Abstract
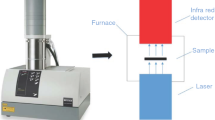
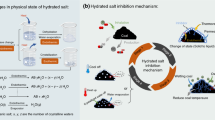
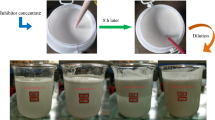
Coal spontaneous combustion (CSC) is a global disaster and detrimental to the ecological environment. This study aims to better apply environmentally friendly dissolvable tiny-foam extinguisher (DTE) to CSC and look further into the inhibition mechanism. Thermogravimetric analysis and differential scanning calorimetry (TG-DSC) were employed to test the oxidation properties of coal samples treated with DTE, NaCl, MgCl2, and CaCl2 inhibitors, and the reaction mechanisms and kinetic parameters in the high-temperature stage of coal oxidation were determined. The results revealed that the inhibition of the four inhibitors was similar in the initial period of the coal oxidation, DTE increased the cracking temperature of the coal by 37 °C, mass loss was a minimum when reaching the ignition temperature, and inhibition was better than the other inhibitors at the low temperature. DTE had higher thermal stability and played a stable role in suppression at the high temperature, while chlorine salt inhibitors promoted the oxidative exothermic reaction. DTE coal sample absorbed forty times more heat during the endothermic stage than raw coal, ten times more than MgCl2, and released a minimum of heat. In the decomposition and combustion stages, the reaction mechanism of coal and oxygen conformed to the three-dimensional diffusion Z.-L.-T. equation, and the apparent activation energy of the DTE-treated coal sample was about 40 kJ/mol higher than raw coal.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Pre-exponential factor, min−1
- CSC:
-
Coal spontaneous combustion
- DTE:
-
Dissolvable tiny-foam extinguisher
- DSC :
-
Differential scanning calorimetry
- E a :
-
Apparent activation energy, kJ·mol−1
- DTG:
-
Differential thermogravimetry
- f(α) :
-
Differential function (dimensionless)
- G(α) :
-
Integrated function (dimensionless)
- R :
-
Universal gas constant (8.314 J/[mol·K])
- r 2 :
-
Correlation degree
- TG:
-
Thermogravimetry
- T D :
-
Thermal equilibrium temperature, ℃
- T 1 :
-
Critical temperature, ℃
- T 2 :
-
Cracking temperature, ℃
- T 3 :
-
Decomposition temperature, ℃
- T 4 :
-
Ignition temperature, ℃
- T 5 :
-
Maximum mass loss rate temperature, ℃
- T 6 :
-
Burnout temperature, ℃
- △ T :
-
Difference between the temperature of the resistance coal sample and the raw coal, ℃
- α :
-
Conversion rate of the coal at a temperature of T
- m 0 :
-
Mass before weightlessness, mg
- m t :
-
Mass at time t, mg
- m f :
-
Mass at the end of masslessness, mg
- β :
-
Constant heating rate, ℃·min−1
References
Achar BN, Brindley GW, Sharp JH (1966). Kinetics and mechanism of dehydroxylation processes. III. Applications and limitations of dynamic methods, in: Proc Int Clay Conf Jerusalem, 1
Arenillas A, Rubiera F, Pevida C, Pis JJ (2001) A comparison of different methods for predicting coal devolatilisation kinetics. J Anal Appl Pyrol 58:685–701
Benfell KE, Beamish BB, Rodgers KA (1996) Thermogravimetric analytical procedures for characterizing New Zealand and Eastern Australian coals. Thermochim Acta 286(1):67–74
BP Statistical Review of World Energy (2021) Available from: https://www.bp.com/content/dam/bp/business-sites/en/global/corporate/pdfs/energy-economics/statistical-review/bp-stats-review-2021-full-report.pdf. Accessed 13 May 2022
Chi K, Wang J, Ma L, Wang J, & Zhou C (2020). Synergistic inhibitory effect of free radical scavenger/inorganic salt compound inhibitor on spontaneous combustion of coal. Combustion Sci Technol, 1–17
Cui C, Jiang S, Shao H, Zhang W, Wang K, Wu Z (2018) Experimental study on thermo-responsive inhibitors inhibiting coal spontaneous combustion. Fuel Process Technol 175:113–122
Deng J, Yang Y, Zhang YN, Liu B, Shu CM (2018) Inhibiting effects of three commercial inhibitors in spontaneous coal combustion. Energy 160:1174–1185
Fan HH, Wang K, Zhai XW, Hu LH (2021) Combustion kinetics and mechanism of pre-oxidized coal with different oxygen concentrations. ACS Omega 6(29):19170–19182
Feng S, Li P, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Li Z (2018) Experimental study on pyrolysis characteristic of coking coal from Ningdong coalfield. J Energy Inst 91(2):233–239
Kam AY, Hixson AN, Perlmutter DD (1976) The oxidation of bituminous coal—I development of a mathematical model. Chem Eng Sci 31(9):815–819
Kizgut S, Yilmaz S (2004) Characterization and non-isothermal decomposition kinetics of some Turkish bituminous coals by thermal analysis. Fuel Process Technol 85(2–3):103–111
Kök MUSTAFA (2008) Recent developments in the application of thermal analysis techniques in fossil fuels. J Therm Anal Calorim 91(3):763–773
Krishnaswamy S, Bhat S, Gunn RD, Agarwal PK (1996) Low-temperature oxidation of coal 1 A single-particle reaction-diffusion model. Fuel 75(3):333–343
Li QW, Xiao Y, Wang CP, Deng J, Shu CM (2019) Thermokinetic characteristics of coal spontaneous combustion based on thermogravimetric analysis. Fuel 250:235–244
Li QW, Xiao Y, Zhong KQ, Shu CM, Lü HF, Deng J, Wu S (2020) Overview of commonly used materials for coal spontaneous combustion prevention. Fuel 275:117981
Lü H, Li B, Deng J, Ye L, Gao W, Shu CM, Bi M (2021) A novel methodology for evaluating the inhibitory effect of chloride salts on the ignition risk of coal spontaneous combustion. Energy 231:121093
Ma T, Zhai XW, Xiao Y, Bai YE, Shen K, Song BB, Hao L, Ren LF, Chen XK (2023b) Study on the influence of key active groups on gas products in spontaneous combustion of coal. Fuel 2023:128020
Ma T, Ren SJ, Zhai XW, Bai YE, Song BB, Hao L, Ren LF, & Chen XK (2023a). Dynamic behavior of oxidative heat release of key active groups for different Jurassiccoal seams in northern Shaanxi. J Therm Anal Calorimetry
Manquais LK, Snape C, Barker J, McRobbie I (2012) TGA and drop tube furnace investigation of alkali and alkaline earth metal compounds as coal combustion additives. Energy Fuels 26(3):1531–1539
Musa SD, Zhonghua T, Ibrahim AO, Habib M (2018) China’s energy status: a critical look at fossils and renewable options. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 81:2281–2290
Niu Z, Liu G, Yin H, Zhou C (2018) Devolatilization behaviour and pyrolysis kinetics of coking coal based on the evolution of functional groups. J Anal Appl Pyrol 134:351–361
Papamatthaiakis N, Laine A, Haapala A et al (2021) New energy crop alternatives for Northern Europe: yield, chemical and physical properties of Giant knotweed (Fallopia sachalinensis var ‘Igniscum’) and Virginia mallow (Sida hermaphrodita). Fuel 304:121349
Qi X, Li Q, Zhang H, Xin H (2017) Thermodynamic characteristics of coal reaction under low oxygen concentration conditions. J Energy Inst 90(4):544–555
Qiao L, Deng C, Lu B, Wang Y, Wang X, Deng H, Zhang X (2022) Study on calcium catalyzes coal spontaneous combustion. Fuel 307:121884
Ren LF, Deng J, Li QW, Ma L, Zou L, Laiwang B, Shu CM (2019) Low-temperature exothermic oxidation characteristics and spontaneous combustion risk of pulverised coal. Fuel 252:238–245
Shi B, Chen C, Liu P (2021) Rheological properties of combustion metamorphic rock slurry for coalfield fire prevention. Bull Eng Geol Env 80(10):8231–8245
Song JJ, Deng J, Zhao JY, Zhang YN, Shu CM (2021) Comparative analysis of exothermic behaviour of fresh and weathered coal during low-temperature oxidation. Fuel 289:119942
Song B, Zhai X, Ma T, Wang B, Hao L, Zhou Y (2023). Effect of water immersion on pore structure of bituminous coal with different metamorphic degrees. Energy, 127449
Sujanti W, Zhang DK (2000) Investigation into the role of inherent inorganic matter and additives in low-temperature oxidation of a Victorian brown coal. Combust Sci Technol 152(1):99–114
Tang Y (2018) Experimental investigation of applying MgCl2 and phosphates to synergistically inhibit the spontaneous combustion of coal. J Energy Inst 91(5):639–645
Tsai YT, Yang Y, Wang C, Shu CM, Deng J (2018) Comparison of the inhibition mechanisms of five types of inhibitors on spontaneous coal combustion. Int J Energy Res 42(3):1158–1171
Wang H, Dlugogorski BZ, Kennedy EM (2003) Coal oxidation at low temperatures: oxygen consumption, oxidation products, reaction mechanism and kinetic modelling. Prog Energy Combust Sci 29(6):487–513
Wang H, Chen C, Huang T, Gao W (2015) CO2 emission of coal spontaneous combustion and its relation with coal microstructure. China J Environ Biol 36:1017–1024
Wang C, Yang Y, Tsai YT, Deng J, Shu CM (2016) Spontaneous combustion in six types of coal by using the simultaneous thermal analysis-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy technique. J Therm Anal Calorim 126(3):1591–1602
Wang C, Xiao Y, Li Q, Deng J, Wang K (2018) Free radicals, apparent activation energy, and functional groups during low-temperature oxidation of Jurassic coal in Northern Shaanxi. Int J Min Sci Technol 28(3):469–475
Wang H, Tan B, Shao Z, Guo Y, Zhang Z, Xu C (2021) Influence of different content of FeS2 on spontaneous combustion characteristics of coal. Fuel 288:119582
Watanabe WS, Zhang DK (2001) The effect of inherent and added inorganic matter on low-temperature oxidation reaction of coal. Fuel Process Technol 74(3):145–160
Xiao Y, Lü HF, Yi X, Deng J, Shu CM (2019) Treating bituminous coal with ionic liquids to inhibit coal spontaneous combustion. J Therm Anal Calorim 135(5):2711–2721
Xu YL, Wang DM, Wang LY, Zhong XX, Chu TX (2012) Experimental research on inhibition performances of the sand-suspended colloid for coal spontaneous combustion. Saf Sci 50(4):822–827
Yang Y, Tsai YT, Zhang Y, Shu CM, Deng J (2018) Inhibition of spontaneous combustion for different metamorphic degrees of coal using Zn/Mg/Al–CO3 layered double hydroxides. Process Saf Environ Prot 113:401–412
Yu SJ, Xie FC, Jia BY, Zhang PF (2012) Influence study of organic and inorganic additive to coal combustion characteristic. Procedia Environ Sci 12:459–467
Yuan L, Smith AC (2011) CO and CO2 emissions from spontaneous heating of coal under different ventilation rates. Int J Coal Geol 88(1):24–30
Zhai XW, Ge H, Wang TY, Shu CM, Li J (2020) Effect of water immersion on active functional groups and characteristic temperatures of bituminous coal. Energy 205:118076
Zhai XW, Pan WJ, Xiao Y, Wang SR, Ouyang LM (2021a) Inhibition of coal spontaneous combustion by an environment-friendly, water-based fire extinguishing agent. J Therm Anal Calorim 144(2):325–334
Zhai XW, Song BB, Wang B, Ma T, Ge H (2021b) Study on the effect and mechanism of water immersion on the characteristic temperature during coal low-temperature oxidation. Nat Resour Res 30(3):2333–2345
Zhang Y, Li Y, Huang Y, Li S, Wang W (2018) Characteristics of mass, heat and gaseous products during coal spontaneous combustion using TG/DSC–FTIR technology. J Therm Anal Calorim 131(3):2963–2974
Zhang H, Gu W, Li YJ, Tang M (2020) Hygroscopic properties of sodium and potassium salts as related to saline mineral dusts and sea salt aerosols. J Environ Sci 95:65–72
Acknowledgements
The authors are very thankful for the support from the Science and Technology Department of Shaanxi Province and Xi’an University of Science and Technology. The authors also acknowledge the Key Laboratory of Coal Fire and Hazard Prevention in Shaanxi Province, China.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers [51974236]), the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi Province (grant numbers [2021JC-48]), and the Shaanxi Provincial Department of Education Youth Innovation Team Building Research Program (grant numbers [21JP078]).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaowei Zhai provided ideas and experimental protocols, supervised the experimental procedure, reviewed the manuscript, guided the research, obtained fundings, and edited the final manuscript. Yujie Zhou performed experiments, processed data, wrote the original manuscript, and revised the final manuscript. Bobo Song performed the experiments, analyzed and interpreted data, and revised the manuscript. Wenjun Pan and Jiuge Wang performed the experiments and methodology. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Shimin Liu
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Synchronous thermal analysis experiments were used to explore the oxidation properties of coal samples treated with DTE, NaCl, MgCl2, and CaCl2 inhibitors.
• The inhibiting effects of DTE and chlorine salt inhibitors on coal spontaneous combustion were compared.
• The reaction mechanism and kinetic parameters of coal samples in the high-temperature stage of coal oxidation were speculated.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, X., Zhou, Y., Song, B. et al. Comparative study on the inhibiting effect of dissolvable tiny-foam extinguishing agent and chlorine salts on coal spontaneous combustion. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 80591–80601 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27948-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27948-5