Abstract
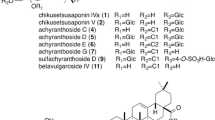
We developed a rapid and simple analytical method for the simultaneous determination of seven 3,28-bidesmosidic triterpenoid saponins in the roots of Codonopsis lanceolata. The saponins are lancemaside A, lancemaside B, lancemaside C, lancemaside E, lancemaside G, foetidissimoside A, and aster saponin Hb. Root samples were extracted with 50% methanol and prepared for analysis. Saponins were detected by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry, and ginsenoside Rb1 was used as an internal standard. The overall recoveries of all saponins were 92–116%, and the relative standard deviation values of intra- and inter-day precision were lower than 3.7 and 7.7%, respectively. Eight root samples collected from Korea and Japan were analyzed using the developed method. Lancemaside A was the most abundant saponin in the root samples from Korea, ranging from 2.65 to 3.64 mg/g dry root. However, the maximum content of lancemaside A among Japanese samples was 0.101 mg/g dry root.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sekita S, Kuroyanagi M, Yasuda K, Mizuno I, Ushijima M, Hayama M, Ichikawa M, Sumihiro M (2005) Drug for ameliorating male climacteric disorder. Patent WO200515426
Ushijima M, Mizuno I, Suzuki E, Amayasu R, Ishii S, Nishihama T, Morihara N, Kashimoto N, Mouri Y, Sumioka I, Kuroyanagi M, Sekita S, Hayama M (2007) Improvement of PADAM-like symptoms in middle-aged men by a designer food containing Codonopsis lanceolata. Pharmacometrics 72:23–30
Ushijima M, Komoto N, Sugizono M, Mizuno I, Sumihiro M, Ichikawa M, Hayama M, Kawahara N, Nakane T, Shirota O, Sekita S, Kuroyanagi M (2008) Triterpene glycosides from the roots of Codonopsis lanceolata. Chem Pharm Bull 56:308–314
Shirota O, Nagamatsu K, Sekita S, Komoto N, Kuroyanagi M, Ichikawa M, Ohta S, Ushijima M (2008) Preparative separation of the saponin lancemaside A from Codonopsis lanceolata by centrifugal partition chromatography. Phytochem Anal (in press). doi:10.1002/pca.1065
Yamaguchi H, Kasai R, Matsuura H, Tanaka O, Fuwa T (1988) High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of acidic saponins of ginseng and related plants. Chem Pharm Bull 36:3468–3473
Yamaguchi H, Matsuura H, Kasai R, Tanaka O, Satake M, Kohda H, Izumi H, Nuno M, Katsuki S, Isoda S, Shoji J, Goto K (1988) Analysis of saponins of wild Panax ginseng. Chem Pharm Bull 36:4177–4181
Saeki T, Nikaido T (2003) Evaluations of saponin properties of HPLC analysis of Platycodon grandiflorum A.DC. Yakugaku zasshi 123:431–441
Bao Y, Li C, Shen H, Nan F (2004) Determination of saikosaponin derivatives in Radix bupleuri and in pharmaceuticals of the Chinese multiherb remedy Xiaochaihu-tang using liquid chromatographic tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 76:4208–4216
Kapusta I, Janda B, Stochmal A, Oleszek W (2005) Determination of saponins in aerial part of Barrel medic (Medicago truncatula) by liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization/mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 53:7654–7660
Ahn MJ, Kim J (2005) Identification and quantification of steroidal saponins in Polygonatum species by HPLC/ESI/MS. Arch Pharm Res 28:592–597
Hattori M, Sakamoto T, Kobashi K, Namba T (1983) Metabolism of glycyrrhizin by human intestinal flora. Planta Med 48:38–42
Kobashi K (1998) Glycosides are natural prodrugs. J Trad Med 15:1–13
Ichikawa M, Ohta S, Komoto N, Ushijima M, Kodera Y, Hayama M, Shirota O, Sekita S, Kuroyanagi M (2008) Rapid identification of triterpenoid saponins in the roots of Codonopsis lanceolata by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Nat Med (in press). doi:10.1007/s11418-008-0270-z
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ichikawa, M., Ohta, S., Komoto, N. et al. Simultaneous determination of seven saponins in the roots of Codonopsis lanceolata by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Nat Med 63, 52–57 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-008-0294-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-008-0294-4