Abstract
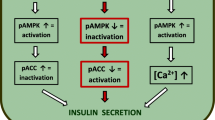
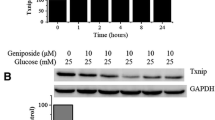
Our previous work showed that geniposide affected glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) via regulating glucose uptake and metabolism in pancreatic β cells; however, the molecular mechanisms remain largely unknown. Substantial evidence suggests that activation of 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) plays a central role in GSIS. Here, we aim to determine the role of AMPK on geniposide-regulated GSIS in rat pancreatic INS-1 cells. The results demonstrated that 6-[4-(2-piperidin-1-yletoxy)-phenyl]-3-pyridin-4-yl-pyrazolo[1,5-α] pyrimidine (Compound C; an AMPK inhibitor) significantly attenuated the effects of geniposide on glucose uptake, energy metabolism, and insulin secretion in INS-1 cells. We also observed that geniposide induced phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), a marker of AMPK activity, in a time-dependent manner in INS-1 cells; however, in the presence of Compound C, the influence of geniposide on ACC phosphorylation was obviously inhibited. Furthermore, the knockdown of AMPK protein with AMPK siRNA treatment decreased the effects of geniposide on glucose uptake, adenosine triphosphate production, and GSIS. All these data indicate that AMPK plays an essential role in geniposide-regulated GSIS in pancreatic β cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J (2001) Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature 414:782–787
Paneni F, Costantino S (2015) Mechanisms-based therapeutic strategies in type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther 5:340–342
Stumvoll M, Goldstein BJ, van Haeften TW (2005) Type 2 diabetes: principles of pathogenesis and therapy. Lancet 365:1333–1346
DeFronzo RA (1997) Insulin resistance: a multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidaemia and atherosclerosis. Neth J Med 50:191–197
Woerle HJ, Carneiro L, Derani A, Goke B, Schirra J (2012) The role of endogenous incretin secretion as amplifier of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in healthy subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 61:2349–2358
Rutter GA, Pullen TJ, Hodson DJ, Martinez-Sanchez A (2015) Pancreatic beta-cell identity, glucose sensing and the control of insulin secretion. Biochem J 466:203–218
Gerdes JM, Christou-Savina S, Xiong Y, Moede T, Moruzzi N, Karlsson-Edlund P, Leibiger B, Leibiger IB, Ostenson CG, Beales PL, Berggren PO (2014) Ciliary dysfunction impairs beta-cell insulin secretion and promotes development of type 2 diabetes in rodents. Nat Commun 5:5308
Zou CY, Gong Y, Liang J (2016) Metabolic signaling of insulin secretion by pancreatic beta-cell and its derangement in type 2 diabetes. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20:391
Ilkova H, Glaser B, Tunckale A, Bagriacik N, Cerasi E (1997) Induction of long-term glycemic control in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients by transient intensive insulin treatment. Diabetes Care 20:1353–1356
Chen JY, Wu H, Li H, Hu SL, Dai MM, Chen J (2015) Anti-inflammatory effects and pharmacokinetics study of geniposide on rats with adjuvant arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol 24:102–109
Guo L, Zheng X, Liu J, Yin Z (2016) Geniposide suppresses hepatic glucose production via AMPK in HepG2 cells. Biol Pharm Bull 39:484–491
Liu HT, He JL, Li WM, Yang Z, Wang YX, Yin J, Du YG, Yu C (2010) Geniposide inhibits interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 production in lipopolysaccharide-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells by blocking p38 and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Inflamm Res 59:451–461
Wu SY, Wang GF, Liu ZQ, Rao JJ, Lu L, Xu W, Wu SG, Zhang JJ (2009) Effect of geniposide, a hypoglycemic glucoside, on hepatic regulating enzymes in diabetic mice induced by a high-fat diet and streptozotocin. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30:202–208
Kojima K, Shimada T, Nagareda Y, Watanabe M, Ishizaki J, Sai Y, Miyamoto K, Aburada M (2011) Preventive effect of geniposide on metabolic disease status in spontaneously obese type 2 diabetic mice and free fatty acid-treated HepG2 cells. Biol Pharm Bull 34:1613–1618
Liu J, Yin F, Zheng X, Jing J, Hu Y (2007) Geniposide, a novel agonist for GLP-1 receptor, prevents PC12 cells from oxidative damage via MAP kinase pathway. Neurochem Int 51:361–369
Liu J, Zheng X, Yin F, Hu Y, Guo L, Deng X, Chen G, Jiajia J, Zhang H (2006) Neurotrophic property of geniposide for inducing the neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells. Int J Dev Neurosci 24:419–424
Liu JH, Yin F, Guo LX, Deng XH, Hu YH (2009) Neuroprotection of geniposide against hydrogen peroxide induced PC12 cells injury: involvement of PI3 kinase signal pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30:159–165
Zhang Y, Yin F, Liu J, Liu Z, Guo L, Xia Z, Zidichouski J (2015) Geniposide attenuates insulin-deficiency-induced acceleration of beta-amyloidosis in an APP/PS1 transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int 89:7–16
Guo LX, Xia ZN, Gao X, Yin F, Liu JH (2012) Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor plays a critical role in geniposide-regulated insulin secretion in INS-1 cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33:237–241
Liu J, Guo L, Yin F, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Wang Y (2013) Geniposide regulates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion possibly through controlling glucose metabolism in INS-1 cells. PLoS One 8:e78315
Guo LX, Liu JH, Yin F (2014) Regulation of insulin secretion by geniposide: possible involvement of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate kinase. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 18:1287–1294
Guo L, Liu CY, Yin F, Liu JH (2016) Possible role of AMPK/SIRT signaling on energy balance in geniposide-treated INS-1 cells. Med Chem 6:33–38
Coughlan KA, Valentine RJ, Ruderman NB, Saha AK (2014) AMPK activation: a therapeutic target for type 2 diabetes? Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 7:241–253
Viollet B, Lantier L, Devin-Leclerc J, Hebrard S, Amouyal C, Mounier R, Foretz M, Andreelli F (2009) Targeting the AMPK pathway for the treatment of Type 2 diabetes. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 14:3380–3400
Zhang BB, Zhou G, Li C (2009) AMPK: an emerging drug target for diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Cell Metab 9:407–416
Peterson JM, Aja S, Wei Z, Wong GW (2012) CTRP1 protein enhances fatty acid oxidation via AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) inhibition. J Biol Chem 287:1576–1587
Fu A, Eberhard CE, Screaton RA (2013) Role of AMPK in pancreatic beta cell function. Mol Cell Endocrinol 366:127–134
Salt IP, Johnson G, Ashcroft SJ, Hardie DG (1998) AMP-activated protein kinase is activated by low glucose in cell lines derived from pancreatic beta cells, and may regulate insulin release. Biochem J 335(Pt 3):533–539
da Silva Xavier G, Leclerc I, Varadi A, Tsuboi T, Moule SK, Rutter GA (2003) Role for AMP-activated protein kinase in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and preproinsulin gene expression. Biochem J 371:761–774
Leclerc I, Rutter GA (2004) AMP-activated protein kinase: a new beta-cell glucose sensor?: regulation by amino acids and calcium ions. Diabetes 53(Suppl 3):S67–S74
Mantovani J, Roy R (2011) Re-evaluating the general(ized) roles of AMPK in cellular metabolism. FEBS Lett 585:967–972
Gleason CE, Lu D, Witters LA, Newgard CB, Birnbaum MJ (2007) The role of AMPK and mTOR in nutrient sensing in pancreatic beta-cells. J Biol Chem 282:10341–10351
Dufer M, Noack K, Krippeit-Drews P, Drews G (2010) Activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in mouse beta-cells. Islets 2:156–163
Winder WW, Hardie DG (1999) AMP-activated protein kinase, a metabolic master switch: possible roles in type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol 277:E1–E10
Alves CR, Ferreira JC, de Siqueira-Filho MA, Carvalho CR, Lancha AH Jr, Gualano B (2012) Creatine-induced glucose uptake in type 2 diabetes: a role for AMPK-alpha? Amino Acids 43:1803–1807
Hutchinson DS, Summers RJ, Bengtsson T (2008) Regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase activity by G-protein coupled receptors: potential utility in treatment of diabetes and heart disease. Pharmacol Ther 119:291–310
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (81373459), Chongqing Science and Technology Committee (CSTC, 2015jcyjbx0064), Chongqing Science Found for Distinguished Young Scholars (2014jcyjjq10003), the Innovation of Science and Technology Leading Talent in Chongqing (2014kjcxljrc0018), and the Innovative Research Team Development Program at the University of Chongqing (CXTDX201601031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors disclose that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, Y., Liu, C., Yin, F. et al. 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase plays an essential role in geniposide-regulated glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in rat pancreatic INS-1 β cells. J Nat Med 71, 123–130 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-016-1038-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-016-1038-5