematite α-Fe2O3 in aqueous media. CrystEngComm, 11: 2264–2267
Zhang D, Zhang X, Ni X, Song J, Zheng H. Fabrication and characterization of Fe3O4 octahedrons via an EDTA-assisted route. Cryst Growth Des, 2007, 7: 2117–2119
Shavel A, Rodriguez-Gonzalez B, Spasova M, Farle M, Liz-Marzan LM. Synthesis and characterization of iron/iron oxide core/shell nanocubes. Adv Funct Mater, 2007, 17: 3870–3876
Gao G, Liu X, Shi R, Zhou K, Shi Y, Ma R, Takayama-Muromachi E, Qiu G. Shape-controlled synthesis and magnetic properties of monodisperse Fe3O4 nanocubes. Cryst Growth Des, 2010, 10: 2888–2894
Guardia P, Batlle-Brugal B, Roca AG, Iglesias O, Morales MP, Serna CJ, Labarta A, Batlle X. Surfactant effects in magnetite nanoparticles of controlled size. J Magn Magn Mater, 2007, 316: E756–E759
Roca AG, Morales MP, O’Grady K, Serna CJ. Structural and magnetic properties of uniform magnetite nanoparticles prepared by high temperature decomposition of organic precursors. Nanotechnology, 2006, 17: 2783–2788
Chen L, Yang X, Chen J, Liu J, Wu H, Zhan H, Liang C, Wu M. Finely continuous shape-tuning and optical properties of hematite nanocrystals. Inorg Chem, 2010, 49: 8411–8420
He Y, Wang S, Li C, Miao Y, Wu Z, Zou B. Synthesis and characterization of functionalized silica-coated Fe3O4 superparamagnetic nanocrystals for biological applications. J Phys D: Appl Phys, 2005, 38: 1342
O’Grady K, Bradbury A. Particle size analysis in ferrofluids. J Magn Magn Mater, 1983, 39: 91–94
Lin XM, Samia ACS. Synthesis, assembly and physical properties of magnetic nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater, 2006, 305: 100–109
Zhang Y, Ying C, Dong L. One-step synthesis and properties of urchin-like PS/α-Fe2O3 composite hollow microspheres. Nanotechnology, 2007, 18: 435608
Liu L, Kou H, Mo W, Liu H, Wang Y. Surfactant-assisted synthesis of α-Fe2O3 nanotubes and nanorods with shape-dependent magnetic properties. J Phys Chem B, 2006, 110: 15218–15223
Linderoth S, Hendriksen PV, Bodker F, Wells S, Davies K, Charles SW, Morup S. On spin-canting in maghemite particles. J Appl Phys, 1994, 75: 6583–6585
Roca AG, Morales MP, O’Grady K, Serna CJ. Structural and magnetic properties of uniform magnetite nanoparticles prepared by high temperature decomposition of organic precursors. Nanotechnology, 2006, 17: 2783
Xu H, Wang X, Zhang L. Selective preparation of nanorods and micro-octahedrons of Fe2O3 and their catalytic performances for thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Powder Technol, 2008, 185: 176–180
Galwey AK, Mohamed MA. Nitryl perchlorate as the essential intermediate in the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Nature, 1984, 311: 642–645
Yin J, Lu Q, Yu Z, Wang J, Pang H, Gao F. Hierarchical ZnO nanorod-assembled hollow superstructures for catalytic and photoluminescence applications. Cryst Growth Des, 2010, 10: 40–43
Singh G, Kapoor IPS, Dubey S, Siril PF. Kinetics of thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate with nanocrystals of binary transition metal ferrites. Propellants Explos Pyrotech, 2009, 34: 72–77
Vyazovkin S, Wight CA. Kinetics of thermal decomposition of cubic ammonium perchlorate. Chem Mater, 1999, 11: 3386–3393
Ma Z. Effect of Fe2O3 in Fe2O3/AP composite particles on thermal decomposition of AP and on burning rate of the composite propellant. Propellants Explos Pyrotech, 2006, 31: 447–451
Reid DL, Russo AE, Carro RV, Stephens MA, LePage AR, Spalding TC, Petersen EL, Seal S. Nanoscale additives tailor energetic materials. Nano Lett, 2007, 7: 2157–2161
Xie X, Li Y, Liu Z, Haruta M, Shen W. Low-temperature oxidation of CO catalysed by Co3O4 nanorod. Nature, 458: 746–749
Cao M, Liu T, Gao S, Sun G, Wu X, Hu C, Wang Z. Single-crystal dendritic micro-pines of magnetic alpha-Fe2O3: Large-scale synthesis, formation mechanism, and properties. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2005, 44: 4197–4201
Kapoor IPS, Srivastava P, Singh G. Nanocrystalline transition metal oxides as catalysts in the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Propellants Explos Pyrotech, 2009, 34: 351–356
Patil PR, Krishnamurthy VN, Joshi SS. Effect of nano-copper oxide and copper chromite on the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Propellants Explos Pyrotech, 2008, 33: 266–270
Sun X, Qiu X, Li L, Li G. ZnO twin-cones: Synthesis, photoluminescence, and catalytic decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Inorg Chem, 2008, 47: 4146–4152
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Liu, W., Chen, J. et al. Facile shape and size-controlled growth of uniform magnetite and hematite nanocrystals with tunable properties. Sci. China Chem. 54, 923–929 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-011-4286-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-011-4286-y