Abstract
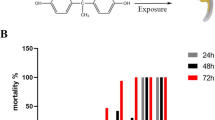
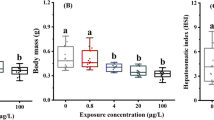
2,4-Dinitrotoluene (2, 4-DNT) is a common environmental pollutant. The toxic effect on mammals of 2,4-DNT has been well studied, but its toxicity on aquatic organisms is little known. In this study, 126 healthy female zebrafish (Danio rerio) were exposed to different concentrations of 2,4-DNT (0, 2, 4, 8, 12 and 16 mg/L) to determine 96-h semi-lethal concentrations (LC50). And then, 90 female zebrafish were exposed to 0, 2, 4 and 8 mg/L 2,4-DNT for 5 days to study liver toxicity. Exposed zebrafish developed hypoxia features, such as floating head and breathing rapidly, and then died. 96-h LC50 of 2,4-DNT in zebrafish was 9.36 mg/L. Histological data revealed that 2,4-DNT severely damaged the liver tissues, following with the round nucleus, dense interstitial tissue, dense arranged hepatocyte cords and more inflammatory cells. Additionally, the further result showed that the lower levels of lipid transport and metabolism (apoα2, mtp, ppar-α and acox) were noticed. But, exposed to 2,4-DNT for 5 days significantly upregulated the expression levels of genes involved in respiration (hif1a, tfa and ho1, p < 0.05). These results indicated that 2,4-DNT exposure disturbed lipid transport and metabolism and oxygen supply in zebrafish, which could contribute to severe damage in liver and death.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the fndings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Baares-Espaa E, García-Villada L, López-Rodas V, Costas E, Flores-Moya A (2006) Effect of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene and 2,4-dinitrotoluene on the growth rate and photosynthetic capacity of the Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa (Kützing) Lemmermann. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 76(4):601
Beauchamp OR, Irons RD, Rickert DE, Couch DB, Hamm TE (1982) A critical review of the literature on nitrobenzene toxicity. Crit Rev Toxicol 11(1):33–84
Capriello T, Grimaldi MC, Cofone R, Aniello SD, Ferrandino I (2019) Effects of aluminium and cadmium on hatching and swimming ability in developing zebrafish. Chemosphere 222(1):243–249
Cengiz EI, Unlu E (2006) Sublethal effects of commercial deltamethrin on the structure of the gill, liver and gut tissues of mosquitofish, Gambusia affinis: a microscopic study. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 21(3):246–253
Chen L, Jin S, Liu Y, Liu F (2014) Presence of semi-olatile organic contaminants in shallow groundwater of selected regions in China. Groundw Monit Remediat 34(4):33–43
Deng Y, Meyer SA, Xin G, Escalon BL, Ai J, Wilbanks MS, Welti R, Garcia-Reyero N, Perkins EJ (2011) Analysis of common and specific mechanisms of liver function affected by nitrotoluene compounds. PLoS One 6(2):14662
Fanta E, Rios FS, Romo S, Vianna A, Freiberger S (2003) Histopathology of the fish Corydoras paleatus contaminated with sublethal levels of organophosphorus in water and food. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 54(2):119–130
Gao Q, Jia YZ, Tao FU, Zheng YS, Zhang XH, Yang GS (2015) Activation of PPARα pathway is resistant to obesity and fatty liver induced by high fat diet and leptin deficiency. Chin J Biochem Mol Biol 31(8):815–826
Gernhöfer M, Pawert M, Schramm M, Müller E, Triebskorn R (2001) Ultrastructural biomarkers as tools to characterize the health status of fish in contaminated streams. J Aquat Ecosyst Stress Recover 8(3):241–260
Lang PZ, Wang Y, Chen DB, Wang N, Zhao XM, Ding YZ (1997) Bioconcentration, elimination and metabolism of 2,4-dinitrotoluene in carps (Cyprinus Carpio L.). Chemosphere 35(8):1810–1815
Lee PJ, Jiang BH, Chin BY, Iyer NV, Alam J, Semenza GL, Choi A (1997) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 mediates transcriptional activation of the heme oxygenase-1 gene in response to hypoxia. J Biol Chem 272(9):5375
Lei Z, Jingbo X (2004) The toxicity of nitrotoluenes to guppy. Ecol Environ 13(1):31–33
Li YL, Xu GY, Xiao JW, Li Z, Zhao HB, Zhou QC, Gui JF, Zhong XP (2017) Studies on the protective role of zebrafish ho1 in response to hypoxia. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 41(1):43–49
Ni H, Peng L, Gao X, Ji H, Ma J, Li Y, Jiang S (2019) Effects of maduramicin on adult zebrafish (Danio rerio): acute toxicity, tissue damage and oxidative stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 168:249–259
Nivedita S, Vatsana G, Singh RA, Kumar GV, Sarita S, Kumar R (2018) 2, 4-Dinitrotoluene (DNT) and 2, 4, 6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) removal kinetics and degradation mechanism using zero valent iron-silica nanocomposite. J Environ Chem Eng 6(4):5196–5203
O’connor D, Hou DY, Ok YS, Song YN, Sarmah AK, Li XR, Tack FMG (2018) Sustainable in situ remediation of recalcitrant organic pollutants in groundwater with controlled release materials: a review. J Control Release 283:200–213
Oppenheimer SJ (2001) Iron and its relation to immunity and infectious disease. J Nutr 131:616–633
Pang Z, Feng L, Zhou JL, Liu ZT (2011) Ecological risk assessment of substituted aromatic hydrocarbons in water of Yangtze river estuary. Environ Chem 30(2):430–434
Rolfs A, Kvietikova I, Gassmann M, Wenger RH (1997) Oxygen-regulated transferrin expression is mediated by hypoxia-inducible factor-1. J Biol Chem 272(32):20055–20062
Shen HY, Yang L, Zhang GX, Yang JL (2010) Study on antioxidant enzyme of brocarded carp as biomarkers of 2,4-DNT pollution in water. Adv Mater Res 113–116:2171–2176
Wang D, Zhong XP, Qiao ZX, Gui JF (2008) Inductive transcription and protective role of fish heme oxygenase-1 under hypoxic stress. J Exp Biol 211(16):2700–2706
Wang N, Chen Q, Hu CY (2010) Cloning and tissue-specific expression of transferriong gene in grass carp. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 34(1):51–56
Wenger RH (2002) Cellular adaptation to hypoxia: O2-sensing protein hydroxylases, hypoxia-inducible transcription factors, and O2-regulated gene expression. FASEB J 16:1151–1162
Wilbanks MS, Gust KA, Sahar A, Imran S, David J, Yaw AC, Meyer SA, Perkins EJ (2014) Validation of a genomics-based hypothetical adverse outcome pathway: 2,4-dinitrotoluene perturbs PPAR signaling thus impairing energy metabolism and exercise endurance. Toxicol Sci 141(1):44–58
Wintz H, Yoo LJ, Loguinov A, Wu YY, Steevens JA, Holland RD, Beger RD, Perkins EJ, Hughes O, Vulpe CD (2006) Gene expression profiles in fathead minnow exposed to 2,4-DNT: correlation with toxicity in mammals. Toxicol Sci 94(1):71–82
Wu H (2000) Effects of dinitrotoluene (DNT) on the immune function of red cell in rats. Ind Health Occup Dis 26(2):88–89
Wu LL, Chen L, Zhang YL, Li JH, Zhao JF (2007) Effects of phenanthrene toxicity on histopathology of Brachydanio rerio gill and liver. Chin J Ecol 26(5):688–692
Wu SM, Tseng YJ, Chen TH (2022) Maternal effect and dietary supplementation of estradiol-17β on female zebrafish (Danio rerio) affects the swimming behavior and stress-coping styles of its offspring. Comp Biochem Physiol C: Toxicol Pharmacol 252:109211–109218
Wu SX, Han X, Xia F, Yang Y, Xu XJ, Deng S, Jiang YH (2022) Enhanced degradation of 2,4-DNT in groudwater by oxalic acid-modified zero-valent iron as persulfate activator. Res Environ Sci 35(1):108–118
Xiong J, Sha H, Zhou H, Peng L, Wu L, Qiu Y, Wang R, Hu X (2019) 2,4-Dinitrotoluene (DNT) perturbs yolk absorption, liver development and lipid metabolism/oxygen transport gene expression in zebrafish embryos and larvae. Int J Mol Sci 20(15):3632
Xu J, Nan J (2012) Effects of 2,4-dinitrotoluene exposure on enzyme activity, energy reserves and condition factors in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). J Hazard Mater 203:299–307
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31201983) and Fujian Key Laboratory of Special Aquatic Formula Feed (No. TMKJZ2102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Data analysis, wrinting, reviewing and editing were performed by Liangxia Su; methodology, data collect and reviewing were performed by Hang Sha; reviewing and supervision were performed by Jun Liu and Rui Wang; methodology and data collect were performed by Le Yu and Huanhuan Li.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This research project has been approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Wuhan polytechnic university (Approval protocol No. WPU-F20150701) and were in accordance with the National Guiding Principles for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all the authors.
Consent for publication
The author confirms that the article described has not been published before; not considering publishing elsewhere.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Bruno Nunes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Su, L., Sha, H., Liu, J. et al. 2,4-Dinitrotoluene (2,4-DNT) exposure induces liver developmental damage and perturbs lipid metabolism and oxygen transport gene expression in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 76104–76111 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27843-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27843-z