Abstract
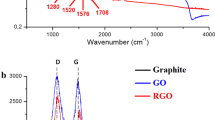
The pace of water contamination is increasing daily due to expanding industrialisation. Finding a feasible solution for effectively remediating various organic and inorganic pollutants from large water bodies remains challenging. However, a nano-engineered advanced hybrid material could provide a practical solution for the efficient removal of such pollutants. This work has reported the development of a highly efficient and reusable absorbent comprising a porous polyurethane (PU) and reduced graphene oxide (rGO) nanosheets (rGOPU) for the removal of different organic oils (industrial oil, engine oil and mustard oil), dyes (MB, MO, RB, EY and MV) and heavy metals (Pb(II), Cr(VI), Cd(II), Co(II) and As(V)). The structure, morphology and properties of the rGOPU hybrid absorbents were analysed by using Raman spectroscopy, field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and Brunner-Emitte-Teller (BET) analysis. The rGOPU possessed both superhydrophobicity and superoleophilicity with water and oil contact angles of about 164° and 0°, respectively. The prepared rGOPU has demonstrated an excellent oil-water separation ability (up to 99%), heavy metals removal efficiency (more than 75%), toxic dye adsorption (more than 55%), excellent recyclability (> 500 times for oils), extraordinary mechanical stability (90% compressible for > 1000 cycles) and high recoverability. This work presents the first demonstration of rGOPU’s multifunctional absorbent capacity in large-scale wastewater treatment for effectively removing a wide variety of organic and inorganic contaminants.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirmed that the data supporting the findings are available within the article. The underlying data for this work can be available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- GO:
-
Graphene oxide
- rGO:
-
Reduced graphene oxide
- PU:
-
Polyurethane
- rGOPU:
-
Reduced graphene oxide-coated polyurethane
- MB:
-
Methylene blue
- MO:
-
Methyl orange
- RB:
-
Rhodamine B
- EY:
-
Eosin yellow
- MV:
-
Methyl violet
- Pb(II):
-
Lead
- Cr(VI):
-
Chromium
- Cd(II):
-
Cadmium
- Co(II):
-
Cobalt
- As(V):
-
Arsenic
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- FESEM:
-
Field emission scanning electron microscopy
- TGA:
-
Thermogravimetric analysis
- BET:
-
Brunner-Emitte-Teller
- q e :
-
Equilibrium adsorption capacity
- q t :
-
Adsorption capacity at time t
- q m :
-
Maximum adsorption capacity
- C o :
-
Initial concentration of pollutant particles
- C e :
-
Equilibrium concentration of pollutant particles
- C t :
-
Concentration of pollutant particles at a certain time t
- V :
-
Volume of the pollutant solution
- w :
-
Weight of the rGOPU sponge
- k 1 :
-
Pseudo-first-order rate constants
- k 2 :
-
Pseudo-second-order rate constants
- K id :
-
Rate constant of intraparticle diffusion
- K L :
-
Langmuir constant
- K F :
-
Freundlich constants
- K T :
-
Equilibrium binding constant
- R :
-
Universal gas constant (8.314 J/K mol)
- E :
-
Mean sorption-free energy
- CNT:
-
Carbon nanotube
- PDMS:
-
Polydimethylsiloxane
- DI:
-
Deionised
References
Ajayi TR, Torto N, Tchokossa P, Akinlua A (2009) Natural radioactivity and trace metals in crude oils: implication for health. Environ Geochem Health 31(1):61–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-008-9155-z
Alam SN, Sharma N, Kumar L (2017) Synthesis of graphene oxide (GO) by modified hummers method and its thermal reduction to obtain reduced graphene oxide (RGO)*. Graphene 06(01):1–18. https://doi.org/10.4236/graphene.2017.61001
Alamgholiloo H, Pesyan NN, Mohammadi R, Rostamnia S, Shokouhimehr M (2021) Synergistic advanced oxidation process for the fast degradation of ciprofloxacin antibiotics using a GO/CuMOF-magnetic ternary nanocomposite. J Environ Chem Eng 9(4):105486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105486
Alinejad M, Henry C, Nikafshar S, Gondaliya A, Bagheri S, Chen N, Singh S, Hodge D, Nejad M (2019) Lignin-based polyurethanes: opportunities for bio-based foams, elastomers, coatings and adhesives. Polymers 11(7):1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11071202
Ayawei N, Ebelegi AN, Wankasi D (2017) Modelling and interpretation of adsorption isotherms. J Chem 2017:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3039817
Aydin O, Gulsah, Sonmez HB (2015) Hydrophobic Poly(Alkoxysilane) organogels as sorbent material for oil spill cleanup. Mar Pollut Bull 96(1–2):155–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.05.033
Bera M, Chandravati PG, Maji PK (2018) Facile one-pot synthesis of graphene oxide by sonication assisted mechanochemical approach and its surface chemistry. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 18(2):902–912. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2018.14306
Bi H, Xie X, Yin K, Zhou Y, Wan S, He L, Xu F, Banhart F, Sun L, Ruoff RS (2012) Spongy graphene as a highly efficient and recyclable sorbent for oils and organic solvents. Adv Funct Mater 22(21):4421–4425. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201200888
Briffa J, Sinagra E, Blundell R (2020) Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 6(9):e04691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04691
Campos NF, Barbosa CMBM, Rodríguez-Díaz JM, Duarte MMMB (2018) Removal of naphthenic acids using activated charcoal: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Adsorpt Sci Technol 36(7–8):1405–1421. https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617418773844
Cao N, Yang B, Barras A, Szunerits S, Boukherroub R (2017) Polyurethane sponge functionalized with superhydrophobic nanodiamond particles for efficient oil/water separation. Chem Eng J 307:319–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.105
Cheng, Chong (Sage), Deng J, Lei B, He A, Zhang X, Ma L, Li S, Zhao C (2013) Toward 3D graphene oxide gels based adsorbents for high-efficient water treatment via the promotion of biopolymers. J Hazard Mater 263:467–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.09.065
de Araujo B, Maria C, do Nascimento GFO, da Costa GRB, da Silva KS, Baptisttella AMS, Ghislandi MG, da Motta Sobrinho MA (2019) Adsorptive removal of dye from real textile wastewater using graphene oxide produced via modifications of hummers method. Chem Eng Commun 206(11):1375–1387. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2018.1534232
de Souza G, Fernando JAM, Rodrigues CHM, Pinto JC (2010) A magnetic composite for cleaning of oil spills on water. Macromol Mater Eng 295(10):942–948. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.201000090
Duman O, Diker CÖ, Tunç S (2021) Development of highly hydrophobic and superoleophilic fluoro organothiol-coated carbonized melamine sponge/RGO composite absorbent material for the efficient and selective absorption of oily substances from aqueous environments. J Environ Chem Eng 9(2):105093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105093
Ejeromedoghene O, Oderinde O, Kang M, Agbedor S, Faruwa AR, Olukowi OM, Guodong F, Daramola MO (2020) Multifunctional metal-organic frameworks in oil spills and associated organic pollutant remediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(34):42346–42368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10322-0
Ekperusi AO, Onyena AP, Akpudo MY, Peter CC, Akpoduado CO and Ekperusi OH (2019) August. In-situ burning as an oil spill control measure and its effect on the environment. SPE Nigeria Annual International Conference and Exhibition, Lagos, Nigeria. https://doi.org/10.2118/198777-MS
Fu F, Wang Q (2011) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J Environ Manage 92(3):407–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.11.011
Gomes BFML, de Araújo CMB, do Nascimento BF, de Luna Freire EMP, Sobrinho MADM, Carvalho MN (2022) Synthesis and application of graphene oxide as a nanoadsorbent to remove Cd (II) and Pb (II) from water: adsorption equilibrium, kinetics, and regeneration. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(12):17358–17372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16943-3
Gros J, Nabi D, Würz B, Wick LY, Brussaard CPD, Huisman J, van der Meer JR, Reddy CM, Arey JS (2014) First day of an oil spill on the open sea: early mass transfers of hydrocarbons to air and water. Environ Sci Technol 48(16):9400–9411. https://doi.org/10.1021/es502437e
Habte AT, Ayele DW (2019) Synthesis and characterization of reduced graphene oxide (RGO) started from graphene oxide (GO) using the tour method with different parameters. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2019:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5058163
Hameed BH, Ahmad AA, Aziz N (2007) Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics of acid dye adsorption on activated palm ash. Chem Eng J 133(1–3):195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.01.032
Hoang AT, Chau MQ (2018) A mini review of using oleophilics skimmers for oil spill recovery. J Mech Eng Res Dev 41(2):92–96. https://doi.org/10.26480/jmerd.02.2018.92.96
Huang L, Zhu P, Li G, Lu D(D), Sun R, Wong C (2014) Core–shell SiO 2 @RGO hybrids for epoxy composites with low percolation threshold and enhanced thermo-mechanical properties. J Mater Chem A 2(43):18246–18255. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA03702B
Jiang L, Fan Z (2014) Design of advanced porous graphene materials: from graphene nanomesh to 3D architectures. Nanoscale 6(4):1922–1945. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR04555B
Karimi-Maleh H, Darabi R, Karimi F, Karaman C, Shahidi SA, Zare N, Baghayeri M, Li F, Rostamnia S, Rouhi J, Rajendran S (2023) State-of-art advances on removal, degradation and electrochemical monitoring of 4-aminophenol pollutants in real samples: a review. Environ Res 222:115338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115338
Kartick B, Srivastava SK, Srivastava I (2013) Green synthesis of graphene. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 13(6):4320–4324. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2013.7461
Kingston PF (2002) Long-term environmental impact of oil spills. Spill Sci Technol Bull 7(1–2):53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1353-2561(02)00051-8
Kishor R, Bharagava RN, Saxena G (2018) ‘Industrial wastewaters’. Pp. 1–25 in Recent Advances in environmental management. In: Boca Raton, Florida : A CRC title, part of the Taylor & Francis imprint, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group, the academic division of T&F Informa plc, 2019, 1st edn. CRC Press
Larramendy ML, Soloneski S (eds) (2015) Emerging pollutants in the environment - current and further implications. https://doi.org/10.5772/60455
Liu Q (2020) Pollution and treatment of dye waste-water. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci 514(5):052001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/514/5/052001
Liu Y, Ma J, Wu T, Wang X, Huang G, Yu L, Qiu H, Li Y, Wang W, Gao J (2013) Cost-effective reduced graphene oxide-coated polyurethane sponge as a highly efficient and reusable oil-absorbent. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(20):10018–10026. https://doi.org/10.1021/am4024252
Loryuenyong V, Totepvimarn K, Eimburanapravat P, Boonchompoo W, Buasri A (2013) Preparation and characterization of reduced graphene oxide sheets via water-based exfoliation and reduction methods. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2013:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/923403
Marcano DC, Kosynkin DV, Berlin JM, Sinitskii A, Sun Z, Slesarev A, Alemany LB, Lu W, Tour JM (2010) Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 4(8):4806–4814. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn1006368
Mohtasham H, Rostami M, Gholipour B, Sorouri AM, Ehrlich H, Ganjali MR, Rostamnia S, Rahimi-Nasrabadi M, Salimi A, Luque R (2023) Nano-architecture of MOF (ZIF-67)-based Co3O4 NPs@N-doped porous carbon polyhedral nanocomposites for oxidative degradation of antibiotic sulfamethoxazole from wastewater. Chemosphere 310:136625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136625
Narayana MV, Narayana Jammalamadaka S (2016) Tuning optical properties of graphene oxide under compressive strain using wet ball milling method. Graphene 05(02):73–80. https://doi.org/10.4236/graphene.2016.52008
Niu Z, Liu L, Zhang L, Chen X (2014) Porous graphene materials for water remediation. Small 10(17):3434–3441. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201400128
Ordinioha B, Brisibe S (2013) The human health implications of crude oil spills in the Niger Delta, Nigeria: an interpretation of published studies. Niger J Med 54(1):10. https://doi.org/10.4103/0300-1652.108887
Osuji I, Achugasim O (2010) Trace metals and volatile aromatic hydrocarbon content of Ukpeliede-I oil spillage site, Niger Delta, Nigeria. J Appl SCI Environ Manag 14(2). https://doi.org/10.4314/jasem.v14i2.57826
Othumpangat S, Fedan J (2022) Oil spills. Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-824315-2.00166-4
Pavlov V, de Aguiar VCM, Hole LR, Pongrácz E (2021) A 30-year probability map for oil spill trajectories in the barents sea to assess potential environmental and socio-economic threats. Resources 11(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources11010001
Pete AJ, Bharti B, Benton MG (2021) Nano-enhanced bioremediation for oil spills: a review. ACS ES&T Eng 1(6):928–946. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsestengg.0c00217
Pholosi A, Naidoo EB, Ofomaja AE (2020) Intraparticle diffusion of Cr(VI) through biomass and magnetite coated biomass: a comparative kinetic and diffusion study. S Afr J Chem Eng 32:39–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajce.2020.01.005
Prince RC (2015) Oil spill dispersants: boon or bane? Environ Sci Technol 49(11):6376–6384. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00961
Radwan EH, Saber MAK, Saber MEK, Fahmy GH (2017) The impact of some organic and inorganic pollutants on fresh water (Rashid, River Nile), Egypt. J Adv Biol 10(2):2133–2145. https://doi.org/10.24297/jab.v10i2.6481
Rasouli S, Rezaei N, Hamedi H, Zendehboudi S, Duan X (2021) Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic membranes for oil-water separation application: a comprehensive review. Mater Des 204:109599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2021.109599
Reynolds JG, Coronado PR, Hrubesh LW (2001) Hydrophobic aerogels for oil-spill clean up – synthesis and characterization. J Non-Cryst Solids 292(1–3):127–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3093(01)00882-1
Saha B, Baek S, Lee J (2017) Highly sensitive bendable and foldable paper sensors based on reduced graphene oxide. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(5):4658–4666. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b10484
Saha B, Purwar P, Lee J, Saha S (2018) Magnetic nanoparticle encapsulation for the manipulation of bacterial movement and spontaneous detection by reduced graphene oxide. Adv Biosyst 2(10):1800095. https://doi.org/10.1002/adbi.201800095
Sahu PS, Verma RP, Dabhade AH, Tewari C, Sahoo NG, Saha B (2023) A novel, efficient and economical alternative for the removal of toxic organic, inorganic and pathogenic water pollutants using GO-modified PU granular composite. Environ Pollut 328:121201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121201
Sahu PS, Verma RP, Saha B (2022a) Synthesis of magnetite-graphene nanocomposite for wastewater treatment. Mater Today: Proc 62:6042–6048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.04.999
Sahu PS, Verma RP, Tewari C, Sahoo NG, Saha B (2022b) Environmental application of amine functionalised magnetite nanoparticles grafted graphene oxide chelants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(57):86485–86498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21407-3
Sharma N, Sharma V, Jain Y, Kumari M, Ragini G, Sharma SK, Sachdev K (2017) Synthesis and characterization of graphene oxide (GO) and reduced graphene oxide (RGO) for gas sensing application. Macromol Symp 376(1):1700006. https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.201700006
Songsaeng S, Thamyongkit P, Poompradub S (2019) Natural rubber/reduced-graphene oxide composite materials: morphological and oil adsorption properties for treatment of oil spills. J Adv Res 20:79–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2019.05.007
Stankovich S, Dikin DA, Piner RD, Kohlhaas KA, Kleinhammes A, Jia Y, Wu Y, Nguyen SBT, Ruoff RS (2007) Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 45(7):1558–1565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2007.02.034
Sun Y, Ma L, Song Y, Phule AD, Lin L, Zhang ZX (2021) Efficient natural rubber latex foam coated by RGO modified high density polyethylene for oil-water separation and electromagnetic shielding performance. Eur Polym J 147:110288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2021.110288
Taghavi R, Rostamnia S, Farajzadeh M, Karimi-Maleh H, Wang J, Kim D, Jang HW, Luque R, Varma RS, Shokouhimehr M (2022) Magnetite metal–organic frameworks: applications in anvironmental remediation of heavy metals, organic contaminants, and other pollutants. Inorg Chem 61(40):15747–15783. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c01939
Tjandra R, Lui G, Veilleux A, Broughton J, Chiu G, Aiping Y (2015) Introduction of an enhanced binding of reduced graphene oxide to polyurethane sponge for oil absorption. Ind Eng Chem Res 54(14):3657–3663. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b00748
Uzoekwe SA (2011) Pollution status and effect of crude oil spillage in Ughoton Stream ecosystem in Niger Delta. J Ecol Nat Environ 3(15). https://doi.org/10.5897/JENE11.071
Verma RP, Sahu PS, Dabhade A, Saha B (2022) Reduced graphene oxide-based stretchable strain sensor for monitoring of physical activities and minute movement. Mater Today: Proc 62:5975–5981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.04.960
Verma RP, Sahu PS, Rathod M, Mohapatra SS, Lee J, Saha B (2022a) Ultra-sensitive and highly stretchable strain sensors for monitoring of human physiology. Macromol Mater Eng 307(3):2100666. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.202100666
Wang H, Wang E, Liu Z, Dong G, Yuan R, Sun L, Zhu Y (2015) A novel carbon nanotubes reinforced superhydrophobic and superoleophilic polyurethane sponge for selective oil–water separation through a chemical fabrication. J Mater Chem A 3(1):266–273. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA03945A
Wang J, Guo X (2020) Adsorption isotherm models: classification, physical meaning, application and solving method. Chemosphere 258:127279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127279
Weber TW, Chakravorti RK (1974) Pore and solid diffusion models for fixed-bed adsorbers. AIChE J 20(2):228–238. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690200204
Xu WC, Shi JZ, Li DL, Cao GR, Feng MK, Wang KT (2015) Application of surface modification in hydrophobic and oleophobic materials research. Mater Res Innov 19(sup10):S10-207–S10-210. https://doi.org/10.1179/1432891715Z.0000000002148
Yang S, Li J, Cheng Z, Li F, Sha S, Hou C, Lu H, Wu J, Sheng Z, Ma J (2022) Graphene-based melamine sponges with reverse wettability for oil/water separation through absorption and filtration. J Environ Chem Eng 10(3):107543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107543
Yu C, Lin W, Jiang J, Jing Z, Hong P, Li Y (2019) Preparation of a porous superhydrophobic foam from waste plastic and its application for oil spill cleanup. RSC Adv 9(65):37759–37767. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA06848A
Yunus S, Sefa-Ntiri B, Anderson B, Kumi F, Mensah-Amoah P, Sackey SS (2019) Quantitative pore characterization of polyurethane foam with cost-effective imaging tools and image analysis: a proof-of-principle study. Polymers 11(11):1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111879
Zaidi SA, Mohamed M, Deyab N (2022) A Simple method for developing efficient room temperature reduced graphene oxide-coated polyurethane sponge and cotton for oil-water separation. Sep Sci Technol:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2022.2074862
Zhang T, Kong L, Zhang M, Qiu F, Rong J, Pan J (2016) Synthesis and characterization of porous fibers/polyurethane foam composites for selective removal of oils and organic solvents from water. RSC Adv 6(89):86510–86519. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA10916K
Zhu H, Chen D, Yang S, Li N, Xu Q, Li H, Wang L, He J, Jiang J, Lu J (2016) A versatile and cost-effective reduced graphene oxide-crosslinked polyurethane sponge for highly effective wastewater treatment. RSC Adv 6(44):38350–38355. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA05450A
Funding
This work was funded by the Science and Engineering Research Board (by the Government of India) (ECR/2018/001192), National Mission on Himalayan Study (NMHS) (NMHS/2022-23/SG 82/02/285) and the Department of Science and Technology (DST/TM/WTI/WIC/2K17/82(G)).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Prateekshya Suman Sahu and Ravi Prakash Verma. Prateekshya Suman Sahu wrote the first draft of the manuscript, and Nanda Gopal Sahoo and Chetna Tewari supported analysis. Dr. Biswajit Saha conceptualised and supervised the work and reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
In this study, there was no participation by any kind of living subject, so obtaining informed permission is not necessary.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
The main highlights of this study are stated below;
•A nano-engineered advanced hybrid material was prepared for the effective remediation of organic and inorganic pollutants.
•Porous polyurethane (PU) and reduced graphene oxide (rGO) nanosheets were utilised in the fabrication of durable, superhydrophobic hybrid rGOPU.
•Various organic oils, dyes and heavy metals were removed using hybrid rGOPU.
•The prepared rGOPU possesses 98% oil-water separation, up to 75% heavy metal removal and about 55% dye adsorption.
•rGOPU’s remarkable properties make it a potential multifunctional absorbent in the treatment of large-scale wastewater for organic and inorganic pollutants.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1936 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sahu, .S., Verma, R.P., Tewari, C. et al. Facile fabrication and application of highly efficient reduced graphene oxide (rGO)-wrapped 3D foam for the removal of organic and inorganic water pollutants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 93054–93069 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28976-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28976-x