Abstract
Purpose
Heavy metal soil pollution in the coal chemical industrial area has attracted increasing attention with the rapid development of the coal chemical industry. The spatial distribution and the source of heavy metals in the soil in coal chemical industrial areas should be investigated to help prevent further heavy metal pollution in industrial areas, and reduce heavy metal exposure to factory workers.
Materials and methods
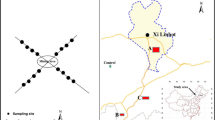
A coal chemical factory in northwest China was studied. A chessboard sampling method was used to collect 153 soil samples. An inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS) and a mercury vapor analyzer were used to quantify five heavy metals (Pb, Hg, Cd, Cr, and As). The spatial distributions of these five heavy metals were simulated using several statistical methods and the spatial maps of the five heavy metal concentrations were obtained.
Results and discussion
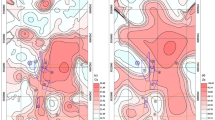
The mean concentrations of the heavy metals excluding Pb were higher than their respective soil background values in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (Ningxia). The concentrations of Hg, Cd, Cr, and As were 4.00, 4.00, 1.50, and 1.08 times of their background concentrations, respectively. In contrast to the production flow chart, the soil on both sides of the trunk road and the coal transport corridor at the factory had relatively high Pb and Cd concentrations. The slag dump of the gasification residues had the highest Cr concentration because of the local prevailing winds. Concentrations of Hg, Cd, and As in the downwind direction of the prevailing winds from the coal combustion unit chimney were significantly high.
Conclusions
In this study, the spatial distributions of five heavy metals (Pb, Hg, Cd, Cr, and As) in the soil at a coal chemical factory were obtained. The respective sources of heavy metals in the soil were determined. The present study provides a theoretical basis for the prevention and treatment of heavy metal pollution in coal chemical factories.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
An YQ, Zhang RQ, Yuan SH (2016) Health risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil in Hebei Province. Occup Health 09:1252–1255
Andersen O (1990) Biological effects of heavy metals. Volume II: metal carcinogenesis. By E. C. Foulkes. Q Rev Biol 68:134
Cai FF, Pu LJ, Zhang J, Zhao Y, Zhu M (2012) Identification and analysis of spatial economic structure in Jiangsu province by applying exploratory spatial data analysis (ESDA). Econ Geogr 32(3):24–30 (in Chinese)
Chen S (2011) Improvement on the pre-treatment methods of the determination of heavy metals in soil. Environ Dev 12:155–156 (in Chinese)
Fan BT (1983) Chemical carcinogens in the environment. Environment Pollution and Prevention 3:21–25 (in Chinese)
Fei F, Debin DU, Heng LI (2013) Spatial-temporal characteristics of scientific and technological resources allocation efficiency in prefecture-level cities of China. Acta Geograph Sin 68(10):1331–1343
Hou JR (1998) Practical Geostatistics. China Land Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Huang GS, Li ZY, Wang JM (2015) Development status of coal chemical industry in China and its influence on the petrochemical industry. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress 02:295–302 [in Chinese]
Li J (2005) Heavy metal pollution and migration on soil-wheat system on both sides of the Zheng-Bian road. Dissertation, Henan University (in Chinese)
Li Y (2011) Experimental study on high temperature removal and migration and transformation of trace elements in coal gasification. Dissertation, Huazhong University of Science and Technology (in Chinese)
Li YZ, Ma JH (2008) Kriging interpolation and its application to environmental noise assessment in Kaifeng. Environ Sci Technol 31(3):103–105 (in Chinese)
Liu SY (1987) Layout of farmland soil monitoring spots and sample collection. Journal of Agro-environment Science 05:24–26 (in Chinese)
Lu J, Sun JM, Zhao CM (2003) Occurrence of As in coal and its behavior during coal combustion. Coal Geology Exploration 05:6–9 (in Chinese)
Reza SK, Baruah U, Singh SK, Das TH (2015) Geostatistical and multivariate analysis of soil heavy metal contamination near coal mining area, northeastern India. Environ Earth Sci 73(9):5425–5433
Sun LM, Bai YY (2008) Analysis of mass distribution and transformation of mercury in coal combustion on coal-fired power plant. Clean Coal Technol 14(5):93–95 (in Chinese)
Tang GA, Yang X (2006) Experimental tutorial on ArcGIS (Geographic Information System) spatial analysis. China Science Publishing and Media Ltd, Beijing (in Chinese)
Wang CL, Zheng WJ, Wang HJ, Zeng XD, Ji SL (2012) The relationship between heavy metals enrichment characteristics and soil acidification for environmental media in Yantai of Shandong Province. Rock Miner Anal 02:361–369
Wang HX (2012) Pollution ecology. Higher Education Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Wang P (2014) Current status of soil heavy metal pollution on both sides of a road in Beijing and risk evaluation. Dissertation, Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture (in Chinese)
Wang Q, Wu XH (2014) A study on parameters setting of ordinary kriging interpolation to total soil nitrogen concentration in Chaihe River Basin. J Yuxi Normal Univ 30(8):28–31 (in Chinese)
Wang XJ, Lai JQ, Lu YH, Li DS, Zhou JH, Wang JW (2008) Main source of soil heavy metal pollution based on factor analysis in Taiyuan. Ecol Environ Sci 17(2):671–676 (in Chinese)
Wang XS, Qin Y (2006) Environmental risk and sources of heavy metals in Xuzhou urban topsoil. Geochimica 35(1):88–94 (in Chinese)
Xu LS, Cheng JF, Zeng HC (2004) Experimental investigation of the release characteristics of trace elements As, Cd, and Cr during the combustion of coal. J Eng Thermal Energy Power 05:478–482+547–548 (in Chinese)
Yang ZP, Lu WX, Liu XR, Xin X (2009) Sources identification of heavy metals in urban soil of Changchun based on principal component analysis. Urban Environ Urban Ecol 5:29–33 (in Chinese)
Zhang CB (2007) Soil heavy metal identification and analysis in classical contamination zone. Dissertation, Nanjing Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese)
Zhang JY, Zheng CG, Liu J, Liu HM (2003) Experimental study on volatility of trace metals in coal combustion. China National Symposium on Combustion 1043–1046 (in Chinese)
Zhang K, Yang JJ, Bai L, Qiang CD, Wang SD (2017) Soil heavy metal pollution and source analysis of a coal chemical factory in northwest China. J Mining Sci Technol 2(02):191–198 (in Chinese)
Zhao JF (2011) Analysis and policy recommendation on coal industry clean-using from the perspective of low-carbon economy. J China Coal Soc 03:514–518
Zhao SH, Chen ZL, Zhang TP, Pan WB, Peng XC, Che R, Ou YJ, Lei GJ, Zhou D (2014) Effects of stabilization treatment on migration and transformation of heavy metals in mineral waste residues. Environ Sci 04:1548–1554 (in Chinese)
Zou W (2008) Focus on vehicular heavy metal pollution. China Quality News (Beijing):06–10 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, No. 2014CB238906) for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Claudio Bini
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Qiang, C. & Liu, J. Spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metals in the soil of coal chemical industrial areas. J Soils Sediments 18, 2044–2052 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-1972-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-1972-9