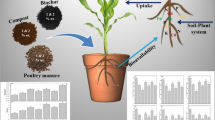
Abstract
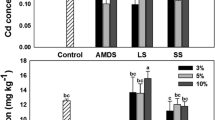
The main purpose of applying organic or inorganic amendments is to guarantee crop safe production in heavy metal contaminated soil. However, previous studies showed that the effects of organic or inorganic composite amendments on the cadmium (Cd) concentration of lettuce (Lactuca sativa var. ramosa Hort) were inconsistent. Accordingly, a sixty-day pot experiment was carried out to examine the impacts of the inorganic materials (lime, L and zeolite, Z), organic materials (biochar, B and compost, C), and their combination on the immobilization of Cd in soil and its uptake by lettuce. The objective was to identify the most suitable soil amendment combination that promotes safe lettuce production. The results revealed that the combined application of BC, LZC, and LBC significantly increased the plant height by 11.09–28.04% and fresh weight by 183.47–207.67%. This improvement can be attributed to enhanced soil quality, such as increased dissolved organic carbon (DOC) by 70.19–80.42%, soil respiration (SR) by 29.04–38.46%, and soil microbial carbon content (SMC) by 36.94–46.63%. Compared to inorganic fertilizers and their combination with organic amendments, organic amendments had a significant impact on reducing shoot Cd concentration by 33.93%-56.55%, while increasing the activity of catalase by 138.87–186.86%. And soil available Cd measured by diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT-Cd) decreased 24.73–88.13% in all treatments. Correlation analysis showed that plant Cd concentration was significantly correlated with soil pH, SR, cation exchange capacity (CEC), DOC and SMC. These results demonstrated that organic amendments, especially the combination of biochar and compost, have greater potential than inorganic amendments and inorganic–organic combinations for realizing safe production of lettuce and improving soil quality in the Cd moderately contaminated acid farmland.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data used or analysed during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Agegnehu G, Bass AM, Nelson PN, Bird MI (2016) Benefits of biochar, compost and biochar-compost for soil quality, maize yield and greenhouse gas emissions in a tropical agricultural soil. Sci Total Environ 543:295–306
Ahmad M, Lee SS, Lee SE, Al-Wabel MI, Tsang DCW, Ok YS (2017) Biochar-induced changes in soil properties affected immobilization/mobilization of metals/metalloids in contaminated soils. J Soils Sediments 17(3):717–730
Alam MGM, Snow ET, Tanaka A (2003) Arsenic and heavy metal contamination of vegetables grown in Samta village, Bangladesh. Sci Total Environ 308(1–3):83–96
Anup D, Patel DP, Manoj K, Ramkrushna GI, Atanu M, Jayanta L, Ngachan SV, Juri B (2017) Impact of seven years of organic farming on soil and produce quality and crop yields in eastern Himalayas, India. Agr Ecosyst Environ 236:142–153
Ashrafi F, Heidari A, Farzam M, Karimi A, Amini M (2023) The interactions of Cr (VI) concentrations and amendments (biochar and manure) on growth and metal accumulation of two species of Salicornia in contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(1):201–218
Bandara T, Franks A, Xu JM, Chathurika J, Tang CX (2021) Biochar aging alters the bioavailability of cadmium and microbial activity in acid contaminated soils. J Hazard Mater 420:12666
Cao L, Wang G, Xu W, Pu H, Yang Y (2018) Effects of application of poplar litter and sludge compost on poplar seedling growth in Cd~(2+)-contaminated soil. J Nanjing For Univ Nat Sci Ed 42(4):68–74
Cesarano G, De Filippis F, La Storia A, Scala F, Bonanomi G (2017) Organic amendment type and application frequency affect crop yields, soil fertility and microbiome composition. Appl Soil Ecol 120:254–264
Cheng L, Qiu Y, Li X, Zhu J (2010) Effect of soil amendment on growth traits, physiological and biochemical indices related to salt tolerance of cotton seedling under salinity stress. J Northeast Agric Univ 41(11):22–27
Cui J, Yang B, Zhang M, Song D et al (2023) Investigating the effects of organic amendments on soil microbial composition and its linkage to soil organic carbon: A global meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 894:164899
Deng A, Luo J, Su C et al (2021) Effects of alkaline humic acid fertilizer amendment on cherry tomato yield and quality and soil improvement. J South Argic 52(5):1282–1290
Duan Y, Wu J, Zhou W et al (2021) Effects of different amendments on the yield of Rheum officinale Baill. and rhizospheric soil fertility under continuous cropping system. J South Argic 52(3):753–761
Fall D, Bakhoum N, Fall F, Diouf F, Ndiaye C, Faye MN, Hocher V, Diouf D (2018) Effect of peanut shells amendment on soil properties and growth of seedlings of Senegalia senegal (L.) Britton, Vachellia seyal (Delile) P. Hurter, and Prosopis juliflora (Swartz) DC in salt-affected soils. Ann For Sci 75(1):11
Fitz WJ, Wenzel WW, Zhang H, Nurmi J, Stipek K, Fischerova Z, Schweiger P, Kollensperger G, Ma LQ, Stingeder G (2003) Rhizosphere characteristics of the arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata L. and monitoring of phytoremoval efficiency. Environ Sci Technol 37(21):5008–5014
Garbowski T, Bar-Michalczyk D, Charazinska S, Grabowska-Polanowska B, Kowalczyk A, Lochynski P (2023) An overview of natural soil amendments in agriculture. Soil Tillage Res 225:105462
Hamid Y, Tang L, Yaseen M, Hussain B, Zehra A, Aziz MZ, He Z-L, Yang X (2019) Comparative efficacy of organic and inorganic amendments for cadmium and lead immobilization in contaminated soil under rice-wheat cropping system. Chemosphere 214:259–268
Hamid Y, Tang L, Hussain B, Usman M, Lin Q, Rashid MS, He Z, Yang X (2020) Organic soil additives for the remediation of cadmium contaminated soils and their impact on the soil-plant system: A review. Sci Total Environ 707:136121
Han L, Zhao X, Jin J, Gao B, Yang Y, Sun K, Li F (2019) Using sequential extraction and DGT techniques to assess the efficacy of plant- and manure-derived hydrochar and pyrochar for alleviating the bioavailability of Cd in soils. Sci Total Environ 678:543–550
Han Q, Fu Y, Qiu R, Ning H, Liu H, Li C, Gao Y (2023) Carbon amendments shape the bacterial community structure in salinized farmland soil. Microbiol Spectr 11(1):e0101222
Hua Y, Heal KV, Friesl-Hanl W (2017) The use of red mud as an immobiliser for metal/metalloid-contaminated soil: A review. J Hazard Mater 325:17–30
Huang L, Wang Q, Zhou Q, Ma L, Wu Y, Liu Q, Wang S, Feng Y (2020) Cadmium uptake from soil and transport by leafy vegetables: A meta-analysis. Environ Pollut 264:114677
Hui CY, Guo Y, Liu LS, Yi J (2022) Recent advances in bacterial biosensing and bioremediation of cadmium pollution: a mini-review. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 38:9
Kallenbach CM, Grandy AS, Frey SD, Diefendorf AF (2015) Microbial physiology and necromass regulate agricultural soil carbon accumulation. Soil Biol Biochem 91:279–290
Khan MA, Khan S, Khan A, Alam M (2017) Soil contamination with cadmium, consequences and remediation using organic amendments. Sci Total Environ 601:1591–1605
Khan MA, Ding X, Khan S, Brusseau ML, Khan A, Nawab J (2018) The influence of various organic amendments on the bioavailability and plant uptake of cadmium present in mine-degraded soil. Sci Total Environ 636:810–817
Kong W, Ye L, Li S, Yuan X, Jiang J (2017) Effects of straw biochar and amendments on heavy metals translocation in corn-soil system in rocky desertification area. Chin J Environ Eng 11(8):4815–4823
Kumar A, Subrahmanyam G, Mondal R, Cabral-Pinto MMS, Shabnam AA, Jigyasu DK, Malyan SK, Fagodiya RK, Khan SA, Yu Z-G (2021) Bio-remediation approaches for alleviation of cadmium contamination in natural resources. Chemosphere 268:128855
Lahori AH, Mierzwa-Hersztek M, Demiraj E, Idir R, Bui TTX, Vu DD, Channa A, Samoon NA (2020) Zhang Z (2020) Clays, Limestone and Biochar Affect the Bioavailability and Geochemical Fractions of Cadmium and Zinc from Zn-Smelter Polluted Soils. Sustainability 12(20):8606
Li S, Tan Z, Liu T, Guo J (2020) Effects of Simulated Nitrogen Deposition on Soil Microbial Carbon and Nitrogen Dynamics of Larix principis-rupprechtii Plantation. J Soil Water Conserv 34(1):268–274
Li Z, Liu S, Ding Y, Sun W, Gao X, Zhao X (2021) Effects of different modifiers on greenhouse gas emissions from dryland apple orchards. J Agro-Environ Sci 40(1):227–236
Li L, Mao K, Ippolito JA, Xing W, Chen X, Zhu W, Cheng Y (2022) Calcium amendments affect heavy metal bioavailability in acidic and calcareous soils. Int J Environ Sci Technol 19(10):10067–10076
Liao P, Huang S, Zeng Y, Shao H, Zhang J, van Groenigen KJ (2021) Liming increases yield and reduces grain cadmium concentration in rice paddies: a meta-analysis. Plant Soil 465(1–2):157–169
Liu L, Li J, Yue F, Yan X, Wang F, Bloszies S, Wang Y (2018) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculation and biochar amendment on maize growth, cadmium uptake and soil cadmium speciation in Cd-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 194:495–503
Liu HY, Ling Y, Liu N, Chen Y, Wei SQ (2022) The determination of regulating thresholds of soil pH under different cadmium stresses using a predictive model for rice safe production. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(58):88008–88017
Liu Q, Chen Z, Wu Y, Huang L, Munir MAM, Zhou Q, Wen Z, Jiang Y, Tao Y, Feng Y (2022b) Inconsistent effects of a composite soil amendment on cadmium accumulation and consumption risk of 14 vegetables. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(47):71810–71825
Liu Q, Chen Z, Huang L, Munir MAM, Wu Y, Wang Q, Ma L, Xu S, Wen Z, Feng Y (2021) The effects of a combined amendment on growth, cadmium adsorption by five fruit vegetables, and soil fertility in contaminated greenhouse under rotation system. Chemosphere 285:131499
Liu Q, Huang L, Chen Z, Wen Z, Ma L, Xu S, Wu Y, Liu Y, Feng Y (2022b) Biochar and its combination with inorganic or organic amendment on growth, uptake and accumulation of cadmium on lettuce. J Clean Prod 370:133610
Lyu Y, Li J, Ye H, Du D, Wuri L, Gan C (2018) Remediation of Heavy Metals Contaminated Acidic Soil by Mixed Inorganic Amendments. Environ Sci Technol 41(10):1–12
Ma L, Liu Y, Wu Y, Wang Q, Sahito ZA, Zhou Q, Huang L, Li T, Feng Y (2021) The effects and health risk assessment of cauliflower co-cropping with Sedum alfredii in cadmium contaminated vegetable field. Environ Pollut 268:115869
Ma Q, Haider FU, Farooq M, Adeel M, Shakoor N, Wu J, Xu J, Wang XW, Luo P, Cai L (2022) Selenium treated foliage and biochar treated soil for improved lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) growth in Cd-polluted soil. J Clean Prod 335:130267
Mahar A, Wang P, Li R, Zhang Z (2015) Immobilization of Lead and Cadmium in Contaminated Soil Using Amendments: A Review. Pedosphere 25(4):555–568
Malik MA, Marschner P, Khan KS (2012) Addition of organic and inorganic P sources to soil - Effects on P pools and microorganisms. Soil Biol Biochem 49:106–113
Mao Y-D, Tie B-Q, Ye C-C, Zhou Y, Yang S-M (2015) Effects of Biochar on Forms and Uptake of Cadmium by Rapeseed in Cadmium-Polluted Soil. J Ecol Rural Environ 31(4):579–582
Mehmood S, Saeed DA, Rizwan M, Khan MN, Aziz O, Bashir S, Ibrahim M, Ditta A, Akmal M, Mumtaz MA, Ahmed W, Irshad S, Imtiaz M, Tu S, Shaheen A (2018) Impact of different amendments on biochemical responses of sesame (Sesarnum indicum L.) plants grown in lead-cadmium contaminated soil. Plant Physiol Biochem 132:345–355
Munir MAM, Liu G, Yousaf B, Ali MU, Abbas Q, Ullah H (2020) Synergistic effects of biochar and processed fly ash on bioavailability, transformation and accumulation of heavy metals by maize (Zea mays L.)in coal-mining contaminated soil. Chemosphere 240:124845
Ndoung OCN, de Figueiredo CC, Ramos MLG (2021) A scoping review on biochar-based fertilizers: enrichment techniques and agro-environmental application. Heliyon 7(12):e08473
Oliver DP, Tiller KG, Alston AM, Cozens GD, Merry RH (1998) Effects of soil pH and applied cadmium on cadmium concentration in wheat grain. Aust J Soil Res 36(4):571–583
Ondrasek G, Kranjcec F, Filipovic L, Filipovic V, Kovacic MB, Badovinac IJ, Peter R, Petravic M, Macan J, Rengel Z (2021) Biomass bottom ash & dolomite similarly ameliorate an acidic low-nutrient soil, improve phytonutrition and growth, but increase Cd accumulation in radish. Sci Total Environ 753:141902
Palansooriya KN, Shaheen SM, Chen SS, Tsang DCW, Hashimoto Y, Hou DY, Bolan NS, Rinklebe J, Ok YS (2020) Soil amendments for immobilization of potentially toxic elements in contaminated soils: A critical review. Environ Int 134:105046
Peter A, Nicula C, Mihaly-Cozmuta A, Mihaly-Cozmuta L, Indrea E, Danciu V, Tutu H, Nsimba EB (2011) Efficiency of amendments based on zeolite and bentonite in reducing the accumulation of heavy metals in tomato organs (Lycopersicum esculentum) grown in polluted soils. Afr J Agric Res 6(21):5010–5023
Radziemska M, Wyszkowski M, Bes A, Mazur Z, Jeznach J, Brtnicky M (2019) The applicability of compost, zeolite and calcium oxide in assisted remediation of acidic soil contaminated with Cr(III) and Cr(VI). Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(21):21351–21362
Rehman ZU, Khan S, Brusseau ML, Shah MT (2017) Lead and cadmium contamination and exposure risk assessment via consumption of vegetables grown in agricultural soils of five-selected regions of Pakistan. Chemosphere 168:1589–1596
Sanchez-Garcia M, Alburquerque JA, Sanchez-Monedero MA, Roig A, Cayuela ML (2015) Biochar accelerates organic matter degradation and enhances N mineralisation during composting of poultry manure without a relevant impact on gas emissions. Biores Technol 192:272–279
Shaheen SM, Rinklebe J, Frohne T, White JR, DeLaune RD (2016) Redox effects on release kinetics of arsenic, cadmium, cobalt, and vanadium in Wax Lake Deltaic freshwater marsh soils. Chemosphere 150:740–748
Shao Y, Ren S, Yang J, Gao W, Gao X (2012) Effect of Organic-inorganic Soil Amendments on Physical and Chemical Conditions of Saline Water Irrigation Soil and Maize Yield. Chin Agric Sci Bull 28(18):111–116
Sharma A, Nagpal AK (2018) Soil amendments: a tool to reduce heavy metal uptake in crops for production of safe food. Rev Environ Sci Bio-Technol 17(1):187–203
Shi W-Y, Shao H-B, Li H, Shao M-A, Du S (2009) Progress in the remediation of hazardous heavy metal-polluted soils by natural zeolite. J Hazard Mater 170(1):1–6
Slapakova B, Jerabkova J, Vorisek K, Tejnecky V, Drabek O (2018) The biochar effect on soil respiration and nitrification. Plant Soil Environ 64(3):114–119
Tang X, Pang Y, Ji P, Gao P, Thanh Hung N, Tong Y (2016) Cadmium uptake in above-ground parts of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 125:102–106
Tang B, Xu HP, Song FM, Ge HG, Chen L, Yue SY, Yang WS (2022) Effect of biochar on immobilization remediation of Cd center dot contaminated soil and environmental quality. Environ Res 204:111840
Veronica Perez-Chaca M, Rodriguez-Serrano M, Molina AS, Pedranzani HE, Zirulnik F, Sandalio LM, Romero-Puertas MC (2014) Cadmium induces two waves of reactive oxygen species in Glycine max (L.) roots. Plant Cell Environ 37(7):1672–1687
Wang H, Zhang W, Chen L, Xu Q, Jiang Y, Sun B (2020) Biochar induced negative priming effect on soil organic carbon mineralisation by changing the microbial community structure across plant growth stages. J Soils Sediments 20(9):3340–3350
Wang F, Wang X, Song N (2021) Polyethylene microplastics increase cadmium uptake in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) by altering the soil microenvironment. Sci Total Environ 784:147133
Wang M, Wu Y, Zhao J, Liu Y, Gao L, Jiang Z, Zhang J, Tian W (2022) Comparison of composting factors, heavy metal immobilization, and microbial activity after biochar or lime application in straw-manure composting. Bioresour Technol 363:27872
Wu Y, Li Y, Zheng C, Zhang Y, Sun Z (2013) Organic amendment application influence soil organism abundance in saline alkali soil. Eur J Soil Biol 54:32–40
Xing Y, Wang J, Kinder CES, Yang X, Slany M, Wang B, Song H, Shaheen SM, Leinweber P, Rinklebe J (2022) Rice hull biochar enhances the mobilization and methylation of mercury in a soil under changing redox conditions: Implication for Hg risks management in paddy fields. Environ Int 168:107484
Xu Y, Seshadri B, Sarkar B, Wang H, Rumpel C, Sparks D, Farrell M, Hall T, Yang X, Bolan N (2018) Biochar modulates heavy metal toxicity and improves microbial carbon use efficiency in soil. Sci Total Environ 621:148–159
Yang Z, Liang J, Tang L, Zeng G, Yu M, Li X, Li X, Qian Y, Wu H, Luo Y, Mo D (2018) Sorption-desorption behaviors of heavy metals by biochar-compost amendment with different ratios in contaminated wetland soil. J Soils Sediments 18(4):1530–1539
Younis U, Malik SA, Rizwan M, Qayyum MF, Ok YS, Shah MHR, Rehman RA, Ahmad N (2016) Biochar enhances the cadmium tolerance in spinach (Spinacia oleracea) through modification of Cd uptake and physiological and biochemical attributes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(21):21385–21394
Yu H, Zou W, Chen J, Chen H, Yu Z, Huang J, Tang H, Wei X, Gao B (2019) Biochar amendment improves crop production in problem soils: A review. J Environ Manag 232:8–21
Yue F, Li J, Wang Y, Liu L (2018) Effects of soil amendments with stalk-derived biochar and chicken manure on the growth and Cd uptake of maize under Cd stress. J Agro-Environ Sci 37(10):2118–2126
Zeng P, Liu J, Zhou H, Wei B, Gu J, Liao Y, Liao B, Luo X (2023a) Co-application of combined amendment (limestone and sepiolite) and Si fertilizer reduces rice Cd uptake and transport through Cd immobilization and Si-Cd antagonism. Chemosphere 316:137859
Zeng G, Liu Z, Guo Z, He J, Ye Y, Xu H, Hu T (2023b) Compost with spent mushroom substrate and chicken manure enhances rice seedling quality and reduces soil-borne pathogens. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:77743–77756
Zhang YF, Wang JM, Feng Y (2021) The effects of biochar addition on soil physicochemical properties: A review. Catena 202:105284
Zhang W, Butterly C, Han B, He J-Z, Chen D (2022) Modified lignite and black coal reduce ammonia volatilization from cattle manure. J Environ Manag 301:113807
Zhao J-Y, Xi Y-G, Dai H-J, Jin S, Tian W (2019) Effects of Compost Combined With Amendments on Available Copper and Cadmium in Soil and Their Accumulation in Romaine. J Ecol Rural Environ 35(11):1460–1467
Zhao H, Huang X, Liu F, Hu X, Zhao X, Wang L, Gao P, Li J, Ji P (2021) Potential of a novel modified gangue amendment to reduce cadmium uptake in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). J Hazard Mater 410:124543
Zhao M, Liu R, Wang X, Zhang J, Wang J, Cao B, Zhao Y, Xu L, Chen Y, Zou G (2022) How do controlled-release fertilizer coated microplastics dynamically affect Cd availability by regulating Fe species and DOC content in soil? Sci Total Environ 850:157886
Zhu J, Zhang Y, Li Z, Ran C, Zhang H, Liu Q, Li X, Shi J (2018) Effects of different soil amendments on soil aggregate composition from a renovated tobacco field. J Nanjing Agric Univ 41(2):341–348
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Research and Development Project of Zhejiang Province (2021C04020), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42277002) and the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. LZ22D010002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jie Yuan: Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft. Qizhen Liu: Conceptualization, Methodology, editing. Zhiqin Chen: Writing – review & editing. Zheyu Wen: Software, Formal analysis. Yaru Liu: Software, Formal analysis. Lukang Huang: Visualization, Investigation. Chao Yu: Visualization, Editing. Ying Feng: Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kitae Baek
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, J., Liu, Q., Chen, Z. et al. Organic amendments perform better than inorganic amendments in reducing the absorption and accumulation of cadmium in lettuce. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 117277–117287 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30449-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30449-0