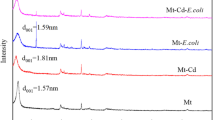
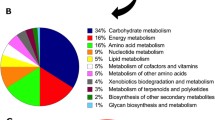
Abstract
Ampicillin and tetracycline are common antibiotics and can threaten humans by inducing antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Microorganisms are usually exposed to a mixed antibiotic system in the environment. However, there are few researches on the specific regulatory mechanisms of clay on microorganisms under the stress of complex antibiotics. In this study, tandem mass tag-based coupled with two-dimensional liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) was employed to recognize and quantify changes in protein expression of Escherichia coli (E. coli) after culture for 15 days, with or without kaolinite in the co-stress of ampicillin and tetracycline. The results indicated that kaolinite could activate metabolic pathways of E. coli such as the energy metabolism, the biosynthesis of other secondary metabolites, and the metabolism of cofactors and vitamins. Particularly, the fatty acid degradation pathway has also been promoted, indicating that in the same unfavorable environment, kaolinite might influence the composition of E. coli cell membranes. This might be due to the change in membrane composition that was a kind of adaptive strategy of bacterial evolution. Moreover, kaolinite could promote multidrug efflux system to export the bacterial intracellular toxic substances, making E. coli survive better in an adverse environment. Consequently, this study not only disclosed the regulation of kaolinite on E. coli in a complex antibiotic environment but also provided new insights into the environmental process of antibiotic resistance.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Al-Wabel MI, Ahmad M, Usman ARA, Sallam AS, Hussain Q, Binyameen RB, Shehu MR, Ok YS (2020) Evaluating the efficiency of different natural clay sediments for the removal of chlortetracycline from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 384:121500
Awfa D, Ateia M, Fujii M, Johnson MS, Yoshimura C (2018) Photodegradation of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in water treatment using carbonaceous-TiO2 composites: a critical review of recent literature. Water Res 142:26–45
Ben Y, Fu C, Hu M, Liu L, Wong MH, Zheng C (2019) Human health risk assessment of antibiotic resistance associated with antibiotic residues in the environment: a review. Environ Res 169:483–493
Blanco P, Hernando-Amado S, Reales-Calderon JA, Corona F, Lira F, Alcalde-Rico M, Bernardini A, Sanchez MB, Martinez JL (2016) Bacterial multidrug efflux pumps: much more than antibiotic resistance determinants. Microorganisms 4
Cai P, Liu X, Ji D, Yang S, Walker SL, Wu Y, Gao C, Huang Q (2018) Impact of soil clay minerals on growth, biofilm formation, and virulence gene expression of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Environ Pollut 243:953–960
Cao Y, Wei X, Cai P, Huang Q, Rong X, Liang W (2011) Preferential adsorption of extracellular polymeric substances from bacteria on clay minerals and iron oxide. Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces 83:122–127
Chen Y, Wang M, Zhou X, Fu H, Qu X, Zhu D (2021) Sorption fractionation of bacterial extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on mineral surfaces and associated effects on phenanthrene sorption to EPS-mineral complexes. Chemosphere 263:128264
Dai G, Wang B, Huang J, Dong R, Deng S, Yu G (2015) Occurrence and source apportionment of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the Beiyun River of Beijing, China. Chemosphere 119:1033–1039
Dai Q, Zhao Y, Dong F, Wang B, Huang Y (2014) Interaction between bentonite and Bacillus litoralis strain SWU9. Appl Clay Sci 100:88–94
Du H, Qu C, Liu J, Chen W, Cai P, Shi Z, Yu XY, Huang Q (2017) Molecular investigation on the binding of Cd(II) by the binary mixtures of montmorillonite with two bacterial species. Environ Pollut 229:871–878
Du S, Shen J-P, Hu H-W, Wang J-T, Han L-L, Sheng R, Wei W-X, Fang Y-T, Zhu Y-G, Zhang L-M, He J-Z (2020) Large-scale patterns of soil antibiotic resistome in Chinese croplands. Sci Total Environ 712:136418
Eboigbodin KE, Newton JR, Routh AF, Biggs CA (2006) Bacterial quorum sensing and cell surface electrokinetic properties. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:669–675
Fernie AR, Carrari F, Sweetlove LJ (2004) Respiratory metabolism: glycolysis, the TCA cycle and mitochondrial electron transport. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:254–261
Flemming H-C, Wingender J (2010) The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:623–633
Flemming H-C, Wingender J, Szewzyk U, Steinberg P, Rice SA, Kjelleberg S (2016) Biofilms: an emergent form of bacterial life. Nat Rev Microbiol 14:563–575
Francoise VB, Jean-Marie P, Ving JL (2006) Inhibitors of bacterial efflux pumps as adjuvants in antibiotic treatments and diagnostic tools for detection of resistance by efflux. Recent Patents on Anti-Infective Drug Discovery 1:157–175
Gadd GM (2010) Metals, minerals and microbes: geomicrobiology and bioremediation. Microbiology 156:609–643
Ghashoghchi RA, Hosseini MR, Ahmadi A (2017) Effects of microbial cells and their associated extracellular polymeric substances on the bio-flocculation of kaolin and quartz. Appl Clay Sci 138:81–88
Gong B, Wu P, Ruan B, Zhang Y, Lai X, Yu L, Li Y, Dang Z (2018) Differential regulation of phenanthrene biodegradation process by kaolinite and quartz and the underlying mechanism. J Hazard Mater 349:51–59
Grkovic S, Brown MH, Skurray RA (2001) Transcriptional regulation of multidrug efflux pumps in bacteria. Semin Cell Dev Biol 12:225–237
Hanamoto S, Ogawa F (2019) Predicting the sorption of azithromycin and levofloxacin to sediments from mineral and organic components. Environ Pollut 255:113180
Hao R, Xiao X, Zuo X, Nan J, Zhang W (2012) Efficient adsorption and visible-light photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride using mesoporous BiOI microspheres. J Hazard Mater 209-210:137–145
Holmes PF, Currie EP, Thies JC, van der Mei HC, Busscher HJ, Norde W (2009) Surface-modified nanoparticles as a new, versatile, and mechanically robust nonadhesive coating: suppression of protein adsorption and bacterial adhesion. J Biomed Mater Res A 91:824–833
Horiyama T, Yamaguchi A, Nishino K (2010) TolC dependency of multidrug efflux systems in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. J Antimicrob Chemother 65:1372–1376
Jiang, D., Huang, Q., Cai, P., Rong, X., Chen, W., (2007) Adsorption of Pseudomonas putida on clay minerals and iron oxide. Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces 54, 217–221
Joshi V, Joung J-G, Fei Z, Jander G (2010) Interdependence of threonine, methionine and isoleucine metabolism in plants: accumulation and transcriptional regulation under abiotic stress. Amino Acids 39:933–947
Jousse C, Dalle C, Canet I, Lagree M, Traikia M, Lyan B, Mendes C, Sancelme M, Amato P, Delort A-M (2018) Metabolomic study of the response to cold shock in a strain of Pseudomonas syringae isolated from cloud water. Metabolomics 14
Khemthong S, Nuonming P, Dokpikul T, Sukchawalit R, Mongkolsuk S (2019) Regulation and function of the flavonoid-inducible efflux system, emrR-emrAB, in Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:5763–5780
Kjelleberg S, Molin S (2002) Is there a role for quorum sensing signals in bacterial biofilms? Curr Opin Microbiol 5:254–258
Knapp CW, Dolfing J, Ehlert PAI, Graham DW (2010) Evidence of increasing antibiotic resistance gene abundances in archived soils since 1940. Environ Sci Technol 44:580–587
Kol S, Majczak W, Heerlien R, van der Berg JP, Nouwen N, Driessen AJM (2009) Subunit a of the F1F0 ATP synthase requires YidC and SecYEG for membrane insertion. J Mol Biol 390:893–901
Koronakis V, Eswaran J, Hughes C (2004) Structure and function of TolC: the bacterial exit duct for proteins and drugs. Annu Rev Biochem 73:467–489
Lai X, Wu P, Ruan B, Liu J, Liu Z, Zhu N, Dang Z (2019) Inhibition effect of kaolinite on the development of antibiotic resistance genes in Escherichia coli induced by sublethal ampicillin and its molecular mechanism. Environ Chem 16:347
Li GL, Zhou CH, Fiore S, Yu WH (2019) Interactions between microorganisms and clay minerals: new insights and broader applications. Appl Clay Sci 177:91–113
Lin D, Ma W, Jin Z, Wang Y, Huang Q, Cai P (2016) Interactions of EPS with soil minerals: a combination study by ITC and CLSM. Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces 138:10–16
Liu D, Zong EY, Huang PF, Yang HS, Yan SL, Li JZ, Li YL, Ding XQ, He SP, Xiong X, Yin YL (2019) The effects of dietary sulfur amino acids on serum biochemical variables, mucosal amino acid profiles, and intestinal inflammation in weaning piglets. Livest Sci 220:32–36
Maged A, Iqbal J, Kharbish S, Ismael IS, Bhatnagar A (2020) Tuning tetracycline removal from aqueous solution onto activated 2:1 layered clay mineral: characterization, sorption and mechanistic studies. J Hazard Mater 384:121320
Marshall CP, Carter EA, Leuko S, Javaux EJ (2006) Vibrational spectroscopy of extant and fossil microbes: relevance for the astrobiological exploration of Mars. Vib Spectrosc 41:182–189
Martinez JL, Sanchez MB, Martinez-Solano L, Hernandez A, Garmendia L, Fajardo A, Alvarez-Ortega C (2009) Functional role of bacterial multidrug efflux pumps in microbial natural ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33:430–449
McMahon S, Anderson R, Saupe E, Briggs D (2016) Experimental evidence that clay inhibits bacterial decomposers: implications for preservation of organic fossils. Geology 44:867–870
McMurry L, Petrucci RE, Levy SB (1980) Active efflux of tetracycline encoded by four genetically different tetracycline resistance determinants in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci 77:3974–3977
McNeil HE, Alav I, Torres RC, Rossiter AE, Laycock E, Legood S, Kaur I, Davies M, Wand M, Webber MA, Bavro VN, Blair JMA (2019) Identification of binding residues between periplasmic adapter protein (PAP) and RND efflux pumps explains PAP-pump promiscuity and roles in antimicrobial resistance. PLoS Pathog 15:e1008101
Misra AK, Thakur MS, Srinivas P, Karanth NG (2000) Screening of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate-producing microorganisms using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Biotechnol Lett 22:1217–1219
Mueller B (2015) Experimental interactions between clay minerals and Bacteria: a review. Pedosphere 25:799–810
Muller JF, Stevens AM, Craig J, Love NG (2007) Transcriptome analysis reveals that multidrug efflux genes are upregulated to protect Pseudomonas aeruginosa from pentachlorophenol stress. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:4550–4558
Nakao R, Ramstedt M, Wai SN, Uhlin BE (2012) Enhanced biofilm formation by Escherichia coli LPS mutants defective in Hep biosynthesis. PLoS One 7:e51241
Nealson KH, Platt T, Hastings JW (1970) Cellular control of the synthesis and activity of the bacterial luminescent system. J Bacteriol 104:313–322
Ng V, Zanazzi G, Timpl R, Talts JF, Salzer JL, Brennan PJ, Rambukkana A (2000) Role of the cell wall phenolic glycolipid-1 in the peripheral nerve predilection of Mycobacterium leprae. Cell 103:511–524
Nies DH (2003) Efflux-mediated heavy metal resistance in prokaryotes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:313–339
Norambuena A, Schwartz MA, Adams JC (2011) Effects of integrin-mediated cell adhesion on plasma membrane lipid raft components and signaling. Mol Biol Cell 22:3456–3464
Olusegun SJ, Mohallem NDS (2020) Comparative adsorption mechanism of doxycycline and Congo red using synthesized kaolinite supported CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Environ Pollut 260:114019
Omarova M, Swientoniewski LT, Tsengam IKM, Panchal A, Yu T, Blake DA, Lvov YM, Zhang D, John V (2018) Engineered clays as sustainable oil dispersants in the presence of model hydrocarbon degrading bacteria: the role of bacterial sequestration and biofilm formation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:14143–14153
Ospina Barrero MA, Pietralonga PAG, Schwarz DGG, Silva Junior A, Paula SO, Moreira MAS (2014) Effect of the inhibitors phenylalanine arginyl ß-naphthylamide (PAßN) and 1-(1-naphthylmethyl)-piperazine (NMP) on expression of genes in multidrug efflux systems of Escherichia coli isolates from bovine mastitis. Res Vet Sci 97:176–181
Papanikou E, Karamanou S, Economou A (2007) Bacterial protein secretion through the translocase nanomachine. Nat Rev Microbiol 5:839–851
Piddock LJV (2006) Clinically relevant chromosomally encoded multidrug resistance efflux pumps in bacteria. Clin Microbiol Rev 19:382–402
Poorni S, Natarajan KA (2013) Microbially induced selective flocculation of hematite from kaolinite. Int J Miner Process 125:92–100
Ren Z, Chen F, Wen K, Lu J (2020) Enhanced photocatalytic activity for tetracyclines degradation with Ag modified g-C3N4 composite under visible light. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 389:112217
Rodriguez-Mozaz S, Chamorro S, Marti E, Huerta B, Gros M, Sànchez-Melsió A, Borrego CM, Barceló D, Balcázar JL (2015) Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in hospital and urban wastewaters and their impact on the receiving river. Water Res 69:234–242
Rong X, Chen W, Huang Q, Cai P, Liang W (2010) Pseudomonas putida adhesion to goethite: studied by equilibrium adsorption, SEM, FTIR and ITC. Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces 80:79–85
Rong X, Huang Q, He X, Chen H, Cai P, Liang W (2008) Interaction of Pseudomonas putida with kaolinite and montmorillonite: a combination study by equilibrium adsorption, ITC, SEM and FTIR. Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces 64:49–55
Ruan B, Wu P, Chen M, Lai X, Chen L, Yu L, Gong B, Kang C, Dang Z, Shi Z, Liu Z (2018) Immobilization of Sphingomonas sp GY2B in polyvinyl alcohol-alginate-kaolin beads for efficient degradation of phenol against unfavorable environmental factors. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 162:103–111
Samuelson JC, Chen M, Jiang F, Möller I, Wiedmann M, Kuhn A, Phillips GJ, Dalbey RE (2000) YidC mediates membrane protein insertion in bacteria. Nature 406:637–641
Shen J, Liu Z, Yu H, Ye J, Long Y, Zhou P, He B (2020) Systematic stress adaptation of Bacillus subtilis to tetracycline exposure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 188:109910
Shrout JD, Nerenberg R (2012) Monitoring bacterial twitter: does quorum sensing determine the behavior of water and wastewater treatment biofilms? Environ Sci Technol 46:1995–2005
Spence A, Kelleher BP (2012) FT-IR spectroscopic analysis of kaolinite–microbial interactions. Vib Spectrosc 61:151–155
Stadlmair LF, Letzel T, Drewes JE, Grassmann J (2018) Enzymes in removal of pharmaceuticals from wastewater: a critical review of challenges, applications and screening methods for their selection. Chemosphere 205:649–661
Su M, Han F, Wu Y, Yan Z, Lv Z, Tian D, Wang S, Hu S, Shen Z, Li Z (2019) Effects of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria on phosphorous release and sorption on montmorillonite. Appl Clay Sci 181:105227
van de Guchte M (2017) Horizontal gene transfer and ecosystem function dynamics. Trends Microbiol 25:699–700
Vasiliadou IA, Papoulis D, Chrysikopoulos CV, Panagiotaras D, Karakosta E, Fardis M, Papavassiliou G (2011) Attachment of Pseudomonas putida onto differently structured kaolinite minerals: a combined ATR-FTIR and 1H NMR study. Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces 84:354–359
Vikesland PJ, Pruden A, Alvarez PJJ, Aga D, Bürgmann H, Li X-D, Manaia CM, Nambi I, Wigginton K, Zhang T, Zhu Y-G (2017) Toward a comprehensive strategy to mitigate dissemination of environmental sources of antibiotic resistance. Environ Sci Technol 51:13061–13069
Vital CE, Giordano A, de Almeida Soares E, Rhys Williams TC, Mesquita RO, Vidigal PMP, de Santana Lopes A, Pacheco TG, Rogalski M, de Oliveira Ramos HJ, Loureiro ME (2017) An integrative overview of the molecular and physiological responses of sugarcane under drought conditions. Plant Mol Biol 94:577–594
Wang H, Wu P, Liu J, Yang S, Ruan B, Rehman S, Liu L, Zhu N (2020) The regulatory mechanism of Chryseobacterium sp resistance mediated by montmorillonite upon cadmium stress. Chemosphere 240:124851
Winzer K, Falconer C, Garber NC, Diggle SP, Camara M, Williams P (2000) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa lectins PA-IL and PA-IIL are controlled by quorum sensing and by RpoS. J Bacteriol 182:6401–6411
Wu H, Chen W, Rong X, Cai P, Dai K, Huang Q (2014) Soil colloids and minerals modulate metabolic activity of Pseudomonas putida measured using microcalorimetry. Geomicrobiol J 31:590–596
Wuijts S, van den Berg HHJL, Miller J, Abebe L, Sobsey M, Andremont A, Medlicott KO, van Passel MWJ, de Roda Husman AM (2017) Towards a research agenda for water, sanitation and antimicrobial resistance. J Water Health 15:175–184
Yan S, Cai Y, Li H, Song S, Xia L (2019) Enhancement of cadmium adsorption by EPS-montmorillonite composites. Environ Pollut 252:1509–1518
Ye S, Zeng G, Wu H, Zhang C, Liang J, Dai J, Liu Z, Xiong W, Wan J, Xu P, Cheng M (2017) Co-occurrence and interactions of pollutants, and their impacts on soil remediation—a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 47:1528–1553
Zemanová V, Pavlík M, Pavlíková D (2017) Cadmium toxicity induced contrasting patterns of concentrations of free sarcosine, specific amino acids and selected microelements in two Noccaea species. PLoS One 12:e0177963
Zhang L, Hu Y, Han F, Wu Y, Tian D, Su M, Wang S, Li Z, Hu S (2019) Influences of multiple clay minerals on the phosphorus transport driven by Aspergillus niger. Appl Clay Sci 177:12–18
Funding
The authors appreciate financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41673092, 41972037), the Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province (2019B1515120015), the Guangdong Science and Technology Program (2020B121201003), Guangdong Special Support Program for Local Innovative and Research Teams Project (2019BT02L218),Guangdong special Support Program for Millions of Leading Engineering Talents (201626011), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, SCUT(2020ZYGXZR070).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Juan Liu: Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing (original draft), visualization, and writing (reviewing and editing). Pingxiao Wu: Resources, supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition. Qing Guo: Conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, writing (reviewing and editing), and visualization. Xiaolin Lai: Conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, writing (reviewing and editing), and visualization. Bo Ruan: Formal analysis, investigation, writing (reviewing and editing), and visualization. Huimin Wang: Formal analysis, investigation, writing (reviewing and editing), and Visualization. Saeed Rehman: Formal analysis, investigation, and writing (reviewing and editing). Meiqing Chen: Formal analysis, investigation, and writing (reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This manuscript does not involve human participants, human data, or human tissue.
Consent for publication
The manuscript does not contain any individual person’s data.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Diane Purchase
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Wu, P., Guo, Q. et al. Kaolinite weakens the co-stress of ampicillin and tetracycline on Escherichia coli through multiple pathways. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 25228–25240 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12356-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12356-4