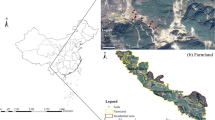
Abstract
Hyperspectral techniques are promising alternatives to traditional methods of investigating potentially toxic metal(loid) contamination. In this study, hyperspectral technology combined with partial least squares regression (PLSR) and extreme learning machine (ELM) established estimation models to predict the contents of copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb) and tin (Sn) in multi-media environments (mine tailings, soils and sediments) surrounding abandoned mineral processing plants in a typical tin-polymetallic mineral agglomeration in Guangxi Autonomous Region. Four spectral preprocessing methods, Savitzky-Golay (SG) smoothing, continuum removal (CR), first derivative (FD) and continuous wavelet transform (CWT), were used to eliminate noise and highlight spectral features. The optimum combinations of spectral preprocessing and machine learning algorithms were explored, then the estimation models with best accuracy were obtained. CWT and CR were excellent spectral pretreatments for the hyperspectral data regardless of the applied algorithms. The coefficients of determination (R2) of estimation models for the best accuracy of various metals (loid) are as follows: Cu (CWT-ELM:0.85), Zn (CR-PLSR:0.93), As (CWT-ELM: 0.86), Cd (CR-PLSR: 0.89), Pb (CWT-PLSR: 0.75) and Sn (CR-ELM: 0.81). In contrast, ELM models had higher accuracy with R2 > 0.80 (except Cd and Pb). In conclusion, ELM-based spectral estimation models are able to predict metal (loid) concentrations with high accuracy and efficiency, providing a potential new combinatorial approach for estimating toxic metal contamination in multi-media environments.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this article.
References
Acosta JA, Faz A, Martínez-Martínez S, Zornoza R, Carmona DM, Kabas S (2011) Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to evaluate heavy metals behavior in mine sites for future reclamation. J Geochem Explor 109(1–3):8–17
Antonucci F, Menesatti P, Holden NM, Canali E, Giorgi S, Maienza A, Stazi SR (2012) Hyperspectral visible and near-infrared determination of copper concentration in agricultural polluted soils. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 43(10):1401–1411
Al Maliki A, Bruce D, Owens G (2014) Prediction of lead concentration in soil using reflectance spectroscopy. Environ Technol Innov 1:8–15
Baumgardner MF et al (1969) "Effects of organic matter on the multispectral properties of soils." Proc Indiana Acad Sci 79:
Bellon-Maurel V, Fernandez-Ahumada E, Palagos B, Roger JM, McBratney A (2010) Critical review of chemometric indicators commonly used for assessing the quality of the prediction of soil attributes by NIR spectroscopy. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 29(9):1073–1081
Ben-Dor E (2002) "Quantitative remote sensing of soil properties.": 173–243
Bian Z, Sun L, Tian K, Liu B, Zhang X, Mao Z, Huang B, Wu L (2021) Estimation of heavy metals in tailings and soils using hyperspectral technology: a case study in a tin-polymetallic mining area. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 107(6):1022–1031
Brewer R, Peard J, Heskett M (2017) A critical review of discrete soil sample data reliability: Part 1—field study results. Soil and Sediment Contamination: an International Journal 26(1):1–22
Chakraborty S, Weindorf DC, Deb S, Li B, Paul S, Choudhury A, Ray DP (2017) Rapid assessment of regional soil arsenic pollution risk via diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Geoderma 289:72–81
Chen H, Teng Y, Lu S, Wang Y, Wang J (2015) Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci Total Environ 512:143–153
Chen HM, Zhu YG (1999) Heavy metal pollution in soils in China: status and coutermeasures. Ambio 28:130–134
Cheng T, Rivard B, Sánchez-Azofeifa A (2010) Spectroscopic determination of leaf water content using continuous wavelet analysis. Remote Sens Environ 115.2:659–670
Clark RN, Roush TL (1984) Reflectance spectroscopy: Quantitative analysis techniques for remote sensing applications. J Geophys Res: Solid Earth 89(B7):6329–6340
Cittadino A, Ocello N, Majul MV, Ajhuacho R, Dietrich P, Igarzabal MA (2020) Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of soils from open dumps in the metropolitan area of Buenos Aires Argentina. Environ Monit Assess 192(5):1–9
CNEMC C (1990) The background concentrations of soil elements of China. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing, China
Demková L, Jezný T, Bobuľská L (2017) Assessment of soil heavy metal pollution in a former mining area–before and after the end of mining activities. Soil and Water Research 12(4):229–236
Diwu PY, Bian XH, Wang ZF, Liu W (2019) Study on the selection of spectral preprocessing methods. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis
Fearn T, Riccioli C, Garrido-Varo A, Guerrero-Ginel JE (2009) On the geometry of SNV and MSC. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 96(1):22–26
Gan FP, Wang RS, Ma AN (2003) Spectral identification tree (SIT) for mineral extraction using AVIRIS data. In multispectral and hyperspectral remote sensing instruments and applications (Vol. 4897, pp. 203–210). International Society for Optics and Photonics
Gholizadeh A, Saberioon M, Ben-Dor E, Borůvka L (2018) Monitoring of selected soil contaminants using proximal and remote sensing techniques: Background, state-of-the-art and future perspectives. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 48(3):243–278
Gholizadeh A, Saberioon M, Ben-Dor E, Rossel RAV, Borůvka L (2020) Modelling potentially toxic elements in forest soils with vis–NIR spectra and learning algorithms. Environ Pollut 267:115574
Gu X, Wang Y, Sun Q, Yang G, Zhang C (2019) Hyperspectral inversion of soil organic matter content in cultivated land based on wavelet transform. Comput Electron Agric 167:105053
Hong Y, Chen S, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Yu L, Liu Y, Liu Y (2018) Rapid identification of soil organic matter level via visible and near-infrared spectroscopy: Effects of two-dimensional correlation coefficient and extreme learning machine. Sci Total Environ 644:1232–1243
Hong Y, Chen S, Chen Y, Linderman M, Mouazen AM, Liu Y, Liu Y (2020) Comparing laboratory and airborne hyperspectral data for the estimation and mapping of topsoil organic carbon: Feature selection coupled with random forest. Soil and Tillage Research 199:104589
Hong Y, Chen Y, Shen R, Chen S, Xu G, Cheng H, Mouazen AM (2021) Diagnosis of cadmium contamination in urban and suburban soils using visible-to-near-infrared spectroscopy. Environ Pollut 291:118128
Hou L, Li X, Li F (2019) Hyperspectral-based inversion of heavy metal content in the soil of coal mining areas. J Environ Qual 48(1):57–63
Hu B, Shao S, Ni H, Fu Z, Hu L, Zhou Y, Shi Z (2020) Current status, spatial features, health risks, and potential driving factors of soil heavy metal pollution in China at province level. Environ Pollut 266:114961
Huang GB, Zhu QY, Siew CK (2006) Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70(1–3):489–501
Huang G, Huang GB, Song S, You K (2015) Trends in extreme learning machines: A review. Neural Netw 61:32–48
Jia X, O’Connor D, Shi Z, Hou D (2021) VIRS based detection in combination with machine learning for mapping soil pollution. Environ Pollut 268:115845
Jiang Q, Li Q, Wang X, Wu Y, Yang X, Liu F (2017) Estimation of soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in different soil layers using VNIR spectroscopy: Effects of spiking on model applicability. Geoderma 293:54–63
Kemper T, Sommer S (2002) Estimate of heavy metal contamination in soils after a mining accident using reflectance spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 36(12):2742–2747
Kebonye NM, John K, Chakraborty S, Agyeman PC, Ahado SK, Eze PN et al (2021) Comparison of multivariate methods for arsenic estimation and mapping in floodplain soil via portable X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy. Geoderma 384:114792
Khosravi V, Ardejani FD, Yousefi S, Aryafar A (2018) Monitoring soil lead and zinc contents via combination of spectroscopy with extreme learning machine and other data mining methods. Geoderma 318:29–41
Lee DT, Yamamoto A (1994) Wavelet analysis: theory and applications. Hewlett Packard J 45:44–44
Li H, Jia S, Le Z (2019) Quantitative analysis of soil total nitrogen using hyperspectral imaging technology with extreme learning machine. Sensors 19(20):4355
Li Z, Ma Z, van der Kuijp TJ, Yuan Z, Huang L (2014) A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: pollution and health risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 468:843–853
Liu G, Zhou X, Li Q, Shi Y, Guo G, Zhao L, Zhang C (2020a) Spatial distribution prediction of soil As in a large-scale arsenic slag contaminated site based on an integrated model and multi-source environmental data. Environ Pollut 267:115631
Liu W, Li M, Zhang M, Long S, Guo Z, Wang H, Yang S (2020b) Hyperspectral inversion of mercury in reed leaves under different levels of soil mercury contamination. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(18):22935–22945
Liu WD (2002) Study on extraction of soil information and data mining by hyperspectral remote sensing. (Doctoral dissertation)
Liu WD, Frédéric B, Zhang B, Zheng LF, Tong QX (2004) Extraction of soil moisture information by hyperspectral remote sensing. Acta Pedol Sin 41(5):706–713
Ma WB, Ta K, Li HD, Yan QW (2016) Hyperspectral inversion of heavy metals in soil of a mining area using extreme learning machine. J Ecol Rural Environ 32(2):213–218
Malmir M, Tahmasbian I, Xu Z, Farrar MB, Bai SH (2019) Prediction of soil macro-and micro-elements in sieved and ground air-dried soils using laboratory-based hyperspectral imaging technique. Geoderma 340:70–80
Montgomery OL (1976) An investigation of the relationship between spectral reflectance and chemical, physical, and genetic characteristics of soils. West Lafayette, Purdue University. Diss. Tese de Doutorado
Mouazen AM, Kuang B, De Baerdemaeker J, Ramon H (2010) Comparison among principal component, partial least squares and back propagation neural network analyses for accuracy of measurement of selected soil properties with visible and near infrared spectroscopy. Geoderma 158(1–2):23–31
Oves M, Khan MS, Zaidi A, Ahmad E (2012) Soil contamination, nutritive value, and human health risk assessment of heavy metals: an overview. Toxicity of heavy metals to legumes and bioremediation 1–27
Qiao P, Yang S, Lei M, Chen T, Dong N (2019) Quantitative analysis of the factors influencing spatial distribution of soil heavy metals based on geographical detector. Sci Total Environ 664:392–413
Qin G, Niu Z, Yu J, Li Z, Ma J, Xiang P (2021) Soil heavy metal pollution and food safety in China: Effects, sources and removing technology. Chemosphere 267:129205
Qu M, Chen J, Huang B, Zhao Y (2020) Enhancing apportionment of the point and diffuse sources of soil heavy metals using robust geostatistics and robust spatial receptor model with categorical soil-type data. Environ Pollut 265:114964
Ren HY, Zhuang DF, Singh AN, Pan JJ, Qiu DS, Shi RH (2009) Estimation of As and Cu contamination in agricultural soils around a mining area by reflectance spectroscopy: A case study. Pedosphere 19(6):719–726
Rinnan Å, Van Den Berg F, Engelsen SB (2009) Review of the most common pre-processing techniques for near-infrared spectra. Trends in Analytical Chemistry (TrAC) 28(10):1201–1222
Savitzky A, Golay MJ (1964) Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal Chem 36(8):1627–1639
Solgi E, Esmaili-Sari A, Riyahi-Bakhtiari A, Hadipour M (2012) Soil contamination of metals in the three industrial estates, Arak Iran. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88(4):634–638
Song SQ, Liang LF, Zhou YZ, Wu H, Zhou X, Zhang XY (2003) The situation and remedial measures of the cropland polluted by heavy metals from mining along the Diaojiang River. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry 22(2):152–155
Song L, Jian J, Tan DJ, Xie HB, Luo ZF, Gao B (2015) Estimate of heavy metals in soil and streams using combined geochemistry and field spectroscopy in Wan-sheng mining area, Chongqing, China. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 34:1–9
Stazi SR, Antonucci F, Pallottino F, Costa C, Marabottini R, Petruccioli M, Menesatti P (2014) Hyperspectral visible–near infrared determination of arsenic concentration in soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 45(22):2911–2920
Sun L, Guo D, Liu K, Meng H, Zheng Y, Yuan F, Zhu G (2019) Levels, sources, and spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils from a typical coal industrial city of Tangshan, China. CATENA 175:101–109
Tan K, Wang H, Zhang Q, Jia X (2018) An improved estimation model for soil heavy metal (loid) concentration retrieval in mining areas using reflectance spectroscopy. J Soils Sediments 18(5):2008–2022
Tan K, Wang H, Chen L, Du Q, Du P, Pan C (2020) Estimation of the spatial distribution of heavy metal in agricultural soils using airborne hyperspectral imaging and random forest. J Hazard Mater 382:120987
Viscarra Rossel RA, Taylor HJ, McBratney AB (2007) Multivariate calibration of hyperspectral γ-ray energy spectra for proximal soil sensing[J]. Eur J Soil Sci 58(1):343–353
Vohland M, Ludwig M, Harbich M, Emmerling C, Thiele-Bruhn S (2016) Using variable selection and wavelets to exploit the full potential of visible–near infrared spectra for predicting soil properties. J near Infrared Spectrosc 24(3):255–269
Wang F, Li C, Wang J, Cao W, Wu Q (2017) Concentration estimation of heavy metal in soils from typical sewage irrigation area of Shandong Province, China using reflectance spectroscopy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(20):16883–16892
Wang F, Gao J, Zha Y (2018) Hyperspectral sensing of heavy metals in soil and vegetation: Feasibility and challenges. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 136:73–84
Wang JN, Zheng LF, Tong QX (1996) Spectral absorption identification model and mapping mineral mapping by airborne high spectral resolution remote sensing data. Proceedings of the Eleventh Thematic Conference-Geologic Remote Sensing: Practical Solutions for Real World Problems
Wold S, Albano C, Dunn WJ, Esbensen K, Hellberg S, Johansson E, Sjöström M (1983) Pattern recognition: finding and using regularities in multivariate data. Food Res Data Anal 3:183–185
Xie XL, Sun B, Hao HT (2007) Relationship between visible-near infrared reflectance spectroscopy and heavy metal of soil concentration. Acta Pedofil Sin 44:982–993
Xie Y, Chen TB, Lei M, Yang J, Guo QJ, Song B, Zhou XY (2011) Spatial distribution of soil heavy metal pollution estimated by different interpolation methods: Accuracy and uncertainty analysis. Chemosphere 82(3):468–476
Yang Q, Li Z, Lu X, Duan Q, Huang L, Bi J (2018) A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 642:690–700
Yu DS, Zhang ZQ, Hao Y, Xue-Zheng SHI, Man-Zhi TAN, Wei-Xia SUN, Wang HJ (2011) Effect of soil sampling density on detected spatial variability of soil organic carbon in a red soil region of China. Pedosphere 21(2):207–213
Zhang B, Guo B, Zou B et al (2022) Retrieving soil heavy metals concentrations based on GaoFen-5 hyperspectral satellite image at an opencast coal mine, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Environ Pollut 300:118981
Zhai M, Hu R, Wang Y, Jiang S et al (2021) Mineral resource science in china: Review and perspective. Geography and Sustainability 2(2):107–114
Zhang S, Shen Q, Nie C, Huang Y, Wang J, Hu Q, Chen Y (2019) Hyperspectral inversion of heavy metal content in reclaimed soil from a mining wasteland based on different spectral transformation and modeling methods. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 211:393–400
Zhou W, Zhang J, Zou M, Liu X, Du X, Wang Q, Li J (2019) Feasibility of using rice leaves hyperspectral data to estimate CaCl 2-extractable concentrations of heavy metals in agricultural soil. Sci Rep 9(1):1–9
Zhou W, Yang H, Xie L, Li H, Huang L, Zhao Y, Yue T (2021) Hyperspectral inversion of soil heavy metals in three-river source region based on random forest model. CATENA 202:105222
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Project of China (2018YFC1802600).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zijin Bian performed the experiments, data analyses and wrote the manuscript; Kang Tian and Lina Sun helped revise the manuscript; Lina Sun, Biao Huang and Longhua Wu helped with the constructive discussion; Benle Liu helped with the experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Written informed consent was obtained from individual or guardian participants.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Marcus Schulz
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bian, Z., Sun, L., Tian, K. et al. Estimation of multi-media metal(loid)s around abandoned mineral processing plants using hyperspectral technology and extreme learning machine. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 19495–19512 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22904-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22904-1