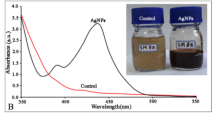
Abstract
Using rhizobacteria as biological fertilizer is gradually expanding in agriculture as excellent substitutes for chemical fertilizers. Bacillus subtilis SL-44 is a plant growth–promoting rhizobacteria screened from the severely salinized cotton rhizosphere soil in Xinjiang. Study showed that indole-3-acetic acid, organic acid production, nitrogen fixation, and other beneficial secondary metabolite secretion can be synthesized by stain SL-44. At the same time, fencyclin, lipopeptide, chitinase, and other antifungal substances were also detected from the secretion of Bacillus subtilis SL-44, which can effectively control plant diseases. Siderophore separated from SL-44 was verified by HPLC, and results showed it was likely bacillibactin. This study also verified that SL-44 has high antifungal activity against Rhizoctonia solani through in vitro antifungal experiments. The B. subtilis SL-44 whole genome was sequenced and annotated to further explore the biotechnological potential of SL-44. And a large number of genes involved in the synthesis of anti-oxidative stress, antibiotic, and toxins were found. Genome-wide analysis provides clear evidence to support the great potential of B. subtilis SL-44 strain to produce multiple bioantagonistic natural products and growth-promoting metabolites, which may facilitate further research into effective therapies for harmful diseases.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Agrawal YK, Kaur H, Menon SK (1999) Poly(styrene-p-hydroxamic acids): synthesis, and ion exchange separation of rare earths. React Funct Polym 39:155–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1381-5148(97)00181-8
Akram W, Ahmad A, Yasin NA, Anjum T, Ali B, Fatima S, Ahmed S, Simirgiotis MJ, Li G (2021) Mechanical strengthening and metabolic re-modulations are involved in protection against Fusarium wilt of tomato by B. subtilis IAGS174. J Plant Interact 16:411–421. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2021.1966107
Alfiky A, L’Haridon F, Abou-Mansour E, Weisskopf L (2022) Disease inhibiting effect of strain Bacillus subtilis EG21 and its metabolites against potato pathogens Phytophthora infestans and Rhizoctonia solani. Phytopathology 112:2099–2109. https://doi.org/10.1094/phyto-12-21-0530-r
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang JH, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Arcand MM, Schneider KD (2006) Plant-and microbial-based mechanisms to improve the agronomic effectiveness of phosphate rock: a review. An Acad Bras Cienc 78:791–807
Baldani JI, Reis VM, Videira SS, Boddey LH, Baldani VLD (2014) The art of isolating nitrogen-fixing bacteria from non-leguminous plants using N-free semi-solid media: a practical guide for microbiologists. Plant Soil 384:413–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2186-6
Baramov T, Schmid B, Ryu H, Jeong J, Keijzer K, von Eckardstein L, Baik MH, Süssmuth RD (2019) Cover feature: how many o‐donor groups in enterobactin does it take to bind a metal cation?(Chem. Eur. J. 28/2019). Chem.–Eur. J. 25, 6851–6851. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201901473
Bland C, Ramsey TL, Sabree F, Lowe M, Brown K, Kyrpides NC, Hugenholtz P (2007) CRISPR recognition tool (CRT): a tool for automatic detection of clustered regularly interspaced palindromic repeats. BMC Bioinf 8:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-8-209
Chakraborty K, Kizhakkekalam VK, Joy M, Dhara S (2021) Difficidin class of polyketide antibiotics from marine macroalga-associated Bacillus as promising antibacterial agents. App.l Microbiol. Biotechnol 105:6395–6408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11390-z
Chakraborty K, Kizhakkekalam VK, Joy M, Chakraborty RD (2022) Bacillibactin class of siderophore antibiotics from a marine symbiotic Bacillus as promising antibacterial agents. App.l Microbiol. Biotechnol 106:329–340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11632-0
Chen W, Wu Z, Liu C, Zhang Z, Liu X (2023) Biochar combined with Bacillus subtilis SL-44 as an eco-friendly strategy to improve soil fertility, reduce Fusarium wilt, and promote radish growth. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 251:114509
Colombo ML, Hanique S, Baurin SL, Bauvois C, De Vriendt K, Van Beeumen JJ, Frere JM, Joris B (2004) The ybxI gene of Bacillus subtilis 168 encodes a class D beta-lactamase of low activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48:484–490. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.48.2.484-490.2004
Conesa A, Gotz S, Garcia-Gomez JM, Terol J, Talon M, Robles M (2005) Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 21:3674–3676. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti610
Crouch SR, Malmstadt H (1967) Mechanistic investigation of molybdenum blue method for determination of phosphate. Anal Chem 39:1084–1089
De Vrieze M, Varadarajan AR, Schneeberger K, Bailly A, Rohr RP, Ahrens CH, Weisskopf L (2020) Linking comparative genomics of nine potato-associated Pseudomonas isolates with their differing biocontrol potential against late blight. Front Microbiol 11:857. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00857
Dertz EA, Stintzi A, Raymond KN (2006) Siderophore-mediated iron transport in Bacillus subtilis and Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Biol Inorg Chem 11:1087–1097. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-006-0151-4
Einloft TC, Bolzan de Oliveira P, Radünz LL, Dionello RG (2021) Biocontrol capabilities of three Bacillus isolates towards aflatoxin B1 producer A. flavus in vitro and on maize grains. Food Control 125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.107978
Finn RD, Coggill P, Eberhardt RY, Eddy SR, Mistry J, Mitchell AL, Potter SC, Punta M, Qureshi M, Sangrador-Vegas A, Salazar GA, Tate J, Bateman A (2016) The Pfam protein families database: towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D279–D285. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1344
Franco-Sierra ND, Posada LF, Santa-Maria G, Romero-Tabarez M, Villegas-Escobar V, Alvarez JC (2020) Bacillus subtilis EA-CB0575 genome reveals clues for plant growth promotion and potential for sustainable agriculture. Funct Integr Genomics 20:575–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-020-00736-x
Freeman JM, Plasterer TN, Smith TF, Mohr SC (1998) Patterns of genome organization in bacteria. Science 279:1827–1827
Glickmann E, Dessaux Y (1995) A critical examination of the specificity of the salkowski reagent for indolic compounds produced by phytopathogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:793–796. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.61.2.793-796.1995
Grandchamp GM, Caro L, Shank EA (2017) Pirated siderophores promote sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Appl Environ Microbiol 83:e03293-e3316
Haack EA, Johnston CT, Maurice PA (2008) Mechanisms of siderophore sorption to smectite and siderophore-enhanced release of structural Fe3+. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:3381–3397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2008.03.027
Hoffmann T, Schutz A, Brosius M, Volker A, Volker U, Bremer E (2002) High-salinity-induced iron limitation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 184:718–727. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.184.3.718-727.2002
Huang Y, Wu Z, He Y, Ye B-C, Li C (2017) Rhizospheric Bacillus subtilis exhibits biocontrol effect against Rhizoctonia solani in pepper (Capsicum annuum). BioMed Res Int 2017. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9397619
Iyer B, Rajput MS, Rajkumar S (2017) Effect of succinate on phosphate solubilization in nitrogen fixing bacteria harbouring chick pea and their effect on plant growth. Microbiol Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2017.05.005
Jha Y, Subramanian R (2014) PGPR regulate caspase-like activity, programmed cell death, and antioxidant enzyme activity in paddy under salinity. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 20:201–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-014-0224-8
Jiang C, Li Z, Shi Y, Guo D, Pang B, Chen X, Shao D, Liu Y, Shi J (2020) Bacillus subtilis inhibits Aspergillus carbonarius by producing iturin A, which disturbs the transport, energy metabolism, and osmotic pressure of fungal cells as revealed by transcriptomics analysis. Int J Food Microbiol. 330:108783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108783
Jilani G, Akram A, Ali RM, Hafeez FY, Shamsi IH, Chaudhry AN, Chaudhry AG (2007) Enhancing crop growth, nutrients availability, economics and beneficial rhizosphere microflora through organic and biofertilizers. Ann Microbiol 57:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03175204
Kilani-Feki O, Khedher SB, Dammak M, Kamoun A, Jabnoun-Khiareddine H, Daami-Remadi M, Tounsi S (2016) Improvement of antifungal metabolites production by Bacillus subtilis V26 for biocontrol of tomato postharvest disease. Biol Control 95:73–82
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Li Q, Li Y, Li X, Chen S (2021) Identification of genes involved in Fe–S cluster biosynthesis of nitrogenase in Paenibacillus polymyxa WLY78. Int J Mol Sci 22:3771. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073771
Maurice PA, Haack EA, Mishra B (2009) Siderophore sorption to clays. Biometals 22:649–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-009-9242-3
May JJ, Wendrich TM, Marahiel MA (2001) The dhb operon of Bacillus subtilis encodes the biosynthetic template for the catecholic siderophore 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate-glycine-threonine trimeric ester bacillibactin. J Biol Chem 276:7209–7217. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M009140200
Mnif I, Grau-Campistany A, Coronel-León J, Hammami I, Triki MA, Manresa A, Ghribi D (2016) Purification and identification of Bacillus subtilis SPB1 lipopeptide biosurfactant exhibiting antifungal activity against Rhizoctonia bataticola and Rhizoctonia solani. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:6690–6699. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5826-3
Nautiyal CS, Govindarajan R, Lavania M, Pushpangadan P (2008) Novel mechanism of modulating natural antioxidants in functional foods: involvement of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria NRRL B-30488. J Agric Food Chem 56:4474–4481. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf073258i
Niazi A, Manzoor S, Bejai S, Meijer J, Bongcam-Rudloff E (2014) Complete genome sequence of a plant associated bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum UCMB5033. Stand Genomic Sci 9:718–725
Nithyapriya S, Lalitha S, Sayyed R, Reddy M, Dailin DJ, El Enshasy HA, Luh Suriani N, Herlambang S (2021) Production, purification, and characterization of bacillibactin siderophore of Bacillus subtilis and its application for improvement in plant growth and oil content in sesame. Sustainability 13:5394
Nosheen S, Ajmal I, Song Y (2021) Microbes as biofertilizers, a potential approach for sustainable crop production. Sustainability 13:1868
Outten FW, Djaman O, Storz G (2004) A suf operon requirement for Fe–S cluster assembly during iron starvation in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 52:861–872. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04025.x
Patel AK, Deshattiwar MK, Chaudhari BL, Chincholkar SB (2009) Production, purification and chemical characterization of the catecholate siderophore from potent probiotic strains of Bacillus spp. Bioresour Technol 100:368–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.05.008
Planchon A, Durambur G, Besnier JB, Plasson C, Gügi B, Bernard S, Mérieau A, Trouvé JP, Dubois C, Laval K (2021) Effect of a Bacillus subtilis strain on flax protection against Fusarium oxysporum and its impact on the root and stem cell walls. Plant, Cell Environ 44:304–322. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13882
Rebecca J. Abergel AMZ, Trisha M. Hoette, and Kenneth N. Raymond* (2009) Enzymatic hydrolysis of trilactone siderophores: where chiral recognition occurs in enterobactin and bacillibactin iron transport. J Am Chem Soc
Reimer D, Nollmann FI, Schultz K, Kaiser M, Bode HB (2014) Xenortide biosynthesis by entomopathogenic Xenorhabdus nematophila. J Nat Prod 77:1976–1980. https://doi.org/10.1021/np500390b
Rizzi A, Roy S, Bellenger J-P, Beauregard PB (2019) Iron homeostasis in Bacillus subtilis requires siderophore production and biofilm formation. Appl Environ Microbiol 85. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.02439-18
Ryu H, Park H, Suh DS, Jung GH, Park K, Lee BD (2014) Biological control of Colletotrichum panacicola on Panax ginseng by Bacillus subtilis HK-CSM-1. J Ginseng Res 38:215–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2014.05.001
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(87)90612-9
Shao J, Xu Z, Zhang N, Shen Q, Zhang R (2014) Contribution of indole-3-acetic acid in the plant growth promotion by the rhizospheric strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9. Biol Fertil Soils 51:321–330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-014-0978-8
Shao J, Li S, Zhang N, Cui X, Zhou X, Zhang G, Shen Q, Zhang R (2015) Analysis and cloning of the synthetic pathway of the phytohormone indole-3-acetic acid in the plant-beneficial Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9. Microb Cell Fact 14:1–13
Soni R, Keharia H (2021) Phytostimulation and biocontrol potential of Gram-positive endospore-forming Bacilli. Planta 254:49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03695-0
Sun B, Bai Z, Bao L, Xue L, Zhang S, Wei Y, Zhang Z, Zhuang G, Zhuang X (2020) Bacillus subtilis biofertilizer mitigating agricultural ammonia emission and shifting soil nitrogen cycling microbiomes. Environ Int 144:105989
Takashima T, Sunagawa R, Uechi K, Taira T (2020) Antifungal activities of LysM-domain multimers and their fusion chitinases. Int J Biol Macromol 154:1295–1302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.11.005
Tatusov RL, Galperin MY, Natale DA, Koonin EV (2000) The COG database: a tool for genome-scale analysis of protein functions and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res 28:33–36. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.33
Wu Z, Huang Y, Li Y, Dong J, Liu X, Li C (2019) Biocontrol of Rhizoctonia solani via induction of the defense mechanism and antimicrobial compounds produced by Bacillus subtilis SL-44 on pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Front Microbiol 10:2676. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02676
Zhang F, Wang B, Liu S, Chen Y, Lin Y, Liu Z, Zhang X, Yu B (2021) Bacillus subtilis revives conventional antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis. Microb Cell Fact 20:102. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-021-01592-5
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22278325, 32060026), Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province (2021NY-141), Xi’an Key Laboratory Performance Assessment Award Subsidy Project (2021JH-201–0004), Agricultural Technology R&D Project of Xi’an Science and Technology Bureau (22NYYF0037), Preferential Funding Projects for Scientific and Technological Activities of Overseas Scholar (2020018), and Key Research and Development Program of Xianyang City (S2021ZDYF-NY-0024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZW constructed the research ideas. HX designed the experimental scheme and carried out the experimental operation, and completed the manuscript writing. XW, JW, TL, SZ, and WW assisted in the experimental operation and data processing. YH made important revisions to the manuscript. XL assisted in guiding this research. All authors approved the final article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Diane Purchase
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, H., He, Y., Wang, X. et al. Identification and characterization of siderophilic biocontrol strain SL-44 combined with whole genome. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 62104–62120 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26272-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26272-2