Abstract
Purpose
It is known for titanium dioxide nanoparticles (nTiO2) during production and application to inevitably enter the soil and aquatic environments, posing potential toxic risks to human health and living environments. This triggers the necessity to clarify the underlying mechanisms governing the fate and transport of nTiO2 with different crystal structures in different soils.
Materials and methods
The anatase and rutile nTiO2 were examined in saturated columns packed with varying the mass fraction (λ) of sand/soil (i.e., red soil and paddy soil) mixtures in the presence of phosphate. Moreover, numerical modeling based upon the two-site kinetic retention model was employed to unravel the retention mechanisms.
Results and discussion
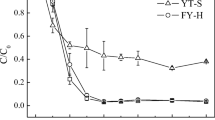
This study showed that the degree of λ was found to have an obvious influence on the transport of nTiO2, irrespective of anatase and rutile. The transportability of nTiO2 was greatly decreased with the increase of λ. The rutile nTiO2 transport was more sensitive to the λ than anatase nTiO2, which especially happened in red soil due to the increased favorable retention sites resulting from the high contents of Fe (47.0 g kg−1) and Al (16.7 g kg−1) and the great specific surface area (38.6 m2 g−1). The second-order attachment coefficient (k2) and the maximum solid-phase concentration (Smax2), obtained by fitting the transport of both nTiO2 in red and paddy soils using two-point kinetic retention model, increased linearly with increasing the λ.
Conclusions
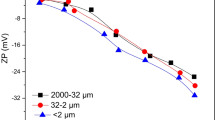
Overall, combined mechanisms (e.g., secondary minimum, particle aggregation, crystalline structure, and surface charge heterogeneity) are responsible for nTiO2 deposition in soils. Our findings provided a convincing theory for evaluating environmental risk of anatase and rutile nTiO2 in different soils.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahamed A, Liang L, Ming Y, Bobacka J, Lisak G (2021) Too small to matter? Physicochemical transformation and toxicity of engineered nTiO2, nSiO2, nZnO, carbon nanotubes, and nAg. J Hazard Mater 404:124107
Atout H, Alvarez MG, Chebli D, Bouguettoucha A, Tichit D, Llorca J, Medina F (2017) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue: preparation of TiO2/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites by direct sol-gel and hydrothermal methods. Mater Res Bull 95:578–587
Bear J, Gomez V, Kefallinos N, Mcgettrick J, Barron A, Dunnill C (2015) Anatase/rutile bi-phasic titanium dioxide nanoparticles for photocatalytic applications enhanced by nitrogen doping and platinum nano-islands. J Colloid Interface Sci 60:29–35
Bierman PM, Rosen CJ, Bloom PR, Nater EA (1995) Soil solution chemistry of sewage-sludge incinerator ash and phosphate fertilizer amended soil. J Environ Qual 24(2):279–285
Brant J, Lecoanet H, Hotze M, Wiesner M (2005) Comparison of electrokinetic properties of colloidal fullerenes (n-C60) formed using two procedures. Environ Sci Technol 39(17):6343–6351
Bradford S, Simunek J, Bettahar M, van Genuchten MT, Ytes S (2003) Modeling colloid attachment, straining, and exclusion in saturated porous media. Environ Sci Technol 37(10):2242–2250
Carp O, Huisman CL, Reller A (2004) Photoinduced reactivity of titanium dioxide. Prog Solid State Ch 32(1–2):33–177
Chen G, Liu X, Su C (2011) Transport and retention of TiO2 rutile nanoparticles in saturated porous media under low-ionic-strength conditions: measurements and mechanisms. Langmuir 27(9):5393–5402
Chen KL, Elimelech M (2006) Aggregation and deposition kinetics of fullerene (C60) nanoparticles. Langmuir 22(26):10994–11001
Chen M, Alim N, Zhang Y, Xu N, Cao X (2018a) Contrasting effects of biochar nanoparticles on the retention and transport of phosphorus in acidic and alkaline soils. Environ Pollut 239:562–570
Chen M, Xu N, Cao X, Zhou K, Chen Z (2015a) Facilitated transport of anatase titanium dioxides nanoparticles in the presence of phosphate in saturated sands. J Colloid Interface Sci 451:134–143
Chen M, Xu N, Christodoulatos C, Wang D (2018b) Synergistic effects of phosphorus and humic acid on the transport of anatase titanium dioxide nanoparticles in water-saturated porous media. Environ Pollut 243:1368–1375
Cheng X, Xu N, Huangfu X, Zhou X, Zhang M (2018) Synergetic effect of hydrochar on the transport of anatase titanium dioxide nanoparticles in the presence of phosphate in saturated quartz sand. Environ Sci Pollut R 25(29):28864–28874
Chen M, Wang D, Yang F, Xu X, Xu N, Cao X (2017) Transport and retention of biochar nanoparticles in a paddy soil under environmentally-relevant solution chemistry conditions. Environ Pollut 230:540–549
Chen M, Zhou K, Lu X, Li Y, Feng G, Xu X, Chen Z, Xu N (2015b) The aggregation and dispersion of anatase and rutile TiO2 nanoparticles in the presence of phosphate. Fresen Environ Bull 24(10):3205–3212
Englehart J, Marion B, Becker M, Wang Y, Abriola L, Pennell K (2016) Influence of a polymer sunscreen additive on the transport and retention of titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Water-Saturated Porous Media. Environ Sci Nano 3:157–168
Fang J, Shan X, Bei W, Lin J, Owens G (2009) Stability of titania nanoparticles in soil suspensions and transport in saturated homogeneous soil columns. Environ Pollut 157(4):1101–1109
Fang J, Shan X, Wen B, Lin J, Owens G, Zhou S (2011) Transport of copper as affected by titania nanoparticles in soil columns. Environ Pollut 159:1248–1256
Fang J, Xu M, Wang D, Wen B, Han J (2013) Modeling the transport of TiO2 nanoparticle aggregates in saturated and unsaturated granular media: effects of ionic strength and pH. Water Res 47:1399–1408
Fang J, Zhang K, Sun P, Lin D, Shen B, Luo Y (2016) Co-transport of Pb2+ and TiO2 nanoparticles in repacked homogeneous soil columns under saturation condition: effect of ionic strength and fulvic acid. Sci Total Environ 571:471–478
Gargiulo G, Bradford S, Simunek J, Ustohal P, Vereecken H, Klumpp E (2007) Bacteria transport and deposition under unsaturated conditions: the role of the matrix grain size and the bacteria surface protein. J Contam Hydrol 92(34):255–273
GunKo V, Zarko V, Leboda R, Chibowski E (2001) Aqueous suspension of fumed oxides: particle size distribution and zeta potential. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 91(1):1–112
Guo P, Xu N, Li D, Huangfu X, Li Z (2018) Aggregation and transport of rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles with montmorillonite and diatomite in the presence of phosphate in porous sand. Chemosphere 204:327–334
Hanaor DAH, Sorrell CC (2011) Review of the anatase to rutile phase transformation. J Mater Sci 46:855–874
Huynh K, Chen K (2011) Aggregation kinetics of citrate and polyvinylpyrrolidone coated silver nanoparticles in monovalent and divalent electrolyte solutions. Environ Sci Technol 45(13):5564–5571
Jiang J, Oberdörster G, Biswas P (2009) Characterization of size, surface charge, and agglomeration state of nanoparticle dispersions for toxicological studies. J Nano Res 11(1):77–89
Johnson P, Sun N, Elimelech M (1996) Colloid transport in geochemically heterogeneous porous media: Modeling and measurements. Environ Sci Technol 30(11):3284–3293
Kiser M, Westerhoff P, Benn T, Wang Y, Perez-Rivera J, Hristovski K (2009) Titanium nanomaterial removal and release from wastewater treatment plants. Environ Sci Technol 43:6757–6763
Li L, Schuster M (2014) Influence of phosphate and solution pH on the mobility of ZnO nanoparticles in saturated sand. Sci Total Environ 472(472C):971–978
Liu C, Xu N, Feng G, Zhou D, Cheng X, Li Z (2017) Hydrochars and phosphate enhancing the transport of nanoparticle silica in saturated sands. Chemosphere 189:213–223
Liu H, Yin H, Tang S, Peng H, Yu X, Lu G, Dang Z (2021) Simultaneous adsorption of Cd2+ and photocatalytic degradation of tris-(2-chloroisopropyl) phosphate (TCPP) by mesoporous TiO2. Chemosphere 267:129238
Liu Y, Zhang C, Hu D, Kuhlenschmidt M, Kuhlenschmidt T, Mylon S, Kong R, Bhargava R, Nguyen T (2013) Role of collector alternating charged patches on transport of Cryptosporidium parvum oocyst in a patchwise charged heterogeneous micromodel. Environ Sci Technol 47(6):2670–2678
Liang Y, Bradford S, Simunek J, Heggen M, Vereecken H, Klumpp E (2013) Retention and remobilization of stabilized silver nanoparticles in an undisturbed loamy sand soil. Environ Sci Technol 47(21):12229–12237
Mukherjee B, Weaver J (2010) Aggregation and charge behavior of metallic and nonmetallic nanoparticles in the presence of competing similarly-charged inorganic ions. Environ Sci Technol 44(9):3332–3338
Mou Y, Lu K, Gao D (2012) Influence of dispersants on dispersion stability of TiO2 suspensions. Adv Mater Res 356(360):476–479
Nowack B, Bucheli T (2007) Occurrence behavior and effects of nanoparticles in the environment. Environ Pollut 150:5–22
Rastghalam ZS, Tao C, Freake B (2018) Fine particle attachment to quartz sand in the presence of multiple interacting dissolved components. Sci Total Environ 645:499–508
Simunek J, van Genuchten MT, Sejna M (2016) Recent developments and applications of the HYDRUS computer software packages. Vadose Zone J 6(7):1–25
Sun P, Zhang K, Jing F, Lin D, Han J (2015) Transport of TiO2 nanoparticles in soil in the presence of surfactants. Sci Total Environ 527–528:420–428
Wang Y, Li Y, Kim H, Walker S, Abriola L, Pennell K (2010) Transport and retention of fullerene nanoparticles in natural soils. J Environ Qual 39(6):1925–1933
Wang Z, Shen C, Du Y, Zhang Y, Li B (2019) Influence of phosphate on deposition and detachment of TiO2 nanoparticles in soil. Front Env Sci Eng 13(5):163–173
Wang D, Su C, Zhang W, Hao X, Long C, Wang Y, Zhou D (2014) Laboratory assessment of the mobility of water-dispersed engineered nanoparticles in a red soil (Ultisol). J Hydrology 519:1677–1687
Wang L, Xu S, Li J (2011) Effects of phosphate on the transport of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in saturated quartz sand. Environ Sci Technol 45(22):9566–9573
Xu N, Cheng X, Wang D, Xu X, Huangfu X, Li Z (2018) Effects of Escherichia coli and phosphate on the transport of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in heterogeneous porous media. Water Res 146:264–274
Xu X, Xu N, Cheng X, Guo P, Chen Z, Wang D (2017) Transport and aggregation of rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles in saturated porous media in the presence of ammonium. Chemosphere 169:9–17
Zhang L, Man ST, Tan OK (2014) Facile in situ synthesis of visible light-active Pt/C-TiO2 nanoparticles for environmental remediation. J Environ Chem Eng 2(2):1214–1220
Zhang X, Sun H, Zhang Z, Niu Q, Chen Y, Crittenden J (2007) Enhanced bioaccumulation of cadmium in carp in the presence of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Chemosphere 67:160–166
Zhu X, Zhou J, Cai Z (2011) TiO2 nanoparticles in the marine environment: impact on the toxicity of tributyltin to abalone (haliotis diversicolor supertexta) embryos. Environ Sci Technol 45(8):3753–3758
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21777110 and 42007130), the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project of Suzhou (SNG2020043), and the Innovative and Entrepreneurial Doctor Program of Jiangsu Province (2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hong Jie Di
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Chen, M., Li, D. et al. Transport of anatase and rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles in soils in the presence of phosphate: mechanisms and numerical modeling. J Soils Sediments 22, 1987–1998 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03211-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03211-1