Abstract
Purpose
Since the mid-2010s, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) analogs made for substance abuse have periodically emerged. In this case, three pieces of blotter paper labeled “1D-LSD” and presumably impregnated with this LSD analog, were seized. Several websites indicate that 1D-LSD is 1-(1,2-dimethylcyclobutane-1-carbonyl)-LSD. Because this analog is much more difficult to synthesize than previously reported LSD analogs, we doubted that the blotter paper contained 1D-LSD. Herein, we determined the structure of the absorbed compound.
Methods
One of the seized specimens was extracted and analyzed using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS), liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS), high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS), and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to estimate the extract components. The estimated compound was then synthesized, yielding an authentic standard. The contents of the seized specimens were identified using authentic standard analysis with GC/MS, LC/MS, and NMR spectroscopy.
Results
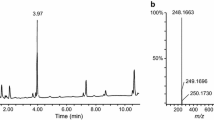
Instrumental analyses confirmed the active compound to be 1-(thiophene-2-carbonyl)-LSD, which was inconsistent with the labeling on drug-infused blotter paper.
Conclusion
As in this case, similar blotter paper analyses should consider the possibility of a mismatch between the label and ingredient. To the authors’ knowledge, this is the first case report in which 1-(thiophene-2-carbonyl)-LSD was seized and the first seizure of an LSD analog in which an aromatic carboxylic acid had been condensed to LSD. This type of lysergamide may become prevalent in the near future, and we should remain alert for newly appearing lysergamides.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stoll A, Hofmann A (1943) Partialsynthese von alkaloiden vom typus des ergobasins. (6. Mitteilung über Mutterkornalkaloide). Helv Chim Acta 26:944–965. https://doi.org/10.1002/hlca.19430260326
EMCDDA. European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA). EMCDDA-Europol 2015 Annual Report on the implementation of Council Decision 2005/387/JHA. Europol. 2016. http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/system/files/publications/4724/TDAN17001ENN_PDFWEB.pdf. Accessed 9 Feb 2022
Troxler F, Hofmann A (1957) Substitutionen am ringsystem der lysergsäure I. substitutionen am indol-stickstoff. 43. Mitteilung über Mutterkornalkaloide Helv Chim Acta 40:1706–1720. https://doi.org/10.1002/hlca.19570400619
Tanaka R, Kawamura M, Hakamatsuka T, Kikura-Hanajiri R (2020) Identification and analysis of LSD derivatives in illegal products as paper sheet. Yakugaku Zassi 140:739–750. https://doi.org/10.1248/yakushi.19-00230
Brandt SD, Kavanagh PV, Westphal F, Stratford A, Elliott SP, Hoang K, Wallach J, Halberstadt AL (2016) Return of the lysergamides. Part I: analytical and behavioural characterization of 1-propionyl- d -lysergic acid diethylamide (1P-LSD). Drug Test Anal 8:891–902. https://doi.org/10.1002/dta.1884
Tanaka R, Kawamura M, Hakamatsuka T, Kikura-Hanajiri R (2020) Identification of LSD derivatives, 1cP-LSD, MIPLA and 1B-LSD in illegal products as paper sheet. Yakugaku Zassi 140:1405–1413. https://doi.org/10.1248/yakushi.20-00124
Brandt SD, Kavanagh PV, Westphal F, Stratford A, Elliott SP, Dowling G, Wallach J, Halberstadt AL (2019) Return of the lysergamides. Part V: analytical and behavioural characterization of 1-butanoyl-d-lysergic acid diethylamide (1B-LSD). Drug Test Anal 11:1122–1133. https://doi.org/10.1002/dta.2613
Brandt SD, Kavanagh PV, Westphal F, Stratford A, Odland AU, Klein AK, Dowling G, Dempster NM, Wallach J, Passie T, Halberstadt AL (2020) Return of the lysergamides. Part VI: Analytical and behavioural characterization of 1-cyclopropanoyl-d-lysergic acid diethylamide (1CP-LSD). Drug Test Anal 12:812–826. https://doi.org/10.1002/dta.2789
Tanaka R, Kawamura M, Mizutani S, Kikura-Hanajiri R (2023) Identification of LSD analogs, 1cP-AL-LAD, 1cP-MIPLA, 1V-LSD and LSZ in sheet products. Forensic Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-023-00661-1
Brandt SD, Kavanagh PV, Westphal F, Pulver B, Morton K, Stratford A, Dowling G, Halberstadt AL (2022) Return of the lysergamides. Part VII: analytical and behavioural characterization of 1-valeroyl-d-lysergic acid diethylamide (1V-LSD). Drug Test Anal 14(4):733–740. https://doi.org/10.1002/dta.3205
Halberstadt AL, Chatha M, Klein AK, McCorvy JD, Meyer MR, Wagmann L, Stratford A, Brandt SD (2020) Pharmacological and biotransformation studies of 1-acyl-substituted derivatives of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Neuropharmacology 172:107856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.107856
Wikipedia 1D-LSD. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/1D-LSD. Accessed 14 Apr 2023
Bassett RA, Chain EB, Corbett K (1973) Biosynthesis of ergotamine by Claviceps purpurea (Fr.) Tul. Biochem J 134:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj1340001
Nichols DE, Frescas S, Marona-Lewicka D, Kurrasch-Orbaugh DM (2002) Lysergamides of Isomeric 2,4-dimethylazetidines map the binding orientation of the diethylamide moiety in the potent hallucinogenic agent N, N-diethyllysergamide (LSD). J Med Chem 45:4344–4349. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm020153s
Okada Y, Segawa H, Yamamuro T, Kuwayama K, Tsujikawa K, Kanamori T, Iwata YT (2023) Decomposition behavior of 1-Acyl-LSD in gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS). Japanese J Forensic Sci Technol 28:834. https://doi.org/10.3408/jafst.834
Illi VO (1979) Phasentransfer-katalysierte N-acylierung von Indol. Synthesis 1979:387–388. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-1979-28695
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no financial or other relations that could lead to a conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file 1: Figure S1.
1H NMR spectrum of synthesized 1T-LSD. Figure S2. 13C NMR spectrum of synthesized 1T-LSD. Figure S3. 1H-13C HMBC spectrum (full-scale) of synthesized 1T-LSD. Figure S4. 1H-13C HMBC spectrum (zoom) of synthesized 1T-LSD. Figure S5. TIC and EIC at m/z 433 by GC/MS for a specimen 1, b specimen 2, c specimen 3, and d synthesized 1T-LSD. Figure S6. Mass spectra of the peak with a retention time of 26.2 min by GC/MS for a specimen 1, b specimen 2, c specimen 3, and d synthesized 1T-LSD. Figure S7. TIC by LC/MS of a specimen 1, b specimen 2, c specimen 3, and d synthesized 1T-LSD. Figure S8. Mass spectra of the peak with a retention time of 9.3 min by LC/MS for a specimen 1, b specimen 2, c specimen 3, and d synthesized 1T-LSD.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Okada, Y., Ueno, K., Nishiwaki, N. et al. Identification of 1-(thiophene-2-carbonyl)-LSD from blotter paper falsely labeled “1D-LSD”. Forensic Toxicol 42, 93–101 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-023-00668-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-023-00668-8