Abstract
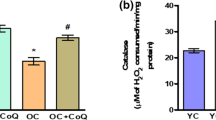
Ferulate (4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid) is a well-known phenolic compound that scavenges free radicals and exerts anti-inflammatory effects. Forkhead box O3a (FOXO3a), a transcription factor that plays important roles in aging processes, decreases with age and is negatively regulated through phosphorylation by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling. The present study investigated the efficacy of short-term ferulate feeding on age-related changes in PI3K/Akt/FOXO3a and upstream insulin signaling pathways in aged rats. In addition, changes in manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) and catalase expression were examined because of their dependence on PI3K/Akt/FOXO3a activity. Short-term feeding experiments were done with a diet containing ferulate that was given to aged rats at doses of 3 or 6 mg kg−1 day−1 for 10 days. Results showed that FOXO3a activity was increased in the ferulate-fed old group compared with the control old group. Also, ferulate suppressed the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway that is responsible for FOXO3a inhibition in aged rats. Plasma insulin levels and the upstream insulin signaling pathway were also modulated by ferulate correspondingly with PI3K/Akt/FOXO3a activity. The age-related decrease in two major antioxidant enzymes, MnSOD and catalase, was blunted by ferulate, which was accompanied by FOXO3a transcriptional activity. The significance of the present study is the finding that short-term feeding of ferulate effectively modulates age-related renal FOXO3a, PI3K/Akt and insulin signaling pathways, and MnSOD and catalase expression, all of which may be beneficial for attenuating the aging process.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alessi DR, Andjelkovi M, Caudwell B, Cron P, Morrice N, Cohen P, Hemmings BA (1996) Mechanism of activation of protein kinase B by insulin and IGF-1. EMBO J 15:6541–6551
Barone E, Calabrese V, Mancuso C (2009) Ferulic acid and its therapeutic potential as a hormetin for age-related diseases. Biogerontology 10:97–108
Belguise K, Guo S, Sonenshein GE (2007) Activation of FOXO3a by the green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces estrogen receptor alpha expression reversing invasive phenotype of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 67:5763–5770
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96:857–868
Chang CJ, Chiu JH, Tseng LM, Chang CH, Chien TM, Wu CW, Lui WY (2006) Modulation of HER2 expression by ferulic acid on human breast cancer MCF7 cells. Eur J Clin Invest 36:588–596
Coschigano KT, Holland AN, Riders ME, List EO, Flyvbjerg A, Kopchick JJ (2003) Deletion, but not antagonism, of the mouse growth hormone receptor results in severely decreased body weights, insulin, and insulin-like growth factor 1 levels and increased life span. Endocrinology 144:3799–3810
Eddy SF, Kane SE, Sonenshein GE (2007) Trastuzumab-resistant HER2-driven breast cancer cells are sensitive to epigallocatechin-3 gallate. Cancer Res 67:9018–9023
Fang J, Zhou Q, Shi XL, Jiang BH (2007) Luteolin inhibits insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signaling in prostate cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 28:713–723
Graf E (1992) Antioxidant potential of ferulic acid. Free Radic Biol Med 13:435–448
Gems D, Sutton AJ, Sundermeyer ML, Albert PS, King KV, Edgley ML, Larsen PL, Riddle DL (1998) Two pleiotropic classes of daf-2 mutation affect larval arrest, adult behavior, reproduction and longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 150:129–155
Janner DD, Jacob MH, Jahn MP, Kucharski LC, Ribeiro MF (2010) Dehydroepiandrosterone effects on Akt signaling modulation in central nervous system of young and aged healthy rats. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 122:142–148
Jin Y, Fan Y, Yan EZ, Liu Z, Zong ZH, Qi ZM (2006) Effects of sodium ferulate on amyloid-beta-induced MKK3/MKK6-p38 MAPK-Hsp27 signal pathway and apoptosis in rat hippocampus. Acta Pharmacol Sin 27:1309–1316
Jin Y, Yan EZ, Li XM, Fan Y, Zhao YJ, Liu Z, Liu WZ (2008) Neuroprotective effect of sodium ferulate and signal transduction mechanisms in the aged rat hippocampus. Acta Pharmacol Sin 29:1399–1408
Jung EH, Kim SR, Hwang IK, Ha TY (2007) Hypoglycemic effects of a phenolic acid fraction of rice bran and ferulic acid in C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice. J Agric Food Chem 55:9800–9804
Jung KJ, Go EK, Kim JY, Yu BP, Chung HY (2009) Suppression of age-related renal changes in NF-kappaB and its target gene expression by dietary ferulate. J Nutr Biochem 20:378–388
Kanski J, Aksenova M, Stoyanova A, Butterfield DA (2002) Ferulic acid antioxidant protection against hydroxyl and peroxyl radical oxidation in synaptosomal and neuronal cell culture systems in vitro: structure–activity studies. J Nutr Biochem 13:273–281
Kerr LD (1995) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Methods Enzymol 254:619–632
Kim DH, Kim JY, Yu BP, Chung HY (2008) The activation of NF-κB through Akt-induced FOXO1 phosphorylation during aging and its modulation by calorie restriction. Biogerontology 9:33–47
Kitamura T, Ogawa W, Sakaue H, Hino Y, Kuroda S, Takata M, Matsumoto M, Maeda T, Konishi H, Kikkawa U, Kasuga M (1998) Requirement for activation of the serine–threonine kinase Akt (protein kinase B) in insulin stimulation of protein synthesis but not of glucose transport. Mol Cell Biol 18:3708–3717
Kops GJ, Burgering BM (1999) Forkhead transcription factors: new insights into protein kinase B (c-akt) signaling. J Mol Med 77:656–665
Kops GJ, Dansen TB, Polderman PE, Saarloos I, Wirtz KW, Coffer PJ, Huang TT, Bos JL, Medema RH, Burgering BM (2002) Forkhead transcription factor FOXO3a protects quiescent cells from oxidative stress. Nature 419:316–321
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural protein during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Larsen PL, Albert PS, Riddle DL (1995) Genes that regulate both development and longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 139:1567–1583
Li M, Chiu JF, Mossman BT, Fukagawa NK (2006) Down-regulation of manganese-superoxide dismutase through phosphorylation of FOXO3a by Akt in explanted vascular smooth muscle cells from old rats. J Biol Chem 281:40429–40439
Li M, Chiu JF, Gagne J, Fukagawa NK (2008) Age-related differences in insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling regulates Akt/FOXO3a and ERK/Fos pathways in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol 217:377–387
Lin K, Dorman JB, Rodan A, Kenyon C (1997) Daf-16: an HNF-3/forkhead family member that can function to double the life-span of Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 278:1319–1322
Ma ZC, Hong Q, Wang YG, Tan HL, Xiao CR, Liang QD, Cai SH, Gao Y (2010a) Ferulic acid attenuates adhesion molecule expression in gamma-radiated human umbilical vascular endothelial cells. Biol Pharm Bull 33:752–758
Ma ZC, Hong Q, Wang YG, Tan HL, Xiao CR, Liang QD, Zhang BL, Gao Y (2010b) Ferulic acid protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells from radiation induced oxidative stress by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways. Biol Pharm Bull 33:29–34
Mandal S, Barik B, Mallick C, De D, Ghosh D (2008) Therapeutic effect of ferulic acid, an ethereal fraction of ethanolic extract of seed of Syzygium cumini against streptozotocin-induced diabetes in male rat. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 30:121–128
Mathew S, Abraham TE (2004) Ferulic acid: an antioxidant found naturally in plant cell walls and feruloyl esterases involved in its release and their applications. Crit Rev Biotechnol 24:59–83
Ogg S, Paradis S, Gottlieb S, Patterson GI, Lee L, Tissenbaum HA, Ruvkun G (1997) The Fork head transcription factor DAF-16 transduces insulin-like metabolic and longevity signals in C. elegans. Nature 389:994–999
Ou S, Kwok KC (2004) Ferulic acid: pharmaceutical functions, preparation and applications in foods. J Sci Food Agric 84:1261–1269
Paez J, Sellers WR (2003) PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathway. A critical mediator of oncogenic signaling. Cancer Treat Res 115:145–167
Park DW, Baek K, Kim JR, Lee JJ, Ryu SH, Chin BR, Baek SH (2009) Resveratrol inhibits foam cell formation via NADPH oxidase 1-mediated reactive oxygen species and monocyte chemotactic protein-1. Exp Mol Med 41:171–179
Rao G, Xia E, Richardson A (1990) Effect of age on the expression of antioxidant enzymes in male Fischer F344 rats. Mech Ageing Dev 53:49–60
Rice L, Handayani R, Cui Y, Medrano T, Samedi V, Baker H, Szabo NJ, Rosser CJ, Goodison S, Shiverick KT (2007) Soy isoflavones exert differential effects on androgen responsive genes in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells. J Nutr 137:964–972
Salih DA, Brunet A (2008) FoxO transcription factors in the maintenance of cellular homeostasis during aging. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20:126–136
Storz P (2011) FOXO transcription factors in the responses to oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 14:593–605
Tan WQ, Wang K, Lv DY, Li PF (2008) Foxo3a inhibits cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through transactivating catalase. J Biol Chem 283:29730–29739
Tian L, Cai Q, Wei H (1998) Alterations of antioxidant enzymes and oxidative damage to macromolecules in different organs of rats during aging. Free Radic Biol Med 24:1477–1484
Tissenbaum HA, Ruvkun G (1998) An insulin-like signaling pathway affects both longevity and reproduction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 148:703–717
Vanhaesebroeck B, Waterfield MD (1999) Signaling by distinct classes of phosphoinositide 3-kinases. Exp Cell Res 253:239–254
Vanhaesebroeck B, Alessi DR (2000) The PI3K-PDK1 connection: more than just a road to PKB. Biochem J 346:561–576
Wu M, Katta A, Gadde MK, Liu H, Kakarla SK, Fannin J, Paturi S, Arvapalli RK, Rice KM, Wang Y, Blough ER (2009) Aging-associated dysfunction of Akt/protein kinase B: S-nitrosylation and acetaminophen intervention. PLoS One 4:e6430
Wu M, Falasca M, Blough ERJ (2011) Akt/protein kinase B in skeletal muscle physiology and pathology. Cell Physiol 226:29–36
Yu BP, Yang R (1996) Critical evaluation of the free radical theory of aging. A proposal for the oxidative stress hypothesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 786:1–11
Zhang T, Yang D, Fan Y, Xie P, Li H (2009) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate enhances ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells via AKT and MAPK pathways. Apoptosis 14:1245–1254
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MEST, no. 2009-0083538). We thank the Aging Tissue Bank for supplying research information.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, Y.J., Kim, D.H., Lee, E.K. et al. Attenuation of age-related changes in FOXO3a activity and the PI3K/Akt pathway by short-term feeding of ferulate. AGE 34, 317–327 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-011-9235-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-011-9235-3