Abstract
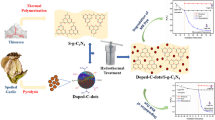
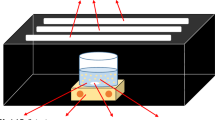
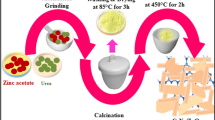
The pyrolysis of melamine was an effective one-pot method for preparing a nanostructured multifunctional photocatalytic based on core/shell g-C3N4@TiO2 heterojunction. Various techniques entirely characterized these materials: X-ray diffraction (XRD) proved to enhance the as-prepared materials’ crystallinity through the variation of dislocation, strain, and crystallite size with TiO2 loading. The stacked layered/sheet-like with a smooth surface of the as-prepared samples have been shown via scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) showed an apparent decrease in the energy bandgap for these nanocomposites with TiO2 loading. All the prepared materials were subjected to visible photocatalytic applications under the same conditions. The dye model (Methylene Blue, MB), and antibiotic model (Amoxicillin, AMO), was photodegraded using the as-prepared nanocomposites under visible light irradiation. In the recombination reduction among TiO2 and g-C3N4 interfaces, g-C3N4 has been effectively utilized as a matrix. Our findings proved that g-C3N4@TiO2 photocatalysts exhibited superior photocatalytic performance. CNT-5 of 2.58 eV bandgap had a higher activity of 99.7 in 50 min for MB and 100% in 20 min for AMO than the other represented photocatalysts in this work. The migration of photogenerated electrons from a g-C3N4 to TiO2 via heterojunction among them as g-C3N4 (1 0 1) removes the electrons accumulated on (1 0 1) of TiO2, improve the photodegradation efficiency. Therefore, the increase in photocatalytic reaction rates, recycling, and the sample’s photostability can be considered the result of successful interactions among the TiO2 and g-C3N4 systems. The suggested photodegradation mechanism of MB and AMO was discussed in detail and compared with previously reported work. Therefore, the photodegradation rate of MB and AMO via CNT-5 composite is 6 and 3 times, respectively, higher than that of g-C3N4 under simulated solar irradiation. This research creates a new perspective on the production of nanocomposite materials in the area of treatment of pharmaceutical and dye contaminants.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data and materials are available upon request.
References
Al-Hajji LA, Ismail AA, Faycal Atitar M, Abdelfattah I, El-Toni AM (2019) Construction of mesoporous g-C3N4/TiO2 nanocrystals with enhanced photonic efficiency. Ceram Int 45:1265–1272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.10.009
Bai X, Wang L, Zong R, Zhu Y (2013) Photocatalytic activity enhanced via g-C3N4 nanoplates to nanorods. J Phys Chem C 117:9952–9961. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp402062d
Cao SW, Low JX, Yu JG, Jaroniec M (2015) Polymeric photocatalysts based on graphitic carbon nitride. Adv Mater 27:2150–2176. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201500033
Chen X, Liu L, Yu PY, Mao SS (2011) Increasing solar absorption for photocatalysis with black hydrogenated titanium dioxide nanocrystals. Science. 331:746–750. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1200448
Chen Z, Dinh HN, Miller E (2013) Photoelectrochemical water splitting. Springer Briefs in Energy. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-8298-7
Chunyong Z, Mingshi L, Lu M, Guohua Z, Zheng C, Yingpin W, Cheng J (2017a) Preparation of high activity TiO2/g-C3N4 photocatalysts via a facile sol-gel method with Ti(OBu)4 as Ti source and melamine as nitrogen source, Rare Metal Materials and Engineering. 46. Issue 2:322–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1875-5372(17)30088-7
Chunyong Z, Mingshi L, Lu M, Guohua Z, Zheng C, Yingpin W, Cheng J (2017b) Preparation of high activity TiO2/g-C3N4 photocatalysts via a facile sol-gel method with Ti(OBu)4 as Ti source and melamine as nitrogen Source. Rare Metal Mater Eng 46(2):0322–0325. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1875-5372(17)30088-7
Davis EA, Mott NF (1970) Conduction in non-crystalline systems V. Conductivity, optical absorption and photoconductivity in amorphous semiconductors. Philos Mag 22:903. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786437008221061
Dong CC, Ji JH, Yang Z (2019) Research progress of photocatalysis based on highly dispersed titanium in mesoporous SiO2. Chin Chem Lett 30:853–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2019.03.020
Dou M, Wang J, Gao B, Xu C, Yang F (2020) Photocatalytic difference of amoxicillin and cefotaxime under visible light by mesoporous g-C3N4: Mechanism, degradation pathway and DFT calculation. Chem Eng J 383:123134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123134
Fajrina N, Tahir M (2019) 2D-montmorillonite-dispersed g-C3N4/TiO2 2D/0Dnanocomposite for enhanced photo-induced H2 evolution from glycerol-water mixture Appl. Surf Sci 471:1053–1064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.12.076
Fang H, Wang Z, Li Y, Peng S, Liu B (2020) The nonmetal modulation of composition and morphology of g-C3N4-based photocatalysts. Appl Catal B Environ 269:118828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118828
Feng M, Qu R, Zhang X, Sun P, Sui Y, Wang L, Wang Z (2015) Degradation of flumequine in aqueous solution by persulfate activated with common methods and polyhydroquinone-coated magnetite/multi-walled carbon nanotubes catalysts. Water Res 85:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.08.011
Fu D, Han G, Liu F, Xiao Y, Wang H, Liu R (2014) Visible-light enhancement of methylene blue photodegradation by graphitic carbon nitridetitania composites. Mater Sci Semicond Process 27:966–974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2014.08.004
Fujishima A, Honda K (1972) Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature. 238:37–38. https://doi.org/10.1038/238037a0
Ganiyu SO, Oturan N, Raffy S, Cretin M, Esmilaire R, van Hullebusch E, Esposito G, Oturan MA (2016) Sub-stoichiometric titanium oxide (Ti4O7) as a suitable ceramic anode for electrooxidation of organic pollutants: a case study of kinetics, mineralization and toxicity assessment of amoxicillin. Water Res 106:171–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.09.056
Gao Y, Yu G, Liu K, Deng S, Wang B, Huang J, Wang Y (2017) Integrated adsorption and visible-light photodegradation of aqueous clofibric acid and carbamazepine by a Fe-based metal-organic framework. Chem Eng J 330:157–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.06.139
Gu L, Wang J, Zou Z, Han X (2014) Graphitic-C3N4-hybridized TiO2 nanosheets with reactive {0 0 1} facets to enhance the UV- and visible-light photocatalytic activity. J Hazard Mater 268:216–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.01.021
Gu W, Lu F, Wang C, Kuga S, Wu L, Huang Y, Wu M (2017) Face-to-face interfacial assembly of ultrathin g-C3N4 and anatase TiO2 nanosheets for enhanced solar photocatalytic activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:28674–28684. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b10010
Hernandez-Alonso MD, Fresno F, Suarez S, Coronado JM (2009) Development of alternative photocatalysts to TiO2: challenges and opportunities. Energy Environ Sci 2:1231–1257. https://doi.org/10.1039/B907933E
Hirte K, Seiwert B, Schüürmann G, Reemtsma T (2016) New hydrolysis products of the beta-lactam antibiotic amoxicillin, their pH-dependent formation and search in municipal wastewater. Water Res 88:880–888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.11.028
Hussien MSA (2021) Facile synthesis of nanostructured Mn-doped Ag3PO4 for visible photodegradation of emerging pharmaceutical contaminants: streptomycin photodegradation. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01831-z
Hussien MSA, Mohammed MI, Yahia IS (2020) Flexible photocatalytic membrane based on CdS/PMMA polymeric nanocomposite films: multifunctional materials. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:45225–45237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10305-1
Jiang Z, Zhu C, Wan W, Qian K (2016) constructing graphite-like carbon nitride modified hierarchical yolk–shell TiO2 spheres for water pollution treatment and hydrogen production. J Mater Chem A 4:1806–1818. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA09919F
Kale D, Thakur P (2015) Highly efficient photocatalytic degradation and mineralization of 4-nitrophenol by graphene decorated ZnO. J Porous Mater 22:797–806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-015-9953-5
Li K, Gao S, Wang Q, Xu H, Wang Z, Huang B, Dai Y, Lu J (2015a) In-situ-reduced synthesis of Ti3+ self-doped TiO2/g-C3N4 heterojunctions with high photocatalytic performance under LED light irradiation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(17):9023–9030. https://doi.org/10.1021/am508505n
Li Y, Wang J, Yang Y, Zhang Y, He D, An Q, Cao G (2015b) Seed-induced growing various TiO2 nanostructures on g-C3N4 nanosheets with much enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light. J Hazard Mater 292:79–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.03.006
Li C, Sun Z, Zhang W, Yu C, Zheng S (2018) highly efficient g-C3N4/TiO2/kaolinite composite with novel three-dimensional structure and enhanced visible light responding ability towards ciprofloxacin and S. aureus. Appl Catal B Environ 220:272–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.08.044
Lightcap IV, Kosel TH, Kamat PV (2010) Anchoring semiconductor and metal nanoparticles on a two-dimensional catalyst mat. Storing and shuttling electrons with reduced graphene oxide. Nano Lett 10:577–583. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl9035109
Liu W, Li Y, Liu F, Jiang W, Zhang D, Liang J (2019) Visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of diclofenac by carbon quantum dots modified porous g-C3N4: mechanisms, degradation pathway and DFT calculation. Water Res 151:8–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.11.084
Ma X, Xiang Q, Liao Y, Wen T, Zhang H (2018) Visible-light-driven CdSe quantum dots/graphene/TiO2 nanosheets composite with excellent photocatalytic activity for E. coli disinfection and organic pollutant degradation. Appl Surf Sci 457:846–855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.07.003
Miranda C, Mansilla H, Yánez J, Obregón S, Colón G (2013) Improved photocatalytic activity of g-C3N4/TiO2 composites prepared by a simple impregnation method. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 253:16–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2012.12.014
Mohamad AM, Salleh WNW, Jaafar J, Rosmi MS, Hir ZAM, Mutalib MA, Ismail AF, Tanemura M (2017) Carbon as amorphous shell and interstitial dopant in mesoporous rutile TiO2: Bio-template assisted sol-gel synthesis and photocatalytic activity. Appl Surf Sci 393:46–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.09.145
Mohamad AM, Zain MFM, Minggu LJ, Kassim MB, Jaafar J, Amin NAS, Ng YH (2019) Revealing the role of kapok fibre as bio-template for In-situ construction of C-doped g-C3N4@C, N co-doped TiO2 core-shell heterojunction photocatalyst and its photocatalytic hydrogen production performance. Appl Surf Sci 476:205–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.01.080
Shao SC, Hu YY, Cheng JH, Chen YC (2018) Research progress on distribution,migration, transformation of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in aquatic environment. Crit Rev Biotechnol 38:1195–1208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2019.03.020
Shen J, Yang H, Shen Q, Feng Y, Cai Q (2014) Template-free preparation and properties of mesoporous g-C3N4/TiO2 nanocomposite photocatalyst. Cryst Eng Comm 16:1868–1872. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CE42513D
Shen L, Xing Z, Zou J (2017) Black TiO2 nanobelts/g-C3N4 nanosheets laminated heterojunctions with efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic performance. Sci Rep 7:41978. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41978
Sher Shah MSA, Park R, Zhang K, Park JH, Yoo PJ (2012) Green synthesis of biphasic TiO2-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites with highly enhanced photocatalytic activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:3893–3901. https://doi.org/10.1021/am301287m
Sobana N, Thirumalai K (2016) Kinetics of solar light assisted degradation of direct red 23 on activated carbon-loaded zinc oxide and influence of operational parameters, Can. Chem Trans 4:77–89. https://doi.org/10.13179/canchemtrans.2016.04.01.0258
Song G, Chu Z, Jin W, Sun H (2015) Enhanced performance of g-C3N4/TiO2 photocatalysts for degradation of organic pollutants under visible light, Chinese J. Chem Eng 23:1326–1334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2015.05.00
Song X, Hu Y, Zheng M, Wei C (2016) Solvent-free in situ synthesis of g-C3N4/{001}TiO2 composite with enhanced UV- and visible-light photocatalytic activity for NO oxidation. Appl Catal B Environ 182:587–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.10.007
Sridharan K, Jang E, Park TJ (2013) Novel visible light active graphitic C3N4- TiO2 composite photocatalyst: Synergistic synthesis, growth and photocatalytic treatment of hazardous pollutants. Appl Catal B Environ 142-143:718–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.05.077
Tauc J, Grigorovici R, Vancu A (1966) Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys Status Solidi 15:627–637. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.19660150224
Thomas M (2016) Effective photocatalytic degradation of Congo red dye using alginate/carboxymethyl cellulose/TiO2 nanocomposite hydrogel under direct sunlight irradiation. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 327:33–43
Tong H, Enomoto N, Inada M, Tanaka Y (2014) Hydrothermal synthesis of mesoporous TiO2-SiO2 core-shell composites for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Hojo. Electrochim Acta 130:329–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.03.032
Tong Z, Yang D, Xiao T, Tian Y, Jiang Z (2015) Biomimetic fabrication of g-C3N4/TiO2 nanosheets with enhanced photocatalytic activity toward organic pollutant degradation. Chem Eng J 260:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.08.072
Tripathi A, Narayanan S (2018) Impact of TiO2 and TiO2/g-C3N4 Nanocomposite to treat industrial wastewater. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 10:280–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2018.07.010
Trovó AG, Pupo Nogueira RF, Agüera A, Fernandez-Alba AR, Malato S (2011) Degradation of the antibiotic amoxicillin by photo-Fenton process – chemical and toxicological assessment. Water Res 45:1394–1402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.10.029
Wang X, Blechert S (2012) Markus Antonietti. Polymeric graphitic carbon nitride for heterogeneous photocatalysis. ACS Catal 2:1596–1606. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs300240x
Wang Q, Tian S, Ning P (2014) Degradation mechanism of methylene blue in a heterogeneous fenton-like reaction catalyzed by ferrocene. Ind Eng Chem Res 53(2):643–649. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie403402q
Wang H, Wu Y, Feng M, Tu W, Xiao T, Xiong T, Ang H, Yuan X, Chew JW (2018) Visible-light-driven removal of tetracycline antibiotics and reclamation of hydrogen energy from natural water matrices and wastewater by polymeric carbon nitride foam. Water Res 144:215–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.07.025
Wang H, Sun Y, Wu Y, Wenguang T, Wu S, Yuan X, Zeng G, Xu ZJ, Li S, Chew JW (2019a) Electrical promotion of spatially photoinduced charge separation via interfacial-built-in quasi-alloying effect in hierarchical Zn2In2S5/Ti3C2(O, OH)x hybrids toward efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution and environmental remediation. Appl Catal B Environ 245:290–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.12.051
Wang X, Zhang H, Liu X (2019b) A free-standing carbon nitride actuator is driven by the ambient humidity. Diam Relat Mater 97:107434. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DIAMOND.2019.05.019
Weng X, Sun Q, Lin S, Chen Z, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2014) Enhancement of catalytic degradation of amoxicillin in aqueous solution using clay supported bimetallic Fe/Ni nanoparticles. CHEMOSPHERE. 103:80–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.11.033
Woolerton TW, Sheard S, Reisner E, Pierce E, Ragsdale SW, Armstrong FA (2010) Efficient and clean photoreduction of CO2 to CO by enzyme-modified TiO2 nanoparticles using visible light. J Am Chem Soc 132:2132–2133. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja910091z
Wu Y, Tao L, Zhao J, Yue X, Deng W, Li Y, Wang C (2015) TiO2/g-C3N4 nanosheets hybrid photocatalyst with enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation. Res Chem Intermed 42:3609–3624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-015-2234-8
Xinmin Y, Zhang X, Zhao J, Xu L, Yan J (2020) Flower-like shaped Bi12TiO20/g-C3N4 heterojunction for effective elimination of organic pollutants: Preparation, characterization, and mechanism study. Appl Organomet Chem 34:5702. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.5702
Yinghua L, Wang H, Li L, Wenquan C (2015) Facile Synthesis of Ag@AgCl Plasmonic photocatalyst and its photocatalytic degradation under visible light. Rare Metal Mater Eng 44:1088–1093. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1875-5372(15)30072-2
Yu K-s, Shi J-y, Zhang Z-l, Liang Y-m, Liu W (2013) Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalysis of ZnO and Er-doped ZnO. J Nanomater 2013:372951. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/372951
Zhang L, Jing D, She X, Liu H, Yang D, Lu Y, Li J, Zheng Z, Guo L (2014) Heterojunctions in g-C3N4/TiO2(B) nanofibres with exposed (001) plane and enhanced visible-light photoactivity. J Mater Chem A 2:2071–2078. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA14047D
Zhang H, Liu F, Wu H, Cao X, Sun J, Lei W (2017) In situ synthesis of g-C3N4/TiO2 heterostructures with enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light. RSC Adv 7:40327–40333. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA06786K
Acknowledgements
The authors express their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University.
Funding
The research groups program at King Khalid University under grant number R.G.P. 2/64/40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, software, and formal analysis. Mai S.A. Hussien, Ibrahim S. Yahia
Visualization and resources. Mai S.A. Hussien, Ibrahim S. Yahia
Data curation, writing - review and editing Mai S.A. Hussien, Ibrahim S. Yahia
Methodology, writing - review and editing, and project administration Mai S.A. Hussien, Ibrahim S. Yahia
Project administration and funding acquisition Ibrahim S. Yahia
Supervision Mai S.A. Hussien, Ibrahim S. Yahia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not Applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sami Rtimi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussien, M.S.A., Yahia, I.S. Hybrid multifunctional core/shell g-C3N4@TiO2 heterojunction nano-catalytic for photodegradation of organic dye and pharmaceutical compounds. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 29665–29680 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12680-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12680-9