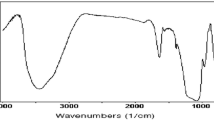
Abstract
The flow of graphene oxide (GO) into natural water systems can adversely affect water environments and ecosystems. In this study, the adsorption effect of calcite on GO under different conditions was studied using calcite as adsorbent. Meanwhile, characterized by a combination of microscopic experiments, including SEM, TEM, XRD, FTIR, Raman, XPS, and AFM, additional research on the performance and the mechanism of GO sorption by calcite was conducted. The findings indicated that the highest adsorption efficiency was observed at a temperature of 303 K, pH 3, a mass of 90 mg of calcite, with an initial concentration of 60 mg L−1 GO, resulting in a 95% adsorption rate. The adsorption isotherm conformed to the model of Langmuir and Temkin, and it is a heat absorption process dominated by monolayer adsorption. The thermodynamic analysis showed that the adsorption was spontaneous and heat-absorbing. The adsorption kinetics conformed to the pseudo-second-order kinetic model, and the sorption procedure is chemisorption. In conclusion, calcite has a good sorption capacity for GO, which can provide a reference for the removal of GO in the aqueous environment.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abba MU, Man HC, Azis RS, Idris AI, Hamzah MH, Abdulsalam M (2021) Synthesis of nano-magnetite from industrial mill chips for the application of boron removal: characterization and adsorption efficacy. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(4):1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041400
Abdoallahzadeh H, Rashtbari Y, Américo-Pinheiro JHP, Azari A, Afshin S, Fazlzadeh M, Poureshgh Y (2023) Application of green and red local soils as a catalyst for catalytic ozonation of fulvic acid: experimental parameters and kinetic. Biomass Convers Biorefinery 1:10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-03895-6
Al-Gaashani R, Najjar A, Zakaria Y, Mansour S, Atieh MA (2019) XPS and structural studies of high quality graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide prepared by different chemical oxidation methods. Ceram Int 45(11):14439–14448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.04.165
Al-Ghouti MA, Da’ana DA (2020) Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: a review. J Hazard Mater 393:122383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122383
Algothmi WM, Bandaru NM, Yu Y, Shapter JG, Ellis AV (2013) Alginate-graphene oxide hybrid gel beads: an efficient copper adsorbent material. J Colloid Interface Sci 397:32–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.01.051
Ali I, Afshinb S, Poureshgh Y, Azari A, Rashtbari Y, Feizizadeh A, Hamzezadeh A, Fazlzadeh M (2020) Green preparation of activated carbon from pomegranate peel coated with zero-valent iron nanoparticles (nZVI) and isotherm and kinetic studies of amoxicillin removal in water. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:36732–36743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09310-1
Alzhavan O, Ghaderi E, Shahsavar M (2013) Graphene nanogrids for selective and fast osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Carbon 59:200–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.03.010
Azari A, Nabizadeh R, Nasseri S, Mahvi AH, Mesdaghinia AR (2020) Comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of dyes adsorption by carbon-based adsorbent materials: classification and analysis of last decade studies. Chemosphere 250:126238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126238
Azari A, Yeganeh M, Gholami M, Salari M (2021) The superior adsorption capacity of 2,4-Dinitrophenol under ultrasound-assisted magnetic adsorption system: Modeling and process optimization by central composite design. J Hazard Mater 418:126348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126348
Azari A, Malakoutian M, Yaghmaeain K, Jaafarzadeh N, Shariatifar N, Mohammadi G, Masoudi MR, Sadeghi R, Hamzeh S, Kamani H (2022a) Magnetic NH2-MIL-101(Al)/chitosan nanocomposite as a novel adsorbent for the removal of azithromycin: modeling and process optimization. Sci Rep 12(1):18990. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-21551-3
Azari A, Nabizadeh R, Mahvi AH, Nasseri S (2022) Integrated Fuzzy AHP-TOPSIS for selecting the best color removal process using carbon-based adsorbent materials: multi-criteria decision making vs. systematic review approaches and modeling of textile wastewater treatment in real conditions. Int J Environ Anal Chem 102(18):7329–7344. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1828395
Azari A, Nabizadeh R, Mahvi AH, Nasseri S (2023) Magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes-loaded alginate for treatment of industrial dye manufacturing effluent: adsorption modelling and process optimisation by central composite face-central design. Int J Environ Anal Chem 103(7):1509–1529. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2021.1877279
Balarak D, Bazzi M, Shehu Z, Chandrika K (2020) Application of surfactant-modified bentonite for methylene blue adsorption from aqueous solution. Orient J Chem 36(02):293–299. https://doi.org/10.13005/ojc/360212
Caceres L, Escudey M, Fuentes E, Baez ME (2010) Modeling the sorption kinetic of metsulfuron-methyl on Andisols and Ultisols volcanic ash-derived soils: Kinetics parameters and solute transport mechanisms. J Hazard Mater 179(1–3):795–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.03.074
Chai JB, Au PI, Mubarak NM, Khalid M, Ng WPQ, Jagadish P, Walvekar R, Abdullah EC (2020) Adsorption of heavy metal from industrial wastewater onto low-cost Malaysian kaolin clay-based adsorbent. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(12):13949–13962. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07755-y
Chowdhury I, Mansukhani ND, Guiney LM, Hersam MC, Bouchard D (2015) Aggregation and stability of reduced graphene oxide: complex roles of divalent cations, pH, and natural organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 49(18):10886–10893. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b01866
Dazzi A, Prater CB (2017) AFM-IR: Technology and applications in nanoscale infrared spectroscopy and chemical imaging. Chem Rev 117(7):5146–5173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.11.146
Dong LY, Jiao F, Qin WQ, Liu W (2019) Selective flotation of scheelite from calcite using xanthan gum as depressant. Miner Eng 138:14–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2019.04.030
El-Yamany NA, Mohamed FF, Salaheldin TA, Tohamy AA, Abd El-Mohsen WN, Amin AS (2017) Graphene oxide nanosheets induced genotoxicity and pulmonary injury in mice. Exp Toxicol Pathol 69(6):383–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2017.03.002
Fiorito E, Porcedda GE, Brundu L, Passiu C, Atzei D, Ennas G, Elsener B, Fantauzzi M, Rossi A (2022) Calcium carbonate as sorbent for lead removal from wastewaters. Chemosphere 296:133897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133897
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2013) Utilization of oil palm biodiesel solid residue as renewable sources for preparation of granular activated carbon by microwave induced KOH activation. Bioresour Technol 130:696–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.11.146
Fu CH, Liu TL, Li LL, Liu HY, Liang QH, Meng XW (2015) Effects of graphene oxide on the development of offspring mice in lactation period. Biomaterials 40:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.11.014
Guo XT, Yang C, Dang Z, Zhang Q, Li YJ, Meng QY (2013) Sorption thermodynamics and kinetics properties of tylosin and sulfamethazine on goethite. Chem Eng J 223:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.02.115
Guo Q, Yang Y, Zhao L, Chen J, Duan G, Yang Z, Zhou R (2022) Graphene oxide toxicity in W1118 flies. Sci Total Environ 805:150302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150302
Hameed BH, Tan IAW, Ahmad AL (2008) Adsorption isotherm, kinetic modeling and mechanism of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol on coconut husk-based activated carbon. Chem Eng J 144(2):235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.01.028
Hasanzadeh M, Ghaedrahmat Z, Kayedi N, Haghighi Fard NJ, Azari A, Afsharizadeh M (2023) Persulfate-assisted heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of furfural from aqueous solutions using TiO2-ZnO/biochar composite. Heliyon 9(11):e21421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21421
Hashemi SY, Azari A, Raeesi M, Yaghmaeian K (2023) Application of Response Surface Methodology (RSM) in optimisation of fluoride removal by magnetic chitosan/graphene oxide composite: kinetics and isotherm study. Int J Environ Anal Chem 103(17):5368–5386. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2021.1938021
Heberling F, Klacic T, Raiteri P, Gale JD, Eng PJ, Stubbs JE, Gil-Diaz T, Begovic T, Lutzenkirchen J (2021) Structure and surface complexation at the calcite(104)-water interface. Environ Sci Technol 55(18):12403–12413. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c03578
Huang GX, Guo HY, Zhao J, Liu YH, Xing BS (2016) Effect of co-existing kaolinite and goethite on the aggregation of graphene oxide in the aquatic environment. Water Res 102:313–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.06.050
Jiang P, Zhou L, Wang W, Li N, Zhang F (2022) Performance and mechanisms of fly ash for graphene oxide removal from aqueous solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(3):3773–3783. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15769-3
Jiang P, Zhou GZ, Li CH, Yu YF, Zhou L, Kang HB (2023) Performance and mechanism of GO removal by gypsum from aqueous solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(16):47052–47064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25473-z
Khajeh M, Barkhordar A (2020) Fe3O4/graphene oxide composite for adsorption of methylene blue and methyl orange in water treatment. J Appl Spectrosc 87(4):701–707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-020-01057-4
Kim YY, Freeman CL, Gong XQ, Levenstein MA, Wang YW, Kulak A, Anduix-Canto C, Lee PA, Li SB, Chen L, Christenson HK, Meldrum FC (2017) The effect of additives on the early stages of growth of calcite single crystals. Angew Chem-Int Edit 56(39):11885–11890. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201706800
Li L, Yang Y, Lv YR, Yin P, Lei T (2020) Porous calcite CaCO3 microspheres: preparation, characterization and release behavior as doxorubicin carrier. Colloids Surf, B 186:110720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110720
Li SS, Guo Q, Jiang L, Ahmed Z, Dang Z, Wu PX (2021) The influence mechanism of dissolved organic matter on the adsorption of Cd (II) by calcite. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(28):37120–37129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14585-z
Li N, Fang JY, Jiang P, Li CH, Kang HB, Wang W (2022a) Adsorption properties and mechanism of attapulgite to graphene oxide in aqueous solution. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(5):2793. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19052793
Li N, Yu SM, Fang JY, Yu YF, Jiang P, Pu SY, Wang W (2022b) Performance and mechanism of illite in removing graphene oxide from aqueous solution. Appl Clay Sci 230:106711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2022.106711
Li N, Yan XY, Dai WH, Lv BF, Wang W (2023) Adsorption properties and mechanism of sepiolite to graphene oxide in aqueous solution. Arabian J Chem 16(4):104595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.104595
Liu MM, Chen W (2013) Graphene nanosheets-supported Ag nanoparticles for ultrasensitive detection of TNT by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Biosens Bioelectron 46:68–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.01.073
Liu J, Zhang JN, Xing L, Wang D, Wang LD, Xiao HN, Ke J (2021) Magnetic Fe3O4/attapulgite hybrids for Cd(II) adsorption: performance, mechanism and recovery. J Hazard Mater 412:125237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125237
Lu XY, Lu TT, Zhang HJ, Shang ZB, Chen JY, Wang Y, Li DL, Zhou YM, Qi ZC (2019) Effects of solution chemistry on the attachment of graphene oxide onto clay minerals. Environ Sci-Process Impacts 21(3):506–513. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8em00480c
Lv B, Yu WJ, Luo JL, Qian B, Asefa MB, Li N (2021) Study on the adsorption mechanism of graphene oxide by calcareous sand in South China Sea. Adsorpt Sci Technol 2021:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/2227570
Mahmoudian MH, Fazlzadeh M, Niari MH, Azari A, Lima EC (2020) A novel silica supported chitosan/glutaraldehyde as an efficient sorbent in solid phase extraction coupling with HPLC for the determination of Penicillin G from water and wastewater samples. Arab J Chem 13(9):7147–7159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.07.020
Mahmoudian MH, Azari A, Jahantigh A, Sarkhosh M, Yousefi M, Razavinasab SA, Afsharizadeh M, Shahraji FM, Pasandi AP, Zeidabadi A, Bardsiri TI, Ghasemian M (2023) Statistical modeling and optimization of dexamethasone adsorption from aqueous solution by Fe3O4@NH2-MIL88B nanorods: Isotherm, Kinetics, and Thermodynamic. Environ Res 236:116773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.116773
Mao B, Calatayud DG, Mirabello V, Hodges BJ, Martins JAR, Botchway SW, Mitchels JM, Pascu SI (2016) Interactions between an aryl thioacetate-functionalized Zn (II) porphyrin and graphene oxide. Adv Funct Mater 26(5):687–697. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201504147
McCormick S, Niang M, Dahm MM (2021) Occupational exposures to engineered nanomaterials: a review of workplace exposure assessment methods. Curr Environ Health Rep 8(3):223–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40572-021-00316-6
Monfared AD, Ghazanfari MH, Jamialahmadi M, Helalizadeh A (2015) Adsorption of silica nanoparticles onto calcite: Equilibrium, kinetic, thermodynamic and DLVO analysis. Chem Eng J 281:334–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.06.104
Nakajima S, Araki S, Sasamoto R, Kanda Y, Yamanaka S (2022) Key particle properties of shells for cadmium chemisorption. Chemosphere 287:132257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132257
Pereira FAR, Sousa KS, Cavalcanti GRS, Fonseca MG, de Souza AG, Alves APM (2013) Chitosan-montmorillonite biocomposite as an adsorbent for copper (II) cations from aqueous solutions. Int J Biol Macromol 61:471–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.08.017
Pereira IC, Carvalho KQ, Passig FH, Ferreira RC, Rizzo-Domingues RCP, Hoppen MI, Macioski G, Nagalli A, Perretto F (2018) Thermal and thermal-acid treated sewage sludge for the removal of dye reactive Red 120: Characteristics, kinetics, isotherms, thermodynamics and response surface methodology design. J Environ Chem Eng 6(6):7233–7246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.10.060
Rabiee F, Sarkhosh M, Azizi S, Jahantigh A, Hashemi SY, Baziar M, Gholami M, Azari A (2022) The superior decomposition of 2,4-dinitrophenol under ultrasound-assisted Fe3O4@TiO2 magnetic nanocomposite: process modeling and optimization, effect of various oxidants and degradation pathway studies. Int J Environ Anal Chem 1:23. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2022.2034798
Razaq A, Bibi F, Zheng XX, Papadakis R, Jafri SHM, Li H (2022) Review on graphene-, graphene oxide-, reduced graphene oxide-based flexible composites: from fabrication to applications. Materials 15(3):1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031012
Saha P, Pyne DK, Ghosh S, Banerjee S, Das S, Ghosh S, Dutta P, Halder A (2018) Effect of an anionic surfactant (SDS) on the photoluminescence of graphene oxide (GO) in acidic and alkaline medium. RSC Adv 8(1):584–595. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra12024a
Souza JP, Baretta JF, Santos F, Paino IMM, Zucolotto V (2017) Toxicological effects of graphene oxide on adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat Toxicol 186:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.02.017
Tizo MS, Blanco LAV, Cagas ACQ, Dela Cruz BRB, Encoy JC, Gunting JV, Arazo RO, Mabayo VIF (2018) Efficiency of calcium carbonate from eggshells as an adsorbent for cadmium removal in aqueous solution. Sustain Environ Res 28(6):326–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.serj.2018.09.002
Wang AL, Li XS, Zhao YB, Wu W, Chen JF, Meng H (2014a) Preparation and characterizations of Cu2O/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites with high photo-catalytic performances. Powder Technol 261:42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2014.04.004
Wang J, Chen ZM, Chen BL (2014b) Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by graphene and graphene oxide nanosheets. Environ Sci Technol 48(9):4817–4825. https://doi.org/10.1021/es405227u
Wang Y, Li SS, Yang HY, Luo J (2020) Progress in the functional modification of graphene/graphene oxide: a review. RSC Adv 10(26):15328–15345. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra01068e
Wang JM, Zhao J, Qin XZ, Wang Z (2021) Theoretical study of adsorption mechanism of heavy metals As and Pb on the calcite (104) surface. Mater Today Commun 26:101742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101742
Wu L, Liu L, Gao B, Munoz-Carpena R, Zhang M, Chen H, Zhou ZH, Wang H (2013) Aggregation kinetics of graphene oxides in aqueous solutions: experiments, mechanisms, and modeling. Langmuir 29(49):15174–15181. https://doi.org/10.1021/la404134x
Yin J, Deng CB, Yu Z, Wang XF, Xu GP (2018) Effective removal of lead ions from aqueous solution using nano illite/smectite clay: isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic modeling of adsorption. Water 10(2):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020210
Yu L, Wang L, Xu WC, Chen LM, Fu ML, Wu JL, Ye DQ (2018) Adsorption of VOCs on reduced graphene oxide. J Environ Sci 67:171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.08.022
Zazouli MA, Azari A, Dehghan S, Malekkolae RS (2016) Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution onto activated carbons developed from eucalyptus bark and Crataegus oxyacantha core. Water Sci Technol 74(4):2021–2035. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.287
Zhang L, Li Y, Guo H, Zhang HH, Zhang N, Hayat T, Sun YB (2019) Decontamination of U(VI) on graphene oxide/Al2O3 composites investigated by XRD, FT-IR and XPS techniques. Environ Pollut 248:332–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.01.126
Zhao J, Cao XS, Wang ZY, Dai YH, Xing BS (2017) Mechanistic understanding toward the toxicity of graphene-family materials to freshwater algae. Water Res 111:18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.12.037
Zhao L, Zhu SQ, Wu H, Zhang XC, Tao QQ, Song LG, Song Y, Guo XL (2020) Deep research about the mechanisms of graphene oxide (GO) aggregation in alkaline cement pore solution. Constr Build Mater 247:118446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118446
Zhu QY, Moggridge GD, D’Agostino C (2016) Adsorption of pyridine from aqueous solutions by polymeric adsorbents MN 200 and MN 500. Part 2: Kinetics and diffusion analysis. Chem Eng J 306:1223–1233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.07.087
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52179107).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Na Li: conceptualization, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. Yingdi Pang: investigation, writing—review and editing. Wei Wang: visualization and formal analysis. Xinyu Yan and Ping Jiang: supervision, project administration. Shimeng Yu: funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, N., Pang, Y., Wang, W. et al. Performance and mechanism of graphene oxide removal from aqueous solutions by calcite: adsorption isotherms, thermodynamics, and kinetics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 8519–8537 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31692-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31692-1