Abstract
Purpose
Lead (Pb(II)) can be accumulated in soil and transferred to humans via the food chain. Therefore, it is essential to improve Pb(II) immobilization during soil remediation.
Materials and methods
Nanosized zero-valent iron (nZVI) from green tea extract (tea polyphenols, TPs) was successfully synthesized as an additive reductant. Further, the nZVI was supported on montmorillonite (Mont), resulting in a GT-nZVI@Mont composite characterized by multiple techniques, including Zeta potential, SEM, TEM, XRD, and XPS. Moreover, the transport experiments and the toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP) were conducted to identify the optimum conditions (i.e., GT-nZVI@Mont dosage, Pb(II) concentration, and pH) for the remediation.
Results and discussion
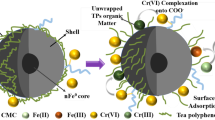
The experimental results showed that the enhanced transportability of GT-nZVI@Mont was about 40% more than that of GT-nZVI. Meanwhile, Pb(II) immobilization was increased at various pH values (especially under anoxic conditions). The Pb(II) immobilization capacity of GT-nZVI@Mont was 900.8 mg∙g-1 (per unit of Fe content), which was significantly higher than 530.1 mg∙g-1 per unit of Fe content in GT-nZVI. Such enhancement could be ascribed to the synergistic effects of the wrapped TP around the Fe0 core and the Mont interlayer support, capable of protecting the Fe0 surface from further oxidation. When GT-nZVI@Mont reacted with the Pb(II) in soil, TPs’ unwrapped coverage increased the reaction sites of Fe0 cores for Pb(II) reduction and adsorption.
Conclusions
GT-nZVI@Mont with sufficient transportability provided efficient in situ remediation of Pb(II) in contaminated soil at a wide pH range.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arancibia-Miranda N, Baltazar SE, Garcia A, Daniela M, Pamela S, Rubio M, Altbir D (2016) Nanoscale zero valent supported by zeolite and montmorillonite: template effect of the removal of lead ion from an aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 301:371–380
Arshadi M, Soleymanzadeh M, Salvacion JWL, Salimivahid F (2014) Nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) supported on sineguelas waste for Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution: kinetics, thermodynamic and mechanism. J Colloid Interface Sci 426:241–251
Balakrishnan H, Ibrahim M, Wahit MU, Hassan A (2011) Polypropylene/organically modified Sabah montmorillonite nanocomposites: surface modification and nanocomposites characterization. Polym Compos 32(12):1927–1936
Bhowmick S, Chakraborty S, Mondal P, Renterghem WV, Berghe SV, Roman-Ross G, Iglesias M (2014) Montmorillonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron for removal of arsenic from aqueous solution: kinetics and mechanism. Chem Eng J 243:14–23
Cabala J, Teper L (2007) Metalliferous constituents of rhizosphere soils contaminated by Zn-Pb mining in southern Poland. Water Air Soil Pollut 178(1–4):351–362
Calderon B, Fullana A (2015) Heavy metal release due to aging effect during zero valent iron nanoparticles remediation. Water Res 83:1–9
Chen M, Xu N, Cao X, Zhou K, Chen Z, Wang Y, Liu C (2015) Facilitated transport of anatase titanium dioxides nanoparticles in the presence of phosphate in saturated sands. J Colloid Interface Sci 451:134–143
Chen G, Shah KJ, Shi L, Chiang PC, You Z (2019) Red soil amelioration and heavy metal immobilization by a multi-element mineral amendment: performance and mechanisms. Environ Pollut 254:112964
Dermatas D, Shen G, Chrysochoou M, Grubb DG, Menounou N, Dutko P (2006) Pb speciation versus TCLP release in army firing range soils. J Hazard Mater 136(1):34–46
Dong H, Lo MCI (2013) Influence of humic acid on the colloidal stability of surface-modified nano zero-valent iron. Water Res 47(1):419–427
Dong H, Lo MCI (2014) Transport of surface-modified nano zero-valent iron (SM-nZVI) in saturated porous media: effects of surface stabilizer type, subsurface geochemistry, and contaminant loading. Water Air Soil Pollut 225(9):2107
Fonseca B, Maio H, Quintelas C, Teixeira A, Tavares T (2009) Retention of Cr (VI) and Pb(II) on a loamy sand soil: kinetics, equilibria and breakthrough. Chem Eng J 152(1):212–219
Frost RL, Xi Y, He H (2010) Synthesis, characterization of palygorskite supported zero-valent iron and its application for methylene blue adsorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 341(1):153–161
Fu R, Yang Y, Xu Z, Zhang X, Guo X, Bi D (2015) The removal of chromium (VI) and lead (II) from groundwater using sepiolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (S-NZVI). Chemosphere 138:726–734
Geng B, Jin Z, Li T, Qi X (2009) Preparation of chitosan-stabilized Fe0 nanoparticles for removal of hexavalent chromium in water. Sci Total Environ 407(18):4994–5000
Guan X, Sun Y, Qin H, Li J, Irene L, Di H, Dong H (2015) The limitations of applying zero-valent iron technology in contaminants sequestration and the corresponding countermeasures: the development in zero-valent iron technology in the last two decades (1994–2014). Water Res 75:224–248
Guo P, Xu N, Li D, Huangfu X, Li Z (2018) Aggregation and transport of rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles with montmorillonite and diatomite in the presence of phosphate in porous sand. Chemosphere 204:327–334
Han L, Li B, Tao S (2020) Graphene oxide-induced formation of a boron-doped iron oxide shell on the surface of nZVI for enhancing nitrate removal. Chemosphere 252:126496
Huang P, Ye Z, Xie W, Chen Q, Li J, Xu Z (2013) Rapid magnetic removal of aqueous heavy metals and their relevant mechanisms using nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI) particles. Water Res 47(12):4050–4058
Huangfu X, Xu N, Yang J, Yang H, Zhang M, Ye Z, Wang S, Chen J (2020) Transport and retention of hydrochar-diatomite nanoaggregates in water-saturated porous sand: effect of montmorillonite and phosphate at different ionic strengths and solution pH. Sci Total Environ 703:134487
Jiang M, Jin X, Lu X, Chen Z (2010) Adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II) onto natural kaolinite clay. Desalination 252(1):33–39
Jung B, O'Carroll D, Sleep B (2014) The influence of humic acid and clay content on the transport of polymer-coated iron nanoparticles through sand. Sci Total Environ 496:155–164
Kanel SR, Manning B, Charlet L, Choi H (2005) Removal of arsenic (III) from groundwater by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol 39:1291–1298
Kanel SR, Greneche JM, Choi H (2006) Arsenic(V) removal from groundwater using nano scale zero-valent iron as a colloidal reactive barrier material. Environ Sci Technol 40(6):2045–2050
Kim SA, Kamala-Kannan S, Lee KJ, Park YJ, Shea PJ, Lee WH (2013) Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by a zeolite-nanoscale zero-valent iron composite. Chem Eng J 217:54–60
Kiprop AK, Coumon MC, Pourtier E, Kimutai S, Kirui S (2013) Synthesis of humic and fulvic acids and their characterization using optical spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR and UV-Visible). Int J Appl Sci Technol 8(3):28–35
Kumar KM, Mandal BK, Kumar KS, Reddy PS, Sreedhar B (2013) Biobased green method to synthesise palladium and iron nanoparticles using Terminalia chebula aqueous extract. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 102(1):128–133
Li X, Zhang W (2007) Sequestration of metal cations with zerovalent iron nanoparticles: a study with high resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HR-XPS). J Phys Chem C 111(19):6939–6946
Li Z, Wang L, Meng J, Liu X, Brookes P (2018) Zeolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: new findings on simultaneous adsorption of Cd(II), Pb(II), and As(III) in aqueous solution and soil. J Hazard Mater 344:1–11
Li Z, Wang L, Wu J, Xu Y, Liu X (2020) Zeolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron for immobilization of cadmium, lead, and arsenic in farmland soils: encapsulation mechanisms and indigenous microbial responses. Environ Pollut 260:114098
Lipczyns-kakochany E, Harms S, Milburn R, Sprah G, Nadarajah N (1994) Degradation of carbon-tetrachloride in the presence of iron and sulfur-containing-compounds. Chemosphere 29:1477–1489
Liu WJ, Jiang H, Yu HQ (2015) Development of biochar-based functional materials: toward a sustainable platform carbon material. Chem Rev 115(22):12251–12285
Liu X, Lai D, Wang Y (2019) Performance of Pb(II) removal by an activated carbon supported nanoscale zero-valent iron composite at ultralow iron content. J Hazard Mater 361:37–48
Lü Y, Li Z, Li J, Chen K, Dong H, Shou J, Li Y (2018) Synergetic effect of pyrite on Cr(VI) removal by zero valent iron in column experiments: an investigation of mechanisms. Chem Eng J 349:522–529
Lyu H, Tang J, Huang Y, Gai L, Zeng EY, Liber K, Gong Y (2017) Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by a novel biochar supported nanoscale iron sulfide composite. Chem Eng J 322:516–524
Mohammed O, Mumford KG, Sleep BE (2020) Effects of hydrogen gas production, trapping and bubble-facilitated transport during nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) injection in porous media. J Contam Hydrol 234:103677
Mueller NC, Braun J, Bruns J (2012) Application of nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI) for groundwater remediation in Europe. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 19(2):550–558
Nadagouda MN, Hoag GE, Collins JB (2009) Green synthesis of Au nanostructures at room temperature using biodegradable plant surfactants. Crystal Growth Design 9(11):4979–4983
Nasiri J, Motamedi E, Mohammad R (2019) Removal of crystal violet from water using β-cyclodextrin functionalized biogenic zero-valent iron nano adsorbents synthesized via aqueous root extracts of ferula persica. J Hazard Mater 367:325–338
Njagi EC, Huang H, Stafford L, Genuino H, Galindo H, Collins J, Hoag G, Suib S (2011) Biosynthesis of iron and silver nanoparticles at room temperature using aqueous sorghum bran extracts. Langmuir 27(1):264–271
Okuo J, Emina A, Omorogbe S, Anegbe B (2017) Synthesis, characterization and application of starch stabilized zerovalent iron nanoparticles in the remediation of Pb-acid battery soil. Environ Nanotechnol Monitor Manag 9:12–17
Palmal LD, Nicola V, Vilardi G (2018) Kinetic modeling of Cr(VI) reduction by nZVI in soil: the influence of organic matter and manganese oxide. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 101(6):692–697
Petala E, Dimos K, Douvalis A, Bakas T, Tucek J, Zboril R, Karakassides MA (2013) Nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on mesoporous silica: characterization and reactivity for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 261:295–306
Phenrat T, Cihan A, Kim HJ, Mital M, Illangasekare T, Lowry GV (2010) Transport and deposition of polymer-modified Fe0 nanoparticles in 2-D heterogeneous porous media: effects of particle concentration, Fe0 content, and coatings. Environ Sci Technol 44(23):9086–9093
Qu J, Liu Y, Li C, Jiang Z, Zhang G, Deng F (2021) Green synthesis of hydrophilic activated carbon supported sulfide nZVI for enhanced Pb(II) scavenging from water: characterization, kinetics, isotherms and mechanisms. J Hazard Mater 403:123607
Shi L, Lin Y, Zhang X, Chen Z (2011a) Synthesis, characterization and kinetics of bentonite supported nZVI for the removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 171(2):612–617
Shi L, Zhang X, Chen Z (2011b) Removal of chromium (VI) from wastewater using bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Water Res 45(2):886–892
Shkol'Nikov EV (2005) Thermodynamic characteristics of the amphoterism of M(OH)2 hydroxides in aqueous media. Russ J Appl Chem 78(11):1786–1790
Su H, Fang Z, Tsang P, Fang J, Zhao D (2016) Stabilisation of nanoscale zero-valent iron with biochar for enhanced transport and in-situ remediation of hexavalent chromium in soil. Environ Pollut 214:94–100
Sun Y, Li X, Cao J, Zhang W, Wang H (2006) Characterization of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 120(1–3):47–56
Tandon PK, Shukla RC, Singh SB (2013) Removal of arsenic(III) from water with clay-supported zerovalent iron nanoparticles synthesized with the help of tea liquor. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:10052–10058
Tomasevic DD, Kozma G, Kerkez DV (2014) Toxic metal immobilization in contaminated sediment using bentonite- and kaolinite-supported nano zero-valent iron. J Nanopart Res 16(8):1–15
Tong M, He L, Rong H, Li M, Kim H (2020) Transport behaviors of plastic particles in saturated quartz sand without and with biochar/Fe3O4-biochar amendment. Water Res 169:115284
Uzum C, Shahwan T, Eroglu AE, Hallam KR, Scott TB, Lieberwirth I (2009) Synthesis and characterization of kaolinite-supported zero-valent iron nanoparticles and their application for the removal of aqueous Cu2+ and Co2+ ions. Appl Clay Sci 43(2):172–181
Wang T, Lin J, Chen Z (2014a) Green synthesized iron nanoparticles by green tea and eucalyptus leaves extracts used for removal of nitrate in aqueous solution. J Clean Prod 83:413–419
Wang T, Jin X, Chen Z, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2014b) Green synthesis of Fe nanoparticles using eucalyptus leaf extracts for treatment of eutrophic wastewater. Sci Total Environ 466–467:210–213
Wang Y, Fang Z, Liang B (2014c) Remediation of hexavalent chromium contaminated soil by stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron prepared from steel pickling waste liquor. Chem Eng J 247:283–290
Wu P, Wu W, Li S, Xing N, Zhu N, Li P, Wu J (2009) Removal of Cd2+ from aqueous solution by adsorption using Fe-montmorillonite. J Hazard Mater 169(1–3):824–830
Xiao J, Gao B, Yue Q, Gao Y, Li Q (2015) Removal of trihalomethanes from reclaimed-water by original and modified nanoscale zero-valent iron: characterization, kinetics and mechanism. Chem Eng J 262:1226–1236
Xiao C, Li H, Zhao Y, Zhang X, Wang X (2020) Green synthesis of iron nanoparticle by tea extract (polyphenols) and its selective removal of cationic dyes. J Environ Manag 275:111262
Xu N, Gao Y (2008) Characterization of hematite dissolution affected by oxalate coating, kinetics and pH. Appl Geochem 23:783–793
Xu N, Cheng X, Zhou K, Xu X, Li Z, Chen J, Wang D, Li D (2018) Facilitated transport of titanium dioxide nanoparticles via hydrochars in the presence of ammonium in saturated sands: effects of pH, ionic strength, and ionic composition. Sci Total Environ 612:1348–1357
Xu N, Huangfu X, Li Z, Wu Z, Li D, Zhang M (2019) Nanoaggregates of silica with kaolinite and montmorillonite: sedimentation and transport. Sci Total Environ 669:893–902
Yirsaw BD, Megharajc M, Chenc Z, Naiduc R (2016) Reduction of hexavalent chromium by green synthesized nano zero valent iron and process optimization using response surface methodology. Environ Technol Innov 5:136–147
Zhang X, Lin S, Chen Z, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2011) Kaolinite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron for removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solution: reactivity, characterization and mechanism. Water Res 45(11):3481–3488
Zhang C, Suen CL, Yang C, Quek SY (2018) Antioxidant capacity and major polyphenol composition of teas as affected by geographical location, plantation elevation and leaf grade. Food Chem 244:109–119
Zhang M, Yi K, Zhang X, Han P, Liu W, Tong M (2020a) Modification of zero valent iron nanoparticles by sodium alginate and bentonite: enhanced transport, effective hexavalent chromium removal and reduced bacterial toxicity. J Hazard Mater 388:121822
Zhang Y, Jiao X, Liu N, Lv J, Yang Y (2020b) Enhanced removal of aqueous Cr(VI) by a green synthesized nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on oak wood biochar. Chemosphere 245:125542
Zhou W, Liu F, Yi S (2018) Simultaneous stabilization of Pb and improvement of soil strength using nZVI. Sci Total Environ 651:877–884
Zhou L, Li A, Ma F (2020) Combining high electron transfer efficiency and oxidation resistance in nZVI with coatings of microbial extracellular polymeric substances to enhance Sb(V) reduction and adsorption. Chem Eng J 395:125168
Zhu H, Jia Y, Wu X, Wang H (2009) Removal of arsenic from water by supported nano zero-valent iron on activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 172(2–3):1591–1596
Zou Y, Wang X, Khan A, Wang P, Liu Y, Alsaedi A, Hayat T, Wang X (2016) Environmental remediation and application of nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites for the removal of heavy metal ions: a review. Environ Sci Technol 50(14):7290–7304
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to appreciate the project financially funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21777110), and Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center of Technology and Material for Water Treatment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Huijun Zhao
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1955 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Ye, Z., Feng, F. et al. Green-synthesized nanosize Mont-supported Fe0 via tea extract for enhanced transport and in situ remediation of Pb(II) in soil. J Soils Sediments 21, 2540–2550 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02950-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02950-x