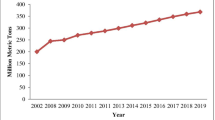
Abstract
Resource utilization of construction and demolition (C&D) waste has great potential to significantly reduce the consumption of natural resources and improve the environment. Meanwhile, establishing a sound policy system and reducing production are the key ways to solve the problem of C&D waste. Numerous studies on C&D waste, recycled concrete aggregate (RA), and recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) have been reported in the literature, with few systematic summaries. From a global perspective, this paper assessed the current situation of C&D waste and the countermeasure of several major economies. Then, this paper systematically introduces the composition structure and characteristics of RA. Modification techniques from macro and micro perspectives of RA and its effect on RAC were also presented. Paper also reviews the environmental impacts of RA and RAC. The results showed that bonded mortar was the most significant defect of RA than natural aggregate (NA). Thus, RA weakened RAC’s microstructure, workability, mechanical properties, and durability. The research on the modification of RA mainly focused on removing bonded mortar and enhancing bonded mortar containing physical or chemical methods. Enhancing bonded mortar was a more effective method than removing bonded mortar. Carbonation and microbially induced calcium carbonate precipitation were highly efficient and environmentally friendly for RA modification. Research progress in quantifying the environmental impacts associated with concrete from waste materials through the LCA methodology is presented. Suggestions and an outlook were given on the critical issues facing RA and RAC. We expect that this work can provide more technical support for C&D waste utilization.























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data is presented in this research.
References
Achal V, Pan X (2014) Influence of calcium sources on microbially induced calcium carbonate precipitation by Bacillus sp. CR2. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173:307–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0842-1
Adessinaa A, Fraja A, Barthélémya J, Chateaub C, Garnierb D (2019) Experimental and micromechanical investigation on the mechanical and durability properties of recycled aggregates concrete. Cem Concr Res 126:105900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2019.105900
Ahmad J, Zhou Z (2023) Properties of concrete with addition carbon nanotubes: a review. Constr Build Mater 393:132066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.132066
Akbarnezhad A, Ong KCG, Zhang MH, Tam CT, Foo TWJ (2011) Microwave-assisted beneficiation of recycled concrete aggregates. Constr Build Mater 25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.085
Akbarnezhad A, Ong K (2013) 10-Separation processes to improve the quality of recycled concrete aggregates (RCA). In: Handbook of recycled concrete and demolition waste, pp 246–269. https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857096906.2.246
Akhtar A, Sarmah AK (2018) Construction and demolition waste generation and properties of recycled aggregate concrete: a global perspective. J Clean Prod 186:262–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.085
Akono AT, Zhan M, Chen J, Shah SP (2021) Nanostructure of calcium-silicate-hydrates in fine recycled aggregate concrete. Cement Concr Compos 115:103827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2020.103827
Al-Bayati HKA, Das PK, Tighe SL, Baaj H (2016) Evaluation of various treatment methods for enhancing the physical and morphological properties of coarse recycled concrete aggregate. Constr Build Mater 112:284–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.02.176
Allujami H, Abdulkareem M, Jassam T, Al-Mansob H, Azmi Ibrahim A, Ng J, Yam H (2022) Mechanical properties of concrete containing recycle concrete aggregates and multi-walled carbon nanotubes under static and dynamic stresses. Case Stud Constr Mater 17:e01651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e01651
AlShareedah O, Nassiri S (2021) Pervious concrete mixture optimization, physical, and mechanical properties and pavement design: a review. J Clean Prod 288:125095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125095
Aslam M, Huang B, Li C (2020) Review of construction and demolition waste management in China and USA. J Environ Manag 264:110445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110445
AWE (2020) Joint media release: $1 billion waste and recycling plan to transform waste industry. minister.awe.gov.au, https://www.dcceew.gov.au/minister. Accessed 1 Aug 2023
Babar A, Marc A, Rawaz R, Nabil BK (2023) A multi-criteria evaluation and optimization of sustainable fiber-reinforced concrete developed with nylon waste fibers and micro-silica. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:62262–62280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26492-6
Babu VS, Mullick AK, Jain KK, Singh PK (2014) Strength and durability characteristics of high-strength concrete with recycled aggregate-influence of processing. J Sustain Cement-Based Mater 4:54–71. https://doi.org/10.1080/21650373.2014.976777
Bahrami N, Zohrabi M, Mahmoudy SA, Akbari M (2020) Optimum recycled concrete aggregate and micro-silica content in self-compacting concrete: rheological, mechanical and microstructural properties. J Build Eng 31:101361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101361
Barhmaiah B, Priyanka ML, Padmakar M (2021) Strength analysis and validation of recycled aggregate concrete. Mater Today: Proc 37:2312–2317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.07.730
Van den Heede P, De Belie N (2012) Environmental impact and life cycle assessment (LCA) of traditional and ‘green’ concretes: literature review and theoretical calculations. Cement Concr Compos 34:431–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2012.01.004
Bergsdal H, Brattebø H, Bohne RA, Müller DB (2007) Dynamic material flow analysis for Norway’s dwelling stock. Build Res Inform 35:557–570. https://doi.org/10.1080/09613210701287588
Bhutta MAR, Hasanah N, Farhayu N, Hussin MW, Tahir MBM, Mirza J (2013) Properties of porous concrete from waste crushed concrete (recycled aggregate). Constr Build Mater 47:1243–1248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.06.022
Bian Y, Li Z, Zhao J, Wang Y (2022) Synergistic enhancement effect of recycled fine powder (RFP) cement paste and carbonation on recycled aggregates performances and its mechanism. J Clean Prod 344:130848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130848
Bian Y, Qiu X, Zhao J, Li Z, Ouyang J (2024) Influence of recycled concrete fine powder on durability of cement mortar. FDMP-Fluid Dyn Mater Process 20(1). https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2023.029299
Blankendaal T, Schuur P, Voordijk H (2022) Reducing the environmental impact of concrete and asphalt: a scenario approach. J Clean Prod 66:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.10.012
Bosque IFSD, Zhu W, Howind T, Matías A, Rojas MISD, Medina C (2017) Properties of interfacial transition zones (ITZs) in concrete containing recycled mixed aggregate. Cement Concr Compos 81:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2017.04.011
Bovea M, Powell J (2016) Developments in life cycle assessment applied to evaluate the environmental performance of construction and demolition wastes. Waste Manag 50:151–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.01.036
Bru K, Touzé S, Bourgeois F, Lippiatt N, Ménard Y (2014) Assessment of a microwave-assisted recycling process for the recovery of high-quality aggregates from concrete waste. Int J Miner Process 126:90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2013.11.009
Bun P, Cyr M, Laniesse P, Bun KN, Idir R, Gastaldini ALG (2022) Concrete made of 100% recycled materials - feasibility study. Resour Conserv Recycl 180:106199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106199
Carneiro JA, Lima PRL, Leite MB, Filho RDT (2014) Compressive stress–strain behavior of steel fiber reinforced-recycled aggregate concrete. Cement Concr Compos 46:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2013.11.006
Chen X, Yang Y, Zhang H, Du X, Chen L, Zhao Q, Li B (2023) Brick-concrete recycled aggregate/powder synergistic preparation of pervious concrete. Constr Build Mater 407:133517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.133517
China Aggregates Association (2021). http://www.zgss.org.cn/zixun/zhuti/12566. Accessed 8 Nov 2021
Chinzorigt G, Lim MK, Yu M, Lee H, Enkbold O, Choi D (2020) Strength, shrinkage and creep and durability aspects of concrete including CO2 treated recycled fine aggregate. Cem Concr Res 136:106062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2020.106062
Claisse P (2014) Book review: properties of concrete, 5th edn. Constr Mater 167:124–124. https://doi.org/10.1680/coma.12.00055
Construction Week Online India (2019) India’s construction industry regains growth momentum. https://www.constructionweekonline.in/business/9399-indias-construction-industry-regains-growth-momentum. Accessed 12 July 2020
Cuenca E, D’Ambrosio L, Lizunov D, Tretjakov A, Volobujeva O, Ferrara L (2021) Mechanical properties and self-healing capacity of Ultra High Performance Fibre Reinforced Concrete with alumina nano-fibres: Tailoring Ultra High Durability Concrete for aggressive exposure scenarios. Cement Concr Compos 118:103956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2021.103956
Das CS, Dey T, Dandapat R, Mukharje BB, Kumar J (2018) Performance evaluation of polypropylene fibre reinforced recycled aggregate concrete. Constr Build Mater 189:649–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.09.036
Debieb F, Courard L, Kenai S, Degeimbre R (2010) Mechanical and durability properties of concrete using contaminated recycled aggregates. Cement Concr Compos 32:421–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2010.03.004
Devi SC, Khan RA (2020) Influence of graphene oxide on sulfate attack and carbonation of concrete containing recycled concrete aggregate. Constr Build Mater 250:118883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118883
Diamond S, Huang J (2001) The ITZ in concrete – a different view based on image analysis and SEM observations. Cement Concr Compos 23:179–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-9465(00)00065-2
Dilbas H, Çakır Ö (2020) Influence of basalt fiber on physical and mechanical properties of treated recycled aggregate concrete. Constr Build Mater 254:119216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119216
Dilbas H, Çakır Ö, Atiş CD (2019) Experimental investigation on properties of recycled aggregate concrete with optimized Ball Milling Method. Constr Build Mater 212:716–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.04.007
Dimitriou G, Savva P, Petrou MF (2018) Enhancing mechanical and durability properties of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr Build Mater 158:228–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.09.137
Duan Z, Singh A, Xiao J, Hou S (2020) Combined use of recycled powder and recycled coarse aggregate derived from construction and demolition waste in self-compacting concrete. Constr Build Mater 254:119323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119323
Elsevier database (2022) https://www.sciencedirect.com
Epa (2020) Construction and demolition debris: material-specific data. https://www.epa.gov/facts-and-figures-aboutmaterials-waste-and-recycling/construction-and-demolition-debris-material. Accessed 1 Jan 2023
Etxeberria M, Vázquez E, Marí A, Barra M (2007) Influence of amount of recycled coarse aggregates and production process on properties of recycled aggregate concrete. Cem Concr Res 37:735–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2007.02.002
European Commission (2015a) Resource efficient use of mixed wastes – member states factsheets. https://ec.europa.eu/environment/waste/studies/mixed_waste.htm. Accessed 13 September 2019
Eurostat (2021) Generation of waste by economic activity [WWW document]. https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/databrowser/view/ten00106/default/table?lang=en. Accessed 8.9.21
Fang X, Zhan B, Poon CS (2021) Enhancement of recycled aggregates and concrete by combined treatment of spraying Ca2+ rich wastewater and flow-through carbonation. Constr Build Mater 277:122202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.122202
Fanijo EO, Kolawole JT, Babafemi AJ (2023) A comprehensive review on the use of recycled concrete aggregate for pavement construction: properties, performance, and sustainability. Clean Mater 9:100199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clema.2023.100199
Feng Z, Zhao Y, Zeng W, Lu Z, Shah SP (2020) Using microbial carbonate precipitation to improve the properties of recycled fine aggregate and mortar. Constr Build Mater 230:116949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.116949
Feng C, Cui B, Huang Y, Guo H, Zhang W, Zhu J (2022) Enhancement technologies of recycled aggregate – enhancement mechanism, influencing factors, improvement effects, technical difficulties, life cycle assessment. Constr Build Mater 317:126168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.126168
Ferdous W, Manalo A, Siddique R, Mendis P, Zhuge Y, Wong HS, Lokuge W, Aravinthan T, Schubel P (2021) Recycling of landfill wastes (tyres, plastics and glass) in construction – a review on global waste generation, performance, application and future opportunities. Resour Conserv Recycl 173:105745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105745
Fiset M, Sanchez LFM, Bilodeau S, Mitchell D, Bastien J (2021) Influence of Alkali-Silica reaction (ASR) on aggregate interlock and shear-friction behavior of reinforced concrete members. Eng Struct 233:111890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2021.111890
Gálvez-Martos JL, Styles D, Schoenberger H, Zeschmar-Lahl B (2018) Construction and demolition waste best management practice in Europe. Resour Conserv Recycl 136:166–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.04.016
Gao C, Huang L, Yan L, Jin R, Chen H (2020) Mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete modified by nano-particles. Constr Build Mater 241:118030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118030
García-González J, Rodríguez-Robles D, Wang J, Belie ND, Pozo JMMD, Guerra-Romero MI, Juan-Valdés A (2017) Quality improvement of mixed and ceramic recycled aggregates by biodeposition of calcium carbonate. Constr Build Mater 154:1015–1023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.08.039
Gokce A, Nagataki S, Saeki T, Hisada M (2004) Freezing and thawing resistance of air-entrained concrete incorporating recycled coarse aggregate: the role of air content in demolished concrete. Cem Concr Res 34:799–806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2003.09.014
Gomes RI, Farinha CB, Veiga R, Brito JD, Faria P, Bastos D (2021) CO2 sequestration by construction and demolition waste aggregates and effect on mortars and concrete performance - an overview. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 152:111668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111668
Gómez-Soberón JMV (2002) Porosity of recycled concrete with substitution of recycled concrete aggregate: an experimental study. Cem Concr Res 32:1301–1311. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(02)00795-0
Gonçalves T, Silva RV, Brito JD, Fernandez JM, Esquinas AR (2020) Mechanical and durability performance of mortars with fine recycled concrete aggregates and reactive magnesium oxide as partial cement replacement. Cement Concr Compos 105:103420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2019.103420
Grabiec AM, Klama J, Zawal D, Krupa D (2012) Modification of recycled concrete aggregate by calcium carbonate biodeposition. Constr Build Mater 34:145–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.02.027
Guo H, Shi C, Guan X, Zhu J, Ding Y, Ling TC, Zhang H, Wang Y (2018) Durability of recycled aggregate concrete – a review. Cement Concr Compos 89:251–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2018.03.008
Hafez H, Kurda R, Kurda R, Al-Hadad B, Mustafa R, Ali B (2020) A critical review on the influence of fine recycled aggregates on technical performance, environmental impact and cost of concrete. Appl Sci 10:1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10031018
Hasan-Ghasemi A, Nematzadeh M (2021) Tensile and compressive behavior of self-compacting concrete incorporating PET as fine aggregate substitution after thermal exposure: experiments and modeling. Constr Build Mater 289:123067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123067
Hoornweg D, Bhada-Tata P (2012) What a waste: a global review of solid waste management. http://hdl.handle.net/10986/17388. Accessed 1 Jan 2023
Hossain MU, Poon CS, Lo IMC, Cheng JCP (2016) Comparative environmental evaluation of aggregate production from recycled waste materials and virgin sources by LCA. Resour Conserv Recycl 109:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2016.02.009
Hossein AH, AzariJafari H, Khoshnazar R (2022) The role of performance metrics in comparative LCA of concrete mixtures incorporating solid wastes: a critical review and guideline proposal. J Clean Prod 140:140–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2022.01.010
Hou Y, Ji X, Su X, Zhang W, Liu L (2014) Laboratory investigations of activated recycled concrete aggregate for asphalt treated base. Constr Build Mater 65:535–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.04.115
Huang B, Wang X, Kua H, Geng Y, Bleischwitz R, Ren J (2018) Construction and demolition waste management in China through the 3R principle. Resour Conserv Recycl 129:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.09.029
Huang J, Zou C, Sun D, Yang B, Yan J (2021) Effect of recycled fine aggregates on alkali-activated slag concrete properties. Structures 30:89–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2020.12.064
Huda SB, Alam MS (2014) Mechanical behavior of three generations of 100% repeated recycled coarse aggregate concrete. Constr Build Mater 65:574–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.05.010
Ibrahim HA, Goh Y, Ng ZA, Yap SP, Mo KH, Yuen CW, Abutaha F (2020) Hydraulic and strength characteristics of pervious concrete containing a high volume of construction and demolition waste as aggregates. Constr Build Mater 253:119251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119251
Ismail S, Ramli M (2013) Engineering properties of treated recycled concrete aggregate (RCA) for structural applications. Constr Build Mater 44:464–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.03.014
Jain MS (2021) A mini review on generation, handling, and initiatives to tackle construction and demolition waste in India. Environ Technol Innov 22:101490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101490
Jain S, Singhal S, Jain NK (2018) Construction and demolition waste (C&DW) in India: generation rate and implications of C&DW recycling. Int J Constr Manag 21(3):261–270. https://doi.org/10.1080/15623599.2018.1523300
Jain S, Singhal S, Jain NK (2019) Construction and demolition waste generation in cities in India: an integrated approach. Int J Sustain Eng 12:333–340. https://doi.org/10.1080/19397038.2019.1612967
Jian SM, Wu B, Hu N (2021) Environmental impacts of three waste concrete recycling strategies for prefabricated components through comparative life cycle assessment. J Clean Prod 115:129463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129463
Jin R, Yuan H, Chen Q (2019) Science mapping approach to assisting the review of construction and demolition waste management research published between 2009 and 2018. Resour Conserv Recycl 140:175–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.09.029
Jin L, Yu H, Wang Z, Fan T (2021) Effect of crack and damaged zone on chloride penetration in recycled aggregate concrete: a seven-phase mesoscale numerical method. Constr Build Mater 291:123383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123383
Jones S, Head BW (2023) The limits of voluntary measures: packaging the plastic pollution problem in Australia. Aust J Public Adm 189:649–659. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8500.12614
Juan M, Gutiérrez P (2009) Study on the influence of attached mortar content on the properties of recycled concrete aggregate. Constr Build Mater 23:872–877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2008.04.012
Kabirifar K, Mojtahedi M, Wang C, Tam VWY (2020) Construction and demolition waste management contributing factors coupled with reduce, reuse, and recycle strategies for effective waste management: a review. J Clean Prod 263:121265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121265
Kaliyavaradhan SK, Ling TC (2017) Potential of CO2 sequestration through construction and demolition (C&D) waste—an overview. J CO2 Util 20:234–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcou.2017.05.014
Kapoor KME, Singh SPPD, Singh BPD (2016) Durability of self-compacting concrete made with Recycled Concrete Aggregates and mineral admixtures. Constr Build Mater 128:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.10.026
Katkhuda H, Shatarat N (2017) Improving the mechanical properties of recycled concrete aggregate using chopped basalt fibers and acid treatment. Constr Build Mater 140:328–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.02.128
Katz A (2004) Treatments for the improvement of recycled aggregate. J Mater Civ Eng 16:597–603. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(2004)16:6(597)
Kaza S, Yao L, Bhada-Tata P, Van Woerden F (2018) What a waste 2.0: a global snapshot of solid waste management to 2050. World Bank Publications. https://scholar.google.com. Accessed 1 Aug 2023
Kazmi SMS, Munir MJ, Wu YF, Patnaikuni I, Zhou Y, Xing F (2019) Influence of different treatment methods on the mechanical behavior of recycled aggregate concrete: a comparative study. Cement Concr Compos 104:103398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2019.103398
Khankhaje E, Rafieizonooz M, Salim MR, Khan R, Mirza J, Siong H, Salmiati, (2021) Sustainable clean pervious concrete pavement production incorporating palm oil fuel ash as cement replacement. J Clean Prod 172:1476–1485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.159
Kim Y, Hanif A, Kazmi SMS, Munir MJ, Park C (2018) Properties enhancement of recycled aggregate concrete through pretreatment of coarse aggregates – comparative assessment of assorted techniques. J Clean Prod 191:339–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.192
Kirthika S, Singh S, Chourasia A (2020) Performance of recycled fine-aggregate concrete using novel mix-proportioning method. J Mater Civ Eng 38(8):04020216. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0003289
Kisku N, Joshi H, Ansari M, Panda SK, Nayak S, Dutta SC (2017) A critical review and assessment for usage of recycled aggregate as sustainable construction material. Constr Build Mater 131:21–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.11.029
Klein NS, Bachmann J, Aguado A, Toralles-Carbonari B (2012) Evaluation of the wettability of mortar component granular materials through contact angle measurements. Cem Concr Res 42:1611–1620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2012.09.001
Knoeri C, Sanyé-Mengual E, Althaus HJ (2013) Comparative LCA of recycled and conventional concrete for structural applications. Int J Life Cycle Assess 18:909–918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-012-0544-2
Kou SC, Poon CS (2008) Mechanical properties of 5-year-old concrete prepared with recycled aggregates obtained from three different sources. Mag Concr Res 60:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1680/macr.2007.00052
Kou SC, Zhan BJ, Poon CS (2014) Use of a CO2 curing step to improve the properties of concrete prepared with recycled aggregates. Cement Concr Compos 45:22–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2013.09.008
Kumar GS, Minocha AK (2018) Studies on thermochemical treatment of recycled concrete fine aggregates for use in concrete. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 20:469–480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-017-0604-6
Kumar S, Putnam V (2008) Cradle to cradle: reverse logistics strategies and opportunities across three industry sectors. Int J Prod Econ 115:305–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2007.11.015
Kwan WH, Ramli M, Kam KJ, Sulieman MZ (2012) Influence of the amount of recycled coarse aggregate in concrete design and durability properties. Constr Build Mater 26:565–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2011.06.059
Lee GC, Choi HB (2013) Study on interfacial transition zone properties of recycled aggregate by micro-hardness test. Constr Build Mater 40:455–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.09.114
Lee HK, Kim HK, Hwang EA (2010) Utilization of power plant bottom ash as aggregates in fiber-reinforced cellular concrete. Waste Manag 30:274–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2009.09.043
Lei B, Li W, Tang Z, Li Z, Tam VWY (2020) Effects of environmental actions, recycled aggregate quality and modification treatments on durability performance of recycled concrete. J Market Res 9:13375–13389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.09.073
Letelier V, Henríquez-Jara BI, Manosalva M, Moriconi G (2019) Combined use of waste concrete and glass as a replacement for mortar raw materials. Waste Manag 94:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.05.041
Li VC (1992) A simplified micromechanical model of compressive strength of fiber-reinforced cementitious composites. Cement Concr Compos 14:131–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/0958-9465(92)90006-H
Li X (2008) Recycling and reuse of waste concrete in China. Resour Conserv Recycl 53:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2008.09.006
Li J, Xiao H, Zhou Y (2009) Influence of coating recycled aggregate surface with pozzolanic powder on properties of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr Build Mater 23:1287–1291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2008.07.019
Li W, Long C, Tam VWY, Poon CS, Duan WH (2017) Effects of nano-particles on failure process and microstructural properties of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr Build Mater 142:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.03.051
Li Y, Zhang S, Wang R, Zhao Y, Men C (2019) Effects of carbonation treatment on the crushing characteristics of recycled coarse aggregates. Constr Build Mater 201:408–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.12.158
Li Y, Fu T, Wang R, Li Y (2020) An assessment of microcracks in the interfacial transition zone of recycled concrete aggregates cured by CO2. Constr Build Mater 236:117543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117543
Li CZ, Zhao Y, Xiao B, Yu B, Tam VWY, Chen Z, Ya Y (2020) Research trend of the application of information technologies in construction and demolition waste management. J Clean Prod 263:121458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121458
Li L, Xuan D, Sojobi AO, Liu S, Chu SH, Poon CS (2021a) Development of nano-silica treatment methods to enhance recycled aggregate concrete. Cement Concr Compos 118:103963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2021.103963
Li Y, Yang X, Lou P, Wang R, Li Y, Si Z (2021b) Sulfate attack resistance of recycled aggregate concrete with NaOH-solution-treated crumb rubber. Constr Build Mater 287:123044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123044
Li P, Chen L, Ma H, Pan G, Sun Z (2023) Spatial distribution characteristics and microscopic mechanisms for enhancing mechanical properties of MWCNTs in recycled coarse aggregate shotcrete. Constr Build Mater 364:129927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129927
Lian S, Ruan S, Zhan S, Unluer C, Meng T, Qian K (2022) Unlocking the role of pores in chloride permeability of recycled concrete: a multiscale and a statistical investigation. Cement Concr Compos 125:104320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2021.104320
Liang C, Lu N, Ma H, Ma Z, Duan Z (2020) Carbonation behavior of recycled concrete with CO2-curing recycled aggregate under various environments. J CO2 Util 39:101185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcou.2020.101185
Liao L, Wu S, Zhang H, Hao R, Zhou Y, Zhao Q, Xie P (2023) The compressive strength and damage mechanisms of pervious concrete based on 2D mesoscale pore characteristics. Constr Build Mater 386:131561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.131561
Limbachiya MC, Leelawat T, Dhir RK (2000) Use of recycled concrete aggregate in high-strength concrete. Mater Struct 33:574–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02480538
Liu Q, Xiao J, Sun Z (2011) Experimental study on the failure mechanism of recycled concrete. Cem Concr Res 41:1050–1057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2011.06.007
Liu K, Wang S, Quan X, Duan W, Nan Z, Wei T, Xu F, Li B (2021) Study on the mechanical properties and microstructure of fiber reinforced metakaolin-based recycled aggregate concrete. Constr Build Mater 294:123554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123554
Lockrey S, Nguyen H, Crossin E, Verghese K (2016) Recycling the construction and demolition waste in Vietnam: opportunities and challenges in practice. J Clean Prod 133:757–766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.05.175
Lu JX, Yan X, He P, Poon CS (2019a) Sustainable design of pervious concrete using waste glass and recycled concrete aggregate. J Clean Prod 234:1102–1112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.260
Lu B, Shi C, Cao Z, Guo M, Zheng J (2019b) Effect of carbonated coarse recycled concrete aggregate on the properties and microstructure of recycled concrete. J Clean Prod 233:421–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.350
Lu B, Shi C, Zheng J, Ling TC (2018) Carbon dioxide sequestration on recycled aggregates. Carbon Dioxide Sequestration in Cementitious Construction Materials 247–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-102444-7.00011-3
Luo S, Ye S, Xiao J, Zheng J, Zhu Y (2018) Carbonated recycled coarse aggregate and uniaxial compressive stress-strain relation of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr Build Mater 188:956–965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.08.159
Martinez-Echevarria MJ, Lopez-Alonso M, Garach L, Alegre J, Poon CS, Agrela F, Cabrera M (2020) Crushing treatment on recycled aggregates to improve their mechanical behaviour for use in unbound road layers. Constr Build Mater 263:120517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120517
Martirena F, Castaño T, Alujas A, Orozco-Morales R, Martinez L, Linsel S (2017) Improving quality of coarse recycled aggregates through cement coating. J Sustain Cement-Based Mater 6:69–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/21650373.2016.1234983
Mazhoud B, Sedran T, Cazacliu B, Cothenet A, Torrenti J (2012) Influence of residual mortar volume on the properties of recycled concrete aggregates. J Build Eng 57:104945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2022.104945
Mehrabi P, Shariati M, Kabirifar K, Jarrah M, Rasekh H, Trung NT, Shariati A, Jahandari S (2021) Effect of pumice powder and nano-clay on the strength and permeability of fiber-reinforced pervious concrete incorporating recycled concrete aggregate. Constr Build Mater 287:122652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122652
Mehta PK, Monteiro PJM (2014) Concrete: microstructure, properties, and materials[M]. McGraw-Hill Education. https://scholar.google.com. Accessed 1 Aug 2023
Menegaki M, Damigos D (2018) A review on current situation and challenges of construction and demolition waste management. Curr Opin Green Sustain Chem 13:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsc.2018.02.010
Merli R, Preziosi M, Acampora A, Lucchetti MC, Petrucci E (2020) Recycled fibers in reinforced concrete: a systematic literature review. J Clean Prod 248:119207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119207
Mi R, Liew K, Pan G, Kuang T (2021) Carbonation resistance study and inhomogeneity evolution of recycled aggregate concretes under loading effects. Cement Concr Compos 118:103916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2020.103916
Mistri A, Bhattacharyya SK, Dhami N, Mukherjee A, SVPD B, (2019) Petrographic investigation on recycled coarse aggregate and identification the reason behind the inferior performance. Constr Build Mater 221:339–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.085
Mistri A, Dhami N, Bhattacharyya SK, Barai SV, Mukherjee A, Biswas WK (2021) Environmental implications of the use of bio-cement treated recycled aggregate in concrete. Resour Conserv Recycl 167:105436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105436
Mohammed H, Giuntini F, Sadique M, Shaw A, Bras A (2022) Polymer modified concrete impact on the durability of infrastructure exposed to chloride environments. Constr Build Mater 317:125771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125771
Montgomery DG, Dhir RK, Henderson NA, Limbachiya MC (1998) Workability and compressive strength properties of concrete containing recycled concrete aggregate. Sustain Constr: Use Recycl Concrete Aggr 287–296. https://www.icevirtuallibrary.com/doi/abs/10.1680/scuorca.27268.0025. Accessed 1 Jan 2023
Moro C, Francioso F, Lopez-Arias M, Velay-Lizancos M (2023) CO2 curing of mortar with natural and recycled concrete aggregate: an environmental and economic assessment. Constr Build Mater 399:132587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2022.01.010
Mukharjee BB, Barai SV (2014) Influence of nano-silica on the properties of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr Build Mater 55:29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.01.003
Nili M, Sasanipour H, Aslani F (2019) The effect of fine and coarse recycled aggregates on fresh and mechanical properties of self-compacting concrete. Materials 12:1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071120
Nuruzzaman M, Kuri JC, Sarker PK (2022) Strength, permeability and microstructure of self-compacting concrete with the dual use of ferronickel slag as fine aggregate and supplementary binder. Constr Build Mater 318:125927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125927
Olorunsogo FT, Padayachee N (2002) Performance of recycled aggregate concrete monitored by durability indexes. Cem Concr Res 32:179–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(01)00653-6
Ortega-Lópeza V, Faleschini F, Pellegrino C, Revilla-Cuesta V, Manso JM (2022) Validation of slag-binder fiber-reinforced self-compacting concrete with slag aggregate under field conditions: durability and real strength development. Constr Build Mater 320:126280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.126280
Ortolan T, Borges P, Silvestro L, Silva S, Possan E, Andrade J (2023) Durability of concrete incorporating recycled coarse aggregates: carbonation and service life prediction under chloride-induced corrosion. Constr Build Mater 404:133267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.133267
Otsuki N, Miyazato SI, Yodsudjai W (2003) Influence of recycled aggregate on interfacial transition zone, strength, chloride penetration and carbonation of concrete. J Mater Civ Eng 15:443–451. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(2003)15:5(443)
Ouyang J, Liu K, Sun D, Xu W, Wang A, Ma R (2020a) A focus on Ca2+ supply in microbial induced carbonate precipitation and its effect on recycled aggregate. J Build Eng 51:104334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2022.10433410.1016/j.jobe.2022.104334
Ouyang K, Shi C, Chu H, Guo H, Song B, Ding Y, Guan X, Zhu J, Zhang H, Wang Y, Zheng J (2020b) An overview on the efficiency of different pretreatment techniques for recycled concrete aggregate. J Clean Prod 263:121264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121264
Pacheco JN, Brito JD, Chastre C, Evangelista L (2021) Bond of recycled coarse aggregate concrete: model uncertainty and reliability-based calibration of design equations. Eng Struct 239:112290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2021.112290
Pan G, Zhan M, Fu M, Wang Y, Lu X (2017) Effect of CO2 curing on demolition recycled fine aggregates enhanced by calcium hydroxide pre-soaking. Constr Build Mater 154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.07.079
Park SB, Seo DS, Lee J (2005) Studies on the sound absorption characteristics of porous concrete based on the content of recycled aggregate and target void ratio. Cem Concr Res 35:1846–1854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2004.12.009
Parker L (2018) A whopping 91% of plastic isn’t recycled. nationalgeographic.com https://www.nationalgeographic.com. Accessed 1 Aug 2023
Parthiban K, Mohan KSR (2017) Influence of recycled concrete aggregates on the engineering and durability properties of alkali activated slag concrete. Constr Build Mater 133:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.12.050
Peng C (2016) Calculation of a building’s life cycle carbon emissions based on Ecotect and building information modeling. J Clean Prod 112:453–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.08.078
Peter MA, Muntean A, Meier SA, Böhm M (2008) Competition of several carbonation reactions in concrete: a parametric study. Cem Concr Res 38:1385–1393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2008.09.003
Phung QT, Maes N, Jacques D, Bruneel E, Driessche IV, Ye G, Schutter GD (2015) Effect of limestone fillers on microstructure and permeability due to carbonation of cement pastes under controlled CO2 pressure conditions. Constr Build Mater 82:376–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.02.093
Plastics-Europe (2019) Plastics – the facts 2019, an analysis of European plastics production, demand and waste data. https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-facts-2019. Accessed 1 Jan 2023
Pu Y, Li L, Wang Q, Shi X, Luan C, Zhang G, Fu L, Abomohra AEF (2021) Accelerated carbonation technology for enhanced treatment of recycled concrete aggregates: a state-of-the-art review. Constr Build Mater 282:122671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122671
Qiu J, Tng DQS, Yang EH (2014) Surface treatment of recycled concrete aggregates through microbial carbonate precipitation. Constr Build Mater 57:144–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.01.085
Rahal KN, Collins MP (1999) Background to the general method of shear design in the 1994 CSA-A23.3 standard. Can J Civ Eng 26:827–839. https://doi.org/10.1139/l99-050
Revilla-Cuesta V, Skaf M, Faleschini F, Manso JM, VanesaOrtega-López V (2020) Self-compacting concrete manufactured with recycled concrete aggregate: an overview. J Clean Prod 262:121362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121362
Rifa A, Subhani S, Bahurudeen A, Santhosh K (2023) A systematic comparison of performance of recycled concrete fine aggregates with other alternative fine aggregates: an approach to find a sustainable alternative to river sand. J Build Eng 78:107695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2023.107695
Ruiz LAL, Ramón XR, Domingo SG (2020) The circular economy in the construction and demolition waste sector – a review and an integrative model approach. J Clean Prod 248:119238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119238
Ruviaro AS, Silvestro L, Pelisser F, Azevedo ARGD, Matos RRD, Gastaldini ALG (2022) Long-term effect of recycled aggregate on microstructure, mechanical properties, and CO2 sequestration of rendering mortars. Constr Build Mater 321:126357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.126357
Santos WF, Quattrone M, John VM, Angulo SC (2017) Roughness, wettability and water absorption of water repellent treated recycled aggregates. Constr Build Mater 146:502–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.04.012
Sasanipour H, Aslani F (2020) Durability properties evaluation of self-compacting concrete prepared with waste fine and coarse recycled concrete aggregates. Constr Build Mater 236:117540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117540
Sasanipour H, Aslani F, Taherinezhad J (2021) Chloride ion permeability improvement of recycled aggregate concrete using pretreated recycled aggregates by silica fume slurry. Constr Build Mater 270:121498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121498
Sayre R, Karagulle D, Frye C, Boucher T, Wolff NH, Breyer S, Wright D, Martin M, Butler K, Graafeiland KV, Touval J, Sotomayor L, McGowan J, Game ET, Possingham H (2020) An assessment of the representation of ecosystems in global protected areas using new maps of World Climate Regions and World Ecosystems. Glob Ecol Conserv 21:e00860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2019.e00860
Scrivener KL, Crumbie AK, Laugesen P (2004) The interfacial transition zone (ITZ) between cement paste and aggregate in concrete. Interface Sci 12:411–421. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:INTS.0000042339.92990.4c
Seo DS, Choi HB (2014) Effects of the old cement mortar attached to the recycled aggregate surface on the bond characteristics between aggregate and cement mortar. Constr Build Mater 59:72–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.02.047
Serres N, Braymand S, Feugeas F (2016) Environmental evaluation of concrete made from recycled concrete aggregate implementing life cycle assessment. J Build Eng 5:24–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2015.11.004
Shaban WM, Yang J, Su H, Liu QF, Tsang DCW, Wang L, Xie J, Li L (2019) Properties of recycled concrete aggregates strengthened by different types of pozzolan slurry. Constr Build Mater 216:632–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.04.231
Shang X, Yang J, Wang S, Zhang M (2021) Fractal analysis of 2D and 3D mesocracks in recycled aggregate concrete using X-ray computed tomography images. J Clean Prod 304:127083. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127083
Shi C, Li Y, Zhang J, Li W, Chong L, Xie Z (2016) Performance enhancement of recycled concrete aggregate – a review. J Clean Prod 112:466–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.08.057
Shi X, Mukhopadhyay A, Zollinger D, Grasley Z (2019) Economic input-output life cycle assessment of concrete pavement containing recycled concrete aggregate. J Clean Prod 225:414–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.288
Silgado SSS, Molina JDA, Mahecha L, Calderón L (2018) Diagnóstico y propuestas para la gestión de los residuos de construcción y demolición en la ciudad de Ibagué (Colombia). Gestión y Ambiente 21(1):9–21. https://doi.org/10.15446/ga.v21n1.69637
Silva RV, Brito JD, Dhirc RK (2014) Properties and composition of recycled aggregates from construction and demolition waste suitable for concrete production. Constr Build Mater 65:201–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.04.117
Silva R, Brito J, Dhir R (2017) Availability and processing of recycled aggregates within the construction and demolition supply chain: a review. J Clean Prod 143:598–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.12.070
Singh LP, Bisht V, Aswathy MS, Chaurasia L, Gupta S (2018) Studies on performance enhancement of recycled aggregate by incorporating bio and nano materials. Constr Build Mater 181:217–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.05.248
Singh A, Miao X, Zhou X, Deng Q, Li J (2023) Use of recycled fine aggregates and recycled powders in sustainable recycled concrete. J Build Eng 18:909–918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2023.107370
Slegers PA, Rouxhet PG (1976) Carbonation of the hydration products of tricalcium silicate. Cem Concr Res 6:381–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-8846(76)90101-0
Song XB, Li CZ, Chen DD, Gu XL (2021) Interfacial mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete reinforced by nano-materials. Constr Build Mater 270:121446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121446
Soto-Paz J, Arroyo O, Torres-Guevara L, Parra-Orobio L, Casallas-Ojeda M (2023) The circular economy in the construction and demolition waste management: a comparative analysis in emerging and developed countries. J Build Eng 78:107724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2023.107724
Souza FDS, Mendes JC, Morais LJB, Silva JS, Peixoto RAF (2022) Mapping and recycling proposal for the construction and demolition waste generated in the Brazilian Amazon. Resour Conserv Recycl 176:105896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105896
Spaeth V, Tegguer AD (2013) Improvement of recycled concrete aggregate properties by polymer treatments. Int J Sustain Built Environ 2:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsbe.2014.03.003
Sun C, Chen Q, Xiao J, Liu W (2020) Utilization of waste concrete recycling materials in self-compacting concrete. Resour Conserv Recycl 161:104930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.104930
Syed Y, Muhammad T, Babar A, Mohamed H (2022) Correction to: mechanical performance and environmental impact of normal strength concrete incorporating various levels of coconut fiber and recycled aggregates. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:83652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23793-0
Tam VWY, Tam CM (2006) A review on the viable technology for construction waste recycling. Resour Conserv Recycl 47:209–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2005.12.002
Tam VWY, Gao XF, Tam CM (2005) Microstructural analysis of recycled aggregate concrete produced from two-stage mixing approach. Cem Concr Res 35:1195–1203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2004.10.025
Tam VWY, Tam CM, Le KN (2007) Removal of cement mortar remains from recycled aggregate using pre-soaking approaches. Resour Conserv Recycl 50:82–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2006.05.012
Tang J, Wu J, Zou Z, Yue A, Mueller A (2018) Influence of axial loading and carbonation age on the carbonation resistance of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr Build Mater 173:707–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.03.269
Tateyashiki H, Shima H, Matsumoto Y, Koga Y (2001) Properties of concrete with high quality recycled aggregate by heat and rubbing method. Proc Jpn Concr Inst 23:61–66 (in Japanese)
THE WORLD BANK (2018a) GDP [Online]. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.CD. Accessed 1 Jan 2023
THE WORLD BANK (2018b) Land area [Online]. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/AG.LND.TOTL.K2. Accessed 1 Jan 2023
THE WORLD BANK (2018c) Population [Online]. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.TOTL. Accessed 1 Jan 2023
Thiery M, Villain G, Dangla P, Platret G (2007) Investigation of the carbonation front shape on cementitious materials: effects of the chemical kinetics. Cem Concr Res 37:1047–1058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2007.04.002
Thomas C, Setién J, Polanco JA (2016) Structural recycled aggregate concrete made with precast wastes. Constr Build Mater 114:536–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.03.203
Trottier C, Ziapour R, Zahedi A, Sanchez L, Locati F (2021) Microscopic characterization of alkali-silica reaction (ASR) affected recycled concrete mixtures induced by reactive coarse and fine aggregates. Cem Concr Res 144:106426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2021.106426
Tsujino M, Noguchi T, Tamura M, Kanematsu M, Maruyama I (2007) Application of conventionally recycled coarse aggregate to concrete structure by surface modification treatment. J Adv Concr Technol 5:13–25. https://doi.org/10.3151/jact.5.13
Tuyan M, Mardani-Aghabaglou A, Ramyar K (2014) Freeze–thaw resistance, mechanical and transport properties of self-consolidating concrete incorporating coarse recycled concrete aggregate. Mater Des 53:983–991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.07.100
U.S. MPCA (2012) Minnesota Pollution Control Agency, Metropolitan Solid Waste Management Policy Plan 2010–2030-Fact Sheet. https://www.pca.state.mn.us/waste/solid-waste-publications. Accessed Jaunary 2012
Ulubeyli S, Kazaz A, Arslan V (2017) Construction and demolition waste recycling plants revisited: management issues. Procedia Eng 172:1190–1197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.02.139
Vieira GL, Schiavon JZ, Borges PM, Silva SRD, Andrade JJDO (2020) Influence of recycled aggregate replacement and fly ash content in performance of pervious concrete mixtures. J Clean Prod 271:122665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122665
Villagrán-Zaccardiae YA, Marsh ATM, Sosa ME, Zega CJ, Belie ND, Bernal SA (2022) Complete re-utilization of waste concretes–valorisation pathways and research needs. Resour Conserv Recycl 177:105955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105955
Wan HW, Shui ZH, Lin ZS, Xiao KT (2003) Environmental assessment for regenerated concrete. J Wuhan Univ Technol 04:17–20+23. https://kns.cnki.net/kns8/manage/export.html?displaymode=NEW&filename=CJFD2003!WHGY200304005!20!6. (In Chinese). Accessed 1 Jan 2023
Wang J, Vandevyvere B, Vanhessche S, Schoon J, Boon N, Belie ND (2017a) Microbial carbonate precipitation for the improvement of quality of recycled aggregates. J Clean Prod 156:355–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.04.051
Wang L, Wang J, Qian X, Chen P, Xu Y, Guo J (2017b) An environmentally friendly method to improve the quality of recycled concrete aggregates. Constr Build Mater 144:432–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.03.191
Wang J, Zhang J, Cao D, Dang H, Ding B (2020) Comparison of recycled aggregate treatment methods on the performance for recycled concrete. Constr Build Mater 234:117366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117366
Wang B, Yan L, Fu Q, Kasal B (2021a) A comprehensive review on recycled aggregate and recycled aggregate concrete. Resour Conserv Recycl 171:105565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105565
Wang X, Yang X, Ren J, Han N, Xing F (2021b) A novel treatment method for recycled aggregate and the mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete. J Market Res 10:1389–1401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.12.095
Wang Y, Xu Y, Zhao Y, Li Q, Wang Y (2022) Comprehensive evaluation method for performance and environmental benefits of mineral admixture concrete. Environ Eng 40:197–205. https://doi.org/10.13205/j.hjgc.202208028. (In Chinese)
Waskow R, Maciel V, Tubino R, Passuello A (2021) Environmental performance of construction and demolition waste management strategies for valorization of recycled coarse aggregate. J Environ Manag 295:113094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113094
World-Counts (2020) Tons of solid waste generated. The World Counts. theworldcounts.com. Accessed 1 Aug 2023
Wu CR, Zhu YG, Zhang XT, Kou SC (2018) Improving the properties of recycled concrete aggregate with bio-deposition approach. Cement Concr Compos 94:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2018.09.012
Wu H, Zuo J, Yuan H, Zillante G, Wang J (2019) A review of performance assessment methods for construction and demolition waste management, Environmental Impact and Cost of Concrete. Resour Conserv Recycl 150:104407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104407
Wu CR, Hong ZQ, Zhang JL, Kou SC (2020) Pore size distribution and ITZ performance of mortars prepared with different bio-deposition approaches for the treatment of recycled concrete aggregate. Cement Concr Compos 111:103631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2020.103631
Xiao J, Xie H, Yang Z (2012) Shear transfer across a crack in recycled aggregate concrete. Cem Concr Res 42:700–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2012.02.006
Xiao J, Li W, Sun Z, Lange DA, Shah SP (2013) Properties of interfacial transition zones in recycled aggregate concrete tested by nanoindentation. Cement Concr Compos 37:276–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2013.01.006
Xiao JZ, Li A, Ding T (2016a) Life cycle assessment on CO2 emission for recycled aggregate concrete. J Southeast Univ (natural Science Edition) 46:1088–1092. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-0505.2016.05.032. (In Chinese)
Xiao J, Ma Z, Ding T (2016b) Reclamation chain of waste concrete: a case study of Shanghai. Waste Manag 48:334–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.09.018
Xiao J, Zhang K, Akbarnezhad K (2018) Variability of stress-strain relationship for recycled aggregate concrete under uniaxial compression loading. J Clean Prod 181:753–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.247
Xie X, Zhang T, Wang C, Yang Y, Bogush A, Khayrulina E, Huang Z, Wei J, Yu Q (2020) Mixture proportion design of pervious concrete based on the relationships between fundamental properties and skeleton structures. Cement Concr Compos 113:103693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2020.103693
Xie J, Kou SC, Ma H, Long WJ, Wang Y, Ye TH (2021) Advances on properties of fiber reinforced recycled aggregate concrete: experiments and models. Constr Build Mater 277:122345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122345
Xie K, Hao W, Xu K, Xu S, Lin J, Wei Z, Zhang J (2023) Boosting the sonophotocatalytic performance of BiOCl by Eu doping: DFT and an experimental study. Ultrason Sonochem 99:106543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2023.106543
Xuan D, Zhan B, Poon CS (2016) Development of a new generation of eco-friendly concrete blocks by accelerated mineral carbonation. J Clean Prod 133:1235–1241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.06.062
Yap SP, Chen PZC, Goh Y, Ibrahim HA, Mo KH, Yue CW (2018) Characterization of pervious concrete with blended natural aggregate and recycled concrete aggregates. J Clean Prod 181:155–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.205
Yu M, Lourie O, Dyer M, Moloni K, Kelly T, Ruoff R (2000) Strength and breaking mechanism of multiwalled carbon nanotubes under tensile load. Science 287(5453):637–640. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.287.5453.637
Zeng Q, Li K, Fen-chong T, Dangla P (2012) Pore structure characterization of cement pastes blended with high-volume fly-ash. Cem Concr Res 42:194–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2011.09.012
Zeng W, Zhao Y, Zheng H, Poon C (2020) Improvement in corrosion resistance of recycled aggregate concrete by nano silica suspension modification on recycled aggregates. Cement Concr Compos 106:103476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2019.103476
Zhan B, Poon CS, Liu Q, Kou S, Shi C (2014) Experimental study on CO2 curing for enhancement of recycled aggregate properties. Constr Build Mater 67:3–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.09.008
Zhan BJ, Xuan DX, Poon CS (2018) Enhancement of recycled aggregate properties by accelerated CO2 curing coupled with limewater soaking process. Cement Concr Compos 89:230–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2018.03.011
Zhan BJ, Xuan DX, Poon CS, Scrivener KL (2020) Characterization of interfacial transition zone in concrete prepared with carbonated modeled recycled concrete aggregates. Cem Concr Res 136:106175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2020.106175
Zhang J, Shi C, Li Y, Pan X, Poon CS, Xie Z (2015) Influence of carbonated recycled concrete aggregate on properties of cement mortar. Constr Build Mater 98:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.08.087
Zhang H, Ji T, Zeng X, Yang Z, Lin X, Liang Y (2018) Mechanical behavior of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) using recycled fine aggregate cured under different conditions and the mechanism based on integrated microstructural parameters. Constr Build Mater 192:489–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.10.117
Zhang C, Wang Y, Zhang X, Ding Y, Xu P (2021) Mechanical properties and microstructure of basalt fiber-reinforced recycled concrete. J Clean Prod 278:123252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123252
Zhang C, Hu M, Maio FD, Sprecher B, Yang X, Tukker A (2022a) An overview of the waste hierarchy framework for analyzing the circularity in construction and demolition waste management in Europe. Sci Total Environ 803:149892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149892
Zhang H, Xiao J, Tang Y, Duan Z, Poon CS (2022b) Long-term shrinkage and mechanical properties of fully recycled aggregate concrete: testing and modelling. Cement Concr Compos 130:104527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2022.104527
Zhao Y, Sheng H (2017) Recycling technologies and pollution potential for contaminated construction and demolition waste in recycling processes. Pollut Control Resour Recov 195–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811754-5.00008-7
Zheng L, Wu H, Zhang H, Duan H, Wang J, Jiang W, Dong B, Liu G, Zuo J, Song Q (2017) Characterizing the generation and flows of construction and demolition waste in China. Constr Build Mater 136:405–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.01.055
Zhu X, Ling Y (2023) Preparation of cement modified by multi-walled carbon nanotubes and investigation of its piezoelectric property. Alex Eng J 81:130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2023.09.028
Zhu YG, Kou SC, Poon CS, Dai JG, Li QY (2013) Influence of silane-based water repellent on the durability properties of recycled aggregate concrete. Cement Concr Compos 35:32–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2012.08.008
Zong S, Liu Z, Li S, Lu Y, Zheng A (2021) Stress-strain behaviour of steel-fibre-reinforced recycled aggregate concrete under axial tension. J Clean Prod 278:123248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123248
Zou D, Wang Z, Shen M, Liu T, Zhou A (2021) Improvement in freeze-thaw durability of recycled aggregate permeable concrete with silane modification. Constr Build Mater 268:121097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121097
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the conditions provided by Sun Yat-sen University.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51908568, No. 52002410), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2019A1515011981), Zhuhai Social Development Field Science & Technology Project (No. ZH22036203200015PWC), and State Key Lab of Subtropical Building Science, South China University of Technology (No. 2022ZB20).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhong Li: writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. Yadong Bian: data curation, writing—original draft. Jihui Zhao: conceptualization, writing—review and editing. Yiren Wang: formal analysis. Xuan Qiu: investigation. Qiang Liu: investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Our study did not require an ethical board approval because it did not contain human or animal trails.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: José Dinis Silvestre
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Bian, Y., Zhao, J. et al. Sustainable building materials-recycled aggregate and concrete: a systematic review of properties, modification techniques, and environmental impacts. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 20814–20852 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32397-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32397-9