Abstract
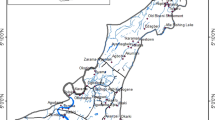
Just recently, heavy metals have been dramatically detected in aquatic animals, especially in fishes; hence, documented method to assess their health risks for humans who eat these contaminated fishes could be helpful. For the sake of this aim, the health risk assessment of four heavy metals including arsenic, cadmium, lead, and copper in three main edible fishes caught from Gorgan bay was studied. Mullet, roach, and common carp have been caught randomly in winter and spring of 2021 from three different fishing sites of Gorgan bay, including Miankaleh wetland, estuary of Qaresu River, and mouth of Chapaghli canal. Heavy metal measurement has been done with MOOPAM method, and risk assessment of fish consumption was assessed by estimated daily (EDI) and weekly intakes (EWI), target hazard quotient (THQ), hazard index (HI), and target cancer risk (TCR) indices. In this study, estimated daily intake (EDI) was much lower than the tolerable daily intake. Although TCR of cadmium within all fishes and arsenic in two fishes were more than acceptable value, THQ and HI values were less than one, and TCR of lead as well as copper was lower than the critical values, which suggests heavy metals of the Gorgan bay have no serious risks to consumer health.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available upon request.
References
Afraei Bandpei MA, Fazli H, Shahla Pour S (2018) Identification and species diversity of fishes in Gorgan Bay. Iranian Sci Fish J 27(2):61–69
Agarwal SK (2009) Heavy metal pollution, Vol. 4. APH publishing
Aghili K, Mohammadi F (2011) Study on catching trend of Liza saliens in the Gorgan Bay. J Biol Sci 4(4):47–56
Ahmed I, Zakiya A, Fazio F (2022) Effects of aquatic heavy metal intoxication on the level of hematocrit and hemoglobin in fishes: a review. Front Environ Sci 10(919204) https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.919204
Arisekar U, Shakila RJ, Shalini R, Jeyasekaran G (2020) Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in aquatic sediments and freshwater fish caught from Thamirabarani River, the western Ghats of south Tamil Nadu. Mar Pollut Bull 159(111496):1–10
Bagheri T, Gholizadeh M, Abarghouei S, Zakeri M, Hedayati A, Rabaniha M, Aghaeimoghadam A, Hafezieh M (2020) Microplastics distribution, abundance and composition in sediment, fishes and benthic organisms of the Gorgan Bay, Caspian Sea. Chemosphere 257:127201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127201
Bakhshalizadeh S, Rostamzadeh Liyafoyi A, Fazio F, Mora-Medina R, Ayala-Soldado N (2022a). Environ Geochem Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01401-x
Bakhshalizadeh S, Mora-Medina R, Fazio F, Parrino V (2022b) Animals 12(2819):1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202819
Baluchi I, Rahmani A, Samari F (2020) Risk assessment of copper and zinc in muscle tissue of Indian mackerel (Rastrelliger Kanagurta) in three areas of Parsian, Assalouyeh and Minab, the Persian Gulf. J Aquat Ecol 10(1):67–77
Coad BW (2017) Review of the freshwater Mullets of Iran (family Mugilidae). Iran Soc Ichthyol 4(2):75–130
Copat C, Arena G, Fiore M, Ledda C, Fallico R, Sciacca S, Ferrante M (2013) Heavy metals concentrations in fish and shellfish from eastern Mediterranean sea: consumption advisories. Food Chem Toxicol 53:33–37
Da Silva CA, Deoliveira Santos S, Garcia CAB, De Pontes GC, Wasserman JC (2019) Metals and arsenic in marine fish commercialized in the NE Brazil: risk to human health. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J 26:695–712
Doğan-Sağlamtimur N, Kumbur H (2010) Metals (Hg, Pb, Cu, and Zn) bioaccumulation in sediment, fish, and human scalp hair: a case study from the city of Mersin along the southern coast of Turkey. Biol Trace Elem Res 136(1):55–70
El-Moselhy KM, Othman AI, Abd El-azem H, El-metwally MEA (2014) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in some tissues of fish in the Red sea, Egypt. Egypt J Basic Appl Sci 1(2):97–105
Elnabris KJ, Muzyed SK, El-ashgar NM (2013) Heavy metal concentrations in some commercially important fishes and their contribution to heavy metals exposure in Palestinian people of Gaza strip (Palestine). J Assoc Arab Univ Basic Appl Sci 13:44–51
Engwa GWA, Ferdinand PU, Nwalo FN, & Unachukwa MN (2019) Mechanism and health effects of heavy metal toxicity in humans. In Ozgur Karcioglu, Banu Arslan (Ed), poisoning in the modern world-new tricks for an old dog, vol. 5 ,pp 1–23. . Retrieved june 19, 2019, from http://www.intechopen.com
Faggio C, Arfuso F, Piccione G, Zumbo A, Fazio F (2014) Effect of three different anticoagulants and storage time on haematological parameters of Mugil cephalus (Linneaus, 1758). Turk J Fish Aquat Sci 14(3):615–621
FAO, WHO (2004) Summary of evaluations performed by the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA 1956–2003), (First Through Sixty First Meetings). ILSI press International Life Sciences Institute
Fazio F, Piccione G (2014) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in blood and tissue of striped Mullet in two Italian lakes. J Aquat Anim Health 26:278–284
Fazio F, Piccione G, Arfuso F, Faggio C (2015) Peripheral blood and head kidney haematopoietic tissue response to experimental blood loss in mullet (Mugil cephalus). Mar Biol Res 11(2):197–202
Fazio F, D’iglio C, Capillo G, Saoca C, Peycheva K, Piccione G, Makedonski L (2020) environmental investigations and tissue bioaccumulation of heavy metals in grey mullet from the Black sea (Bulgaria) and the Ionian sea (Italy). J Anim 10(1739):1–12
Hedayati A, Gholizadeh M, Bagheri T, Abarghouei S, Zamani W (2022) Microplastics in marine ecosystems. Sustain Aquat Res 1(2):63–73
Humtsoe N, Davoodi R, Kulkarni BG, Chavan B (2007) Effect of arsenic on the enzymes of the rohu carp labeo rohita (hamilton, 1822). Raffles Bull Zool 14:17–19
IARC (2012) IARC Monographs on the Identification of Carcinogenic Hazards to Humans. The International Agency for Research on Cancer, France (Last update January 2020)
Ihunwo OC, Dibofori-orji AN, Olowo C, Ibezim-Ezeani MU (2020) Distribution and risk assessment of some heavy metals in surface water sediment and grey mullet (Mugil cephalus) from contaminated creek in Woji, southern Nigeria. Mar Pollut Bull 154(111042):1–7
Iran Fisheries Organization (IFO), 2020. In: Annual Iranian Fisheries Statistics 2014 and 2018. Fisheries Design and Program Office, Tehran, Iran, p. 64
Kalani N, Riazi B, Karbassi AR, Moattar F (2014) Heavy metal concentrations in Liza saliens muscle and human health risk estimates from fish consumption in Gomishan International Wetland, Iran. J Aquat Anim Fish 5(17):65–79
Khoshravan H, Naqinezhad A, Alinejad-Tabrizi T, Yanina T (2019) Gorgan Bay environmental consequences due to the Caspian Sea rapid water level change. Casp J Environ Sci 17(3):213–226
Li J, Huang ZY, Hu Y, Yang H (2013) Potential risk assessment of heavy metals by consuming shellfish collected from Xiamen, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(5):2937–2947
Loghmani M, Tootooni MM, Sharifian S (2022) Risk assessment of trace element accumulation in two species of edible commercial fish Scomberoides commersonnianus and Cynoglossus arel from the northern waters of the Oman Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 174(113201):1–7
Makedonski L, Peycheva K, Stancheva M (2017) Determination of heavy metals in selected Black Sea fish species. Food Control 73:313–318
Mclean C, Miskiewicz AG, Roberts EA (1991) Effect of three primary treatment sewage outfalls on metal concentrations in the fish Cheilodactylus fuscus collected along the coast of Sydney, Australia. Mar Pollut Bull 22(3):134–140
MOOPAM (Manual of Oceanographic Observation and Pollution Analysis) (1999) Regional organization for the protection of marine environmental (ROPME, Kuwait), p. 220
Obeidi R, Dahaz T, Ziaeian Nourbakhsh H, Ghanbari F (2018) Determination the level of essential heavy metals in muscle of Lethrinus nebulosus in Bushehr seaport. Iran Sci Fish J 27(5):149–156
Petkovsek SA, Grudnik ZM, Pokorny B (2012) Heavy metals and arsenic concentrations in 10 fish species from the Salek lakes (Slovenia): assessment of potential human health risk due to fish consumption. Environ Monit Assess 184:2647–2662
Rizk R, Juzsakova T, Ben Ali M, Ali Rawash M, Domokos E, Hedfi A, Almalki M, Boufahja F, MShafik H, Redey A (2022) Comprehensive environmental assessment of heavy metal contamination of surface water, sediments and Nile tilapia in lake Nasser, Egypt. J King Saud Univ-Sci 34(101748):1–11
Salehi Borban S, Gharachorloo M, Zamani F (2017) Check amount of heavy metals in muscle and fish oil Rutilus frisii kutum, Clupeonella cultriventris and Liza saliens. J Food Hyg 6(24):75–87
Sekhar KC, Chary NS, Kamala CT, Suman Raj DS, Rao AS (2003) Fractionation studies and bioaccumulation of sediment-bound heavy metals in Kolleru lake by edible fish. Environ Int 29(7):1001–1008
Solgi E (2015) Estimation of daily intake and potential risk of cadmium and lead in consumers of Liza salines in the eastern coast of the Caspian Sea. J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci 24(122):382–388
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metals toxicity and the environment. Nat Inst Health 101:133–164
Tkachenko H, Kurhaluk N, Kasiyan O, Kaminski P (2021) Dietary nutrients and health risks from exposure to some heavy metals through the consumption of the farmed common carp ( Cyprinus carpio). J Environ Health Sci Eng 19:793–804
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (2006) USEPA regional screening level (RSL) summary table: November 2006
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (2012) EPA region III risk based concentration (RBC) Table 2008
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (2015) Risk based screening table
USEPA (US Environmental Protection Agency) (2000) EPA/823-B94–004: guidance for assessing chemical contamination data for use in fish advisories volume II, Risk Assessment and Fish Consumption Limits. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington
Varol M, Kurt Kaya G, Rasit Sunbul M (2019) Evaluation of health risks for exposure to arsenic and heavy metals through consumption of ten fish species. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:33311–33320
Wang X, Wu JP, Yu B, Fei Dong K, Ma D, Xiao G, Zhang C (2020) Heavy metals in aquatic products and the health risk assessment to population in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(18):22708–22719
Funding
This study was supported by University of Tehran as Ph.D. research grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Toktam Bagheri: investigation, methodology; Ali Misaghi, project administration, supervision, resources, writing; Ali Taheri Mirghaed: supervision, data curation, validation; Abolfazl Kamkar: conceptualization, software; Aliakbar Hedayati: roles/writing — original draft; Hessameddin Akbarein: formal analysis, visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All experimental procedures related to the fish were approved by the Animal Care and Ethical Committee of GUASNR, which were in accordance with ethical standards in laboratory animal guideline for ethical review of animal welfare.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bagheri, T., Misaghi, A., MirGhaed, A.T. et al. Health risk assessment of some heavy metals detected in edible fishes of Gorgan Bay, Caspian Sea (Iran), for human. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 44480–44489 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-25082-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-25082-2