Abstract
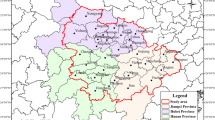
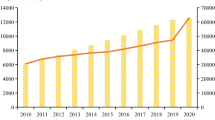
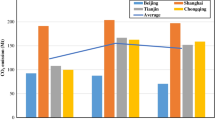
Studying urban carbon emission efficiency is vital for promoting city collaboration in combating climate change. Prior research relied on traditional econometric models, lacking spatial spillover effects understanding at the urban scale. To provide a more comprehensive and visually insightful representation of the evolving characteristics of carbon emission efficiency and its spatial clustering effects and to establish a comprehensive set of indicators to explore the spatial spillover pathways of urban carbon emission efficiency, we conducted an analysis focusing on 42 cities in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. By employing the index decomposition method, the super-efficiency SBM model, spatial autocorrelation analysis, and the spatial Durbin model, the study calculates the urban carbon emission efficiency from 2011 to 2019 and analyzes the spatial spillover effects and influencing factors of urban carbon emission efficiency. The main conclusions are as follows: (1) Jiangxi Province displayed stable urban carbon emission efficiency evolution, while Hubei and Hunan showed significant internal disparities. (2) Positive spatial correlation exists in urban carbon emission efficiency, with an imbalanced distribution. (3) Various factors influence urban carbon emission efficiency. Technological innovation and economic development have positive direct and indirect impacts, whereas industrial structure, urbanization, population, and energy consumption have negative effects. Spatial spillover effects of vegetation coverage are insignificant. These methods and findings offer insights for future research and policy formulation to promote regional sustainable development and carbon emission reduction.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bu Y, Wang E, Jiang Z (2021) Evaluating spatial characteristics and influential factors of industrial wastewater discharge in China: a spatial econometric approach. Ecol Ind 121:107219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107219
Cao J, Law SH, Samad AR, Mohamad WN, Wang J, Yang X (2022) Effect of financial development and technological innovation on green growth—analysis based on spatial Durbin model. J Clean Prod 365:132865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132865
CCSY (2020) China city statistical yearbook. China statistics press, Beijing
CESY (2020) China energy statistical yearbook. China statistics press, Beijing
Chen F, Shen S, Li Y, Xu H (2022) The impact of urban density on spatial carbon performance: a case study on Shanghai. Urban Prob 41(02):96–103. https://doi.org/10.13239/j.bjsshkxy.cswt.220210
Choi Y, Zhang N, Zhou P (2012) Efficiency and abatement costs of energy-related CO2 emissions in China: a slacks-based efficiency measure. Appl Energy 98:198–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.03.024
Chu X, Jin Y, Wang X, Wang X, Song X (2022) The evolution of the spatial-temporal differences of municipal solid waste carbon emission efficiency in China. Energies 15:3987. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15113987
Chuai X, Huang X, Wang W, Wen J, Chen Q, Peng J (2012) Spatial econometric analysis of carbon emissions from energy consumption in China. J Geog Sci 22:630–642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-012-0952-z
Dong F, Long R, Bian Z, Xu X, Yu B, Wang Y (2017) Applying a Ruggiero three-stage super-efficiency DEA model to gauge regional carbon emission efficiency: evidence from China. Nat Hazards 87:1453–1468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-2826-2
Fang T, Fang D, Yu B (2022) Carbon emission efficiency of thermal power generation in China: empirical evidence from the micro-perspective of power plants. Energy Policy 165:112955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2022.112955
Fu W, Duan Y, Xiong X (2022) Technological innovation, industrial agglomeration and efficiency of new urbanization. Econ Geogr 42(01):90–97. https://doi.org/10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2022.01.011
Gao P, Yue S, Chen H (2021) Carbon emission efficiency of China’s industry sectors: from the perspective of embodied carbon emissions. J Clean Prod 283:124655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124655
Gong W, Zhang H, Wang C, Wu B, Yuan Y, Fan S (2022) Analysis of urban carbon emission efficiency and influencing factors in the Yellow River Basin. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:14641–14655. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23065-x
Guo X, Wang X, Wu X, Chen X, Li Y (2022) Carbon emission efficiency and low-carbon optimization in Shanxi Province under “dual carbon” background. Energies 15:2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15072369
Huang X, Tian P (2023) How does heterogeneous environmental regulation affect net carbon emissions: spatial and threshold analysis for China. J Environ Manage 330:117161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.117161
Jing Q, Hou H, Bai H, Xu H (2019) A top-bottom estimation method for city-level energy-related CO2 emissions. China Environ Sci 39(01):420–427. https://doi.org/10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.2019.0052
Lesage JP (2008) An introduction to spatial econometrics. Revue d'économie industrielle 19–44. https://doi.org/10.4000/rei.3887
Li J, Huang X, Kwan M-P, Yang H, Chuai X (2018) The effect of urbanization on carbon dioxide emissions efficiency in the Yangtze River Delta, China. J Clean Prod 188:38–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.198
Li Y, Sun X, Bai X (2022) Differences of carbon emission efficiency in the belt and road initiative countries. Energies 15:1576. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15041576
Lin G, Jiang D, Dong D, Fu J, Li X (2020) Spatial characteristic of coal production-based carbon emissions in Chinese mining cities. Energies 13:453. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13020453
Liu F, Liu C (2019) Regional disparity, spatial spillover effects of urbanisation and carbon emissions in China. J Clean Prod 241:118226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118226
Liu B, Tian C, Li Y, Song H, Ma Z (2018) Research on the effects of urbanization on carbon emissions efficiency of urban agglomerations in China. J Clean Prod 197:1374–1381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.295
Liu L, Zhang Y, Gong X, Li M, Li X, Ren D, Jiang P (2022a) Impact of digital economy development on carbon emission efficiency: a spatial econometric analysis based on Chinese provinces and cities. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19:14838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192214838
Liu X, Yang M, Niu Q, Wang Y, Zhang J (2022b) Cost accounting and sharing of air pollution collaborative emission reduction: a case study of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China. Urban Clim 43:101166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.uclim.2022.101166
Meng C, Du X, Zhu M, Ren Y, Fang K (2023) The static and dynamic carbon emission efficiency of transport industry in China. Energy 274:127297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.127297
Qin X, Du D, Kwan M-P (2019) Spatial spillovers and value chain spillovers: evaluating regional R&D efficiency and its spillover effects in China. Scientometrics 119:721–747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-019-03054-7
Qin Q, Yan H, Liu J, Chen X, Ye B (2020) China’s agricultural GHG emission efficiency: regional disparity and spatial dynamic evolution. Environ Geochem Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00744-7
Sun W, Dong H (2022) Measurement of provincial carbon emission efficiency and analysis of influencing factors in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:38292–38305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-25031-z
Sun W, Huang C (2020) How does urbanization affect carbon emission efficiency? Evidence from China. J Clean Prod 272:122828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122828
Sun W, Huang C (2022) Predictions of carbon emission intensity based on factor analysis and an improved extreme learning machine from the perspective of carbon emission efficiency. J Clean Prod 338:130414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130414
Sun Z, Sun Y, Liu H, Cheng X (2023) Impact of spatial imbalance of green technological innovation and industrial structure upgradation on the urban carbon emission efficiency gap. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-023-02395-3
Tang K, Xiong C, Wang Y, Zhou D (2021) Carbon emissions performance trend across Chinese cities: evidence from efficiency and convergence evaluation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:1533–1544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10518-4
Tone K (2001) A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur J Oper Res 130(3):498–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(99)00407-5
Wang S, Chen B (2016) Energy–water nexus of urban agglomeration based on multiregional input–output tables and ecological network analysis: a case study of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region. Appl Energy 178:773–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.06.112
Wang S, Huang Y (2019) Spatial spillover effect and driving forces of carbon emission intensity at the city level in China. Acta Geographica Sinica 74(06):1131–1148. https://doi.org/10.11821/dlxb201906005
Wang T, Li H (2023) Have regional coordinated development policies promoted urban carbon emission efficiency? —the evidence from the urban agglomerations in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:39618–39636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24915-4
Wang K, Wu M, Sun Y, Shi X, Sun A, Zhang P (2019a) Resource abundance, industrial structure, and regional carbon emissions efficiency in China. Resour Policy 60:203–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2019.01.001
Wang Y, Duan F, Ma X, He L (2019b) Carbon emissions efficiency in China: key facts from regional and industrial sector. J Clean Prod 206:850–869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.09.185
Wang G, Han Q, de Vries B (2020a) A geographic carbon emission estimating framework on the city scale. J Clean Prod 244:118793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118793
Wang R, Hao J-X, Wang C, Tang X, Yuan X (2020b) Embodied CO2 emissions and efficiency of the service sector: evidence from China. J Clean Prod 247:119116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119116
Wang Q, Zhang C, Li R (2022) Towards carbon neutrality by improving carbon efficiency - a system-GMM dynamic panel analysis for 131 countries’ carbon efficiency. Energy 258:124880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.124880
Wang Q, Li L, Li R (2023a) Uncovering the impact of income inequality and population aging on carbon emission efficiency: an empirical analysis of 139 countries. Sci Total Environ 857:159508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159508
Wang Y, Ren Y, Wu D, Qian W (2023) Eco-efficiency evaluation and productivity change of Yangtze River Economic Belt in China: a meta-frontier Malmquist-Luenberger index perspective. Energy Efficiency 16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-023-10105-9
Wen S, Jia Z, Chen X (2022) Can low-carbon city pilot policies significantly improve carbon emission efficiency? Empirical evidence from China. J Clean Prod 346:131131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131131
Wu X, Tian Z, Kuai Y, Song S, Marson SM (2022) Study on spatial correlation of air pollution and control effect of development plan for the city cluster in the Yangtze River Delta. Socioecon Plann Sci 83:101213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seps.2021.101213
Xie Z, Wu R, Wang S (2021) How technological progress affects the carbon emission efficiency? Evidence from national panel quantile regression. J Clean Prod 307:127133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127133
Xu Y, Cheng Y, Zheng R, Wang Y (2022) Spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of carbon emission efficiency in the Yellow River Basin of China: comparative analysis of resource and non-resource-based cities. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19:11625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811625
Yan D, Lei Y, Li L, Song W (2017) Carbon emission efficiency and spatial clustering analyses in China’s thermal power industry: evidence from the provincial level. J Clean Prod 156:518–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.04.063
Yu N, de Jong M, Storm S, Mi J (2013) Spatial spillover effects of transport infrastructure: evidence from Chinese regions. J Transp Geogr 28:56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2012.10.009
Zeng L, Lu H, Liu Y, Zhou Y, Hu H (2019) Analysis of regional differences and influencing factors on China’s carbon emission efficiency in 2005–2015. Energies 12:3081. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12163081
Zeng S, Li G, Wu S, Dong Z (2022) The impact of green technology innovation on carbon emissions in the context of carbon neutrality in China: evidence from spatial spillover and nonlinear effect analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19:730. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020730
Zhang C, Chen P (2021) Industrialization, urbanization, and carbon emission efficiency of Yangtze River Economic Belt—empirical analysis based on stochastic frontier model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:66914–66929. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15309-z
Zhang M, Liu Y (2022) Influence of digital finance and green technology innovation on China’s carbon emission efficiency: empirical analysis based on spatial metrology. Sci Total Environ 838:156463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156463
Zhang Y, Xu X (2022) Carbon emission efficiency measurement and influencing factor analysis of nine provinces in the Yellow River basin: based on SBM-DDF model and Tobit-CCD model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:33263–33280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18566-8
Zhang F, Jin G, Li J, Wang C, Xu N (2020a) Study on dynamic total factor carbon emission efficiency in China’s urban agglomerations. Sustainability 12:2675. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12072675
Zhang Y, Wang W, Liang L, Wang D, Cui X, Wei W (2020b) Spatial-temporal pattern evolution and driving factors of China’s energy efficiency under low-carbon economy. Sci Total Environ 739:140197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140197
Zhang C, Wang Z, Luo H (2022a) Spatio-temporal variations, spatial spillover, and driving factors of carbon emission efficiency in RCEP members under the background of carbon neutrality. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:36485–36501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24778-9
Zhang C, Zhou Y, Li Z (2022b) Low-carbon innovation, economic growth, and CO2 emissions: evidence from a dynamic spatial panel approach in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:25792–25816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23890-0
Zhang R, Tai H, Cheng K, Zhu Y, Hou J (2022c) Carbon emission efficiency network formation mechanism and spatial correlation complexity analysis: Taking the Yangtze River Economic Belt as an example. Sci Total Environ 841:156719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156719
Zhang J, Huang R, He S (2023) How does technological innovation affect carbon emission efficiency in the Yellow River Economic Belt: the moderating role of government support and marketization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:63864–63881. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26755-2
Zhou Q, Zhang X, Shao Q, Wang X (2019a) The non-linear effect of environmental regulation on haze pollution: empirical evidence for 277 Chinese cities during 2002–2010. J Environ Manage 248:109274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109274
Zhou Y, Liu W, Lv X, Chen X, Shen M (2019b) Investigating interior driving factors and cross-industrial linkages of carbon emission efficiency in China’s construction industry: based on super-SBM DEA and GVAR model. J Clean Prod 241:118322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118322
Zhou X, Yu J, Li J, Li S, Zhang D, Wu D, Pan S, Chen W (2022) Spatial correlation among cultivated land intensive use and carbon emission efficiency: a case study in the Yellow River Basin, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:43341–43360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18908-6
Funding
This research is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41871179).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TW: conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, data curation, writing—original draft, formal analysis, writing—review and editing. HL: resources, methodology, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any authors.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: V.V.S.S. Sarma
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 27.1 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Li, H. Assessing the spatial spillover effects and influencing factors of carbon emission efficiency: a case of three provinces in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 119050–119068 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30677-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30677-4