Abstract
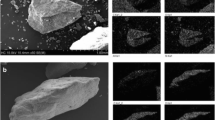
The aim of the present study is to estimate the different chemical fractionations of copper (Cu) and selenium (Se) in coal samples of different coal mining areas. The Cu and Se bound to various chemical fractions of coal collected from two mining fields of Sindh, Pakistan, have been determined by BCR sequential extraction scheme (BCR-SES). The long duration of the BCR sequential scheme (51 h) was reduced by a time-saving shaking device (ultrasonic bath) termed as ultrasonic-assisted extraction (USE) depending on the same operating conditions and extracting solutions used for BCR sequential extraction scheme. The both trace elements were determined in aquifer water, sampled from different depth of both coal mining fields. In addition, the groundwater of dug well in the vicinity of coal mining areas were also analyzed for Cu and Se using reported extraction methodologies. The partitioning of Cu and Se bound with different chemical fractions of coal was successfully made by proposed USE, within 2 h as compared to long duration of BCR-SES (51 h). The Cu and Se concentrations in acid-soluble fractions of coal samples were > 10%, enhanced by USE extraction procedure than those values gained via BCR-SES (p < 0.01). About 67 to 69% of Cu were found in the first three fractions, whereas their remaining amount corresponding to 31 to 33%, respectively bound with crystalline/residual fraction, while up to 66.1 to 71.1% of total Se contents extracted in three extractable phases, followed up to 28.9 to 33.8% of it was bound with residual phase. The concentrations of Cu and Se in groundwater of different aquifers were found in decreasing order as AQ1 > AQII > AQIII; the same trend was observed for two aquifers of Lakhra coal mining, whereas the groundwater samples have two to three folds higher levels of Se than WHO limit. The Cu levels in water samples were significantly lower than the recommended limit of WHO for drinking water (p < 0.01).



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable
References
Acikkapi AN, Tuzen M, Hazer B (2019) A newly synthesized graft copolymer for magnetic solid phase microextraction of total selenium and its electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometric determination in food and water samples. Food Chem 284:1–7
Adewumi AJ, Laniyan TA (2021) Ecological and human health risks associated with metals in water from Anka Artisanal Gold Mining Area, Nigeria. Hum Ecol Risk Assess: an Intern J 27:307–326
Agrawal P, Mittal A, Prakash R, Kumar M, Singh TB, Tripathi SK (2010) Assessment of contamination of soil due to heavy metals around coal fired thermal power plants at Singrauli region of India. Bull Environ ContamToxicol 85:219–223
Ali J, Kazi TG, Afridi HI, Baig JA, Arain MS, Farooq S (2016) The evaluation of sequentially extracted mercury fractions in Thar coal samples by using different extraction schemes. Int J Coal Geol 156:50–58
Altunay N, Tuzen M (2021) A simple and green ultrasound liquid–liquid microextraction method based on low viscous hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for the preconcentration and separation of selenium in water and food samples prior to HG-AAS detection. Food Chem 364:130371
Arain SA, Kazi TG, Afridi HI, Arain MS, Panhwar AH, Khan N, Shah F (2016) A new dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction using ionic liquid based microemulsion coupled with cloud point extraction for determination of copper in serum and water samples. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 126:186–192
Botsou F, Sungur A, Kelepertzis E, Kypritidou Z, Daferera O, Massas I, Soylak M (2022) Estimating remobilization of potentially toxic elements in soil and road dust of an industrialized urban environment. Environ Monit Assess 194:1–18
Chowdhury A, Maiti SK (2016) Identifying the source and accessing the spatial variations, contamination status, conservation threats of heavy metal pollution in the river waters of Sunderban biosphere reserve, India. J Coast Conserv 2:1519–1541
Dai S, Ren D, Zhou Y, Chou CL, Wang X, Zhao L, Zhu X (2008) Mineralogy and geochemistry of a superhigh-organic-sulfur coal, Yanshan Coalfield, Yunnan, China: evidence for a volcanic ash component and influence by submarine exhalation. Chem Geo 255:182–194
Dai S, Ren D, Chou CL, Finkelman RB, Seredin VV, Zhou Y (2012) Geochemistry of trace elements in Chinese coals: a review of abundances, genetic types, impacts on human health, and industrial utilization. Int J Coal Geol 94:3–21
Dai S, Xiaoyun Y, Colin R, Ward JC, Hower LZ, Xibo W, Lixin Z, Deyi R, Robert BF (2018) Valuable elements in Chinese coals: a review. Inter Geo Rev 60:590–620
Donahue CJ, Rais EA (2009) Proximate analysis of coal. J Chem Educ 86:222
EPA, USEPAUS (2011) Exposure factors handbook 2011 edition (final), Washington, DC
Fakhri Y, Khaneghah AM, Conti GO, Ferrante M, Khezri A, Darvishi A, Ahmadi M, Hasanzadeh V, Rahimizadeh A, Keramati H (2018) Probabilistic risk assessment (Monte Carlo simulation method) of Pb and Cd in the onion bulb (Allium cepa) and soil of Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:30894–30906
Fan Y, Zhuo Y, Lou Y, Zhu Z, Li L (2017) SeO2 adsorption on CaO surface: DFT study on the adsorption of a single SeO2 molecule. Appl Surf Sci 413:366–371
Federation WE, Association APH (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association (APHA), Washington, p 21
Finkelman RB (1993) Trace and minor elements in coal. In Org geochemistry Springer, New York 593–607
Finkelman RB (2004) Potential health impacts of burning coal beds and waste banks. Int J Coal Geol 59:19–24
Fu B, Hower JC, Dai SF, Mardon SM, Liu GJ (2018) Determination of chemical speciation of arsenic and selenium in high-As coal combustion ash by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy: examples from a Kentucky stoker ash. ACS Omega 3:17637–17645
Galhardi JA, Bonotto DM (2016) Hydrogeochemical features of surface water and groundwater contaminated with acid mine drainage (AMD) in coal mining areas: a case study in southern Brazil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:18911–18927
George A, Shen B, Kang D, Yang J, Luo J (2020) Emission control strategies of hazardous trace elements from coal-fired power plants in China. J Environ Sci 93:66–90
Ghaffari HR, Kamari Z, Ranaei V, Pilevar Z, Akbari M, Moridi M, Khaneghah AM (2021) The concentration of potentially hazardous elements (PHEs) in drinking water and non-carcinogenic risk assessment: a case study in Bandar Abbas, Iran. Environ Res 201:111567
Gholami Z, Abtahi M, Golbini M, Parseh I, Alinejad A, Avazpour M, Mousavi Khaneghah A (2019) The concentration and probabilistic health risk assessment of nitrate in Iranian drinking water: a case study of Ilam city. Toxin Rev 40:1–10
Gleyzes C, Tellier S, Astruc M (2002) Fractionation studies of trace elements in contaminated soils and sediments: a review of sequential extraction procedures. TrAC Trends Analyt Chem 21:451–467
Graber JM, Stayner LT, Cohen RA, Conroy LM (2014) Attfield MD (2014) Respiratory disease mortality among US coal miners; results after 37 years of follow-up. Occup Environ Med 71:30–39
Greenway GM, Song QJ (2002) An ultrasound accelerated sequential extraction method and its application for element partitioning studies in compost from mixed waste streams. J Environ Monit 4:950–955
Gupta R (2007) Advanced coal characterization: a review. Energy Fuels 21:451–460
Gurdal G (2011) Abundances and modes of occurrence of trace elements in the Can coals heavy metals in sediment by conventional, ultrasound and microwave assisted single extraction methods: a comparison with modified sequential extraction procedure. J Hazard Mater 154:998–1006
Haneef F, Akıntuğ B (2016) Quantitative assessment of heavy metals in coal-fired power plant’s waste water. Int J Sci Tech 2:135–149
Huang Y, Gong H, Hu H, Fu B, Yuan B, Li S, Yao H (2021) Migration and emission behavior of arsenic and selenium in a circulating fluidized bed power plant burning arsenic/selenium-enriched coal. Chemosphere 263:127920
Jamali MK, Kazi TG, Arain MB, Afridi HI, Jalbani N, Memon AR (2007) Heavy metal contents of vegetables grown in soil, irrigated with mixtures of wastewater and sewage sludge in Pakistan, using ultrasonic-assisted pseudo-digestion. J Agron Crop Sci 193:218–228
Kamarehie B, Jafari A, Zarei A, Fakhri Y, Ghaderpoori M, Alinejad A (2019) Non-carcinogenic health risk assessment of nitrate in bottled drinking waters sold in Iranian markets: a Monte Carlo simulation. Accredit Qual Assur 24:417–426
Karami MA, Fakhri Y, Rezania S, Alinejad AA, Mohammadi AA, Yousefi M, Ghaderpoori M, Saghi MH, Ahmadpour M (2019) Non-carcinogenic health risk assessment due to fluoride exposure from tea consumption in iran using monte carlo simulation. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:4261
Kazi TG, Jamali MK, Siddiqui A, Kazi GH, Arain MB, Afridi HI (2006) An ultrasonic assisted extraction method to release heavy metals from untreated sewage sludge samples. Chemosphere 63:411–420
Lashari AA, Kazi TG, Ali J, Afridi HI, Baig JA (2018) Evaluation of sequential extraction schemes for the ETAAS determination of cadmium concentrations in coal samples from the Thar coalfield, Pakistan. At Spectrosc 39:203–209
Lashari AA, Kazi TG, Baig JA, Afridi HI (2020) Fractionation of lead in lignite coal samples of Thar coalfield, Pakistan by time-saving single-step based on BCR sequential extraction scheme. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 39:13439
Latorre CH, García JB, Martín SG, Crecente RP (2013) Solid phase extraction for the speciation and preconcentration of inorganic selenium in water samples: a review. Anal Chim Acta 80:37–49
Levandowski J, Kalkreuth W (2009) Chemical and petrographical characterization of feed coal, fly ash and bottom ash from the Figueira Power Plant, Paraná, Brazil. Int J Coal Geol 77:269–281
Li X, Dai S, Zhang W, Li T, Zheng X, Chen W (2014) Determination of As and Se in coal and coal combustion products using closed vessel microwave digestion and collision/reaction cell technology (CCT) of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Int J Coal Geol 124:1–4
Li Q, Chen P, Chen J, Hu Y (2018) Modes of occurrence of Cr Co, Ni, Cu, Cd, and Pb in the main coal seams of southwestern China’s Nantong coalfield. Geochem Int 56:1220–1232
Liang J, Feng CT, Zeng GM, Gao X, Zhong MZ, Li XD, Li X, He XY, Fang YL (2017) Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in surface soils in a typical coal mine city, Lianyuan, China. Environ Pollut 225:681–690
Liu D (2006) Research on environmental effect and comprehensive utilization of coal-waste rocks. J Meteorol Res Environ 22:60–62
Lucas SA, Planner J (2012) Grounded or submerged bulk carrier: the potential for leaching of coal trace elements to seawater. Mar Pollut Bull 64:1012–1017
Mahapatra D (2016) A review on steam coal–Sampling & preparation. AIJRSTEM 13:1–9
Mardon SM, Hower JC (2004) Impact of coal properties on coal combustion by-product quality: examples from a Kentucky power plant. Int J Coal Geol 59:153–169
Matong JM, Nyaba L, Nomngongo PN (2016) Fractionation of trace elements in agricultural soils using ultrasound assisted sequential extraction prior to inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometric determination. Chemosphere 154:249–257
Meij R, Te Winkel BH (2009) Trace elements in world steam coal and their behaviour in Dutch coal-fired power stations: a review. Int J Coal Geol 773:289–293
Moore F, Nematollahi M, Keshavarzi B (2015) Heavy metals fractionation in surface sediments of Gowatr bay-Iran. Environ Monit Assess 187:4117
Murthy A, Patra HS (2006) Ecological, socio-economic and health impact assessment due to coal mining—a case study of Talabira Coal Mines in Orissa. Vasundhara, Orissa, India
Nagle RD, Rowe CL, Congdon JD (2001) Accumulation and selective maternal transfer of contaminants in the turtle Trachemys scripta associated with coal ash deposition. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 40:531–536
Nazir R, Khan M, Masab M, Rehman HU, Rauf NU, Shahab S, Shaheen Z (2015) Accumulation of heavy metals (Ni, Cu, Cd, Cr, Pb, Zn, Fe) in the soil, water and plants and analysis of physico-chemical parameters of soil and water collected from Tanda Dam Kohat. J Pharm Sci 7:89
Njuguna SM, Makokha VA, Yan X, Gituru RW, Wang Q, Wang J (2019) Health risk assessment by consumption of vegetables irrigated with reclaimed waste water: a case study in Thika (Kenya). J Environ Manag 231:576–581
Ozkantar N, Yilmaz E, Soylak M, Tuzen M (2020) Pyrocatechol violet impregnated magnetic graphene oxide for magnetic solid phase microextraction of copper in water, black tea and diet supplements. Food Chem 321:126737
Panhwar AH, Tuzen M, Kazi TG (2017) Ultrasonic assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method based on deep eutectic solvent for speciation, preconcentration and determination of selenium species (IV) and (VI) in water and food samples. Talanta 175:352–358
Quick JC (2010) Carbon dioxide emission factors for US coal by origin and destination. Environ Sci Tech 44:2709–2714
Qureshi AA, Kazi TG, Baig JA, Arain MB, Afridi HI (2020) Exposure of heavy metals in coal gangue soil, in and outside the mining area using BCR conventional and vortex assisted and single step extraction methods. Impact on orchard grass. Chemosphere 255:126960
Raj D, Abhiroop C, Subodh KM (2017) Ecological risk assessment of mercury and other heavy metals in soils of coal mining area: a case study from the eastern part of a Jharia coal field, India. Hum Ecol Risk Assess: Int J 23:767–787
Rayman MP, Infante HG, Sargent M (2010) Food-chain selenium and human health: spotlight review. Ann Ist Super Sanita 46:279–283
Ribeiro J, Flores D, Ward CR, Silva LF (2010) Identification of nanominerals and nanoparticles in burning coal waste piles from Portugal. Sci Total Environ 408:6032–6041
Saikia BK, Ward CR, Oliveira MLS, Hower JC, Braga M, Silva LF (2014) Geochemistry and nano-mineralogy of two medium-sulfur Northeast Indian coals. Int J Coal Geol 121:26–34
Shen FH, Liu J, Zhang Z, Yang YJ (2016) Temporal measurements and kinetics of selenium release during coal combustion and gasification in a fluidized bed. J Hazard Mater 310:40–47
Silva LFO, Izquierdo M, Querol X, Finkelman RB, Oliveira MLS, Wollenschlager M, Towler M, Pérez-López R, Macias F (2011) Leaching of potential hazardous elements of coal cleaning rejects. Environ Monit Assess 175:109–126
Singh S, Oswal M, Raja SW, Santra S, Acharya R, Behera BR, Singh KP (2020) Chemical characterization of Indian coal and coal residues by PIGE and PIXE spectroscopies using proton beams from tandem particle accelerators. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B : Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms 478:205–217
Soylak M, Uzek U, Narin I, Tuzen M, Turkoglu O, Elci L (2004) Application of the sequential extraction procedure for dust samples from Kayseri-Turkey. Fresenius Environ Bull 13:454–457
Standard A (2008) D3174–04 in standard test method for ash in the analysis sample of coal and coke from coal. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA
Sungur A, Soylak M, Yilmaz E, Yilmaz S, Ozcan H (2015) Characterization of heavy metal fractions in agricultural soils by sequential extraction procedure: the relationship between soil properties and heavy metal fractions. Soil Sediment Contam: an Inter J 24:1–15
Sungur A, Gur ENGIN, Everest T, Soylak M, Ozcan H (2019) Assessment of relationship between geochemical fractions of barium in soil of cherry orchards and plant barium uptake and determination by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. At Spectrosc 40:173
Tang XY, Huang WH (2004) Trace elements in Chinese coal. The Commercial Press (In Chinese), Beijing
Tian HZ, Wang Y, Xue ZG, Cheng K, Qu YP, Chai FH, Hao JM (2010) Trend and characteristics of atmospheric emissions of Hg, As, and Se from coal combustion in China, 1980–2007. Atmospheric Chem Phys 10:11905–11919
Tiewsoh LS, Sivek M, Jirásek J (2017) Traditional energy resources in India (coal, crude oil, natural gas): a review. Energy Sources, Part b: Econ Plan Policy 12:110–118
Tokalıoglu S, Kartal S (2008) Synthesis and application of a new chelating resin functionalized with salicylaldoxime for the determination of Pb (II), Ni (II), Cu (II) and Mn (II) ions in water samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchim Acta 162:87–92
Trechera P, Moreno T, Cordoba P, Moreno N, Zhuang X, Li B, Querol X (2021) Comprehensive evaluation of potential coal mine dust emissions in an open-pit coal mine in Northwest China. Int J Coal Geol 235:103677
Tuzen M, Pekiner OZ (2015) Ultrasound-assisted ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometric for selenium speciation in foods and beverages. Food Chem 188:619–624
Vinceti M, Bonvicini F, Bergomi M, Malagoli C (2010) Possible involvement of overexposure to environmental selenium in the etiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a short review. Ann Ist Super 46:279–283
Wang S, Mulligan CN (2006) Effect of natural organic matter on arsenic release from soils and sediments into groundwater. Environ Geochem Health 28:197–214
Wang X, Jiang Y, Zhou G, Wang P, Wang R, Zhao L, Chou CL (2015) Behavior of minerals and trace elements during natural coking: a case study of an intruded bituminous coal in the Shuoli mine, Anhui Province, China. Energy Fuels 29:4100–4113
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 4th edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Willett JC, Finkelman RB, Kalkrueth W, Gonçalves GSAB (2006) World coal quality inventory: Brazil. US Geological Survey Open-file Report 1241
Yao Y (2016) Enhancement of mass transfer by ultrasound: application to adsorbent regeneration and food drying/dehydration. Ultrason Sonochem 31:512–531
Yenilmez F, Kuter N, Emil MK, Aksoy A (2011) Evaluation of pollution levels at an abandoned coal mine site in Turkey with the aid of GIS. Int J Coal Geol 86:12–19
Zhang H, He PJ, Shao LM (2008) Flow analysis of heavy metals in MSW 606 incinerators for investigating contamination of hazardous components. Environ Sci Technol 42(608):6217
Acknowledgements
Author Ayaz Ali would like to thank the National Centre of Excellence in Analytical Chemistry (NCEAC) University of Sindh Jamshoro for providing financial support and excellent research lab facilities for scholars to carry out research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ayaz Ali: investigation, validation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, software. Tasneem Gul Kazi: supervision, investigation, validation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, software. Jameel Ahmed Baig: supervision, investigation, conceptualization. Hassan Imran Afiridi: investigation, validation Sadam Hussain Junejo: statistical analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Shimin Liu
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lashari, A.A., Kazi, T.G., Baig, J.A. et al. Chemical association of copper and selenium in coals of Sindh by time saving single step strategy and their impact on groundwater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 38650–38662 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-25039-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-25039-5