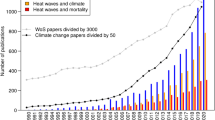
Abstract
Adequate water, electricity, and food are essential for sustainable development. Regional conflicts intensified by global water, energy, and food shortages necessitate a rethinking of the security and interdependence of these resources. However, most earlier scholars concentrated on the subsystems of the water-energy-food nexus (WEF nexus), lacking holistic studies. Therefore, to understand the history and current state of research on the WEF nexus and predict future research directions, this study analyzed 1313 journal articles from the Web of Science database between 2007 and 2022 using the bibliometric analysis and Citespace software. The findings in this study indicate that (1) the progress of the WEF nexus research can be classified into three stages between 2007 and 2022: the early stage (2007–2010), the fast-developing stage (2011–2015), and the steady and in-depth stage (2016–2022). The WEF nexus has become a hot zone for academic research. (2) Map of the network of countries, institutions, and author collaborations implies tight academic collaboration among countries, institutions, and writers. (3) Climate change, integrated WEF nexus, sustainable development, and security are research hotspots in this field. Meanwhile, energy security, circular economy, and resource allocation are advanced subjects in this field. These key findings can provide managers and researchers with valuable information for decision-making.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made available on the request.
References
Ahmad S, Jia H, Chen Z et al (2020) Water-energy nexus and energy efficiency: a systematic analysis of urban water systems. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 134:110381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.110381
Ahmadzadeh H, Morid S, Delavar M et al (2016) Using the SWAT model to assess the impacts of changing irrigation from surface to pressurized systems on water productivity and water saving in the Zarrineh Rud catchment. Agric Water Manag 175:15–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2015.10.026
AI-Saidi M, Elagib NA (2017) Towards understanding the integrative approach of the water, energy and food nexus. Sci Total Environ 574:1131–1139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.046
Al-Ansari T, Korre A, Nie Z et al (2015) Development of a life cycle assessment tool for the assessment of food production systems within the energy, water and food nexus. Sustainable Production and Consumption 2:52–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2015.07.005
Albrecht TR, Crootof A, Scott CA (2018) The water-energy-food nexus: a systematic review of methods for nexus assessment. Environ Res Lett 13(4):043002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aaa9c6
Allan JA (2003) Virtual water-the water, food, and trade nexus. Useful concept or misleading metaphor? Water International 28(1):106–113. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508060.2003.9724812
Allouche J, Middleton C, Gyawali D (2019) The water-energy-food nexus: power, politics, and justice. Routledge, Abingdon, Oxon
Al-Thani NA, Govindan R, Al-Ansari T (2020) Maximising nutritional benefits within the energy, water and food nexus. J Clean Prod 266:121877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121877
Araya A, Hoogenboom G, Luedeling E et al (2015) Assessment of maize growth and yield using crop models under present and future climate in southwestern Ethiopia. Agric for Meteorol 214:252–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2015.08.259
Arthur M, Liu G, Hao Y et al (2019) Urban food-energy-water nexus indicators: a review. Resour Conserv Recycl 151:104481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104481
Aviso KB, Tan RR, Culaba AB et al (2011) Fuzzy input–output model for optimizing eco-industrial supply chains under water footprint constraints. J Clean Prod 19(2–3):187–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2010.09.003
Bazilian M, Rogner H, Howells M et al (2011) Considering the energy, water and food nexus: towards an integrated modelling approach. Energy Policy 39(12):7896–7906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2011.09.039
Bhaduri A, Ringler C, Dombrowski I et al (2015) Sustainability in the water–energy–food nexus. Water International 40(5–6):723–732. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508060.2015.1096110
Biggs EM, Bruce E, Boruff B et al (2015) Sustainable development and the water–energy–food nexus: a perspective on livelihoods. Environ Sci Policy 54:389–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2015.08.002
Borge-Diez D, García-Moya FJ, Rosales-Asensio E (2022) Water energy food nexus analysis and management tools: a review. Energies 15(3):1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15031146
Brouwer F, Anzaldi G, Laspidou C, Munaretto C et al (2018) Commentary to SEI report ‘Where is the added value? A review of the water-energy-food nexus literature’. Work Package Number: WP7
Cai X, Wallington K, Shafiee-Jood M et al (2018) Understanding and managing the food-energy-water nexus–opportunities for water resources research. Adv Water Resour 111:259–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2017.11.014
Chen C (2006) CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol 57(3):359–377. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.20317
Chen S, Chen B (2016) Urban energy–water nexus: a network perspective. Appl Energy 184:905–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.03.042
Chenu K, Porter JR, Martre P et al (2017) Contribution of crop models to adaptation in wheat. Trends Plant Sci 22(6):472–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2017.02.003
Corona-López E, Román-Gutiérrez AD, Otazo-Sánchez EM et al (2021) Water-Food Nexus assessment in agriculture: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(9):4983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094983
Dai J, Wu S, Han G et al (2018) Water-energy nexus: a review of methods and tools for macro-assessment. Appl Energy 210:393–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.08.243
Deng P, Chen J, Chen D et al (2017) The evolutionary characteristics analysis of the coupling and coordination among water, energy and food: take Jiangsu Province as an example. J Water Res Water Eng 28(6):232–238
D’Odorico P, Davis KF, Rosa L et al (2018) The global food-energy-water nexus. Rev Geophys 56(3):456–531. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017RG000591
El-Gafy I (2017) Water–food–energy nexus index: analysis of water–energy–food nexus of crop’s production system applying the indicators approach. Appl Water Sci 7(6):2857–2868. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-017-0551-3
Endo A, Tsurita I, Burnett K et al (2017) A review of the current state of research on the water, energy, and food nexus. J Hydrol: Reg Stud 11:20–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2015.11.010
Fang D, Chen B (2017) Linkage analysis for the water–energy nexus of city. Appl Energy 189:770–779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.04.020
Feng K, Siu YL, Guan D et al (2012) Assessing regional virtual water flows and water footprints in the Yellow River Basin, China: a consumption based approach. Appl Geogr 32(2):691–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2011.08.004
Gain AK, Giupponi C, Benson D (2015) The water–energy–food (WEF) security nexus: the policy perspective of Bangladesh. Water International 40(5–6):895–910. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508060.2015.1087616
Garcia DJ, You F (2016) The water-energy-food nexus and process systems engineering: a new focus. Comput Chem Eng 91:49–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2016.03.003
Giupponi C, Gain AK (2017) Integrated spatial assessment of the water, energy and food dimensions of the sustainable development goals. Reg Environ Change 17(7):1881–1893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-016-0998-z
Gleick P (1994) Water and energy. Annu Rev Energy Environ 19:267–299
Gu A, Teng F, Lv Z (2016) Exploring the nexus between water saving and energy conservation: Insights from industry sector during the 12th Five-Year Plan period in China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 59:28–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.285
Hachaichi M, Egieya J (2022) Water-food-energy nexus in global cities: solving urban challenging interdependencies together. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1956052/v1
Han X, Hua E, Engel BA et al (2022) Understanding implications of climate change and socio-economic development for the water-energy-food nexus: a meta-regression analysis. Agric Water Manag 269:107693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2022.107693
Hellegers P et al (2008) Interactions between water, energy, food and environment: evolving perspectives and policy issues. Water Policy 10(S1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.2166/wp.2008.048
Hightower M, Pierce SA (2008) The energy challenge. Nature 452(7185):285–286. https://doi.org/10.1038/452285a
Hoff, H., 2011. Understanding the nexus. Background paper for the Bonn 2011 Conference: The Water, Energy and Food Security Nexus. Stockholm Environment Institute (SEI). Stockholm, Sweden.
Holtermann T, Nandalal KDW (2015) The water–energy–food nexus and climate change adaptation. Change Adapt Socio-Ecological Syst 2(1). https://doi.org/10.1515/cass-2015-0022
Howells M, Hermann S, Welsch M et al (2013) Integrated analysis of climate change, land-use, energy and water strategies. Nat Clim Chang 3(7):621–626. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1789
Hussey K, Pittock J, (2012) The energy–water nexus: managing the links between energy and water for a sustainable future. Ecology and society 17(1). https://www.jstor.org/stable/26268988
Ingram J (2011) A food systems approach to researching food security and its interactions with global environmental change. Food Security 3(4):417–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-011-0149-9
Johnson JA, Runge CF, Senauer B et al (2014) Global agriculture and carbon trade-offs. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(34):12342–12347. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1412835111
Keairns DL, Darton RC, Irabien A (2016) The energy-water-food nexus. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng 7:239–262. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-080615-033539
Kurian M (2017) The water-energy-food nexus: trade-offs, thresholds and transdisciplinary approaches to sustainable development. Environ Sci Policy 68:97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2016.11.006
Lee M, Keller AA, Chiang PC et al (2017) Water-energy nexus for urban water systems: a comparative review on energy intensity and environmental impacts in relation to global water risks. Appl Energy 205:589–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.08.002
Li X, Liu J, Zheng C et al (2016) Energy for water utilization in China and policy implications for integrated planning. International Journal of Water Resource Development 32:477–494. https://doi.org/10.1080/07900627.2015.1133403
Li M, Fu Q, Singh VP et al (2019) An optimal modelling approach for managing agricultural water-energy-food nexus under uncertainty. Sci Total Environ 651:1416–1434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.291
Li R, Wang Q, Liu Y et al (2021) Per-capita carbon emissions in 147 countries: the effect of economic, energy, social, and trade structural changes. Sust Prod Consum 27:1149–1164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2021.02.031
Liu J, Mao G, Hoekstra AY et al (2018) Managing the energy-water-food nexus for sustainable development. Appl Energy 210(15):377–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.10.064
Mannan M, Al-Ansari T, Mackey HR et al (2018) Quantifying the energy, water and food nexus: a review of the latest developments based on life-cycle assessment. J Clean Prod 193:300–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.050
Martinez-Hernandez E, Leach M, Yang A (2017) Understanding water-energy-food and ecosystem interactions using the nexus simulation tool NexSym. Appl Energy 206(15):1009–1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.09.022
Medina-Santana AA, Flores-Tlacuahuac A, Cárdenas-Barrón LE et al (2020) Optimal design of the water-energy-food nexus for rural communities. Comput Chem Eng 143:107120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2020.107120
Mei H, Li YP, Suo C et al (2020) Analyzing the impact of climate change on energy-economy-carbon nexus system in China. Appl Energy 262:114568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114568
Miller-Robbie L, Ramaswami A, Amerasinghe P (2017) Wastewater treatment and reuse in urban agriculture: exploring the food, energy, water, and health nexus in Hyderabad. India Environ Res Letters 12(7):075005. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aa6bfe
Mimi ZA, Jamous SA (2010) Climate change and agricultural water demand: impacts and adaptations. African J Environ Sci Technol 4(4). http://www.academicjournals.org/AJEST
Mohtar RH, Daher B (2012) Water, energy, and food: the ultimate nexus. Encyclopedia of agricultural, food, and biological engineering. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group
Molajou A, Afshar A, Khosravi M et al (2021). A new paradigm of water, food, and energy nexus. Environ Sci Pollut Res1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13034-1
Namany S, Al-Ansari T (2021) Energy, water, food nexus decision-making for sustainable food security. The Water–Energy–Food Nexus 191–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0239-9_7
Niu Y, Xie G, Xiao Y et al (2021) Spatiotemporal patterns and determinants of grain self-sufficiency in China. Foods 10(4):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040747
Opejin AK, Aggarwal RM, White DD et al (2020) A bibliometric analysis of food-energy-water nexus literature. Sustainability 12(3):1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12031112
Owen A, Scott K, Barrett J (2018) Identifying critical supply chains and final products: an input-output approach to exploring the energy-water-food nexus. Appl Energy 210:632–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.09.069
Pacetti T, Lombardi L, Federici G (2015) Water–energy nexus: a case of biogas production from energy crops evaluated by water footprint and life cycle assessment (LCA) methods. J Clean Prod 101:278–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.03.084
Pellegrini P, Fernández RJ (2018) Crop intensification, land use, and on-farm energy-use efficiency during the worldwide spread of the green revolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci 115(10):2335–2340. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.171707211
Piao S, Ciais P, Huang Y et al (2010) The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 467(7311):43–51. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09364
Ramaswami A, Boyer D, Nagpure AS et al (2017) An urban systems framework to assess the trans-boundary food-energy-water nexus: implementation in Delhi. India Environ Res Letters 12(2):025008. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aa5556
Ramos HM, Mello M, De PK (2010) Clean power in water supply systems as a sustainable solution: from planning to practical implementation. Water Supply 10(1):39–49. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2010.720
Rasul G, Sharma B (2016) The nexus approach to water–energy–food security: an option for adaptation to climate change. Climate Policy 16(6):682–702. https://doi.org/10.1080/14693062.2015.1029865
Rockström J, Steffen W, Noone K et al (2009) A safe operating space for humanity. Nature 461(7263):472–475. https://doi.org/10.1038/461472a
Rulli MC, Bellomi D, Cazzoli A et al (2016) The water-land-food nexus of first-generation biofuels. Sci Rep 6(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22521
Salem HS, Pudza MY, Yihdego Y (2022) Water strategies and water–food nexus: challenges and opportunities towards sustainable development in various regions of the world. Sustain Water Res Manag 8(4):1–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-022-00676-3
Salmoral G, Yan X (2018) Food-energy-water nexus: a life cycle analysis on virtual water and embodied energy in food consumption in the Tamar catchment, UK. Resour Conserv Recycl 133:320–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.01.018
Sanders KT, Masri SF (2016) The energy-water agriculture nexus: the past, present and future of holistic resource management via remote sensing technologies. J Clean Prod 117:73–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.01.034
SE4All. 2016. The sustainable energy for all initiative. Ending energy poverty.
Shang Y, Hei P, Lu S et al (2018) China’s energy-water nexus: assessing water conservation synergies of the total coal consumption cap strategy until 2050. Appl Energy 210:643–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.11.008
She W, Wu Y, Huang H et al (2017) Integrative analysis of carbon structure and carbon sink function for major crop production in China’s typical agriculture regions. J Clean Prod 162:702–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.05.108
Shrestha AB, Aryal R (2011) Climate change in Nepal and its impact on Himalayan glaciers. Reg Environ Change 11(1):65–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-010-0174-9
Siciliano G, Rulli MC, D’odorico P (2017) European large-scale farmland investments and the land-water-energy-food nexus. Adv Water Resour 110:579–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2017.08.012
Simpson GB, Jewitt GPW (2019) The development of the water-energy-food nexus as a framework for achieving resource security: a review. Front Environ Sci 7:8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2019.00008
Sims REH (2011) “Energy-smart” food for people and climate. In: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO).
Smajgl A, Ward J, Pluschke L (2016) The water–food–energy nexus–realising a new paradigm. J Hydrol 533:533–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.12.033
Soleimanian E, Afshar A, Molajou A (2022) A review on water simulation models for the WEF nexus: development perspective. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(53):79769–79785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19849-w
Stevens L, Gallagher M (2015) The energy–water–food nexus at decentralized scales: synergies, trade-offs and how to mANAGE THEM. Practical Action Publishing, Rugby
Tortorella MM, Di Leo S, Cosmi C et al (2020) A methodological integrated approach to analyse climate change effects in agri-food sector: the TIMES Water-Energy-Food Module. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(21):7703. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17217703
UNFCC COP 27 (The United Nations Climate Change Conference). 2022. Amplifying our climate justice stories on a world stage. https://www.dscej.org/cop27
Vora N, Shah A, Bilec MM et al (2017) Food–energy–water nexus: quantifying embodied energy and GHG emissions from irrigation through virtual water transfers in food trade. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(3):2119–2128. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02122
Wada Y, Van Beek LPH, Wanders N et al (2013) Human water consumption intensifies hydrological drought worldwide. Environ Res Lett 8(3):034036. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/8/3/034036
Walker RV, Beck MB, Hall JW et al (2014) The energy-water-food nexus: strategic analysis of technologies for transforming the urban metabolism. J Environ Manage 141:104–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.01.054
Wang XC, Klemeš JJ, Long X et al (2020) Measuring the environmental performance of the EU27 from the water-energy-carbon nexus perspective. J Clean Prod 265:121832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121832
Wang X, Müller C, Elliot J et al (2021) Global irrigation contribution to wheat and maize yield. Nat Commun 12(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21498-5
Waughray D (2011) Water security, the water-food-energy-climate nexus: the World Economic Forum Water Initiative. Island Press, Washington, DC
WEF, Ed., 2011. Water security: water–food–energy–climate nexus. The World Economic Forum Water Initiative. Island Press, Washington D.C., USA.
Weitz N, Strambo C, Kemp-Benedict E et al (2017) Closing the governance gaps in the water-energy-food nexus: Insights from integrative governance. Glob Environ Chang 45:165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2017.06.006
West TO, Marland G (2002) A synthesis of carbon sequestration, carbon emissions, and net carbon flux in agriculture: comparing tillage practices in the United States. Agr Ecosyst Environ 91(1–3):217–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8809(01)00233-X
White DJ, Hubacek K, Feng K et al (2018) The water-energy-food nexus in East Asia: a tele-connected value chain analysis using inter-regional input-output analysis. Appl Energy 210:550–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.05.159
Yan X, Fang L, Mu L (2020) How does the water-energy-food nexus work in developing countries? An empirical study of China. Sci Total Environ 716:134791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134791
Yang YCE, Ringler C, Brown C et al (2016) Modeling the agricultural water–energy–food nexus in the Indus River Basin, Pakistan. J Water Resour Plan Manag 142(12):04016062. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000710
Yoon PR, Lee SH, Choi JY et al (2022) Analysis of climate change impact on resource intensity and carbon emissions in protected farming systems using water-energy-food-carbon nexus. Resour Conserv Recycl 184:106394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106394
Yu L, Xiao Y, Zeng XT et al (2020) Planning water-energy-food nexus system management under multi-level and uncertainty. J Clean Prod 251:119658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119658
Zhang C, Chen X, Li Y et al (2018) Water-energy-food nexus: concepts, questions and methodologies. J Clean Prod 195:625–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.194
Zhang P, Zhang L, Chang Y et al (2019) Food-energy-water (FEW) nexus for urban sustainability: a comprehensive review. Resour Conserv Recycl 142:215–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.11.018
Zhang L, Liu Y, Zhan H et al (2021) Influence of solar activity and EI Niño-Southern Oscillation on precipitation extremes, streamflow variability and flooding events in an arid-semiarid region of China. J Hydrol 601:126630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126630
Zhang X, Guo P, Zhang F et al (2021) Optimal irrigation water allocation in Hetao Irrigation District considering decision makers’ preference under uncertainties. Agric Water Manag 246:106670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106670
Zhou Y, Li H, Wang K et al (2016) China’s energy-water nexus: spillover effects of energy and water policy. Glob Environ Chang 40:92–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2016.07.003
Zhu J, Kang S, Zhao W et al (2020) A bibliometric analysis of food–energy–water nexus: progress and prospects. Land 9(12):504. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9120504
Zscheischler J, Martius O, Westra S et al (2020) A typology of compound weather and climate events. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment 1(7):333–347. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-020-0060-z
Funding
This work was supported by the Chengdu University of Technology Postgraduate Innovative Cultivation Program (Grant numbers [CDUT2022BJCX012]) and the Philosophy and Social Science Research Fund of Chengdu University of Technology (Grant numbers [ZDJS202204]).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yangxi Lv: conceptualization, methodology, validation, writing — original draft, funding acquisition. Mingkang Yuan: data curation, supervision, writing — review and editing, funding acquisition. Xiaofeng Zhou: visualization, software, validation. Yuanmin Wang: data curation, editing and typesetting. Xiaobing Qu: software, validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The experimental scheme was formulated by the water resources allocation guidelines of Dujiangyan Management Committee and obtained personal written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Eyup Dogan
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• The WEF nexus has received increasing attention.
• The relationships of WEF nexus subsystems have been thoroughly investigated.
• The progress of WEF nexus research is evaluated using a distinctive framework of bibliometric analysis in this article.
• Future research challenges for the WEF nexus are identified in this paper, with climate change and carbon emissions as external factors.
• The findings in this study can provide a research perspective for managers and researchers.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, Y., Yuan, M., Zhou, X. et al. The water-energy-food nexus: a systematic bibliometric analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 121354–121369 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29863-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29863-1