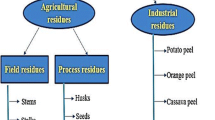
Abstract
The prevalence of organic solid waste worldwide has turned into a problem that requires comprehensive treatment on all fronts. The amount of agricultural waste generated by agro-based industries has more than triplet. It not only pollutes the environment but also wastes a lot of beneficial biomass resources. These wastes may be utilized as a different option/source for the manufacturing of many goods, including biogas, biofertilizers, biofuel, mushrooms and tempeh as the primary ingredients in numerous industries. Utilizing agro-industrial wastes as good raw materials may provide cost reduction and lower environmental pollution levels. Agro-industrial wastes are converted into biofuels, enzymes, vitamin supplements, antioxidants, livestock feed, antibiotics, biofertilizers and other compounds via solid-state fermentation (SSF). By definition, SSF is a method used when there is little to no free water available. As a result, it permits the use of solid materials as biotransformation substrates. Through SSF methods, a variety of microorganisms are employed to produce these worthwhile things. SSFs are therefore reviewed and discussed along with their impact on the production of value-added items. This review will provide thorough essential details information on recycling and the use of agricultural waste.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdel-Aty AM, Bassuiny RI, Barakat AZ, Mohamed SA (2019) Upgrading the phenolic content, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of garden cress seeds using solid-state fermentation by Trichoderma reesei. J Appl Microbiol 127:1454–1467. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14394
Abdullah JJ, Greetham D, Pensupa N, Tucker GA, Du C (2016) Optimizing cellulase production from municipal solid waste (MSW) using solid-state fermentation (SSF). J Renew Energy 6(3):1–10. https://doi.org/10.4172/2090-4541.1000206
Agrawal T, Jadhav SK, Quraishi A (2019) Bioethanol production from an agro-waste, deoiled rice bran by Saccharomyces cerevisiae MTCC 4780 via optimization of fermentation parameters. Intl J Thai Soc of IHE on Env Environment Asia 12(1):20–24. https://doi.org/10.14456/ea.2019.3
Akhtar T, Hashmi AS, Tayyab M, Anjum AA, Saeed S, Ali S (2020) Bioconversion of agricultural waste to butyric acid through solid state fermentation by Clostridium tyrobutyricum. Waste and Biomass Valorization 11:2067–2073
Akyüz A, Ersus S (2021) Optimization of enzyme assisted extraction of protein from the sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) leaves for alternative plant protein concentrate production. Food Chem 335:127673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127673
Alias C, Bulgari D, Gobbi E (2022) It works! organic-waste-assisted Trichoderma spp. solid-state fermentation on agricultural digestate. Microorganisms 10(1):164. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10010164
Arora NK, Fatima T, Mishra I, Verma M, Mishr J, Mishra V (2018) Environmental sustainability: challenges and viable solutions. Environ Sustain 1(4):309–340
Aruna TE (2019) Production of value-added product from pineapple peels using solid state fermentation. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 57:102193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2019.102193
Baiyeri KP, Chukwudi UP, Chizaram CA, Aneke N (2019) Maximizing rice husk waste for Daucus carota production. Int J Recycl Org Waste Agric 8(1):399–406
Ballardo C, Barrena R, Artola A, Sánchez A (2017) A novel strategy for producing compost with enhanced biopesticide properties through solid-state fermentation of biowaste and inoculation with Bacillus thuringiensis. Waste Manag 70:53–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.09.041
Banat IM, Carboué Q, Saucedo-Castaneda G, de Jesús C-MJ (2021) Biosurfactants: the green generation of speciality chemicals and potential production using Solid-State fermentation (SSF) technology. Bioresour Technol 320:124222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124222
Banu JR, Sharmila VG, Ushani U, Amudha V, Kumar G (2020) Impervious and influence in the liquid fuel production from municipal plastic waste through thermo-chemical biomass conversion technologies-A review. Sci Total Environ 718:137287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137287
Barrangou R, Fremaux C, Deveau H, Richards M, Boyaval P, Moineau S et al (2007) CRISPR provides acquired resistance against viruses in prokaryotes. Science 315(5819):1709–1712
Barcelos MC, Ramos CL, Kuddus M, Rodriguez-Couto S, Srivastava N, Ramteke PW et al (2020) Enzymatic potential for the valorization of agro-industrial by-products. Biotechnol Lett 42:1799–1827
Bashan Y, de-Bashan LE, Prabhu SR, Hernandez JP (2014) Advances in plant growth-promoting bacterial inoculant technology: formulations and practical perspectives (1998–2013). Plant Soil 378:1–33
Bastos RG, Ribeiro HC (2020) Citric acid production by the solid-state cultivation consortium of and from sugarcane bagasse. Open Biotechnol J 14(1). https://doi.org/10.2174/1874070702014010032
Bharathiraja S, Suriya J, Krishnan M, Manivasagan P, Kim SK (2017) Production of enzymes from agricultural wastes and their potential industrial applications. Adv Food Nutr Res 80:125–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.afnr.2016.11.003
Bibi F, Ilyas N, Arshad M, Khalid A, Saeed M, Ansar S, Batley J (2022) Formulation and efficacy testing of bio-organic fertilizer produced through solid-state fermentation of agro-waste by Burkholderia cenocepacia. Chemosphere 291:132762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132762
Botella C, Diaz A, De Ory I, Webb C, Blandino A (2007) Xylanase and pectinase production by Aspergillus awamori on grape pomace in solid state fermentation. Process Biochem 42(1):98–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2006.06.025
Broeren ML, Kuling L, Worrell E, Shen L (2017) Environmental impact assessment of six starch plastics focusing on wastewater-derived starch and additives. Resour Conserv Recycl 127:246–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.09.001
Cerda A, Artola A, Barrena R, Font X, Gea T, Sánchez A (2019) Innovative production of bioproducts from organic waste through solid-state fermentation. Front Sustain Food Syst 3:63. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2019.00063
Chakrapani G, Zare M, Ramakrishna S (2022) Biomaterials from the value-added food wastes. Bioresour Technol Rep 19:101181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2022.101181
Chilakamarry CR, Sakinah AM, Zularisam AW, Sirohi R, Khilji IA, Ahmad N, Pandey A (2022) Advances in solid-state fermentation for bioconversion of agricultural wastes to value-added products: Opportunities and challenges. Bioresour Technol 343:126065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126065
Chimphango AFA, Mugwagwa LR, Swart M (2020) Extraction of multiple value-added compounds from agricultural biomass waste: a review. Valorization of Biomass to Value-Added Commodities: Current Trends, Challenges, and Future Prospects 163–192
Daâssi D, Zouari-Mechichi H, Frikha F, Rodríguez-Couto S, Nasri M, Mechichi T (2016) Sawdust waste as a low-cost support-substrate for laccases production and adsorbent for azo dyes decolorization. J Environ Health Sci Eng 14(1):1–12
De la Cruz QR, Roussos S, Hernández D, Rodríguez R, Castillo F, Aguilar CN (2015) Challenges and opportunities of the bio-pesticides production by solid-state fermentation: filamentous fungi as a model. Crit Rev Biotechnol 35(3):326–333. https://doi.org/10.3109/07388551.2013.857292
da Silveira JS, Durand N, Lacour S, Belleville MP, Perez A, Loiseau G, Dornier M (2019) Solid-state fermentation as a sustainable method for coffee pulp treatment and production of an extract rich in chlorogenic acids. Food Bioprod Process 115:175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2019.04.001
Dey G, Banerjee P, Sharma RK, Maity JP, Etesami H, Shaw AK, Chen CY (2021) Management of phosphorus in salinity-stressed agriculture for sustainable crop production by salt-tolerant phosphate-solubilizing bacteria—a review. Agronomy 11(8):1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081552
Dong JW, Cai L, Li XJ, Duan RT, Shu Y, Chen FY et al (2016) Production of a new tetracyclic triterpene sulfate metabolite sambacide by solid-state cultivated Fusarium sambucinum B10. 2 using potato as substrate. Bioresour Technol 218:1266–1270
Duhan A, Oliver DP, Rashti MR, Du J, Kookana RS (2020) Organic waste from sugar mills as a potential soil ameliorant to minimise herbicide runoff to the Great Barrier Reef. Sci Total Environ 713:136640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136640
Esakkiraj P, Usha R, Palavesam A, Immanuel G (2012) Solid-state production of esterase using fish processing wastes by Bacillus altitudinis AP-MSU. Food Bioprod Process 90(3):370–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2011.12.008
Fidelis M, de Moura C, Kabbas Junior T, Pap N, Mattila P, Mäkinen S, Putnik P, Bursać Kovačević D, Tian Y, Yang B, Granato D (2019) Fruit seeds as sources of bioactive compounds: Sustainable production of high value-added ingredients from by-products within circular economy. Molecules 24(21):3854. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213854
Freitas F, Torres CA, Reis MA (2017) Engineering aspects of microbial exopolysaccharide production. Bioresour Technol 245:1674–1683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.092
Ghorbani M, Asadi H, Abrishamkesh S (2019) Effects of rice husk biochar on selected soil properties and nitrate leaching in loamy sand and clay soil. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 7(3):258–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2019.05.005
Glick BR (2018) Soil microbes and sustainable agriculture. Pedosphere 28(2):167–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(15)60020-7
González-García S, Gullón P, Gullón B (2019) Bio-compounds production from agri-food wastes under a biorefinery approach: exploring environmental and social sustainability. In: Quantification of Sustainability Indicators in the Food Sector. Springer Singapore, pp 25–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-2408-6_2
Guan Y, Wang Q, Lv C, Wang D, Ye X (2021) Fermentation time-dependent pectinase activity is associated with metabolomics variation in Bacillus licheniformis DY2. Process Biochem 101:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2020.11.007
Gupta GK, Shukla P (2020) Insights into the resources generation from pulp and paper industry wastes: challenges, perspectives and innovations. Bioresour Technol 297:122496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122496
Hanlon P, Sewalt V (2021) GEMs: genetically engineered microorganisms and the regulatory oversight of their uses in modern food production. Crit Rev Food Sci 61(6):959–970. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1749026
Hassan AA, Ismail SA (2021) Production of antifungal N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase chitinolytic enzyme using shrimp byproducts. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 34:102027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2021.102027
Hossain SS, Mathur L, Roy PK (2018) Rice husk/rice husk ash as an alternative source of silica in ceramics: A review. J Asian Ceram Soc 6(4):299–313. https://doi.org/10.1080/21870764.2018.1539210
Itelima JU, Bang WJ, Onyimba IA, Sila MD, Egbere OJ (2018) Bio-fertilizers as key player in enhancing soil fertility and crop productivity: a review. Direct Res J Agric Food Sci 6(3):73–83. http://hdl.handle.net/123456789/1999
Jacoby R, Peukert M, Succurro A, Koprivova A, Kopriva S (2017) The role of soil microorganisms in plant mineral nutrition—current knowledge and future directions. Front Plant Sci 8:1617. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01617
Jagtap S, Bhatt C, Thik J, Rahimifard S (2019) Monitoring potato waste in food manufacturing using image processing and internet of things approach. Sustainability 11(11):3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113173
Jana K, De S (2016) Environmental impact of an agro-waste based polygeneration without and with CO2 storage: life cycle assessment approach. Bioresour Technol 216:931–940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.06.039
Janveja C, Rana SS, Soni SK (2014) Optimization of valorization of biodegradable kitchen waste biomass for production of fungal cellulase system by statistical modeling. Waste Biomass Valorization 5(5):807–821
Javed A, Ahmad A, Tahir A, Shabbir U, Nouman M, Hameed A (2019) Potato peel waste-its nutraceutical, industrial and biotechnological applacations. AIMS Agric Food 4(3):807–823. https://doi.org/10.3934/agrfood.2019.3.807
Jindal N, Khattar JS (2018) Microbial polysaccharides in food industry. In: Biopolymers for food design. Academic Press, pp 95–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811449-0.00004-9
Jinek M, Chylinski K, Fonfara I, Hauer M, Doudna JA, Charpentier E (2012) A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 337(6096):816–821. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1225829
Kaaniche F, Hamed A, Elleuch L, Chakchouk-mtibaa A, Mellouli L (2020) Purification and characterization of seven bioactive compounds from the newly isolated Streptomyces cavourensis TN638 strain via solid-state fermentation. Microb Pathog 142:104106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104106
Kadar NAH, Rahim NS, Yusof R, Nasir NAHA, Hamid HA (2021) A review on potential of algae in producing biodegradable plastic. Int J Adv Eng Res Sci 3(1):13–26
Karak T, Bhagat RM, Bhattacharyya P (2012) Municipal solid waste generation, composition, and management: the world scenario. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42(15):1509–1630. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2011.569871
Karma BR, Chavan UD, Nimbalkar CA, Kahar SP (2017) Rheometry of roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) seed oil. Int J Pure App Biosci 5(2):987–993. https://doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.2846
Kumar A, Sengupta B, Dasgupta D, Mandal T, Datta S (2016) Recovery of value-added products from rice husk ash to explore an economic way for recycle and reuse of agricultural waste. Rev Environ Sci 15(1):47–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-015-9388-0
Kumla J, Suwannarach N, Sujarit K, Penkhrue W, Kakumyan P, Jatuwong K et al (2020) Cultivation of mushrooms and their lignocellulolytic enzyme production through the utilization of agro-industrial waste. Molecules 25(12):2811. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122811
LaTurner ZW, Bennett GN, San KY, Stadler LB (2020) Single cell protein production from food waste using purple non-sulfur bacteria shows economically viable protein products have higher environmental impacts. J Clean Prod 276:123114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123114
Leong HY, Chang CK, Khoo KS, Chew KW, Chia SR, Lim JW et al (2021) Waste biorefinery towards a sustainable circular bioeconomy: a solution to global issues. Biotechnol Biofuels 14(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-021-01939-5
López-Pérez M, Viniegra-González G (2016) Production of protein and metabolites by yeast grown in solid state fermentation: present status and perspectives. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 91(5):1224–1231. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4819
Lourenço LA, Alberton Magina MD, Tavares LBB, Ulson G, de Souza SMA, García Román M, Altmajer Vaz D (2018) Biosurfactant production by Trametes versicolor grown on two-phase olive mill waste in solid-state fermentation. Environ Technol 39:3066–3076. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1374471
Luo Y, Wang Q (2014) Recent development of chitosan-based polyelectrolyte complexes with natural polysaccharides for drug delivery. Int J Biol Macromol 64:353–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.12.017
Maean S, Abdelhafez A, Hassan E (2022) Utilization of agro-wastes for bioethanol production. Arab Univ J Agric Sci 1:43–53. https://doi.org/10.21608/ajs.2022.114247.1449
Mantzouridou FT, Paraskevopoulou A, Lalou S (2015) Yeast flavour production by solid state fermentation of orange peel waste. Biochem Eng J 101:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2015.04.013
Martău GA, Unger P, Schneider R, Venus J, Vodnar DC, López-Gómez JP (2021) Integration of solid state and submerged fermentations for the valorization of organic municipal solid waste. J Fungus 7(9):766. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7090766
Marzo C, Díaz AB, Caro I, Blandino A (2019) Valorization of agro-industrial wastes to produce hydrolytic enzymes by fungal solid-state fermentation. Waste Manag Res 37(2):149–156. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X187986
Matsakas L, Gao Q, Jansson S, Rova U, Christakopoulos P (2017) Green conversion of municipal solid wastes into fuels and chemicals. Electron J Biotechnol 26:69–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbt.2017.01.004
Matsakas L, Kekos D, Loizidou M, Christakopoulos P (2014) Utilization of household food waste for the production of ethanol at high dry material content. Biotechnol Biofuels 7(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-7-4
Meftaul IM, Venkateswarlu K, Dharmarajan R, Annamalai P, Megharaj M (2020) Pesticides in the urban environment: a potential threat that knocks at the door. Sci Total Environ 711:134612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134612
Mehmood T, Ahmed S, Waseem R, Saeed S, Ahmed W, Irfan M, Ullah A (2022a) Valorization of fruit peels into biovanillin and statistical optimization of process using Enterobacter hormaechei through solid-state fermentation. Fermentation 8(2):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8020040
Mehmood T, Saleem F, Javed S, Nawaz S, Sultan A, Safdar A et al (2022b) Biotransformation of agricultural by-products into Biovanillin through solid-state fermentation (SSF) and optimization of different parameters using response surface methodology (RSM). Fermentation 8(5):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8050206
Meini MR, Cabezudo I, Galetto CS, Romanini D (2021) Production of grape pomace extracts with enhanced antioxidant and prebiotic activities through solid-state fermentation by Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus oryzae. Food Biosci 42:101168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2021.101168
Mo J, Yang Q, Zhang N, Zhang W, Zheng Y, Zhang Z (2018) A review on agro-industrial waste (AIW) derived adsorbents for water and wastewater treatment. J Environ Manag 227:395–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.08.069
Mohamed SA, Saleh RM, Kabli SA, Al-Garni SM (2016) Influence of solid state fermentation by Trichoderma spp. on solubility, phenolic content, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities of commercial turmeric. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 80(5):920–928
Mostafa NA, Farag AA, Abo-dief HM, Tayeb AM (2018) Production of biodegradable plastic from agricultural wastes. Arab J Chem 11(4):546–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.04.008
Mushimiyimana I, Tallapragada P (2017) Bioethanol production from agro wastes by acid hydrolysis and fermentation process. J Sci Ind Res 75:383–388
Obi CN (2019) Solid state fermentation: substrates uses and applications in biomass and metabolites production—a review. South Asian Res J Biol Appl Biosci 1(1):20–29
Oliveira F, Salgado JM, Abrunhosa L, Pérez-Rodríguez N, Domínguez JM, Venâncio A, Belo I (2017) Optimization of lipase production by solid-state fermentation of olive pomace: from flask to laboratory-scale packed-bed bioreactor. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 40(7):1123–1132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-017-1774-2
Ong KL, Kaur G, Pensupa N, Uisan K, Lin CSK (2018) Trends in food waste valorization for the production of chemicals, materials and fuels: case study South and Southeast Asia. Bioresour Technol 248:100–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.06.076
Papadaki A, Fernandes KV, Chatzifragkou A, Aguieiras ECG, da Silva JAC, Fernandez-Lafuente R et al (2018) Bioprocess development for biolubricant production using microbial oil derived via fermentation froms confectionery industry wastes. Bioresour Technol 267:311–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.016
Pajeú T, Emmanuelle A, Souza C, Marcos R, Brandão P, De C-t GM et al (2016) Purification of a fibrinolytic protease from Mucor subtilissimus UCP 1262 by aqueous two-phase systems (PEG/sulfate). J Chromatogr B1025:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.04.046
Panzella L, Moccia F, Nasti R, Marzorati S, Verotta L, Napolitano A (2020) Bioactive phenolic compounds from agri-food wastes: An update on green and sustainable extraction methodologies. Front Nutr 7:60. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2020.00060
Parashar A, Jin Y, Mason B, Chae M, Bressler DC (2016) Incorporation of whey permeate, a dairy effluent, in ethanol fermentation to provide a zero waste solution for the dairy industry. J Dairy Sci 99(3):1859–1867. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2015-10059
Pardeep-Sukan A, Roy I, Keshavarz T (2014) Agro-industrial waste materials as substrates for the production of poly (3-hydroxybutyric acid). J Biomater Nanobiotechnol 5(4):229–240. https://doi.org/10.4236/jbnb.2014.54027
Paritosh K, Kushwaha SK, Yadav M, Pareek N, Chawade A, Vivekanand V (2017) Food waste to energy: an overview of sustainable approaches for food waste management and nutrient recycling. Biomed Res Int 2017:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2370927
Patidar MK, Nighojkar S, Kumar A, Nighojkar A (2018) Pectinolytic enzymes-solid state fermentation, assay methods and applications in fruit juice industries: a review. 3 Biotech 8(4):1–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1220-4
Pinela J, Omarini AB, Stojković D, Barros L, Postemsky PD, Calhelha RC et al (2020) Biotransformation of rice and sunflower side-streams by dikaryotic and monokaryotic strains of Pleurotus sapidus: impact on phenolic profiles and bioactive properties. Food Res Int 132:109094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109094
Pourkarimi S, Sadeh MS, Hallajisani A, Hajikhani M, Moradi M, Alizadeh O, Nouralishahi A (2022) Investigation of catalytic pyrolysis of Azolla filiculoides and Ulva fasciata for bio-oil production. Biochem Eng J 178:108278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2021.108278
Ramirez-Morales D, Perez-Villanueva ME, Chin-Pampillo JS, Aguilar-Mora P, Arias-Mora V, Masis-Mora M (2021) Pesticide occurrence and water quality assessment from an agriculturally influenced Latin-American tropical region. Chemosphere 262:127851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127851
Rashad MM, Mahmoud AE, Ali MM, Nooman MU, Al-Kashef AS (2015) Antioxidant and anticancer agents produced from pineapple waste by solid state fermentation. Int J Toxicol Pharmacol Res 7(6):287–296
Ravindran R, Hassan SS, Williams GA, Jaiswal AK (2018) A review on bioconversion of agro-industrial wastes to industrially important enzymes. Bioengineering 5(4):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering5040093
Sadh PK, Chawla P, Bhandari L, Duhan JS (2018) Bio-enrichment of functional properties of peanut oil cakes by solid state fermentation using Aspergillus oryzae. J Food Meas 12(1):622–633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-017-9675-2
Saeed S, Aslam S, Mehmood T, Naseer R, Nawaz S, Mujahid H, Firyal S, Anjum AA, Sultan A (2020) Production of gallic acid under solid-state fermentation by utilizing waste from food processing industries. Waste Biomass Valorization 12:155–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-00980-z
Saeed S, Aslam S, Mehmood T, Naseer R, Nawaz S, Mujahid H et al (2021) Production of gallic acid under solid-state fermentation by utilizing waste from food processing industries. Waste Biomass Valorization 12(1):155–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-00980-z
Saghir M, Zafar S, Tahir A, Ouadi M, Siddique B, Hornung A (2019) Unlocking the potential of biomass energy in Pakistan. Front Energy Res 7:24. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2019.00024
Saharan P, Sadh PK, Duhan JS (2017) Comparative assessment of effect of fermentation on phenolics, flavanoids and free radical scavenging activity of commonly used cereals. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 12:236–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2017.10.013
Saharan P, Sadh PK, Duhan S, Duhan JS (2020) Bio-enrichment of phenolic, flavonoids content and antioxidant activity of commonly used pulses by solid-state fermentation. J Food Meas 14(3):1497–1510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-020-00399-z
Saini JK, Saini R, Tewari L (2015) Lignocellulosic agriculture wastes as biomass feedstocks for second-generation bioethanol production: concepts and recent developments. 3. Biotech 5(4):337–353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-014-0246-5
Saleh F, Hussain A, Younis T, Ali S, Rashid M, Ali A et al (2020) Comparative growth potential of thermophilic amylolytic Bacillus sp. on unconventional media food wastes and its industrial application. Biocatal Agric. Biotechnol 27(12):3499–3504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.09.045
Saranraj P, Sayyed RZ, Hamzah KJ, Asokan N, Sivasakthivelan P, Al-Tawaha ARMA (2022a) Efficient substrates for microbial synthesis of biosurfactants. In: Sayyed RZ (ed) Biosurfatnats: Production and applications Bioremediation Vol III. CRC Press- Taylor and Francis Group, USA, pp 1–18
Saranraj P, Sayyed RZ, Sivasakthivelan P, Hasan MS, Al-Tawaha ARMA, Amala K (2022b) Microbial biosurfactants: methods of investigation, characterization, current market value and applications. In: Sayyed RZ (ed) Biosurfatnats: Production and applications Bioremediation Vol III. CRC Press- Taylor and Francis Group, USA, pp 19–34
Saranraj P, Sivasakthivelan P, Hamzah KJ, Hasan MS, Tawaha ARMA (2022c) Microbial fermentation technology for biosurfactants production. In: Sayyed, Enshasy HE (eds) Biosurfatnats: Production and applications in Food and Agriculture Vol II. CRC Press- Taylor & Francis group, USA, pp 63–81
Sarlaki E, Kermani AM, Kianmehr MH, Vakilian KA, Hosseinzadeh-Bandbafha H, Ma NL et al (2021) Improving sustainability and mitigating environmental impacts of agro-biowaste compost fertilizer by pelletizing-drying. Environ Pollut 285:117412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117412
Seidavi AR, Zaker-Esteghamati H, Scanes CG (2019) Present and potential impacts of waste from poultry production on the environment. Worlds Poult Sci J 75(1):29–42. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0043933918000922
Sharma A, Singh G, Arya SK (2020) Biofuel from rice straw. J Clean Prod 277:124101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124101
Sharma K, Garg VK (2019) Recycling of lignocellulosic waste as vermicompost using earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(14):14024–14035. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04639-8
Shen D, Shen H, Yang Q, Chen S, Dun Y, Liang Y et al (2021) Deciphering succession and assembly patterns of microbial communities in a two-stage solid-state fermentation system. Microbiol spectr 9(2):e00718–e00721. https://doi.org/10.1128/Spectrum.00718-21
Singh RP, Tingirikari JMR (2021) Agro waste derived pectin poly and oligosaccharides: Synthesis and functional characterization. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 31:101910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2021.101910
Singh R, Das R, Sangwan S, Rohatgi B, Khanam R, Peera SK et al (2021) Utilisation of agro-industrial waste for sustainable green production: a review. Environ Sustain 4:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42398-021-00200-x
Sun D, Liao J, Sun L, Wang Y, Liu Y, Deng Q et al (2019) Effect of media and fermentation conditions on surfactin and iturin homologues produced by Bacillus natto NT - 6: LC – MS analysis. AMB Express 9:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-019-0845-y
Suresh PV, Nidheesh T, Pal GV (2015) “Enzymes in seafood processing.” In: Chandrasekaran M (ed) Enzymes in Food and Beverage Processing. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp. 354–377
Teles AS, Chávez DW, Oliveira RA, Bon EP, Terzi SC, Souza EF et al (2019) Use of grape pomace for the production of hydrolytic enzymes by solid-state fermentation and recovery of its bioactive compounds. Food Res Int 120:441–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.10.083
Torres MD, Domínguez H (2020) Valorisation of potato wastes. Int J Food Sci Technol 55(6):2296–2304. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.14228
Try S, De-Coninck J, Voilley A, Chunhieng T, Waché Y (2018) Solid state fermentation for the production of γ-decalactones by Yarrowia lipolytica. Process Biochem 64:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2017.10.004
Ubando AT, Felix CB, Chen WH (2020) Biorefineries in circular bioeconomy: a comprehensive review. Bioresour Technol 299:122585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122585
Uçkun Kiran E, Trzcinski AP, Ng WJ, Liu Y (2014) Enzyme production from food wastes using a biorefinery concept. Waste Biomass Valorization 5(6):903–917. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-014-9311-x
Varadharajan S, Subramaniyan V (2014) Production of biosurfactant by Pseudomonas aeruginosa PB3A using agroindustrial wastes as a carbon source. Malays J Microbiol 10(1):57–62
Venkatanagaraju E, Divakar G (2015) Production and purification of alkaline fibrinolytic enzyme from Bacillus cereusGD55 under solid state. Curr Trends Biotechnol Pharm 9:348–356
Verduzco-Oliva R, Gutierrez-Uribe JA (2020) Beyond enzyme production: Solid state fermentation (SSF) as an alternative approach to produce antioxidant polysaccharides. Sustainability 12(2):495. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12020495
Vikas OV, Mridul U (2014) Bioconversion of papaya peel waste into vinegar using Acetobacter aceti. Int J Sci Res 3(11):409–411
Volpi MPC, Santos VS, Ribeiro APB, Santana MHA, Bastos RG (2019) The role of lignocellulosic composition and residual lipids in empty fruit bunches on the production of humic acids in submerged fermentations. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 187:957–964. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2850-z
Wang C, Yang B, Wang J (2019) Generation of Streptomyces hygroscopicus cell factories with enhanced ascomycin production by combined elicitation and pathway - engineering strategies. Biotechnol Bioeng:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.27158
Werle LB, Abaide ER, Felin TH, Kuhn KR, Tres MV, Zabot GL et al (2020) Gibberellic acid production from Gibberella fujikuroi using agro-industrial residues. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 25:101608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101608
Xin X, Ambati RR, Cai Z, Lei B (2019) Development of universal purification protocols for fibrinolytic enzyme-producing bacilli. CyTA - J Food 17:112–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/19476337.2018.1561521
Xu L, Geelen D (2018) Developing biostimulants from agro-food and industrial by-products. Front Plant Sci 9:1567. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01567
Yazid AN, Barrena R, Komilis D, Sánchez A (2017) Solid-state fermentation as a novel paradigm for organic waste valorization: a review. Sustainability 9(2):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9020224
Zhang QW, Lin LG, Ye WC (2018) Techniques for extraction and isolation of natural products: A comprehensive review. Chin Med 13:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13020-018-0177-x
Zhang Y, Wei R, Azi F, Jiao L, Wang H, He T, Liu X, Wang R, Lu B (2022) Solid-state fermentation with Rhizopus oligosporus RT-3 enhanced the nutritional properties of soybeans. Front Nutr 9:972860. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.972860
Zabermawi NM, Alsulaimany FA, El-Saadony MT, El-Tarabily KA (2022) New eco-friendly trends to produce biofuel and bioenergy from microorganisms: An updated review. Saudi J Biol Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.02.024
Zambrano C, Kotogán A, Bencsik O, Papp T, Vágvölgyi C, Mondal KC, Krisch J, Takó M (2018) Mobilization of phenolic antioxidants from grape, apple and pitahaya residues via solid state fungal fermentation and carbohydrase treatment. LWT 89:457–465
Funding
This work was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University in Abha, Saudi Arabia, provided funding for this search through large groups (Project under Grand number R.G.P. 2/213/44).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors equally contributed to this manuscript. The original draft was written by Fatima Bibi. Supervision and conceptualization by Noshin Ilyas. Software, validation and review-editing were by Maimona Saeed and Sumera Shabir. Resources and conceptualization were by Ali. A. Shati and Mohammad Y. Alfaifi. Graphics by Kassian T.T. Reviewing-editing was by Ameshod, Subrata Chowdhury and Riyazali Zafarali Sayyed. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bibi, ., Ilyas, N., Saeed, M. et al. Innovative production of value-added products using agro-industrial wastes via solid-state fermentation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 125197–125213 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28765-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28765-6