Abstract
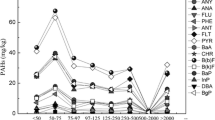
The Fenton method to remediate oil-contaminated soils has long suffered from low utilization of ·OH, resulting in waste of costs during practical application. This study investigated the efficient utilization of ·OH in oxidation using three different soils contaminated with oil (S1, S2, and S3). The mechanisms of promoting oxidation of long-chain alkanes by self-produced surfactant-like substance at the solid-liquid interface were studied. These results (take S1 as an example) showed that the average ·OH utilization rate of oxidized long-chain alkanes (Ka) at the solid-liquid interface reached 88.34 (mg/kg∙(a.u.)), which was higher than the non-solid-liquid interface stage (I: 54.02 (mg/kg∙(a.u.)), II: 67.36 (mg/kg∙(a.u.))). Meanwhile, the average oxidation of long-chain alkanes could increase unit ·OH intensity added (Kb) in the solid-liquid interface (990.00 mg/kg), which was much higher than Kb of the non-solid-liquid interface stage (I: 228.34 mg/kg, II: −1.48 mg/kg). Furthermore, there was a significant correlation between the proportion of humic acid-like in soil organic matter and the oxidation of long-chain alkanes at the solid-liquid interface. Thus, the surfactant-like substance generated during oxidation promoted the oxidation of long-chain alkanes at the solid-liquid interface. Moreover, when the surfactant-like substance had a matching degree (φ) with the long-chain alkanes (S1 0.18, S2 0.15, and S3 0.25), the efficiency of the ·OH utilization reached the peak, and the direct oxidation of long-chain alkanes at the solid-liquid interface was finally achieved (S1: 1373.00 mg/kg, S2: 1473.18 mg/kg, and S3: 1034.37 mg/kg). The appropriate surfactant-like substance agents in the construction can reduce the dosing of H2O2 and the construction costs by improving the efficient utilization of ·OH.
Graphical Abstract
Study on the mechanism promoting oxidation of long-chain alkanes by self-produced surfactant-like substance at the solid-liquid interface.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data presented in this study are available in the article.
References
Akpoveta OV, Medjor WO, Medjor EA (2018) Fenton treatment via oxidative mechanism and its kinetics on soil polluted with automatic gas oil. Petroleum 4:452–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petlm.2018.03.001
Alavi N, Mesdaghinia AR, Naddafi K et al (2014) Biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in a soil polluted sample by oil-based drilling cuttings. Soil Sediment Contam 23:586–597. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2014.847900
Chen W, Westerhoff P, Leenheer JA, Booksh K (2003) Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 37:5701–5710. https://doi.org/10.1021/es034354c
Chiou CT, Mcgroddy SE, Kile DE (1998) Partition characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on soils and sediments. Environ Sci Technol 32:264–269. https://doi.org/10.1021/es970614c
Çiner F, Gökkuş Ö (2013) Treatability of dye solutions containing disperse dyes by Fenton and Fenton-solar light oxidation processes. Clean - Soil, Air, Water 41:80–85. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201000500
Conte P, Agretto A, Spaccini R, Piccolo A (2005) Soil remediation: humic acids as natural surfactants in the washings of highly contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 135:515–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.10.006
Fontmorin JM, Burgos Castillo RC, Tang WZ, Sillanpää M (2016) Stability of 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline-N-oxide as a spin-trap for quantification of hydroxyl radicals in processes based on Fenton reaction. Water Res 99:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.04.053
Gao Y, Yuan X, Lin X et al (2015) Low-molecular-weight organic acids enhance the release of bound PAH residues in soils. Soil Tillage Res 145:103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2014.09.008
Geng W, Wei Y, Ke Y et al (2023) Unveiling molecular transformations of soil organic matter after remediation by chemical oxidation based on ESI-FT-ICR-MS analysis. ACS ES&T Eng. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsestengg.2c00423
Gökkuş Ö, Çoşkun F, Kocaoğlu M, Yıldız YŞ (2014) Determination of optimum conditions for color and COD removal of Reactive Blue 19 by Fenton oxidation process. Desalin Water Treat 52:6156–6165. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.812523
Gou Y, Ma J, Yang S, Song Y (2022) Insights into the effects of Fenton oxidation on PAH removal and indigenous bacteria in aged subsurface soil. Environ Pollut 298:118872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.118872
Huang J, Wang M, Luo S et al (2023) In situ preparation of highly graphitized N-doped biochar geopolymer composites for efficient catalytic degradation of tetracycline in water by H2O2. Environ Res 219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.115166
Huguenot D, Mousset E, van Hullebusch ED, Oturan MA (2015) Combination of surfactant enhanced soil washing and electro-Fenton process for the treatment of soils contaminated by petroleum hydrocarbons. J Environ Manage 153:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.01.037
Karthick A, Roy B, Chattopadhyay P (2019) A review on the application of chemical surfactant and surfactant foam for remediation of petroleum oil contaminated soil. J Environ Manage 243:187–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.04.092
Li D, Quan X, Zhang Y, Zhao Y (2008) Microwave-induced thermal treatment of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. Soil Sediment Contam 17:486–496. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320380802304375
Lin TC, Pan PT, Cheng SS (2010) Ex situ bioremediation of oil-contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 176:27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.10.080
Liu JW, Wei KH, Xu SW et al (2021) Surfactant-enhanced remediation of oil-contaminated soil and groundwater: a review. Sci Total Environ 756:144142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144142
Mater L, Rosa EVC, Berto J et al (2007) A simple methodology to evaluate influence of H2O2 and Fe2+ concentrations on the mineralization and biodegradability of organic compounds in water and soil contaminated with crude petroleum. J Hazard Mater 149:379–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.04.005
Oh SY, Shin DS (2014) Treatment of diesel-contaminated soil by Fenton and persulfate oxidation with zero-valent iron. Soil Sediment Contam 23:180–193. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2014.808170
Ouriache H, Arrar J, Namane A, Bentahar F (2019) Treatment of petroleum hydrocarbons contaminated soil by Fenton like oxidation. Chemosphere 232:377–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.060
Paixão IC, López-Vizcaíno R, Solano AMS et al (2020) Electrokinetic-Fenton for the remediation low hydraulic conductivity soil contaminated with petroleum. Chemosphere 248:126029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126029
Qin J, Zhang S, Zhu Y et al (2021) Calcium superphosphate as an inorganic stabilizer for modified-Fenton treatment of diesel-contaminated soil with two different exogenous iron sources. J Clean Prod 294:126255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126255
Romero A, Santos A, Cordero T et al (2011) Soil remediation by Fenton-like process: phenol removal and soil organic matter modification. Chem Eng J 170:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.03.022
Salati S, Papa G, Adani F (2011) Perspective on the use of humic acids from biomass as natural surfactants for industrial applications. Biotechnol Adv 29:913–922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.07.012
Su S, Wang W, Liu B et al (2021) Enhancing surface interactions between humic surfactants and cupric ion: DFT computations coupled with MD simulations study. J Mol Liq 324:114781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114781
Sutton NB, Grotenhuis T, Rijnaarts HH (2014) Impact of organic carbon and nutrients mobilized during chemical oxidation on subsequent bioremediation of a diesel-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 97:64–70
Tsai TT, Kao CM (2009) Treatment of petroleum-hydrocarbon contaminated soils using hydrogen peroxide oxidation catalyzed by waste basic oxygen furnace slag. J Hazard Mater 170:466–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.04.073
Urdiales C, Sandoval MP, Escudey M et al (2018) Surfactant properties of humic acids extracted from volcanic soils and their applicability in mineral flotation processes. J Environ Manage 227:117–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.08.072
Usman M, Hanna K, Faure P (2018) Remediation of oil-contaminated harbor sediments by chemical oxidation. Sci Total Environ 634:1100–1107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.092
Watts RJ (1992) Hydrogen peroxide for physicochemically degrading petroleum-contaminated soils. Remediat J 2:413–425. https://doi.org/10.1002/rem.3440020407
Watts RJ, Stanton PC (1999) Mineralization of sorbed and NAPL-phase hexadecane by catalyzed hydrogen peroxide. Water Res 33:1405–1414. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00343-1
Xia C, Liu Q, Zhao L et al (2022) Enhanced degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in soil by FeS@BC activated persulfate and its mechanism. Sep Purif Technol 282:120060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.120060
Xu J, Fan X, Huang F, Li X (2017a) Iron bound to soil organic matter catalyzes H2O2 to oxidize crude oil in soil. J Hazard Mater 322:516–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.10.018
Xu J, Li L, Guo Y et al (2018) Novel iron bound to soil organic matter catalyzes H2O2 to oxidize long-chain alkanes effectively in soil. Chem Eng J 339:566–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.127
Xu J, Li X, Huang T (2017b) Abatement of sorbed crude oil by heterogeneous fenton process using a contaminated soil pre-impregnated with dissolved Fe(II) and humic acid. Soil Sediment Contam 26:195–209. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2017.1269721
Xu J, Pancras T, Grotenhuis T (2011a) Chemical oxidation of cable insulating oil contaminated soil. Chemosphere 84:272–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.03.044
Xu J, Wang J, Wang C et al (2020) Effective oxidation of crude oil in soils by consuming less hydroxyl radical with target iron. Chem Eng J 380:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122414
Xu J, Xin L, Huang T, Chang K (2011b) Enhanced bioremediation of oil contaminated soil by graded modified Fenton oxidation. J Environ Sci 23:1873–1879. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60654-7
Xu X, Li X, Li X, Li H (2009) Degradation of melatonin by UV, UV/H2O2, Fe2+/H2O2 and UV/Fe2+/H2O2 processes. Sep Purif Technol 68:261–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2009.05.013
Yang J, Zhang X, Tang J et al (2022) Removal efficiency and mechanism of refractory organic matter from landfill leachate MBR effluent by the MoS2-enhanced Fe0/H2O2 system. J Environ Chem Eng 10:108391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108391
Zhao X, Liu W, Fu J et al (2016) Dispersion, sorption and photodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in dispersant-seawater-sediment systems. Mar Pollut Bull 109:526–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.04.064
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51778524) and the Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi (No. 2019ZDLSF06-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study conception and design. Jinlan Xu: methodology, data curation, validation, funding acquisition, and supervision. Fengsen Li: methodology, data curation, writing-original draft, and validation. Shengyang Luo: data curation, formal analysis, supervision, and methodology. Qihang Shi: data curation and investigation. Zezhuang Cao: data curation. Lu Liu: data curation. Shujun Xue: data curation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ricardo A. Torres-Palma
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 2150 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Li, F., Luo, S. et al. Study on the mechanism promoting oxidation of long-chain alkanes by self-produced surfactant-like substance at the solid-liquid interface. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 117676–117687 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29991-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29991-8