Abstract
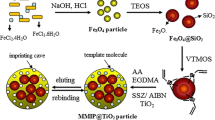
In this paper, molecularly imprinted Zr-doped TiO2 photocatalysts (MIP-ZrO2-TiO2) were prepared by the molecularly imprinted sol–gel method for the photocatalytic degradation study of hydroquinone (HQ) as the target pollutant. For the effectiveness of the MIP-ZrO2-TiO2 catalyst in degrading HQ, the effects of Zr doping ratio, imprinted molecule dosage, calcination conditions, and pollutant concentration on its photocatalytic activity were investigated. XRD, TEM, XPS, and other techniques were used to evaluate the materials, and the findings revealed that MIP-ZrO2-TiO2 films with imprinted HQ were successfully produced on the ZrO2-TiO2 surface. The optimal preparation conditions were n(Ti):n(Zr) = 100:8, m(HQ) = 1.5 g, 550 °C for the calcination temperature, and 2 h for the calcination duration. The optimum reaction conditions were 10 mg/L HQ concentration, 1 g/L catalyst dose, and a pH of 6.91. According to the findings of photocatalytic tests, during 30 min of UV lamp (365 nm) irradiation, the degradation rates of MIP-ZrO2-TiO2, ZrO2-TiO2, and TiO2 for HQ were 90.58%, 83.94%, and 58.30%, respectively. The findings revealed that the doping of Zr metal and the addition of imprinted molecules improved the photocatalytic activity of TiO2, which can be used for the efficient treatment of low concentrations of hard-to-degrade hydroquinone.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Akhavan O, Ghaderi E (2009) Photocatalytic reduction of graphene oxide nanosheets on TiO2 thin film for photoinactivation of bacteria in solar light irradiation. J Phys Chem C 113(47):20214–20220. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp906325q
An F, Gao B, Feng X (2008) Adsorption and recognizing ability of molecular imprinted polymer MIP-PEI/SiO2 towards phenol. J Hazard Mater 157(2):286–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.12.095
Bai L, Wei M, Hong E, Shan D, Liu L, Yang W, Tang X, Wang B (2020) Study on the controlled synthesis of Zr/TiO2/SBA-15 nanophotocatalyst and its photocatalytic performance for industrial dye reactive red X–3B. Mater Chem and Phys 246:122825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.122825
Bi L, Chen Z, Li L, Kang J, Zhao S, Wang B, Yan P, Li Y, Zhang X, Shen J (2021) Selective adsorption and enhanced photodegradation of diclofenac in water by molecularly imprinted TiO2. J Hazard Mater 407:124759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124759
Canillas M, Chinarro E, Freitas M, Pêgo AP, Moreno B (2020) Titanium dioxide catalytic activity contributes to the process of free radical scavenging. J Catal 381:186–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2019.09.030
Chen J, Guo L, Zhu H, Qiu Y, Yin D, Zhang T, Chen J, Peng Y, Li J (2021) Balancing redox and acidic properties for optimizing catalytic performance of SCR catalysts: a case study of nanopolyhedron CeOx-supported WOx. J Environ Chem Eng 9(5):105828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105828
Chen X, Liu X, Zhu L, Tao X, Wang X (2022) One-step fabrication of novel MIL-53(Fe, Al) for synergistic adsorption-photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline. Chemosphere 291:133030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133032
Ebrahimi M, Akhavan O (2022) Nanomaterials for photocatalytic degradations of analgesic, mucolytic and anti-biotic/viral/inflammatory drugs widely used in controlling SARS-CoV-2. Catalysts 12(6):667. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12060667
Fahri AN, Ilyas S, Anugrah MA, Heryanto H, Azlan M, Ola ATT, Rahmat R, Yudasari N, Tahir D (2022) Bifunctional purposes of composite TiO2/CuO/carbon dots (CDs): faster photodegradation pesticide wastewater and high performance electromagnetic wave absorber. Mater 26:101588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtla.2022.101588
Fukahori S, Fujiwara T, Ito R, Funamizu N (2011) pH-Dependent adsorption of sulfa drugs on high silica zeolite: modeling and kinetic study. Desalination 275(1):237–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.03.006
García-Contreras LA, Flores-Flores JO, Arenas-Alatorre JÁ, Chávez-Carvayar JÁ (2022) Synthesis, characterization and study of the structural change of nanobelts of TiO2 (H2Ti3O7) to nanobelts with anatase, brookite and rutile phases. J Alloy Compd 923:166236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166236
Hsieh P, Aljuffali IA, Fang C, Chang S, Fang J (2014) Hydroquinone-salicylic acid conjugates as novel anti-melasma actives show superior skin targeting compared to the parent drugs. J Dermatol Sci 76(2):120–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2014.08.013
Iglesias J, Melero JA, Bautista LF, Morales G, Sánchez-Vázquez R, Andreola MT, Lizarraga-Fernández A (2011) Zr-SBA-15 as an efficient acid catalyst for FAME production from crude palm oil. Catal Today 167(1):46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2010.11.060
Jovalekic C, Zdujic M, Atanasoska L (2009) Surface analysis of bismuth titanate by Auger and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J Alloy Compd 469(1–2):441–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.01.131
Kanakaraju D, Glass BD, Oelgemoeller M (2014) Titanium dioxide photocatalysis for pharmaceutical wastewater treatment. Environ Chem Lett 12(1):27–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-013-0428-0
Kerzic PJ, Liu WS, Pan MT, Fu H, Zhou Y, Schnatter AR, Irons RD (2010) Analysis of hydroquinone and catechol in peripheral blood of benzene-exposed workers. Chem-Biol Interact 184(1):182–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2009.12.010
Khosravikia M, Rahbar-Kelishami A (2022) A simulation study of an applied approach to enhance drug recovery through electromembrane extraction. J Mol Liq 358:119210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2022.119210
Li Z, Li H, Zeng X, Liu S, Yang Y (2023) Adsorption and photodegradation of tetracycline by mannose-grafted chitosan composite films: performance, mechanism and availability. Chem Eng J 458:141455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.141455
Luo XP, Zhu SP, Wang JY, Wang CY, Wu M (2017) Characterization and computation of Yb/TiO2 and its photocatalytic degradation with benzohydroxamic acid. Int J Env Res Pub He 14(12):1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14121471
Martoni LVL, Gomes NO, Prado TM, Calegaro ML, Oliveira ON Jr, Machado SAS, Raymundo-Pereira PA (2022) Carbon spherical shells in a flexible photoelectrochemical sensor to determine hydroquinone in tap water. J Environ Chem Eng 10(3):107556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107556
Qi HP, Wang HL (2020) Facile synthesis of Pr-doped molecularly imprinted TiO2 mesocrystals with high preferential photocatalytic degradation performance. Appl Surf Sci 511:145607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.145607
Rezania S, Taib SM, Md Din MF, Dahalan FA, Kamyab H (2016) Comprehensive review on phytotechnology: heavy metals removal by diverse aquatic plants species from wastewater. J Hazard Mater 318:587–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.07.053
Song Y, Tian J, Gao S, Shao P, Qi J, Cui F (2017) Photodegradation of sulfonamides by g-C3N4 under visible light irradiation: effectiveness, mechanism and pathways. Appl Catal b: Environ 210:88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.03.059
Tang Y, Zong E, Wan H, Xu Z, Zheng S, Zhu D (2012) Zirconia functionalized SBA-15 as effective adsorbent for phosphate removal. Micropor and Mesopor Mat 155:192–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2012.01.020
Tao X, Zhu L, Wang X, Chen X, Liu X (2022) Preparation of Zr/Y co-doped TiO2 photocatalyst and degradation performance of hydroquinone. Environ Sci Pollut R 29(27):40854–40864. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18155-1
Tian S, He Y, Zhang L, Li S, Bai Y, Wang Y, Wu J, Yu J, Guo X (2022) CNTs/TiO2- loaded carbonized nanofibrous membrane with two-type self-cleaning performance for high efficiency oily wastewater remediation. Colloid Surface A 656:130306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.130306
Trabelsi H, Bensalah N, Gadri A (2015) Anodic oxidation of aqueous wastes containing hydroquinone on BDD electrode. J Adv Oxid Technol 18(1):155–160. https://doi.org/10.1515/jaots-2015-0119
Wang W, Niu Q, Zeng G, Zhang C, Huang D, Shao B, Zhou C, Yang Y, Liu Y, Guo H, Xiong W, Lei L, Liu S, Yi H, Chen S, Tang X (2020) 1D porous tubular g-C3N4 capture black phosphorus quantum dots as 1D/0D metal-free photocatalysts for oxytetracycline hydrochloride degradation and hexavalent chromium reduction. Appl Catal B: Environ 273:119051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119051
Wang C, Lei Y, Lv Q, Wang P, Kong W, Wan F, Chen W (2022) Abundant oxygen vacancies promote bond breaking of hydrogen peroxide on 3D urchin-like Pd/W18O49 surface to achieve high-performance catalysis of hydroquinone oxidation. Appl Catal B: Environ 315:121547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121547
Yu H, Li S, Peng S, Yu Z, Chen F, Liu X, Guo J, Zhu B, Huang W, Zhang S (2023) Construction of rutile/anatase TiO2 homojunction and metal-support interaction in Au/TiO2 for visible photocatalytic water splitting and degradation of methylene blue. Int J Hydrogen Energ 48(3):975–990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.10.010
Zhang X, Jiang SP (2022) Layered g-C3N4/TiO2 nanocomposites for efficient photocatalytic water splitting and CO2 reduction: a review. Mater Today Energy 23:100904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtener.2021.100904
Zhang SN, Feng M, Liu Y, Wang DA (2020) Ta2O5 NTs-TiO2 nanodots heterostructure photocatalyst material for enhanced photodegradation and photoelectrochemical performance under simulated solar light. J Nanopart Res 22(12):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-05100-5
Zhang Z, Yi G, Li P, Wang X, Wang X, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Sun Q (2021) Electrochemical oxidation of hydroquinone using Eu-doped PbO2 electrodes: electrode characterization, influencing factors and degradation pathways. Electroanal Chem 895:115493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2021.115493
Zhang Z, Yi G, Li P, Wang X, Wang X, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Sun Q (2022) Eu/GO/PbO2 composite based anode for highly efficient electrochemical oxidation of hydroquinone. Colloid Surface A 642:128632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.128632
Zhu L, Liu X, Wang X, Meng X (2020) Evaluation of photocatalytic selectivity of Ag/Zn modified molecularly imprinted TiO2 by multiwavelength measurement. Sci Total Environ 703:134732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134732
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51672196).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ke Peng: conceptualization, software, validation, investigation, data curation, writing—review and editing. Xian Liu: validation, investigation. Xi Wu: validation. Hang Yu: validation. Jiachen He: validation. Ke Chen: validation. Lei Zhu: visualization, supervision. Xun Wang: visualization, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
There are no ethical issues in this article.
Consent to participate
All the authors agree to participate in this paper.
Consent for publication
All the authors agree to the publication of this paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, K., Liu, X., Wu, X. et al. Study on the preparation of molecularly imprinted ZrO2-TiO2 photocatalyst and the degradation performance of hydroquinone. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 83575–83586 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28295-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28295-1