Abstract
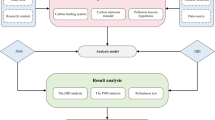
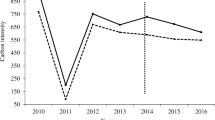
The China government focuses on changes in carbon emission efficiency with establishing carbon emission trade exchange (CETE). It is meaningful to study whether the pilot CETEs can facilitate the betterment of carbon emission efficiency. Using the data of 283 cities in China within 2006–2019, this article gauges the carbon emission efficiency with the SBM-DEA model. This paper analyzes the impact of China’s pilot CETEs, which was gradually launched from 2013 to 2014, on carbon emission efficiency through the time-varying difference-in-difference (DID) model. Finally, the mediating effect model is further used to analyze the impact mechanism of the pilot CETEs on carbon emission efficiency from the perspectives of innovation investment and pollution control investment. The results reveal that the carbon emission efficiency of each city from 2006 to 2019 is not very ideal. All cities have some room to facilitate the carbon emission efficiency. The pilot CETEs have increased the carbon emission efficiency and reduced carbon dioxide emission. The policy influences the carbon emission efficiency through innovation investment and pollution control investment, which represent long-run and short-run mechanism respectively.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Al-Mulali U, Saboori B, Ozturk I (2015) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Vietnam. Energy Policy 76:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2014.11.019
Baron RM, Kenny DA (1986) The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol 51:1173–1182. https://doi.org/10.1037//0022-3514.51.6.1173
Blackman A, Kildegaard A (2010) Clean technological change in developing-country industrial clusters: Mexican leather tanning. Environ Econ Pol Stud 12:115–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10018-010-0164-7
Beck T, Levine R, Levkov A (2010) Big bad banks? The winners and losers from bank deregulation in the United States. J Financ 65(5):1637–1667. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6261.2010.01589.x
Bu M, Qiao Z, Liu B (2020) Voluntary environmental regulation and firm innovation in China. Econ Modell 89:10–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2019.12.020
Charnes A, Cooper WW, Rhodes E (1978) Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur J Oper Res 2:429–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(78)90138-8
Chen Y, Ma X, Yan P, Wang M (2021a) Operating efficiency in Chinese universities: an extended two-stage network DEA approach. J Manag Sci Eng 6(4):482–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmse.2021.08.005
Cheng Z, Liu J, Li L, Gu X (2020) Research on meta-frontier total-factor energy efficiency and its spatial convergence in Chinese provinces. Energ Econ 86:104702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2020.104702
Chen Z, Zhang X, Chen F (2021b) Do carbon emission trading schemes stimulate green innovation in enterprises? Evidence from China. Technol Forecast Soc Change 168:120744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120744
Gao D, Li G, Li Y (2021a) Government cooperation, market integration, and energy efficiency in urban agglomerations—based on the quasi-natural experiment of the Yangtze River Delta Urban Economic Coordination Committee. Energy Environ 10:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1177/0958305X211047480
Du K, Li P, Yan Z (2019) Do green technology innovations contribute to carbon dioxide emission reduction? Empirical evidence from patent data. Technol Forecasting Soc Change 146:297–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2019.06.010
Fare R, Grosskopf S, Pasurka CA (2007) Environmental production functions and environmental directional distance functions. Energy 32(7):1055–1066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2006.09.005
Gao D, Li Y, Yang QY (2021b) Can pollution charges reform promote industrial SO2 emissions reduction? — evidence from 189 China’s cities. Energy Environ 32(1):96–112. https://doi.org/10.1177/0958305X20919410
Gao D, Li G, Li Y, Gao K (2022a) Does FDI improve green total factor energy efficiency under heterogeneous environmental regulation? Evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(17):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-021-17771-1
Gao D, Li Y, Li G (2022b) Boosting the green total factor energy efficiency in urban China: does low-carbon city policy matter? Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(37):56341–56356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19553-9
Gao D, Li G, Yu JY (2022c) Does digitization improve green total factor energy efficiency? Evidence from Chinese 213 cities. Energy 247:123395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.123395
Huang G, Pan W, Hu C, Pan WL, Dai WQ (2021) Energy utilization efficiency of china considering carbon emission—based on provincial panel data. Sustainability 13(2):877–890. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020877
Hu Y, Ren S, Wang Y, Chen X (2020) Can carbon emission trading scheme achieve energy conservation and emission reduction? Evidence from the industrial sector in China. Energy Econ 85:104590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2019.104590
Iacobucci D, Saldanha N, Deng X (2007) A meditation on mediation: evidence that structural equations models perform better than regressions. J Consum Psychol 17(2):139–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1057-7408(07)70020-7
Ignatius J, Ghasemi MR, Zhang FA, Emrouznejad A, Hatami-Marbini A (2016) Carbon efficiency evaluation: an analytical framework using fuzzy DEA. Eur J Oper Res 253:428–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2016.02.014
Jia S, Qiu Y, Yang C (2021) Sustainable development goals, financial inclusion, and grain security efficiency. Agronomy 11(12):2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11122542
Jia S, Yang C, Wang M, Failler P (2022) Heterogeneous impact of land-use on climate change: study from a spatial perspective. Front Environ Sci 10(840603):1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.840603
Judd CM, Kenny DA (1981) Process analysis: estimating mediation in treatment evaluations. Eval Rev 5(5):602–619. https://doi.org/10.1177/0193841X8100500502
Li G, Gao D, Li Y (2022) Dynamic environmental regulation threshold effect of technical progress on green total factor energy efficiency: evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(6):8804–8815. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-021-16292-1
Lin B, Du K (2015) Modeling the dynamics of carbon emission performance in China: a parametric Malmquist Index approach. Energy Econ 49:550–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2015.03.028
Qiang O, Tina-tian W, Ying D, Zhu-ping L, Jahanger A (2021) The impact of environmental regulations on export trade at provincial level in China: evidence from panel quantile regression. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(16):24098–24111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17676-z
Porter ME, van der Linde C (1995) Toward a new conception of the environment-competitiveness relationship. J Econ Perspect 9:97–118. https://doi.org/10.1257/jep.9.4.97
Qi SZ, Cheng SH, Cui JB (2021) Environmental and economic effects of China’s carbon market pilots: empirical evidence based on a DID model. J Clean Prod 279:28801–28810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123720
Rajpurohit SS, Sharma R (2020) Impact of economic and financial development on carbon emission: evidence from emerging Asian economies. Manag Environ Qual 32(2):145–159. https://doi.org/10.1108/MEQ-03-2020-0043
Ren S, Hao Y, Wu H (2022) The role of outward foreign direct investment (OFDI) on green total factor energy efficiency: does institutional quality matters? Evidence China 76(2):102587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2022.102587
Samuel A, Kwame MKE (2018) Financial development and environmental degradation: does political regime matter? J Clean Prod 197:1472–1479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.252
Sarwar S, Alsaggaf MI (2021) The role of governance indicators to minimize the carbon emission: a study of Saudi Arabia. Meq 32(5):970–988. https://doi.org/10.1108/MEQ-11-2020-0275
Shao S, Yang L (2014) Natural resource dependence, human capital accumulation, and economic growth: a combined explanation for the resource curse and the resource blessing. Energy Policy 74:632–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2014.07.007
Sobel ME (1987) Direct and indirect effects in linear structural equation models. Sociol Methods Res 16(1):155–176. https://doi.org/10.1177/0049124187016001006
Su Y, Li Z, Yang C (2021) Spatial interaction spillover effects between digital financial technology and urban ecological efficiency in China: an empirical study based on spatial simultaneous equations. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(16):8535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18168535
Sun W, Huang C (2020) How does urbanization affect carbon emission efficiency? Evidence from China. J Clean Prod 272:122828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122828
Tone K (2001) A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur J Oper Res 130:498–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(99)00407-5
Wang Q, Zhou P, Shen N, Wang S (2013) Measuring carbon dioxide emission performance in Chinese provinces: a parametric approach. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 21:324–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.12.061
Wen S, Jia Z, Chen X (2022) Can low-carbon city pilot policies significantly improve carbon emission efficiency? Empirical evidence from China. J Clean Prod 346:131131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131131
Wu H, Hao Y, Ren S (2020) How do environmental regulation and environmental decentralization affect green total factor energy efficiency: evidence from China. Energy Econ 91:104880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2020.104880
Wu JX, Wu YR, Guo XM, Cheong TS (2016) Convergence of carbon dioxide emissions in Chinese cities: a continuous dynamic distribution approach. Energy Policy 91:207–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2015.12.028
Xie ZH, Wu R, Wang SJ (2021) How technological progress affects the carbon emission efficiency? Evidence from national panel quantile regression. J Clean Prod 307:127–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127133
Yang C, Li T, Albitar K (2021) Does energy efficiency affect ambient PM2.5? The moderating role of energy investment. Front Environ Sci 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2021.707751
Yang T, Chen W, Zhou K, Minglun R (2018) Regional energy efficiency evaluation in China: a super efficiency slack-based measure model with undesirable outputs. J Clean Prod 198:859–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.098
Yang X, Jiang P, Pan Y (2020) Does China’s carbon emission trading policy have an employment double dividend and a Porter effect? Energy Pol 142:111492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111492
Yang ZS, Wei XX (2019) The measurement and influences of China’s urban total factor energy efficiency under environmental pollution: based on the game cross-efficiency DEA. J Clean Prod 209:439–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.271
Yeh T, Chen TP, Lai P-Y (2010) A comparative study of energy utilization efficiency between Taiwan and China. Energy Policy 38:2386–2394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2009.12.030
Zhang YJ, Liu JY (2019) Does carbon emission trading affect the financial performance of high energy-consuming firms in China? Nat Hazards 95(1–2):91–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-018-3434-5
Zhang YJ, Peng YL, Ma CQ, Shen B (2017) Can environmental innovation facilitate carbon emission reduction? Evid China Energy Pol 100:18–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.10.005
Zhang Y, Zhang JK (2019) Estimating the impacts of emission trading scheme on low-carbon development. J Clean Prod 238:117652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117913
Zhang HJ, Duan MS, Deng Z (2019) Have China’s pilot emission trading schemes promoted carbon emission reductions? The evidence from industrial sub-sectors at the provincial level. J Clean Prod 234:912–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.247
Zhou A, Li J (2020) Impact of income inequality and environmental regulation on environmental quality: evidence from China. J Clean Prod 274:123008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123008
Zhu N, Zhu C, Emrouznejad A (2020) A combined machine learning algorithms and DEA method for measuring and predicting the efficiency of Chinese manufacturing listed companies. J Manag Sci Eng 6(4):435–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmse.2020.10.001
Funding
This work was supported by National Social Science Fund Project, China (No: 16BJY014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Jing Chen, Wenlin Gui, and Yunying Huang. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Jing Chen, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. The manuscript was revised by Wenlin Gui and Yunying Huang. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Gui, W. & Huang, Y. The impact of the establishment of carbon emission trade exchange on carbon emission efficiency. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 19845–19859 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23538-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23538-z