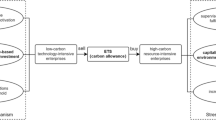
Abstract
The carbon emission reduction behaviour of enterprises is a crucial element for achieving the “double-carbon” target. Based on the panel data of China’s Shanghai and Shenzhen A-share nonfinancial listed companies from 2008 to 2022, this paper explores the impact of corporate carbon emission reduction on financing constraints using the fixed effect model and further dissects the path and heterogeneity of its impact. The results show that carbon emission reduction can significantly alleviate the level of financing constraints. The path test shows that corporate carbon emission reduction alleviates financing constraints through gaining business credit, improving information transparency, and increasing government subsidies. The heterogeneity analysis shows that carbon emission reduction in less economically developed regions, non-heavily polluting industries, and nonstate-owned enterprises has a better effect on alleviating financing constraints than in economically developed regions, heavily polluting industries and state-owned enterprises. Additionally, relevant policy recommendations are put forward, which are conducive to promoting enterprises to actively reduce carbon emissions and facilitate the achievement of the dual carbon goal.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abeysekara WCSM, Siriwardana M, Meng S (2023) Economic consequences of climate change impacts on the agricultural sector of South Asia: a case study of Sri Lanka. Econ Anal Policy 77:435–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2022.12.003
Andriof J, Waddock SA (2001) Unfolding stakeholder thinking: Theory, responsibility, and engagement. Green-leaf Publishing Limited, Sheffield
Bai SX, Han YM, Zhang DG (2019) Research on the correlation between carbon emission reduction and enterprise value. Friends Acc 7:148–155
Benkraiem R, Shuwaikh F, Lakhal F, Guizani A (2022) Carbon performance and firm value of the world’s most sustainable companies. Econ Model 116:106002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2022.106002
Blinken A (2021) Tackling the crisis and seizing the opportunity: America’s global climate leadership. Speech at the Chesapeake Bay Foundation. Retrieved February, 23, 2022
Cao HM, Qu XY (2022) Does the fulfillment of social responsibility inhibit inefficient corporate investment based on the mediating effect of business credit. Friends of Accounting 8:31–37
Chang Y, Du X, Zeng Q (2021) Does environmental information disclosure mitigate corporate risk? Evidence from China. J Contemp Acc Econ 17(1):100239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcae.2020.100239
Chen J, Zheng HQ (2020) Financing constraints, customer bargaining ability and corporate social responsibility. Acc Res 8:50–63
Chen H, Huang HM, Li CL (2017) Research on the influence of carbon information voluntary disclosure on corporate--- financing constraint based on the heterogeneity of property rights. Price Theory Practice 09:136–139. https://doi.org/10.19851/j.cnki.cn11-1010/f.2017.09.034
Chen Z, Yin M, Zhou M (2022) Does environmental regulatory pressure affect corporate debt financing? Resources. Conserv Recycl 184:106405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106405
Cheng FX, Shao SL, Xu LF, Sun LC (2015) Optimal strategy of government subsidized initiative carbon reduction. China Population Res Environ 25(7):32–39. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2015.07.005
Cull R, Xu LC, Zhu T (2009) Formal finance and trade credit during China’s transition. J Financ Intermed 18(2):173–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfi.2008.08.004
Cull R, Li W, Sun B et al (2015) Government connections and financial constraints: evidence from a large representative sample of Chinese firms. J Corp Finan 32:271–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcorpfin.2014.10.012
Deegan C, Gordon B (1996) A study of the environmental disclosure practices of Australian corporations. Account Bus Res 26(3):187–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/00014788.1996.9729510
Deng BF, Tao CJ, Ji L (2020) Firms’ Targeted Poverty Alleviation and the Ease of Financial Constraints. J Financ Econ 12:138–151. https://doi.org/10.16538/j.cnki.jfe.20200817.301
Dhaliwal DS, Li OZ, Tsang A, Yang YG (2011) Voluntary nonfinancial disclosure and the cost of equity capital: the initiation of corporate social responsibility reporting. Account Rev 86(1):59–100. https://doi.org/10.2308/accr.00000005
Donaldson T, Preston LE (1998) The stakeholder theory of the corporation: concepts, evidence and implications. Corp Stakeholders 20(1):65–91. https://doi.org/10.3138/9781442673496-011
Dou Y, Zhao J, Malik MN, Dong K (2021) Assessing the impact of trade openness on CO2 emissions: evidence from China - Japan - ROK FTA countries. J Environ Manage 296:113241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113241
Dröge S, Feist M (2022) The G7 summit: advancing international climate cooperation. german institute for international and security affairs. Berlin, Germany
Fabbri D, Klapper LF (2016) Bargaining power and trade credit. J Corp Finan 41:66–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcorpfin.2016.07.001
Feng M, Ge W, Li C et al (2012) How do earnings manipulators guide investors. SSRN Electron J. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.1942076
Francis JR, Khurana IK, Pereira R (2005) Disclosure incentives and effects on cost of capital around the world. Account Rev 80(4):1125–1162. https://doi.org/10.2308/accr.2005.80.4.1125
Gu LL, Guo JH, Wang HY (2020) Corporate social responsibility, financing constraints, and the financialization of enterprises. J Financ Res 476(2):109–127
Freeman RE, Evan WM (1990) Corporate governance: a stakeholder interpretation. J Behav Econ 19(4):337–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/0090-5720(90)90022-y
Hadlock CJ, Pierce JR (2010) New evidence on measuring financial constraints: Moving beyond the KZ Index. Rev Financ Studies 23(5):1909–1940. https://doi.org/10.1093/rfs/hhq009
Hooghiemstra R (2000) Communication and impression management new perspective Why companies engage in corporate social reporting. J Bus Ethics 27(1):55–68. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006400707757
Hossain M, Mitra S, Rezaee Z, Sarath B (2011) Corporate governance and earnings management in the pre–and post–sarbanes-oxley act regimes. J Acc Audit Financ 26(2):279–315. https://doi.org/10.1177/0148558x11401218
Hsu AW, Wang T (2013) Does the market value corporate response to climate change? Omega 41(2):195–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2011.07.009
Hu LF (2021) Study on the influence and mechanism of corporate strategy on financing constraint. Nankai Econ Studies 1:58–84. https://doi.org/10.14116/j.nkes.2021.01.005
Huang Y, Bai F, Shang M, Ahmad M (2023) On the fast track: the benefits of ESG performance on the commercial credit financing. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:83961–83974. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28172-x
Ju XS, Die L, Yu YH (2013) Financing constraints, working capital management and the persistence of firm innovation. Econ Res J 1:4–16
Kang K-N, Park H (2012) Influence of government R&D support and inter-firm collaborations on innovation in Korean biotechnology SMEs. Technovation 32(1):68–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2011.08.004
Kaplan SN, Zingales L (1997) Do investment––cash flow sensitivities provide useful measures of financing constraints? Quart J Econ 112(1):169–215. https://doi.org/10.2307/2951280
Lee K-H, Min B, Yook K-H (2015) The impacts of carbon (CO2) emissions and environmental research and development (R&D) investment on firm performance. Int J Prod Econ 167:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2015.05.018
Li HY, Liu D (2016) Marketization process, voluntary disclosure, and cost of equity capital. Account Res 01:71-78+96
Li L, Liu Q, Tang D, Xiong J (2017) Media reporting, carbon information disclosure, and the cost of equity financing: evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(10):9447–9459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8614-4
Li Q, Ruan W, Shi H, Xiang E, Zhang F (2022) Corporate environmental information disclosure and bank financing: moderating effect of formal and informal institutions. Bus Strateg Environ 31(7):2931–2946
Li JL, Yang Z, Yi JL (2023) Does ESG performance help lower corporate debt financing costs? –– Micro evidence from listed companies. Enterp Econ 2:89–99. https://doi.org/10.13529/j.cnki.enterprise.economy.2023.02.009
Ling AF, You X, Li LQ (2023) The impact of targeted poverty alleviation on systemic extreme tail risk: “Window Dressing” or “Immunity Tool”? systems engineering-theory & practice
Liu DX, Peng CC (2018) Government regulation, carbon information disclosure and financing constraints. Finance Acc Newsl 27(17):23–129
Liu F, Yu J, Shen Y, He L (2022) Does the resource-dependent motivation to disclose environmental information impact company financing? Evidence from renewable energy companies of China. Renew Energy 181:156–166
Lombart C, Louis D (2012) Consumer satisfaction and loyalty: two main consequences of retailer personality. J Retail Consum Serv 19(6):644–652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2012.08.007
Lu JY, Zhang S (2021) Corporate social responsibility, media attention and financing constraints. Friends Acc 10:110–116
Lv JY, Li MX (2023) Carbon information disclosure, internal control quality, and corporate debt financing costs. The Chinese Certified Public Accountant 08:76–83. https://doi.org/10.16292/j.cnki.issn1009-6345.2023.08.011
Ma W, Gai YX (2019) Enterprise life cycle, carbon information disclosure and financing constraints––empirical evidence based on heavily polluting industries. J Ind Technol Econ 303(1):109–116. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-910X.2019.01.014
Meng X, Chen L, Gou D (2023) The impact of corporate environmental disclosure quality on financing constraints: the moderating role of internal control. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(12):33455–33474
Myers SC, Majluf NS (1984) Corporate financing and investment decisions when firms have information that investors do not have. J Financ Econ 13(2):187–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-405x(84)90023-0
Pachauri RK, Reisinger A (2007) Climate change 2007: synthesis report. Contribution of working groups I, II and III to the fourth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2007. Working Groups I, II and III to the Fourth Assessment
Pan JP, Weng RY, Pan Y (2021) The win-win effect of corporate social responsibility: evidence from targeted poverty alleviation programs. J Financ Res 7:134–153
Petrovits CM (2006) Corporate-sponsored foundations and earnings management. J Acc Econ 41(3):335–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacceco.2005.12.001
Porter ME, Kramer MR (2006) The link between competitive advantage and corporate social responsibility. Harv Bus Rev 84(12):78–92
Rahman M (2023) The virtuous circle between green product innovation and performance: the role of financial constraint and corporate brand. J Bus Res 154 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.09.001
Shen HT, Wang LY, Wan T (2011) Can corporate social report and assurance be effective signals? An analysis based on reputation theory. Audit Res 4:87–93
Shen H, Zheng S, Adams J, Jaggi B (2020) The effect stakeholders have on voluntary carbon disclosure within Chinese business organizations. Carbon Manag 11(5):455–472. https://doi.org/10.1080/17583004.2020.1805555
Shi BB, Xia XX, Jiang FX (2023) A survey of financial constraint research: An analysis based on China’s institutional context. J Central Univ Finan Econ 1:58–68. https://doi.org/10.19681/j.cnki.jcufe.2023.01.001
Siddique MA, Akhtaruzzaman M, Rashid A et al (2021) Carbon disclosure, carbon performance and financial performance: international evidence. Int Rev Financ Anal 75:1–15
Sognnaes I, Gambhir A, van de Ven DJ, Nikas A, Anger-Kraavi A, Bui H, Peters GP (2021) A multi-model analysis of long-term emissions and warming implications of current mitigation efforts. Nat Climate Chang 11(12):1055–1062
Sun XJ, Zhai SP, Yu S (2019) Can flexible tax enforcement ease corporate financing constraints? Evidence from a natural experiment on tax-paying credit rating disclosure. China Ind Econ 3:81–99. https://doi.org/10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2019.03.015
Sun Y, Wu Y, Wang ZQ (2023) Impact of green credit policy on ‘real⁃to⁃virtual’ transformation of high⁃pollution enterprises. China Popul Resour Environ 3:91–101
Tan Y, Xia F (2011) Stock price and the investment of listed companies in China: the research from the integration of earnings management and investors’ sentiment. Acc Res 8:30–3995
Wang G, Lou X, Shen J et al (2022a) Corporate carbon information disclosure and financing costs: the moderating effect of sustainable development. Sustainability 14(15):9159. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159159
Wang XM, Long YX, Xu NZ, Liu P (2022b) Research on carbon information disclosure standards of listed companies based on environmental management perspective. Financ Acc Newsl 15:11–24. https://doi.org/10.16144/j.cnki.issn1002-8072.2022.15.025
Wei J, Zuo Y (2018) The certification effect of R&D subsidies from the central and local governments: evidence from China. R&D Manag 48(5):615–626. https://doi.org/10.1111/radm.12333
Wei ZH et al (2014) Financial ecological environment and corporate financial constraints: evidence from Chinese listed firms. Acc Res 5:73–8095
Wen ZL, Ye BJ (2014) Analyses of mediating effects: the development of methods and models. Adv Psychol Sci 22(5):731–745. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1042.2014.00731
WuYY QJ, Xian Q, Chen JD (2021) The carbon emission reduction effect of China’s carbon market: from the perspective of the coordination between market mechanism and administrative intervention. China Industrial Economics 8:114–132. https://doi.org/10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2021.08.007
Xia LJ, Chen XY (2007) Marketization SOE reform strategy and endogenously determined corporate governance structure. Econ Res J 7:82–95136
Xu GQ, Wu JY (2023) Carbon information disclosure and capital market opening—a practical test based on Shanghai-Hong Kong Stock Connect and Shenzhen-Hong Kong Stock Connect. Climate Chang Res 19(2):227–237. https://doi.org/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2022.156
Xu L, Lin SY, Qian SF (2021) The slow-release effect of environmental information disclosure and green technology innovation on financing constraints. Secur Mark Her 9:23–33
Yang J, Zhang M, Liu YC (2020) How does carbon information disclosure affect debt financing cost —a study based on mediating effect of debt default risk. J Beijing Institute Technol (social Sci Ed) 22(4):28–38. https://doi.org/10.15918/j.jbitss1009-3370.2020.2236
Zeng AM, Leng HY, Wei ZH (2020) Operating cash flow transparency, market attention and stock price crash risk. Finance Trade Res 6:98–110. https://doi.org/10.19337/j.cnki.34-1093/f.2020.06.009
Zhang YM et al (2017) Accounting conservatism, financial constraints and investment efficiency. Acc Res 9:35–4096
Zhang C, Hu M, Cao YQ (2022) The impact of carbon information disclosure on financing cost under the new economic background. Friends Acc 24:26–22
Zhang XY, Shi GF, Xue JX (2023a) ESG performance and corporate investment and financing under the impact of economic policy uncertainty. Taxation Econ 248(3):75–83
Zhang Y, Wang J, Chen J et al (2023b) Does environmental regulation policy help improve business performance of manufacturing enterprises? evidence from China. Environ Dev Sustain 25:4335–4364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02245-2
Zhang JN, Sun H, Ma XY (2021) The impact of carbon information disclosure on corporate debt financing cost: a study based on the dual regulatory effects of environmental regulation and executive incentives. Chinese Certified Public Acc. https://doi.org/10.16292/j.cnki.issn1009-6345.2021.12.013
Zhao Q (2022) Review of research on carbon information disclosure. Finance Acc Res 1:47–51
Zhao Q, Zhou J (2022) Carbon information disclosure quality, peer effect and corporate financing constraints: based on the analysis of the panel data of Shanghai and Shenzhen A-share industrial enterprises from 2016 to 2020. Finance Acc Res 12:65–73
Zheng F, Shen XH, Lu R (2021) Heterogeneous influence of government subsidies on enterprise performance: based on the perspective of industry life cycle. Economic Survey 38(1):96–104. https://doi.org/10.15931/j.cnki.1006-1096.2021.01.007
Funding
This study was funded by MOE (Ministry of Education in China) Project of Humanities and Social Science (Grant No. 23YJC630126); the Talent Introduction Project of Anhui Agricultural University (Grant rc382305); the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (Grant No.1908085MG237).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. RL contributed to conceptualization, data collection, econometric model, empirical analysis and manuscript writing; KW helped in conceptualization, econometric model; SC helped in writing—review and editing; WL helped in conceptualization, manuscript review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Nicholas Apergis
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Wang, K., Chen, S. et al. Impact of corporate carbon emission reduction on financing constraints. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 115228–115245 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30309-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30309-x