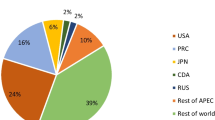
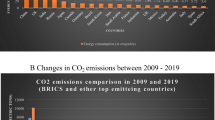
Abstract
Over the last few decades, environmental deterioration has accelerated significantly. Environmental degradation has been a subject of research across the world because of its impact on billions of people. However, there has been no international agreement on lowering the utilization of energy and CO2 emissions (CO2), while demand for fossil fuels grows in emerging economies. On the other hand, the recent COP26 summit brought all parties together to accelerate action toward reaching the goals of the Paris Agreement and the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change. Although previous research shows that international trade promotes positive socioeconomic outcomes, other experts argue that it contributes to natural resource shortages and ecological deterioration. Thus, the current research considers the effect of international trade, renewable energy use and technological innovation on consumption-based carbon emissions (CCO2), coupled with the role of financial development and economic growth in the BRICS economies between 1990 and 2018. Moreover, this research utilizes the common correlated effects mean group (CCEMG), augmented mean group (AMG) and Dumitrescu and Hurlin (2012) causality methods to assess these interrelationships. The study findings reveal that renewable energy use, exports and technological innovation mitigate CCO2, whereas economic growth and imports trigger CCO2 in the BRICS economies. The panel causality outcomes also reveal that all the variables except financial development can predict CCO2 emissions. Based on the study findings, we recommend the adoption of policies, regulations and the development of legislative frameworks that promote technological innovation and the shift toward sustainable energy.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data is readily available on request from the corresponding author.
Notes
International Renewable Energy Agency.
Abbreviations
- AMG:
-
Augmented mean group
- BRICS:
-
Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa
- CO2 :
-
Carbon emissions
- CCO2 :
-
Consumption-based carbon emission
- CCEMG:
-
Common correlated effects mean group
- CSD:
-
Cross-sectional dependence
- GDP:
-
Economic growth
- GHGs:
-
Greenhouse gas emissions
- EXP:
-
Exports
- EMT:
-
Ecological modernization theory
- FD:
-
Financial development
- IMP:
-
Import
- REC:
-
Renewable energy use
- TEC:
-
Technological innovation
References
Acheampong AO, Adams S, Boateng E (2019) Do globalization and renewable energy contribute to carbon emissions mitigation in Sub-Saharan Africa? Sci Total Environ 677:436–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.353
Acheampong AO, Amponsah M, Boateng E (2020) Does financial development mitigate carbon emissions? Evidence from heterogeneous financial economies. Energy Econ 88:104768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2020.104768
Adebayo TS, Acheampong AO (2021) Modelling the globalization-CO2 emission nexus in Australia: evidence from quantile-on-quantile approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(7):9867–9882
Adebayo TS, Kirikkaleli D (2021) Impact of renewable energy consumption, globalization, and technological innovation on environmental degradation in Japan: application of wavelet tools. Environ Dev Sustain 23(11):16057–16082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01322-2
Adebayo TS, Rjoub H (2021) Assessment of the role of trade and renewable energy consumption on consumption-based carbon emissions: evidence from the MINT economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(41):58271–58283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14754-0
Adebayo TS, Awosusi AA, Rjoub H, Panait M, Popescu C (2021) Asymmetric impact of international trade on consumption-based carbon emissions in MINT Nations. Energies 14(20):6581
Adebayo TS, Agyekum EB, Kamel S, Zawbaa HM, Altuntaş M (2022a) Drivers of environmental degradation in Turkey: designing an SDG framework through advanced quantile approaches. Energy Rep 8:2008–2021
Adebayo TS, Awosusi AA, Rjoub H, Agyekum EB, Kirikkaleli D (2022b) The Yuping influence of renewable energy usage on consumption-based carbon emissions in MINT economies. Heliyon 8(2):e08941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e08941
Adedapo AT, Adebayo TS, Akadiri SS, Usman N (2022) Does interaction between technological innovation and natural resource rent impact environmental degradation in newly industrialized countries? New evidence from method of moments quantile regression. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(2):3162–3169
Adedoyin FF, Gumede MI, Bekun FV, Etokakpan MU, Balsalobre-lorente D (2020) Modelling coal rent, economic growth and CO2 emissions: does regulatory quality matter in BRICS economies? Sci Total Environ 710:136284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136284
Adedoyin FF, Ozturk I, Agboola MO, Agboola PO, Bekun FV (2021) The implications of renewable and non-renewable energy generating in Sub-Saharan Africa: the role of economic policy uncertainties. Energy Pol 150:112115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2020.112115
Adeshola I, Adebayo TS, Oladipupo SD, Rjoub H (2021) Wavelet analysis of impact of renewable energy consumption and technological innovation on CO2 emissions: evidence from Portugal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 43(3):1–18
Adewale Alola A, Ozturk I, Bekun FV (2021) Is clean energy prosperity and technological innovation rapidly mitigating sustainable energy-development deficit in selected sub-Saharan Africa? A Myth or Reality Energy Policy 158:112520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112520
Agboola MO, Adebayo TS, R5joub H, Adeshola I, Agyekum EB, Kumar NM (2021) Linking economic growth, urbanization, and environmental degradation in China: what is the role of hydroelectricity consumption? Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(13):6975–6990
Ahmad F, Draz MU, Ozturk I, Su L, Rauf A (2020) Looking for asymmetries and nonlinearities: the nexus between renewable energy and environmental degradation in the Northwestern provinces of China. J Clean Prod 266:121714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121714
Ahmad M, Ahmed Z, Yang X, Hussain N, Sinha A (2021) Financial development and environmental degradation: do human capital and institutional quality make a difference? Gondwana Res 23(3):112–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2021.09.012
Akadırı SS, Alola AA, Usman O (2021) Energy mix outlook and the EKC hypothesis in BRICS countries: a perspective of economic freedom vs. economic growth. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(7):8922–8926
Akadiri SS, Adebayo TS, Rjoub H (2022) On the relationship between economic policy uncertainty, geopolitical risk and stock market returns in South Korea: a quantile causality analysis. Ann Financ Econ 7(2):22–34
Akinsola GD, Adebayo TS, Odugbesan JA, Olanrewaju VO (2021) Determinants of environmental degradation in Thailand: empirical evidence from ARDL and wavelet coherence approaches. Pollution 7(1):181–196
Akinsola GD, Awosusi AA, Kirikkaleli D, Umarbeyli S, Adeshola I, Adebayo TS (2022) Ecological footprint, public-private partnership investment in energy, and financial development in Brazil: a gradual shift causality approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(7):10077–10090
Ali M, Kirikkaleli D (2021) The asymmetric effect of renewable energy and trade on consumption-based CO2 emissions: the case of Italy. Integr Environ Assess Manag 2(11):12–36. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.4516
Ali S, Khan Z, Umar M, Kirikkaleli D, Jiao Z (2020) Consumption-based carbon emissions and International trade in G7 countries: the role of environmental innovation and renewable energy. Sci Total Environ 730:138945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138945
Aliprandi F, Stoppato A, Mirandola A (2016) Estimating CO2 emissions reduction from renewable energy use in Italy. Renew Energy 96:220–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.04.022
Alola AA (2019) The trilemma of trade, monetary and immigration policies in the United States: accounting for environmental sustainability. Sci Total Environ 658:260–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.212
Alola AA, Bekun FV, Sarkodie SA (2019) Dynamic impact of trade policy, economic growth, fertility rate, renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on ecological footprint in Europe. Sci Total Environ 685:702–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.139
Alola AA, Adebayo TS, Onifade ST (2021) Examining the dynamics of ecological footprint in China with spectral granger causality and quantile-on-quantile approaches. Int J Sustain Dev World Ecol 29(3):263–276. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504509.2021.1990158
An H, Razzaq A, Haseeb M, Mihardjo LW (2021) The role of technology innovation and people’s connectivity in testing environmental Kuznets curve and pollution heaven hypotheses across the Belt and Road host countries: new evidence from Method of Moments Quantile Regression. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(5):5254–5270
Anwar A, Sinha A, Sharif A, Siddique M, Irshad S, Anwar W, Malik S (2021) The nexus between urbanization, renewable energy consumption, financial development, and CO2 emissions: evidence from selected Asian countries. Environ Dev Sustain 10(3):23–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01716-2
Awosusi AA, Kirikkaleli D, Akinsola GD, Adebayo TS, Mwamba MN (2021) Can CO2 emissions and energy consumption determine the economic performance of South Korea? A time series analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(29):38969–38984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13498-1
Awosusi AA, Mata MN, Ahmed Z, Coelho MF, Altuntaş M, Martins JM, Martins JN, Onifade ST (2022) How do renewable energy, economic growth and natural resources rent affect environmental sustainability in a globalized economy? Evidence from Colombia based on the gradual shift causality approach. Front Energy Res 9:1–3
Awosusi AA, Adebayo TS, Altuntaş M, Agyekum EB, Zawbaa HM, Kamel S (2022) The dynamic impact of biomass and natural resources on ecological footprint in BRICS economies: a quantile regression evidence. Energy Rep 8:1979–1994
Bekhet HA, Matar A, Yasmin T (2017) CO2 emissions, energy consumption, economic growth, and financial development in GCC countries: dynamic simultaneous equation models. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 70:117–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.11.089
Bekun FV, Alola AA, Sarkodie SA (2019) Toward a sustainable environment: nexus between CO2 emissions, resource rent, renewable and nonrenewable energy in 16-EU countries. Sci Total Environ 657:1023–1029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.104
Boutabba MA (2014) The impact of financial development, income, energy and trade on carbon emissions: evidence from the Indian economy. Econ Model 40:33–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2014.03.005
Charfeddine L, Kahia M (2019) Impact of renewable energy consumption and financial development on CO2 emissions and economic growth in the MENA region: a panel vector autoregressive (PVAR) analysis. Renew Energy 139:198–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.01.010
Chen Y, Lee C-C (2020) Does technological innovation reduce CO2 emissions? Cross-Country Evidence. J Clean Prod 263:121550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121550
Cheng C, Ren X, Dong K, Dong X, Wang Z (2021) How does technological innovation mitigate CO2 emissions in OECD countries? Heterogeneous analysis using panel quantile regression. J Environ Manage 280:111818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111818
Chien F, Anwar A, Hsu CC, Sharif A, Razzaq A, Sinha A (2021) The role of information and communication technology in encountering environmental degradation: proposing an SDG framework for the BRICS countries. Technol Soc 65:101587
Destek MA, Sarkodie SA (2019) Investigation of environmental Kuznets curve for ecological footprint: the role of energy and financial development. Sci Total Environ 650:2483–2489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.017
Ding Q, Khattak SI, Ahmad M (2021) Towards sustainable production and consumption: assessing the impact of energy productivity and eco-innovation on consumption-based carbon dioxide emissions (CCO2) in G-7 nations. Sustain Prod Consum 27:254–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2020.11.004
Dingru L, Ramzan M, Irfan M, Gülmez Ö, Isik H, Adebayo TS, Husam R (2021) The role of renewable energy consumption towards carbon neutrality in BRICS nations: does globalization matter? Front Environ Sci 9(4):7–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2021.796083
Dogan E, Seker F (2016) Determinants of CO2 emissions in the European Union: the role of renewable and non-renewable energy. Renew Energy 94:429–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.03.078
Dumitrescu E-I, Hurlin C (2012) Testing for Granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels. Econ Model 29(4):1450–1460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2012.02.014
Eberhardt M (2012) Estimating panel time-series models with heterogeneous slopes. Stand Genomic Sci 12(1):61–71. https://doi.org/10.1177/1536867X1201200105
Fan H, Hossain MI (2018) Technological innovation, trade openness, CO2 emission and economic growth: comparative analysis between China and India. Int J Energy Econ Pol 8(6):240–257
Fatima T, Shahzad U, Cui L (2021) Renewable and nonrenewable energy consumption, trade and CO2 emissions in high emitter countries: does the income level matter? J Environ Planning Manage 64(7):1227–1251. https://doi.org/10.1080/09640568.2020.1816532
Fernández-Amador O, Francois JF, Oberdabernig DA, Tomberger P (2017) Carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth: an assessment based on production and consumption emission inventories. Ecol Econ 135:269–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2017.01.004
Fu Q, Álvarez-Otero S, Sial MS, Comite U, Zheng P, Samad S, Oláh J (2021) Impact of renewable energy on economic growth and CO2 emissions—evidence from BRICS countries. Processes 9(8):1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9081281
GCA (2019) Global carbon atlas, Retrieved from http://www.globalcarbonatlas.org/en/CO2-emissions. Accessed 12 Feb 2022
Granger CW, Engle R (1983) Applications of spectral analysis in econometrics. Handb Stat 3:93–109
Gyamfi BA, Adebayo TS, Bekun FV, Agyekum EB, Kumar NM, Alhelou HH, Al-Hinai A (2021) Beyond environmental Kuznets curve and policy implications to promote sustainable development in Mediterranean. Energy Rep 7:6119–6129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2021.09.056
Hasanov FJ, Liddle B, Mikayilov JI (2018) The impact of international trade on CO2 emissions in oil exporting countries: territory vs consumption emissions accounting. Energy Econ 74:343–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2018.06.004
Hasanov FJ, Khan Z, Hussain M, Tufail M (2021) Theoretical framework for the carbon emissions effects of technological progress and renewable energy consumption. Sustain Dev 29(5):810–822. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2175
Hashem Pesaran M, Yamagata T (2008) Testing slope homogeneity in large panels. J Econom 142(1):50–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeconom.2007.05.010
He X, Adebayo TS, Kirikkaleli D, Umar M (2021b) Consumption-based carbon emissions in Mexico: an analysis using the dual adjustment approach. Sustain Prod Consum 27:947–957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2021.02.020
He K, Ramzan M, Awosusi AA, Ahmed Z, Ahmad M, Altuntaş M (2021a) Does globalization moderate the effect of economic complexity on CO2 emissions? Evidence from the top 10 energy transition economies. Front Environ Sci 34(5):45–55. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2021.778088
Hussain M. & Khan J. A. (2021). The nexus of environment-related technologies and consumption-based carbon emissions in top five emitters: empirical analysis through dynamic common correlated effects estimator. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15333-z
IEEFA (2016) Institute for energy economics and financial analysis. Retrieved from https://ieefa.org/. Accessed 12 Feb 2022
IRENA (2016) Renewable energy target setting. International Renewable Energy Agency. Retrieved from https://www.irena.org. Accessed 23 Dec 2021
IRENA (2017) Renewable energy target setting. Abu Dhabi, UAE: International Renewable Energy Agency. Retrieved from: https://www.irena.org/publications/2015/Jun/Renewable-Energy-Target-Setting. Accessed 8 Feb 2022
Kapetanios G, Pesaran MH, Yamagata T (2011) Panels with non-stationary multifactor error structures. J Econom 160(2):326–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeconom.2010.10.001
Khan Z, Ali M, Jinyu L, Shahbaz M, Siqun Y (2020a) Consumption-based carbon emissions and trade nexus: evidence from nine oil exporting countries. Energy Economics 89:104806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2020.104806
Khan Z, Ali M, Kirikkaleli D, Wahab S, Jiao Z (2020b) The impact of technological innovation and public-private partnership investment on sustainable environment in China: consumption‐based carbon emissions analysis. Sustain Dev 28(5):1317–1330. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2086
Khattak SI, Ahmad M, Khan ZU, Khan A (2020) Exploring the impact of innovation, renewable energy consumption, and income on CO2 emissions: new evidence from the BRICS economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(12):13866–13881. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07876-4
Kihombo S, Ahmed Z, Chen S, Adebayo TS, Kirikkaleli D (2021) Linking financial development, economic growth, and ecological footprint: what is the role of technological innovation? Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(43):61235–61245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14993-1
Kirikkaleli D, Adebayo TS (2021) Do renewable energy consumption and financial development matter for environmental sustainability? New Global Evidence. Sustain Dev 29(4):583–594
Kirikkaleli D, Güngör H, Adebayo TS (2022) Consumption‐based carbon emissions, renewable energy consumption, financial development and economic growth in Chile. Bus Strategy Environ 31(3):1123–1137. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2945
Knight KW, Schor JB (2014) Economic growth and climate change: a cross-national analysis of territorial and consumption-based carbon emissions in high-income countries. Sustainability 6(6):3722–3731. https://doi.org/10.3390/su6063722
Li M, Ahmad M, Fareed Z, Hassan T, Kirikkaleli D (2021) Role of trade openness, export diversification, and renewable electricity output in realizing carbon neutrality dream of China. J Environ Manage 297:113419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113419
Liddle B (2018) Consumption-based accounting and the trade-carbon emissions nexus. Energy Econ 69:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2017.11.004
Lin B, Zhu J (2019) The role of renewable energy technological innovation on climate change: empirical evidence from China. Sci Total Environ 659:1505–1512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.449
Lin X, Zhao Y, Ahmad M, Ahmed Z, Rjoub H, Adebayo TS (2021) Linking innovative human capital, economic growth, and CO2 emissions: an empirical study based on Chinese provincial panel data. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(16):8503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18168503
Mensah CN, Long X, Boamah KB, Bediako IA, Dauda L, Salman M (2018) The effect of innovation on CO2 emissions of OCED countries from 1990 to 2014. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(29):29678–29698
Miao Y, Razzaq A, Adebayo TS, Awosusi AA (2022) Do renewable energy consumption and financial globalisation contribute to ecological sustainability in newly industrialized countries? Renew Energy 185(12):688–697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.01.073
Mikayilov JI, Galeotti M, Hasanov FJ (2018) The impact of economic growth on CO2 emissions in Azerbaijan. J Clean Prod 197:1558–1572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.269
Mikayilov JI, Hasanov FJ, Liddle B (2018) The impact of international trade on CO2 emissions in oil exporting countries: territory vs consumption emissions accounting. Energy Econ 74:343–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2018.06.004
Odugbesan JA, Adebayo TS (2021) Modeling CO2 emissions in South Africa: empirical evidence from ARDL based bounds and wavelet coherence techniques. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(8):9377–9389
Odugbesan JA, Adebayo TS, Awosusi AA, Akinsola GD, Wong WK, Rjoub H (2021) Sustainability of energy-induced growth nexus in Brazil: do carbon emissions and urbanization matter? Sustainability 13(8):4371
OEC (2021) Observatory of economic complexity. Retrieved from: https://atlas.cid.harvard.edu/. Accessed 10 Feb 2022
Oladipupo SD, Adebayo TS, Awosusi AA, Agyekum EB, Jayakumar A, Kumar NM (2021) Dominance of fossil fuels in Japan’s national energy mix and implications for environmental sustainability. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(14):7347–7356
Onifade ST, Alola AA, Adebayo TS, Obumneke M (2022) Does it take international integration of natural resources to ascend the ladder of environmental quality in the newly industrialized countries? Resour Pol 4(2):23–33
Orhan A, Adebayo TS, Genç SY, Kirikkaleli D (2021) Investigating the linkage between economic growth and environmental sustainability in India: do agriculture and trade openness matter? Sustainability 13(9):4753. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094753
Ozturk I, Acaravci A (2016) Energy consumption, CO2 emissions, economic growth, and foreign trade relationship in Cyprus and Malta. Energy Sources B: Econ Plan Policy 11(4):321–327
Paramati SR, Mo D, Gupta R (2017) The effects of stock market growth and renewable energy use on CO2 emissions: evidence from G20 countries. Energy Econ 66:360–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2017.06.025
Pata UK (2021a) Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption, economic complexity, CO2 emissions, and ecological footprint in the USA: testing the EKC hypothesis with a structural break. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(1):846–861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10446-3
Pata UK (2021b) Linking renewable energy, globalization, agriculture, CO2 emissions and ecological footprint in BRIC countries: a sustainability perspective. Renew Energy 173(23):197–208
Pesaran MH (2006) Estimation and Inference in large heterogeneous panels with a multifactor error structure. Econometrica 74(4):967–1012. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0262.2006.00692.x
Pesaran MH (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross‐section dependence. J Appl Econom 22(2):265–312
Pesaran MH, Smith R (1995) Estimating long-run relationships from dynamic heterogeneous panels. J Econ 68(1):79–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4076(94)01644-F
Rahman MM (2020) Environmental degradation: the role of electricity consumption, economic growth and globalisation. J Environ Manage 253:109742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109742
Ramzan M, Adebayo TS, Iqbal HA, Awosusi AA, Akinsola GD (2021) The environmental sustainability effects of financial development and urbanization in Latin American countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(41):57983–57996
Razzaq A, Wang Y, Chupradit S, Suksatan W, Shahzad F (2021) Asymmetric inter-linkages between green technology innovation and consumption-based carbon emissions in BRICS countries using quantile-on-quantile framework. Technol Soc 66:101656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101656
Razzaq A, Sharif A, Najmi A, Tseng ML, Lim MK (2021) Dynamic and causality interrelationships from municipal solid waste recycling to economic growth, carbon emissions and energy efficiency using a novel bootstrapping autoregressive distributed lag. Resour Conserv Recycl 166:105372
Sarkodie SA, Adams S (2018) Renewable energy, nuclear energy, and environmental pollution: accounting for political institutional quality in South Africa. Sci Total Environ 643:1590–1601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.320
Sekali J, Bouzahzah M (2019) Financial development and environmental quality: empirical evidence for Morocco. Int J Energy Econ Pol 9(2):67–74
Shahbaz M, Kumar Tiwari A, Nasir M (2013) The effects of financial development, economic growth, coal consumption and trade openness on CO2 emissions in South Africa. Energy Pol 61:1452–1459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2013.07.006
Shahbaz M, Shahzad SJH, Mahalik MK, Hammoudeh S (2018) Does globalisation worsen environmental quality in developed economies? Environ Model Assess 23(2):141–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-017-9574-2
Shan S, Ahmad M, Tan Z, Adebayo TS, Man Li RY, Kirikkaleli D (2021) The role of energy prices and non-linear fiscal decentralization in limiting carbon emissions: tracking environmental sustainability. Energy 234:121243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.121243
Solarin SA, Al-Mulali U, Musah I, Ozturk I (2017) Investigating the pollution haven hypothesis in Ghana: an empirical investigation. Energy 124:706–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.02.089
Solarin SA, Al-Mulali U, Gan GGG, Shahbaz M (2018) The impact of biomass energy consumption on pollution: evidence from 80 developed and developing countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(23):22641–22657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2392-5
Su ZW, Umar M, Kirikkaleli D, Adebayo TS (2021) Role of political risk to achieve carbon neutrality: evidence from Brazil. J Environ Manag 298:113463
Sulaiman C, Abdul-Rahim AS, Ofozor CA (2020) Does wood biomass energy use reduce CO2 emissions in European Union member countries? Evidence from 27 members. J Clean Prod 253:119996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.119996
Sun Y, Bao Q, Siao-Yun W, Islam MU, Razzaq A (2022) Renewable energy transition and environmental sustainability through economic complexity in BRICS countries: fresh insights from novel Method of Moments Quantile regression. Renew Energy 184:1165–1176
Tamazian A, Chousa JP, Vadlamannati KC (2009) Does higher economic and financial development lead to environmental degradation: evidence from BRIC countries. Energy Pol 37(1):246–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2008.08.025
Udemba EN, Adebayo TS, Ahmed Z, Kirikkaleli D (2021) Determinants of consumption-based carbon emissions in Chile: an application of non-linear ARDL. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(32):43908–43922. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13830-9
Umar M, Ji X, Kirikkaleli D, Xu Q (2020) COP21 roadmap: do innovation, financial development, and transportation infrastructure matter for environmental sustainability in China? J Environ Manage 271:111026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111026
Wang KH, Liu L, Adebayo TS, Lobonț OR, Claudia MN (2021) Fiscal decentralization, political stability and resources curse hypothesis: a case of fiscal decentralized economies. Resour Pol 72:102071
Westerlund J (2007) Testing for Error correction in panel data*. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 69(6):709–748. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0084.2007.00477.x
World Bank (2021) World development indicators. Retrieved from http://data.worldbank.org/country. Accessed 5 Dec 2021
Xu D, Salem S, Awosusi AA, Abdurakhmanova G, Altuntaş M, Oluwajana D, Kirikkaleli D, Ojekemi O (2022) Load capacity factor and financial globalization in Brazil: the role of renewable energy and urbanization. Front Environ Sc 6(9):4–20. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2021.823185
Yii K-J, Geetha C (2017) The Nexus between technology innovation and CO2 emissions in Malaysia: evidence from granger causality test. Energy Procedia 105:3118–3124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.654
Yuping L, Ramzan M, Xincheng L, Murshed M, Awosusi AA, BAH SI, Adebayo TS (2021) Determinants of carbon emissions in Argentina: the roles of renewable energy consumption and globalization. Energy Rep 7:4747–4760
Zhang L, Li Z, Kirikkaleli D, Adebayo TS, Adeshola I, Akinsola GD (2021) Modeling CO2 emissions in Malaysia: an application of Maki cointegration and wavelet coherence tests. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(20):26030–26044. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12430-x
Zhuang Y, Yang S, Razzaq A, Khan Z (2021) Environmental impact of infrastructure-led Chinese outward FDI, tourism development and technology innovation: a regional country analysis. J Environ Plan Manag 1–33
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OO designed the experiment and collected the dataset. The introduction and literature review sections were written by HR, and OO constructed the methodology section and empirical outcomes in the study. HR, AAA and EBA contributed to the validation and review of the study. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study followed all ethical practices during writing.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Arshian Sharif
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ojekemi, O.S., Rjoub, H., Awosusi, A.A. et al. Toward a sustainable environment and economic growth in BRICS economies: do innovation and globalization matter?. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 57740–57757 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19742-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19742-6