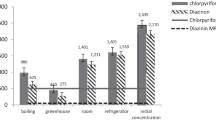
Abstract
Numerous natural preparations in traditional Chinese medicine are prepared as decoctions. Processing factors (PFs) comparing the levels of pesticide residues in decoctions to those in the corresponding unprocessed products should be considered in exposure assessments. Thus, this study determined the residue levels of six pesticides (chlorpyrifos, phoxim, imidacloprid, thiamethoxam, fenpropathrin, and emamectin benzoate), as well as 3,5,6-trichloropyridinol, the primary metabolite of chlorpyrifos, and clothianidin, the main metabolite of thiamethoxam in Baishao, Paeoniae radix lactiflora (Fam. Ranunculaceae). The results showed that significant time-response effects were present for the release of pesticides from P. radix. The PFs calculated were < 1, indicating a significant reduction in pesticide residues after TCM processing. The water solubility and partition coefficient values of the pesticides may have played a basic role in the dissipation of the residues during the TCM decocting process. A risk assessment based on the hazard quotient with PFs revealed that exposure to pesticide residues in P. radix was far below the levels that might pose a health risk. In conclusion, the results presented here are of theoretical and practical value for the safety evaluation of TCMs.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Addy-Orduna LM, Brodeur JC, Mateo R (2019) Oral acute toxicity of imidacloprid, thiamethoxam and clothianidin in eared doves: a contribution for the risk assessment of neonicotinoids in birds. Sci Total Environ 650:1216–1223
Bajwa U, Sandhu KS (2014) Effect of handling and processing on pesticide residues in food-a review. J Food Sci Technol 51:201–220
Bastos LCS, de Almeida Costa EA, Pereira PAP (2017) Development, validation and application of an UFLC-DAD-ESI-MS method for determination of carbonyl compounds in soybean oil during continuous heating. Food Chem 218:518–524
Bonnechère A, Hanot V, Jolie R, Hendrickx M, Bragard C, Bedoret T, Van Loco J (2012) Processing factors of several pesticides and degradation products in carrots by household and industrial processing. J Food Res 1:68
Chen H, Pan M, Pan R, Zhang M, Liu X, Lu C (2015) Transfer rates of 19 typical pesticides and the relationship with their physicochemical property. J Agric Food Chem 63:723–730
Chen S, Liu A, Li Q, Toru S, Zhu G, Sun Y, Dai Y, Zhang J, Zhang T, Takehisa T, Liu CX (2016) Research strategies in standard decoction of medicinal slices. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica 41:1367–1375
Dai Y, Li Q, Tong J, Verpoorte R, Zhao SJ, Qin XM, Chen S (2019) Quality marker identification based on standard decoction of differently processed materials of Ephedrae Herba. J Ethnopharmacol 237:47–54
Đorđević TM, Šiler-Marinković SS, Đurović RD, Dimitrijević-Branković SI, Umiljendić JSGU (2013) Stability of the pyrethroid pesticide bifenthrin in milled wheat during thermal processing, yeast and lactic acid fermentation, and storage. J Sci Food Agric 93(13):3377–3383
Durgnat JM, Heuser J, Andrey D, Perrin C (2005) Quality and safety assessment of ginseng extracts by determination of the contents of pesticides and metals. Food Addit Contam 22:1224–1230
Fang Q, Shi Y, Cao H, Tong Z, Xiao J, Liao M, Wu X, Hua R (2017) Degradation dynamics and dietary risk assessments of two neonicotinoid insecticides during Lonicera japonica planting, drying, and tea brewing processes. J Agric Food Chem 65:1483–1488
Gao W, Yan M, Xiao Y, Lv Y, Peng C, Wan X, Hou R (2018) Rinsing tea before brewing decreases pesticide residues in tea infusion. J Agric Food Chem 67:5384–5393
Gong J, Zheng K, Yang G, Zhao S, Zhang K, Hu D (2019) Determination, residue analysis, risk assessment and processing factor of pymetrozine and its metabolites in Chinese kale under field conditions. Food Addit Contam Part A 36(1):141–151
Harris ES, Cao S, Littlefield BA, Craycroft JA, Scholten R, Kaptchuk T, Fu Y, Wang W, Liu Y, Chen H, Zhao Z, Clardy J, Woolf AD (2011) Eisenberg DM, Heavy metal and pesticide content in commonly prescribed individual raw Chinese Herbal Medicines. Sci Total Environ 409:4297–4305
Huan Z, Xu Z, Jiang W, Chen Z, Luo J (2015) Effect of Chinese traditional cooking on eight pesticides residue during cowpea processing. Food Chem 170:118–122
Jankowska M, Kaczynski P, Hrynko I, Lozowicka B (2016) Dissipation of six fungicides in greenhouse-grown tomatoes with processing and health risk. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(12):11885–11900
Jankowska M, Łozowicka B, Kaczyński P (2019) Comprehensive toxicological study over 160 processing factors of pesticides in selected fruit and vegetables after water, mechanical and thermal processing treatments and their application to human health risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 652:1156–1167
Kong LY, Tan RX (2015) Artemisinin, a miracle of traditional Chinese medicine. Nat Prod Rep 32:1617–1621
Kontou S, Tsipi D, Tzia C (2004) Stability of the dithiocarbamate pesticide maneb in tomato homogenates during cold storage and thermal processing. Food Addit Contam 21:1083–1089
Li SL, Lai SF, Song JZ, Qiao CF, Liu X, Zhou Y, Cai H, Cai BC, Xu HX (2010) Decocting-induced chemical transformations and global quality of Du–Shen–Tang, the decoction of ginseng evaluated by UPLC–Q-TOF-MS/MS based chemical profiling approach. J Pharm Biomed Anal 53:946–957
Li Z, Nie J, Lu Z, Xie H, Kang L, Chen Q, Li A, Zhao X, Xu G, Yan Z (2016) Cumulative risk assessment of the exposure to pyrethroids through fruits consumption in China–Based on a 3-year investigation. Food Chem Toxicol 96:234–243
Lin AX, Chan G, Hu Y, Ouyang D, Ung COL, Shi L, Hu H (2018) Internationalization of traditional Chinese medicine: current international market, internationalization challenges and prospective suggestions. Chin Med 13:9
Liu T, Zhang C, Peng J, Zhang Z, Sun X, Xiao H, Sun K, Pan L, Liu X, Tu K (2016) Residual behaviors of six pesticides in shiitake from cultivation to postharvest drying process and risk assessment. J Agric Food Chem 64:8977–8985
Lozowicka B, Jankowska M, Hrynko I, Kaczynski P (2016) Removal of 16 pesticide residues from strawberries by washing with tap and ozone water, ultrasonic cleaning and boiling. Environ Monit Assess 188:51
Maštovská K, Hajšlová J, Godula M, Křivánková J, Kocourek V (2001) Fast temperature programming in routine analysis of multiple pesticide residues in food matrices. J Chromatogr A 907:235–245
Matsuda K, Buckingham SD, Kleier D, Rauh JJ, Grauso M, Sattelle DB (2001) Neonicotinoids: insecticides acting on insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22:573–580
Muscarella DE, Keown JF, Bloom SE (1984) Evaluation of the genotoxic and embryotoxic potential of chlorpyrifos and its metabolites in vivo and in vitro. Environ Mutagen 6(1):13–23
N.P. Committee (2015) Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, part 1. Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, pp 392–393
Neuwirthová N, Bílková Z, Vašíčková J, Hofman J, Bielská L (2018) Concentration/time-dependent dissipation, partitioning and plant accumulation of hazardous current-used pesticides and 2-hydroxyatrazine in sand and soil. Chemosphere 203:219–227
Pan R, Chen HP, Zhang ML, Wang QH, Jiang Y, Liu X (2015) Dissipation pattern, processing factors, and safety evaluation for dimethoate and its metabolite (Omethoate) in tea (Camellia Sinensis). PLoS One 10(9):e0138309
Parween T, Jan S, Fatma T (2018) Variation in elemental composition as influenced by chlorpyrifos application in mung bean (Vigna radiata L.). Saudi J Biol Sci 25:1439–1445
Randhawa MA, Anjum FM, Ahmed A, Randhawa MS (2007) Field incurred chlorpyrifos and 3, 5, 6-trichloro-2-pyridinol residues in fresh and processed vegetables. Food Chem 103:1016–1023
Scholz R, Herrmann M, Kittelmann A, von Schledorn M, van Donkersgoed G, Graven C, van der Velde-Koerts T, Anagnostopoulos C, Bempelou E, Michalski B (2018) Database of processing techniques and processing factors compatible with the EFSA food classification and description system FoodEx 2 Objective 1: Compendium of Representative Processing Techniques investigated in regulatory studies for pesticides. EFSA Support Publ 15:1508E
Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China (2016) National food safety standard-maximum residue limits for pesticides in food (GB/T 2763-2016). Standards Press of China, Beijing
Stanisavljević N, Samardžić J, Janković T, Šavikin K, Mojsin M, Topalović V, Stevanović M (2015) Antioxidant and antiproliferative activity of chokeberry juice phenolics during in vitro simulated digestion in the presence of food matrix. Food Chem 175:516–522
Wang J, Lin K, Taylor A, Gan J (2018) In vitro assessment of pyrethroid bioaccessibility via particle ingestion. Environ Int 119:125–132
World Health Organization (WHO), Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) (2006) Updating, the principles and methods of risk assessment: MRLs for pesticides and veterinary drugs. AO, Rome pp 31–36
Xiao JJ, Li Y, Fang QK, Shi YH, Liao M, Wu XW, Hua RM, Cao HQ (2017) Factors affecting transfer of pyrethroid residues from herbal teas to infusion and influence of physicochemical properties of pesticides. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14:1157
Xiao JJ, Duan JS, Xu X, Li SN, Wang F, Fang QK, Liao M, Cao HQ (2018) Behavior of pesticides and their metabolites in traditional Chinese medicine Paeoniae Radix Alba during processing and associated health risk. J Pharm Biomed Anal 161:20–27
Xiao JJ, Xu X, Wang F, Ma JJ, Liao M, Shi YH, Fang Q, Cao HQ (2019) Analysis of exposure to pesticide residues from traditional Chinese medicine. J Hazard Mater 365:857–867
Xue J, Li H, Liu F, Xue J, Chen X, Zhan J (2014) Transfer of difenoconazole and azoxystrobin residues from chrysanthemum flower tea to its infusion. Food Addit Contam Part A 31(4):666–675
Zhao L, Ge J, Liu F, Jiang N (2014) Effects of storage and processing on residue levels of chlorpyrifos in soybeans. Food Chem 150:182–186
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 31772201).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Haiqun Cao, Jinjing Xiao, and Yanhong Shi designed the experiments; Jinjing Xiao, Jinjuan Ma, Fan Wang, and Xing Xu carried out the experiments; Jinjing Xiao analyzed the experimental data and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent to publish
Not applicable
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 87 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, J., Ma, J., Wang, F. et al. Effect of decocting on the pesticide residues in Paeoniae radix lactiflora and corresponding exposure risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 16655–16662 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11945-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11945-z