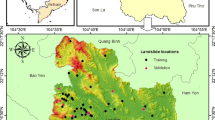
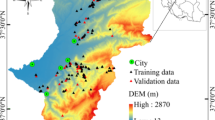
Abstract
Land subsidence is a worldwide threat. In arid and semiarid lands, groundwater depletion is the main factor that induce the subsidence resulting in environmental damages and socio-economic issues. To foresee and prevent the impact of land subsidence, it is necessary to develop accurate maps of the magnitude and evolution of the subsidences. Land subsidence susceptibility maps (LSSMs) provide one of the effective tools to manage vulnerable areas and to reduce or prevent land subsidence. In this study, we used a new approach to improve decision stump classification (DSC) performance and combine it with machine learning algorithms (MLAs) of naïve Bayes tree (NBTree), J48 decision tree, alternating decision tree (ADTree), logistic model tree (LMT), and support vector machine (SVM) in land subsidence susceptibility mapping (LSSSM). We employ data from 94 subsidence locations, among which 70% were used to train learning hybrid models and the other 30% were used for validation. In addition, the models’ performance was assessed by ROC-AUC, accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, odd ratio, root-mean-square error (RMSE), kappa, frequency ratio, and F-score techniques. A comparison of the results obtained from the different models reveals that the new DSC-ADTree hybrid algorithm has the highest accuracy (AUC = 0.983) in preparing LSSSMs as compared to other learning models such as DSC-J48 (AUC = 0.976), DSC-NBTree (AUC = 0.959), DSC-LMT (AUC = 0.948), DSC-SVM (AUC = 0.939), and DSC (AUC = 0.911). The LSSSMs generated through the novel scientific approach presented in our study provide reliable tools for managing and reducing the risk of land subsidence.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
The models and code that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abelson M, Yechieli Y, Baer B, Lapid G, Behar N, Calvo R, Rosensaft M (2017) Natural versus human control on subsurface salt dissolution and development of thousands of sinkholes along the Dead Sea coast. J Geophys Res Earth Surf, 122 (6), https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JF004219
Abidin H, Andreas H, Gumilar I, Sidiq TP, Fukuda Y (2013) Land subsidence in coastal city of Semarang (Indonesia): characteristics, impacts and causes. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 4(3):226–240
Arabameri A, Pradhan B, Rezaei K, Yamani M, Pourghasemi HR, Lombardo L (2018) Spatial modelling of gully erosion using evidential belief function, logistic regression, and a new ensemble of evidential belief function–logistic regression algorithm. Land Degrad Dev 29(11):4035–4049
Arabameri A, Chen W, Blaschke T, Tiefenbacher JP, Pradhan B, Tien Bui D (2020) Gully head-cut distribution modeling using machine learning methods—a case study of NW Iran. Water 12(1):16
Arabameri, Saha S, Roy J, Tiefenbacher J, Cerda A, Biggs T, Pradhan B, ThaoThi Ngo P, Collin A (2020b) A novel ensemble computational intelligence approach for the spatial prediction of land subsidence susceptibility. Sci Total Environ 138595
Arabameri A, Chandra Pal S, Rezaie F, Chakrabortty R, Chowdhuri I, Blaschke T, Thi Ngo PT (2021a) Comparison of multi-criteria and artificial intelligence models for land-subsidence susceptibility zonation. J Environ Manage 284:112067
Arabameri A, Lee S, Rezaie F, Chandra Pal S, Asadi Nalivan O, Saha A, Chowdhuri I, Moayedi H (2021b) Performance evaluation of GIS-based novel ensemble approaches for land subsidence susceptibility mapping. Front Earth Sci 9:663678. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.663678
Bagheri-Gavkosh M, Hosseini SM, Ataie-Ashtiani B ... Ashrafi S (2021) Land subsidence: a global challenge. Sci Total Environ. 778, 146193
Ben-Hur A, Horn D, Siegelmann HT, Vapnik V (2001) Support vector clustering. J Mach Learn Res, 2(Dec): 125–137
Bendarzsevszkij A, Eszterhai V, Gere L, Klemensits P, Polyák E (2017) World Economic Forum
Bhargava N, Sharma G, Bhargava R, Mathuria M (2013) Decision tree analysis on j48 algorithm for data mining. Proceedings of International J Adv Res Comput Sci Softw Eng, 3(6)
Bhattarai R, Alifu H, Maitiniyazi A, Kondoh A (2017) Detection of land subsidence in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal, using DInSAR technique. Land 6(2):39
Birkle P, Torres Rodrı´guez V, Gonza´lez Partida E (1998) The water balance for the Basin of the Valley of Mexico and implications for future water consumption. Hydrogeol J 6(4):500-517
Biswajeet P, Saro L (2007) Utilization of optical remote sensing data and GIS tools for regional landslide hazard analysis using an artificial neural network model. Earth Sci Front 14(6):143–151
Brambati A, Carbognin L, Quaia T, Teatini P, Tosi L (2003) The Lagoon of Venice: geological setting, evolution and land subsidence. Episodes 26(3):264–268
Burbey TJ (2002) The influence of faults in basin-fill deposits on land subsidence, Las Vegas Valley, Nevada, USA. Hydrogeol J 10(5):525–538
Calderhead A, Therrien R, Rivera A, Martel R, Garfias J (2011) Simulating pumping-induced regional land subsidence with the use of InSAR and field data in the Toluca Valley Mexico. Adv Water Resour 34(1):83–97
Chang Z, Du Z, Zhang F, Huang F, Chen J, Li W, Guo Z (2020) Landslide susceptibility prediction based on remote sensing images and GIS: comparisons of supervised and unsupervised machine learning models. Remote Sensing 12(3):502
Changxing S, Dian Z, Lianyuan Y, Bingyuan L, Zulu Z, Ouyang Z (2007) Land subsidence as a result of sediment consolidation in the Yellow River Delta. J Coastal Res 2007(231):173–181
Chaussard E, Wdowinski S, Cabral-Cano E, Amelung F (2014) Land subsidence in central Mexico detected by ALOS InSAR time-series. Remote Sens Environ 140:94–106
Chen S, Shen B, Wang X, Yoo S-J (2019) A strong machine learning classifier and decision stumps based hybrid adaboost classification algorithm for cognitive radios. Sensors 19(23):5077
Chen W, Fan L, Li C, Pham BT (2020) Spatial prediction of landslides using hybrid integration of artificial intelligence algorithms with frequency ratio and index of entropy in Nanzheng county, china. Appl Sci 10(1):29
Chen W, Zhang S, Li R, Shahabi H (2018) Performance evaluation of the GIS-based data mining techniques of best-first decision tree, random forest, and naïve Bayes tree for landslide susceptibility modeling. Sci Total Environ 644:1006–1018
Cheng Y, Fu L (2022) Nonlinear seismic inversion by physics-informed Caianiello convolutional neural networks for overpressure prediction of source rocks in the offshore Xihu depression, East China. J Petrol Sci Eng 215:110654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2022.110654
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support-Vector Networks. Machine Learning 20(3):273–297
Dai Z, Li X, Lan B (2023) Three-dimensional modeling of tsunami waves triggered by submarine landslides based on the smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. J Marine Sci Eng 11(10):2015
Demirpolat AB, Das M (2019) Prediction of viscosity values of nanofluids at different pH values by alternating decision tree and multilayer perceptron methods. Appl Sci 9(7):1288
Derczynski L (2016) Complementarity, F-score, and NLP Evaluation, Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC'16), pp. 261–266
Dong W, Zhao J, Qu J, Xiao S, Li N, Hou S ... Li Y (2023) abundance matrix correlation analysis network based on hierarchical multihead self-cross-hybrid attention for hyperspectral change detection. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 61
Dong W, Yang Y, Qu J, Xiao S, Li Y (2023) Local information-enhanced graph-transformer for hyperspectral image change detection with limited training samples. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens, 61
Fan C, Li H, Qin Q, He S, Zhong C (2020) Geological conditions and exploration potential of shale gas reservoir in Wufeng and Longmaxi Formation of southeastern Sichuan Basin, China. J Petrol Sci Eng 191:107138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107138
Feizizadeh B, Blaschke T (2013) Land suitability analysis for Tabriz County, Iran: a multi-criteria evaluation approach using GIS. J Environ Planning Manage 56(1):1–23
Freund Y, Mason L (1999) The alternating decision tree learning algorithm, icml, pp. 124–133
Ghorbanzadeh O, Blaschke T, Aryal J, Gholaminia K (2018) A new GIS-based technique using an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for land subsidence susceptibility mapping. J Spat Sci: 1–17
Frumkin A, Raz E (2001) Collapse and subsidence associated with salt karstification along the Dead Sea. Carbonates Evaporites 16(2):117–130
Gong SL, Li C, Yang SL (2009) The microscopic characteristics of Shanghai soft clay and its effect on soil body deformation and land subsidence. Environ Geol 56(6):1051–1056
Gao C, Hao M, Chen J, Gu C (2021) Simulation and design of joint distribution of rainfall and tide level in Wuchengxiyu Region China. Urban Climate 40:101005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.uclim.2021.101005
Hall M, Frank E, Holmes G, Pfahringer Peter Reutemann B, Witten I (2009) The WEKA data mining software: an update. ACM SIGKDD explorations newsletter, 11(1): 10-18
He M, Dong J, Jin Z, Liu C, Xiao J, Zhang F ... Deng L (2021) Pedogenic processes in loess-paleosol sediments: clues from Li isotopes of leachate in Luochuan loess. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 299, 151-162
Hong H, Pradhan B, Xu C, Bui DT (2015) Spatial prediction of landslide hazard at the Yihuang area (China) using two-class kernel logistic regression, alternating decision tree and support vector machines. CATENA 133:266–281
Hu D, Li Y, Yang X, Liang X, Zhang K, Liang X, ... Taciroglu E (2023) Experiment and application of NATM tunnel deformation monitoring based on 3D laser scanning. Struct Control Health Monit 2023:3341788. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/3341788
Hu R, Yue Z, Wang LU, Wang S (2004) Review on current status and challenging issues of land subsidence in China. Eng Geol, 76(1-2): 65-77
Hu X, Mei H, Zhang H, Li Y, Li M (2021) Performance evaluation of ensemble learning techniques for landslide susceptibility mapping at the Jinping county, Southwest China. Nat Hazards 105:1663–1689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04371-4
Huang H, Guo M, Zhang W, Huang M (2022) Seismic behavior of strengthened RC columns under combined loadings. J Bridge Eng, 27(6).
Huang H, Huang M, Zhang W, Guo M, Chen Z ... Li M (2021a) Progressive collapse resistance of multistory RC frame strengthened with HPFL-BSP. J Build Eng, 43, 103123
Huang H, Yuan Y, Zhang W, Li M (2021b) Seismic behavior of a replaceable artificial controllable plastic hinge for precast concrete beam-column joint. Eng Struct 245:112848
Iba W, Langley P (1992) Induction of one-level decision trees, Machine Learning Proceedings 1992. Elsevier, pp. 233–240
Jiang S, Zuo Y, Yang M, Feng R (2021) Reconstruction of the Cenozoic tectono-thermal history of the Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China: Constraints from apatite fission track and vitrinite reflectance data. J Petrol Sci Eng 205:108809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108809
Jun X, Lu Y, Lei Z, Hui X (2014) Boosting decision stumps to do pairwise classification. Electron Lett 50(12):866–868
Karimi H, Taheri K (2010) Hazards and mechanism of sinkholes on Kaboudar Ahang and Famenin plains of Hamadan Iran. Nat Hazards 55:481–499
Keesstra SD, Bouma J, Wallinga J, Tittonell P, Smith P, Bardgett RD (2016) The significance of soils and soil science towards realization of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Soil 2:111–128
Keesstra S, Mol G, de Leeuw J, Okx J, de Cleen M, Visser S (2018) Soil-related sustainable development goals: four concepts to make land degradation neutrality and restoration work. Land 7(4):133
Kohavi, R., 1996. Scaling up the accuracy of naive-Bayes classifiers: a decision-tree hybrid, Kdd, pp. 202–207.
Landwehr N, Hall M, Frank E (2005) Logistic Model Trees. Machine Learning 59(1–2):161–205
Lee S, Park I (2013) Application of decision tree model for the ground subsidence hazard mapping near abandoned underground coal mines. J Environ Manage 127:166–176
Li H, Zhao X, Chi H, Zhang J-j (2009) Prediction and analysis of land subsidence based on improved BP neural network model. J Tianjin Univ, 1(42): 60-64
Li J, Zhang Y, Lin L., Zhou Y (2023a) Study on the shear mechanics of gas hydrate-bearing sand-well interface with different roughness and dissociation. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82(11):404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03432-9
Li Z, Gao M, Lei Z, Tong L, Sun J, Wang Y,... Jiang X. (2023b) Ternary cementless composite based on red mud, ultra-fine fly ash, and GGBS: synergistic utilization and geopolymerization mechanism. Case Studies in Construction Materials 19:e2410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2023.e02410
Li X, Li X, Wang Y, Hu Y, Zhou C, Zhang H (2022) Numerical investigation on stratum and surface deformation in underground phosphorite mining under different mining methods. Front Earth Sci (Lausanne), 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2022.831856
Lim T-S, Loh W-Y, Shih Y-S (2000) A comparison of prediction accuracy, complexity, and training time of thirty-three old and new classification algorithms. Mach Learn 40(3):203–228
Luo J, Wang G, Li G, Pesce G (2022) Transport infrastructure connectivity and conflict resolution: a machine learning analysis. Neural Comput Appl 34(9):6585–6601
Luo J, Wang Y, Li G (2023) The innovation effect of administrative hierarchy on intercity connection: The machine learning of twin cities. J Innov Knowl 8(1):100293
Lyu H-M, Shen S-L, Zhou A, Yang J (2019) Risk assessment of mega-city infrastructures related to land subsidence using improved trapezoidal FAHP. Sci Total Environ 135310
Ma K, Zhang Y, Ruan M, Guo J, Chai T (2019) Land subsidence in a coal mining area reduced soil fertility and led to soil degradation in arid and semi-arid regions. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(20):3929
Ma R, Wang Y, Ma T, Sun Z, Yan S (2006) The effect of stratigraphic heterogeneity on areal distribution of land subsidence at Taiyuan, northern China. Environ Geol 50(4):551–568
Ma S, Qiu H, Yang D, Wang J, Zhu Y, Tang B ... Cao M (2023) Surface multi-hazard effect of underground coal mining. Landslides, 20(1), 39-52
Mi C, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Wang J, Feng Y ... Zhang Z (2023) A vision-based displacement measurement system for foundation pit. IEEE Trans Instrument Measure, 72
Mahmoudpour M, Khamehchiyan M, Nikudel MR, Ghassemi MR (2016) Numerical simulation and prediction of regional land subsidence caused by groundwater exploitation in the southwest plain of Tehran Iran. Eng Geol 201:6–28
Maulana MF, Defriani M (2020) Logistic model tree and decision tree J48 algorithms for predicting the length of study period. PIKSEL: Penelitian Ilmu Komputer Sistem Embedded and Logic, 8(1): 39–48
Miao R, Liu Y, Wu L, Wang D, Liu Y, Miao Y, Ma J (2022) Effects of long-term grazing exclusion on plant and soil properties vary with position in dune systems in the Horqin Sandy Land. CATENA, 209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2021.105860
Morris JA, Gardner MJ (1988) Calculating confidence intervals for relative risks (odds ratios) and standardised ratios and rates. Br Med J (clin Res Ed) 296(6632):1313–1316
Mohammady M, Dustmohammadian AH, Amiri M, Kia Kianian M (2021) Investigating quantitative changes of groundwater in the Semnan plain. Water Resour Eng 13:61–70
Navas JM, Telfer TC, Ross LG (2012) Separability indexes and accuracy of neuro-fuzzy classification in geographic information systems for assessment of coastal environmental vulnerability. Eco Inform 12:43–49
Nabavi MH (1987) Geological map of Semnan Quadrangle Scale 1:100,000. Geological Survey of Iran
Naeimi A, Alavi SA, Madanipour S (2022) Structural analysis and the late Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the SE Alborz Mountains in northern Iran: insights into the ArabiaEurasia collision. Geopersia 12(2):241–264
Nguyen V-N, Yariyan P, Amiri M, Dang Tran A, Pham TD, Do MP, Thi Ngo PT, Nhu V-H, Quoc Long N, Tien Bui DA (2020) A new modeling approach for spatial prediction of flash flood with biogeography optimized CHAID tree ensemble and remote sensing data. Remote Sensing 12(9):1373
Nhu V-H, Janizadeh S, Avand M, Chen W, Farzin M, Omidvar E, Shirzadi A, Shahabi HJ, Clague J, Jaafari A, Mansoorypoor F, Thai Pham B, Ahmad BB, Lee S (2020a) Gis-based gully erosion susceptibility mapping: a comparison of computational ensemble data mining models. Appl Sci 10(6):2039
Nhu V-H, Shirzadi A, Shahabi H, Singh SK, Al-Ansari N, Clague JJ, Jaafari A, Chen W, Miraki S, Dou J, Luu C, Górski K, Thai Pham B, Nguyen HD, Ahmad BB (2020b) Shallow landslide susceptibility mapping: a comparison between logistic model tree, logistic regression, naïve Bayes tree, artificial neural network, and support vector machine algorithms. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(8):2749
Oh H-J, Lee S (2011) Integration of ground subsidence hazard maps of abandoned coal mines in Samcheok Korea. Intl J Coal Geol 86(1):58–72
Oh H-J, Syifa M, Lee C-W, Lee S (2019) Land subsidence susceptibility mapping using Bayesian, functional, and meta-ensemble machine learning models. Appl Sci 9(6):1248
Oliver J, Hand D (1994) David, Averaging over decision stumps, in machine learning. ECML-94, European Conference on Machine Learning, Catania, Italy, pp. 231–241
Pacheco J, Arzate J, Rojas E, Arroyo M, Yutsis V, Ochoa G (2006) Delimitation of ground failure zones due to land subsidence using gravity data and finite element modeling in the Querétaro valley. México Engineering Geology 84(3–4):143–160
Panigrahi R, Borah S (2018) Rank allocation to J48 group of decision tree classifiers using binary and multiclass intrusion detection datasets. Procedia Comput Sci 132:323–332
Parise M (2015) A procedure for evaluating the susceptibility to natural and anthropogenic sinkholes. Georisk 9(4):272–285. https://doi.org/10.1080/17499518.2015.1045002
Parise M, Ravbar NZ, Ivanovic V, Mikszewski A, Kresic N, Ma´dl-Szonyi J, Kukuric N (2015) Hazards in Karst and managing water resources quality. In: Stevanovic Z (ed) Karst aquifers—characterization and engineering. Professional practice in earth sciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12850-4_17, Springer, pp 601–687
Parise M, Gabrovsek F, Kaufmann G, Ravbar N (eds) 2018. Advances in karst research: theory, fieldwork and applications. Geological Society, London Special Publication 466, ISBN 978–1–78,620–359–5
Parise M (2019) Sinkholes. In: WHITE W.B., CULVER D.C. & PIPAN T. (Eds.), Encyclopedia of Caves. Academic Press, Elsevier, 3rd edition, ISBN ISBN 978–0–12–814124–3, p. 934–942
Park I, Lee J, Saro L (2014) Ensemble of ground subsidence hazard maps using fuzzy logic. Central Eur J Geosci 6(2):207–218
Perrin J, Cartannaz C, Noury G, Vanoudheusden E (2015) A multicriteria approach to karst subsidence hazard mapping supported by weights-of-evidence analysis. Eng Geol 197:296–305
Pfahringer B, Holmes G, Kirkby R (2001) Optimizing the induction of alternating decision trees, Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Springer, pp. 477–487
Pham BT, Jaafari A, Prakash I, Singh S, Quoc NK, Tien Bui D (2019) Hybrid computational intelligence models for groundwater potential mapping. CATENA 182:104101
Pham BT, Bui DT, Pourghasemi HR, Indra P, Dholakia M (2017a) Landslide susceptibility assesssment in the Uttarakhand area (India) using GIS: a comparison study of prediction capability of naïve bayes, multilayer perceptron neural networks, and functional trees methods. Theoret Appl Climatol 128(1–2):255–273
Pham BT, Bui DT, Prakash I, Dholakia M (2017b) Hybrid integration of multilayer perceptron neural networks and machine learning ensembles for landslide susceptibility assessment at Himalayan area (India) using GIS. CATENA 149:52–63
Pourghasemi H, Moradi H, Aghda SF, Gokceoglu C, Pradhan B (2014) GIS-based landslide susceptibility mapping with probabilistic likelihood ratio and spatial multi-criteria evaluation models (North of Tehran, Iran). Arab J Geosci 7(5):1857–1878
Pradhan B, Abokharima MH, Jebur MN, Tehrany MS (2014) Land subsidence susceptibility mapping at Kinta Valley (Malaysia) using the evidential belief function model in GIS. Nat Hazards 73(2):1019–1042
Quinlan J (1993a) The Morgan Kaufmann series in machine learning. San Mateo
Quinlan JR (1993b) C4. 5: Programming for machine learning. Morgan Kauffmann, 38: 48
Quinlan JR (1993c) The Morgan Kaufmann series in machine learning.
Rahmati O, Ghorbanzadeh O, Teimurian T, Mohammadi F, Tiefenbacher JP, Falah F, Pirasteh S, Ngo P-TT, Bui DT (2019) Spatial modeling of snow avalanche using machine learning models and geo-environmental factors: comparison of effectiveness in two mountain regions. Remote Sensing 11(24):2995
Ren C, Yu J, Liu S, Yao W, Zhu Y ... Liu X (2022) A plastic strain-induced damage model of porous rock suitable for different stress paths. Rock Mech Rock Eng, 55(4), 1887-1906
Rezaei, M., Yazdani Noori, Z., Dashti Barmaki, M., 2020. Land subsidence susceptibility mapping using analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and Certain Factor (CF) models at Neyshabur plain, Iran. Geocarto International 1–20
Saha S, Roy J, Arabameri A, Blaschke T, Tien Bui D (2020) Machine learning-based gully erosion susceptibility mapping: a case study of Eastern India. Sensors 20(5):1313
Sasaki Y (2007) The Truth of the F-Measure. 2007
Schapire RE (2003). The boosting approach to machine learning: an overview, Nonlinear estimation and classification. Springer, pp. 149–171
Seifi A, Riahi H (2020) Estimating daily reference evapotranspiration using hybrid gamma test-least square support vector machine, gamma test-ANN, and gamma test-ANFIS models in an arid area of Iran. J Water Climate Chang 11(1):217–240
Shang M, Luo J (2021) The Tapio decoupling principle and key strategies for changing factors of chinese urban carbon footprint based on cloud computing. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(4):2101
Shi Y, Xi J, Hu D, Cai Z, Xu K (2023) RayMVSNet++: Learning ray-based 1D implicit fields for accurate multi-view stereo. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 45(11):13666–13682
Sikandar A, Anwar W, Bajwa UI, Wang X, Sikandar M, Yao L (2018) Decision tree based approaches for detecting protein complex in protein protein interaction network (PPI) via link and sequence analysis. IEEE Access 6:22108–22120
Stevanovic´, Z (2013) Global trend and negative synergy: climate changes and groundwater over-extraction. in: proceedings international conference on “Climate change impact on water resources”, 17–18 Oct 2013, Institute of Water Manag J Cerni & WSDAC, Belgrade, pp 42–45
Stevanović Z (2018) Global distribution and use of water from karst aquifers. Geol. Soc. London. Spec Publ 466:217–236
Stevanovic´ Z, Balint Z, Gadain H, Trivic´ B, Marobhe I, Milanovic S (2012) Hydrogeological survey and assessment of selected areas in Somaliland and Puntland. Technical report no. W-20, FAO-SWALIM (GCP/SOM/049/EC) Project (http://www.faoswalim.org/water_reports) Nairobi
Sumner M, Frank E, Hall M (2005) Speeding up logistic model tree induction, European conference on principles of data mining and knowledge discovery. Springer, pp. 675–683
Suykens JA, Vandewalle J (1999) Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process Lett 9(3):293–300
Süzen ML, Doyuran V (2004) A comparison of the GIS based landslide susceptibility assessment methods: multivariate versus bivariate. Environ Geol 45(5):665–679
Szumilas M (2010) Explaining odds ratios. J Canadian Acad Child Adolesc Psych 19(3):227
Su Y, Wang J, Li D, Wang X, Hu L, Yao Y ... Kang Y (2023) End-to-end deep learning model for underground utilities localization using GPR. Automation in Construction, 149, 104776
Taheri, K. (2005). Sinkhole hazards in Karst terrains (with emphasis on Sinkholes of Hamedan). West Regional Water Authority of Iran, Kermanshah. [in Farsi].
Taheri K, Gutie´rrez F, Mohseni H, Raeisi E, Taheri M (2015) Sinkhole susceptibility mapping using the analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and magnitude-frequency relationships: a case study in Hamadan province, Iran. Geomorphology, 234:64-79
Taheri K, Taheri M, Parise M (2016) Impact of intensive groundwater exploitation on an unprotected covered karst aquifer: a case study in Kermanshah Province, western Iran. Environ Earth Sciences 75:1221
Taheri K, Shahabi H, Chapi K, Shirzadi A, Gutiérrez F, Khosravi K (2019) Sinkhole susceptibility mapping: a comparison between Bayes-based machine learning algorithms. Land Degrad Dev 30(7):730–745. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3255
Tang Y-Q, Cui Z-D, Wang J-X, Yan L-P, Yan X-X (2008) Application of grey theory-based model to prediction of land subsidence due to engineering environment in Shanghai. Environ Geol 55(3):583–593
Teatini P, Ferronato M, Gambolati G, Bertoni W, Gonella M (2005) A century of land subsidence in Ravenna Italy. Environ Geol 47(6):831–846
Tien Bui D, Shahabi H, Shirzadi A, Chapi K, Pradhan B, Chen W, Khosravi K, Panahi M, Bin Ahmad B, Saro L (2018) Land subsidence susceptibility mapping in South Korea using machine learning algorithms. Sensors 18(8):2464
Viera AJ (2008) Odds ratios and risk ratios: what’s the difference and why does it matter? South Med J 101(7):730–734
Visser S, Keesstra S, Maas G, De Cleen M (2019) Soil as a basis to create enabling conditions for transitions towards sustainable land management as a key to achieve the SDGs by 2030. Sustainability 11(23):6792
Wang Q, Li W (2017) A GIS-based comparative evaluation of analytical hierarchy process and frequency ratio models for landslide susceptibility mapping. Phys Geogr 38(4):318–337
Wang Y-Q, Wang Z-F, Cheng W-C (2019) A review on land subsidence caused by groundwater withdrawal in Xi’an, China. Bull Eng Geol Env 78(4):2851–2863
Wu Y, Ke Y, Chen Z, Liang S, Zhao H, Hong H (2020) Application of alternating decision tree with AdaBoost and bagging ensembles for landslide susceptibility mapping. CATENA 187:104396
Wu J, Shi X, Xue Y, Zhang Y, Wei Z, Yu J (2008) The development and control of the land subsidence in the Yangtze Delta China. Environ Geol 55(8):1725–1735
Yang H, Zhang X, Li Z, Cui J (2022) Region-level traffic prediction based on temporal multi-spatial dependence graph convolutional network from GPS data. Remote Sensing 14(2):303
Yin J, Yu D, Wilby R (2016) Modelling the impact of land subsidence on urban pluvial flooding: a case study of downtown Shanghai, China. Sci Total Environ 544:744–753
Yin L, Wang L, Li T, Lu S, Yin Z, Liu X ... Zheng W (2023a) U-Net-STN: a novel end-to-end lake boundary prediction model. Land, 12(8), 1602
Yin L, Wang L, Li J, Lu S, Tian J, Yin Z ... Zheng W (2023b) YOLOV4_CSPBi: enhanced land target detection model. Land, 12(9), 1813
Yin L, Wang L, Li T, Lu S, Tian J, Yin Z ... Zheng W (2023c) U-Net-LSTM: time series-enhanced lake boundary prediction model. Land, 12(10), 1859
Yu J, Zhu Y, Yao W, Liu X, Ren C, Cai Y ... Tang X (2021) Stress relaxation behaviour of marble under cyclic weak disturbance and confining pressures. Measurement, 182, 109777
Zhang C, Duan C, Sun L (2023) Inter-storey isolation versus base isolation using friction pendulum systems. Int J Struct Stab Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219455424500226
Zhi-xiang T, Pei-xian L, Li-li Y, Ka-zhong D (2009) Study of the method to calculate subsidence coefficient based on SVM. Procedia Earth Planet Sci 1(1):970–976
Zhou Z (2012) Ensemble methods: foundations and algorithms. Chapman and Hall/CRC, Cambridge
Zhu J, Yang Y, Yu J, Gong X (2015) Land subsidence of coastal areas of Jiangsu Province, China: historical review and present situation. Proc Intl Assoc Hydrol Sci 372:503
Zhuo Z, Du L, Lu X, Chen J, Cao Z (2022) Smoothed Lv Distribution Based Three-Dimensional Imaging for Spinning Space Debris. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 60:1–13
Zhu W, Chen J, Sun Q, Li Z, Tan W ... Wei Y (2022) Reconstructing of high-spatial-resolution three-dimensional electron density by ingesting SAR-derived VTEC into IRI model. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 19
Funding
This work was sponsored in part by the key talent introduction project of Xihua University Foundation (Z17109). Dr. Chenchen Fan helped us in revising the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by AA. The first draft of the manuscript was written by AA, MS, and RZ commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
All authors have consented.
Consent for publication
All authors have consent.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, R., Arabameri, A. & Santosh, M. Land subsidence susceptibility mapping: a new approach to improve decision stump classification (DSC) performance and combine it with four machine learning algorithms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 15443–15466 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32075-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32075-w