Abstract
Purpose
Floodplain soils are often contaminated with toxic elements such as Ba, Cr, Sr, and V. For an adequate risk assessment of such contaminated sites, the assessment of factors affecting the leaching of those elements from riverine soils into water is fundamental. Since the redox potential (EH) can be important within this context, we aimed to assess the impact of pre-set redox conditions on the dynamics of Ba, Cr, Sr, and V in a floodplain soil.
Materials and methods
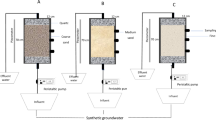
To achieve this aim, we used an automatic biogeochemical microcosm system allowing computer-controlled regulation of EH by adapting the supply of N2 or O2 to the soil suspension. With this system, the effect of EH on the dynamics of Ba, Cr, Sr, and V was studied mechanistically.
Results and discussion
Chromium and V were negatively correlated with EH possibly due to co-precipitation of these metals with Fe (hydr)oxides at high EH. Vanadium might additionally be oxidized from more soluble V(IV) to less soluble V(V) with rising EH. Barium and Sr were positively correlated with EH, which might be attributed to their association with dissolved organic carbon (DOC). The influence of pH on the dynamics of the studied elements seemed to be of minor importance in our study. A significant negative correlation was observed between the specific UV absorbance at 254 nm (SUVA 254) and EH indicating that oxidizing conditions favored the removal of aromatic DOC molecules from solution via binding to Fe (hydr)oxides.
Conclusions
Redox potential is important for metal fate in the current study. Results imply an absorption of Cr and V to Fe (hydr)oxides and an interaction with DOC while particularly Ba and Sr dynamics may be influenced by DOC. In the future, different V species in wetland soils under pre-definite redox conditions should be determined and further studies should elucidate the specific role of DOC and sulfur (S) chemistry on the dynamics of the studied metals.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel CDT, Sharma SK, Malolo YN, Maeng SK, Kennedy MD, Amy GL (2012) Attenuation of bulk organic matter, nutrients (N and P), and pathogen indicators during soil passage: effect of temperature and redox conditions in simulated soil aquifer treatment (SAT). Water Air Soil Pollut 223:5205–5220
Agnieszka J, Barbara G (2012) Chromium, nickel and vanadium mobility in soils derived from fluvioglacial sands. J Hazard Mater 237–238:315–322
Aide M (2005) Geochemical assessment of iron and vanadium relationships in oxic soil environments. Soil Sediment Contam 14:403–416
Aiken GR, Hsu-Kim H, Ryan JN (2011) Influence of dissolved organic matter on the environmental fate of metals, nanoparticles, and colloids. Environ Sci Technol 45:3196–3201
Amirbahman A, Sigg L, vonGunten U (1997) Reductive dissolution of Fe(III) (hydr)oxides by cysteine: kinetics and mechanism. J Colloid Interface Sci 194:194–206
Amrhein C, Mosher PA, Brown AD (1993) The effects of redox on Mo, U, B, V, and as solubility in evaporation pond soils. Soil Sci 155:249–255
Antić-Mladenović S, Rinklebe J, Frohne T, Staerk H-J, Wennrich R, Tomić Z, Ličina V (2010) Impact of controlled redox conditions on nickel in a serpentine soil. J Soils Sediments 11:406–415
Baken S, Larsson MA, Gustafsson JP, Cubadda F, Smolders E (2012) Ageing of vanadium in soils and consequences for bioavailability. Eur J Soil Sci 63:839–847
Beck M, Dellwig L, Schnetger B, Brumsack HJ (2008) Cycling of trace metals (Mn, Fe, Mo, U, V, Cr) in deep pore waters of intertidal flat sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:2822–2840
Bell JML, Philp JC, Kuyukina MS, Ivshina IB, Dunbar SA, Cunningham CJ, Anderson P (2004) Methods evaluating vanadium tolerance in bacteria isolated from crude oil contaminated land. J Microbiol Methods 58:87–100
Bisone S, Blais JF, Drogui P, Mercier G (2012) Toxic metal removal from polluted soil by acid extraction. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:3739–3755
Blume H-P, Deller B, Leschber R, Paetz A, Schmidt SK, Wilke B-M (2000) Handbuch der Bodenuntersuchung Und Ergänzungslieferungen Bd. 1 bis 7. DIN Vorschriften (in German). Wiley-VCH Beuth, Berlin
Blume H-P, Stahr K, Leinweber P (2011) Bodenkundliches Praktikum: eine Einführung in pedologisches Arbeiten für Ökologen, insbesondere Land- und Forstwirte, und für Geowissenschaftler (in German). 3., neubearb. Aufl. edn. Spektrum, Heidelberg
Brümmer G (1974) Redox potentials and redox processes of manganese, iron and sulfur-compounds in hydromorphic soils and sediments. Geoderma 12:207–222
Bundesbodenschutzverordnung (1999) Directive of the execution of the federal protection act (Federal soil protection and hazardous waste directive — BBodSchV) (in German)
Carbonell AA, Pulido R, DeLaune RD, Patrick WH (1999) Soluble barium in barite and phosphogypsum amended Mississippi River alluvial sediment. J Environ Qual 28:316–321
Chen ZL, Owens G (2008) Trends in speciation analysis of vanadium in environmental samples and biological fluids—a review. Anal Chim Acta 607:1–14
Choppala G, Bolan N, Lamb D, Kunhikrishnan A (2013) Comparative sorption and mobility of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) species in a range of soils: implications to bioavailability. Water Air Soil Pollut 224. doi: 10.1007/s11270-11013-11699-11276
Deutscher Wetterdienst (2011) Wetter und Klima - Deutscher Wetterdienst - Klimadaten (in German). www.dwd.de
Dimović S, Smičiklas I, Šljivić-Ivanović M, Dojčinović B (2012) Speciation of 90Sr and other metal cations in artificially contaminated soils: the influence of bone sorbent addition. J Soils Sediments 13:383–393
Du Laing G, Vanthuyne DR, Vandecasteele B, Tack FM, Verloo MG (2007) Influence of hydrological regime on pore water metal concentrations in a contaminated sediment-derived soil. Environ Pollut 147:615–625
Du Laing G, Meers E, Dewispelaere M, Rinklebe J, Vandecasteele B, Verloo MG, Tack FMG (2009a) Effect of water table level on metal mobility at different depths in wetland soils of the Scheldt Estuary (Belgium). Water Air Soil Pollut 202:353–367
Du Laing G, Rinklebe J, Vandecasteele B, Meers E, Tack FM (2009b) Trace metal behaviour in estuarine and riverine floodplain soils and sediments: a review. Sci Total Environ 407:3972–3985
Falkner KK, Klinkhammer GP, Bowers TS, Todd JF, Lewis BL, Landing WM, Edmond JM (1993) The behavior of barium in anoxic marine waters. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 57:537–554
Ferris FG, Hallberg RO, Lyven B, Pedersen K (2000) Retention of strontium, cesium, lead and uranium by bacterial iron oxides from a subterranean environment. Appl Geochem 15:1035–1042
Fiedler S, Kalbitz K (2003) Concentrations and properties of dissolved organic matter in forest soils as affected by the redox regime. Soil Sci 168:793–801
Fortoul TI et al (2014) Overview of environmental and occupational vanadium exposure and associated health outcomes: an article based on a presentation at the 8th International Symposium on Vanadium Chemistry, Biological Chemistry, and Toxicology, Washington DC, August 15–18, 2012. J Immunotoxicol 11:13–18
Frohne T, Rinklebe J, Diaz-Bone RA, Du Laing G (2011) Controlled variation of redox conditions in a floodplain soil: impact on metal mobilization and biomethylation of arsenic and antimony. Geoderma 160:414–424
Frohne T, Rinklebe J, Langer U, Du Laing G, Mothes S, Wennrich R (2012) Biogeochemical factors affecting mercury methylation rate in two contaminated floodplain soils. Biogeosciences 9:493–507
Frohne T, Rinklebe J, Diaz-Bone RA (2014) Contamination of floodplain soils along the Wupper River, Germany, with As, Co, Cu, Ni, Sb, and Zn and the Impact of Pre-definite Redox Variations on the Mobility of These Elements. Soil Sediment Contam Int J 23:779–799
Gäbler HE, Glüh K, Bahr A, Utermann J (2009) Quantification of vanadium adsorption by German soils. J Geochem Explor 103:37–44
Graham AM, Bouwer EJ (2010) Rates of hexavalent chromium reduction in anoxic estuarine sediments: pH effects and the role of acid volatile sulfides. Environ Sci Technol 44:136–142
Grybos M, Davranche M, Gruau G, Petitjean P, Pedrot M (2009) Increasing pH drives organic matter solubilization from wetland soils under reducing conditions. Geoderma 154:13–19
Heier KS (1972) Alkalis, alkali metals, and alkaline earth metals. In: Fairbridge RW (ed) The encyclopedia of geochemistry and environmental sciences. Dowdon, Hutchinson, and Ross, Stroudsburg
Henkel S et al (2012) Diagenetic barium cycling in Black Sea sediments—a case study for anoxic marine environments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 88:88–105
Hseu Z-Y (2006) Concentration and distribution of chromium and nickel fractions along a serpentinitic toposequence. Soil Sci 171:341–353
Huang J-H, Ilgen G, Matzner E (2011) Fluxes and budgets of Cd, Zn, Cu, Cr and Ni in a remote forested catchment in Germany. Biogeochemistry 103:59–70
Husson O (2013) Redox potential (Eh) and pH as drivers of soil/plant/microorganism systems: a transdisciplinary overview pointing to integrative opportunities for agronomy. Plant Soil 362:389–417
IUSS-FAO (ed) (2014) World reference base for soil resources vol 106. World Soil Resources Reports. FAO, Rome
Johnson J, Schewel L, Graedel TE (2006) The contemporary anthropogenic chromium cycle. Environ Sci Technol 40:7060–7069
Kabata-Pendias A (2011) Trace elements in soils and plants. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Kamel NH (2010) Adsorption models of 137Cs radionuclide and Sr (II) on some Egyptian soils. J Environ Radioact 101:297–303
Kamika I, Momba MNB (2011) Comparing the tolerance limits of selected bacterial and protozoan species to vanadium in wastewater systems. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:2525–2539
Korbecki J, Baranowska-Bosiacka I, Gutowska I, Chlubek D (2012) Biochemical and medical importance of vanadium compounds. Acta Biochim Pol 59:195–200
Kotas J, Stasicka Z (2000) Chromium occurrence in the environment and methods of its speciation. Environ Pollut 107:263–283
Krishna AK, Govil PK (2007) Soil contamination due to heavy metals from an industrial area of Surat, Gujarat, Western India. Environ Monit Assess 124:263–275
Kumpiene J et al (2009) Impact of water saturation level on arsenic and metal mobility in the Fe-amended soil. Chemosphere 74:206–215
Langer U, Rinklebe J (2009) Lipid biomarkers for assessment of microbial communities in floodplain soils of the Elbe River (Germany). Wetlands 29:353–362
Lee G, Park J, Harvey OR (2013) Reduction of Chromium(VI) mediated by zero-valent magnesium under neutral pH conditions. Water Res 47:1136–1146
Liszewski MJ, Rosentreter JJ, Miller KE, Bartholomay RC (2000) Chemical and physical properties affecting strontium distribution coefficients of surficial-sediment samples at the Idaho National Engineering and Environmental Laboratory, Idaho. Environ Geol 39:411–426
Masscheleyn PH, Pardue JH, Delaune RD, Patrick WH (1992) Chromium redox chemistry in a lower Mississippi Valley Bottomland Hardwood Wetland. Environ Sci Technol 26:1217–1226
McKnight DM, Bencala KE, Zellweger GW, Aiken GR, Feder GL, Thorn KA (1992) Sorption of dissolved organic-carbon by hydrous aluminum and iron-oxides occurring at the confluence of Deer Creek with the Snake River, Summit County, Colorado. Environ Sci Technol 26:1388–1396
Menzie CA, Southworth B, Stephenson G, Feisthauer N (2008) The importance of understanding the chemical form of a metal in the environment: the case of barium sulfate (Barite). Hum Ecol Risk Assess 14:974–991
Monnin C (1989) An ion interaction-model for the volumetric properties of natural-waters—density of the solution and partial molal volumes of electrolytes to high-concentrations at 25-Degrees-C. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53:1177–1188
Mukherjee B, Patra B, Mahapatra S, Banerjee P, Tiwari A, Chatterjee M (2004) Vanadium—an element of atypical biological significance. Toxicol Lett 150:135–143
Naeem A, Westerhoff P, Mustafa S (2007) Vanadium removal by metal (hydr)oxide adsorbents. Water Res 41:1596–1602
Ohgami N, Hori S, Ohgami K, Tamura H, Tsuzuki T, Ohnuma S, Kato M (2012) Exposure to low-dose barium by drinking water causes hearing loss in mice. Neurotoxicology 33:1276–1283
Palumbo B, Bellanca A, Neri R, Roe MJ (2001) Trace metal partitioning in Fe–Mn nodules from Sicilian soils, Italy. Chem Geol 173:257–269
Public Health Service Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Public health statement - Strontium (2004). www.atsdr.cdc.gov. Accessed 22.04.2013
Reddy KR, DeLaune RD (2008) Biogeochemistry of wetlands: science and applications. CRC, Boca Raton [u.a.]
Rennert T, Rinklebe J (2009) Release of Ni and Zn from contaminated floodplain soils under saturated flow conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut 205:93–105
Richard FC, Bourg ACM (1991) Aqueous geochemistry of chromium—a review. Water Res 25:807–816
Rifkin E, Gwinn P, Bouwer E (2004) Chromium and sediment toxicity. Environ Sci Technol 38:267A–271A
Rinklebe J, Du Laing G (2011) Factors controlling the dynamics of trace metals in frequently flooded soils. In: Selim HM (ed) Dynamics and Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in the Root Zone. CRC Press. Taylor & Francis Group, pp 245–270
Rinklebe J, Langer U (2006) Microbial diversity in three floodplain soils at the Elbe River (Germany). Soil Biol Biochem 38:2144–2151
Rinklebe J, Langer U (2008) Floodplain soils at the Elbe river, Germany, and their diverse microbial biomass. Arch Agron Soil Sci 54:259–273
Riscassi AL, Scanlon TM (2011) Controls on stream water dissolved mercury in three mid-Appalachian forested headwater catchments. Water Resour Res 47:W12512, doi 12510.11029/12011wr010977
Santos IR et al (2011) Uranium and barium cycling in a salt wedge subterranean estuary: the influence of tidal pumping. Chem Geol 287:114–123
Schenk R (1994) Verteilung und Dynamik von Schwermetallen in Sedimenten der Wupper (in German). PhD Thesis, Heinrich-Heine Universität
Seliman AF, Borai EH, Lasheen YF, Abo-Aly MM, DeVol TA, Powell BA (2010) Mobility of radionuclides in soil/groundwater system: comparing the influence of EDTA and four of its degradation products. Environ Pollut 158:3077–3084
Shaheen SM, Rinklebe J (2014) Geochemical fractions of chromium, copper, and zinc and their vertical distribution in floodplain soil profiles along the Central Elbe River, Germany. Geoderma 228–229:142–159
Shaheen SM, Rinklebe J, Frohne T, White J, DeLaune R (2014) Biogeochemical factors governing Co, Ni, Se, and V dynamics in periodically flooded Egyptian North Nile Delta rice soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 78:1065–1078
Shock SS, Bessinger BA, Lowney YW, Clark JL (2007) Assessment of the solubility and bioaccessibility of barium and aluminum in soils affected by mine dust deposition. Environ Sci Technol 41:4813–4820
Tack FMG, Singh SP, Verloo MG (1998) Heavy metal concentrations in consecutive saturation extracts of dredged sediment derived surface soils. Environ Pollut 103:109–115
Takeno, N (2005) Atlas of Eh-pH diagrams. http://www.gsj.jp/GDB/869openfile/files/no0419/openfile419e.pdf. Accessed 31.01.2013
Tsialtas JT, Matsi T, Barbayiannis N, Sdrakas A, Veresoglou DS (2003) Strontium absorption by two Trifolium species as influenced by soil characteristics and liming. Water Air Soil Pollut 144:363–373
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (2007) Microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludges, soils, and oils vol 3051A
Wang G, Staunton S (2005) Evolution of Sr distribution coefficient as a function of time, incubation conditions and measurement technique. J Environ Radioact 81:173–185
Wang Y, Tang C, Wu J, Liu X, Xu J (2012) Impact of organic matter addition on pH change of paddy soils. J Soils Sediments 13:12–23
Wanty RB, Goldhaber MB (1992) Thermodynamics and kinetics of reactions involving vanadium in natural systems—accumulation of vanadium in sedimentary-rocks. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:1471–1483
Wehrli B, Stumm W (1989) Vanadyl in natural-waters—adsorption and hydrolysis promote oxygenation. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53:69–77
Weishaar JL, Aiken GR, Bergamaschi BA, Fram MS, Fujii R, Mopper K (2003) Evaluation of specific ultraviolet absorbance as an indicator of the chemical composition and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon. Environ Sci Technol 37:4702–4708
Whittleston RA, Stewart DI, Mortimer RJ, Tilt ZC, Brown AP, Geraki K, Burke IT (2011) Chromate reduction in Fe(II)-containing soil affected by hyperalkaline leachate from chromite ore processing residue. J Hazard Mater 194:15–23
Wupperverband (2011) FluGGS: FlussgebietsGeoinformationsSystem des Wupperverbandes (in German). http://fluggs.wupperverband.de/internet/initParams.do. Accessed 04.04. 2011
Yu KW, Rinklebe J (2011) Advancement in soil microcosm apparatus for biogeochemical research. Ecol Eng 37:2071–2075
Yu KW, Bohme F, Rinklebe J, Neue HU, DeLaune RD (2007) Major biogeochemical processes in soils—a microcosm incubation from reducing to oxidizing conditions. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71:1406–1417
Zarate-Valdez JL, Zasoski RJ, Lauchli A (2006) Short-term effects of moisture content on soil solution pH and soil Eh. Soil Sci 171:423–431
Zibret G, Van Tonder D, Zibret L (2013) Metal content in street dust as a reflection of atmospheric dust emissions from coal power plants, metal smelters, and traffic. Environ Sci Pollut R 20:4455–4468
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mrs. M. Braun and Mr. C. Vandenhirtz for technical assistance and Prof. Dr. A.V. Hirner, University of Duisburg-Essen, for the kind access to ICP-MS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Yong Sik Ok
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Demonstration of the dynamics of EH and pH measured every 10 min during the experiment (circles with crosses represent sampling points).(PPTX 149 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frohne, T., Diaz-Bone, R.A., Du Laing, G. et al. Impact of systematic change of redox potential on the leaching of Ba, Cr, Sr, and V from a riverine soil into water. J Soils Sediments 15, 623–633 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-014-1036-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-014-1036-8