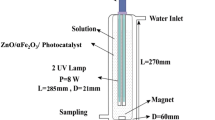
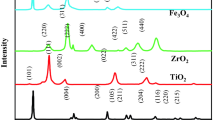
Abstract
The present research studies the photocatalytic degradation of a pesticide using TiO2 and Fe3O4 nanoparticles supported on ZnO mesoporous (mZnO) substrate. Chlorpyrifos is an organophosphate pesticide with a C9H11Cl3NO3PS chemical formula. It is broadly utilized in agricultural fields to control product pests. The chlorpyrifos toxicity is acute and still dangerous to any aquatic organisms. The mZnO/TiO2-Fe3O4 material was characterized using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and N2 adsorption and desorption (Brunauer-Emmett-Teller; BET). In order to optimize three important operating parameters, i.e., chlorpyrifos concentration, mZnO/TiO2-Fe3O4 nanocomposite amount, and pH, for photocatalytic degradation of chlorpyrifos, response surface methodology (RSM) was applied. The central composite design (CCD) including 20 experiments was used to conduct experiments. The highest photodegradation performance of about 94.8% was obtained for a chlorpyrifos concentration of 8 ppm, a pH of 10, and an amount of mZnO/TiO2-Fe3O4 nanocomposite of 60 mg. The degradation of chlorpyrifos using mZnO/TiO2-Fe3O4 presented good performance (more than 94%). The photocatalytic reaction followed pseudo-first-order kinetics with a rate constant of 0.058 min−1 for chlorpyrifos degradation. The results propose that mZnO/TiO2-Fe3O4 nanocomposite is a suitable alternative for the degradation of chlorpyrifos in aqueous solution. The improved photocatalytic efficiency could be attributed to the effective separation of electron-hole pairs via a Z-scheme mechanism.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmaruzzaman M, Gupta VK (2011) Rice husk and its ash as low-cost adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:13589–13613. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie201477c
Ali I, Gupta VK, Khan TA, Asim M (2012) Removal of arsenate from aqueous solution by electro-coagulation method using Al-Fe electrodes. Int J Electrochem Sci 7:1898–1907
Ali I, Alharbi OM, Alothman ZA, Alwarthan A (2018) Facile and eco-friendly synthesis of functionalized iron nanoparticles for cyanazine removal in water. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 171:606–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.07.071
Asfaram A, Ghaedi M, Agarwal S, Tyagi I, Gupta VK (2015) Removal of basic dye Auramine-O by ZnS: Cu nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon: optimization of parameters using response surface methodology with central composite design. RSC Adv 5:18438–18450. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA15637D
Ayodhya D, Veerabhadram G (2019) Fabrication of Schiff base coordinated ZnS nanoparticles for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of chlorpyrifos pesticide and detection of heavy metal ions. J Materiomics 5:446–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2019.02.002
Budarz JF, Cooper EM, Gardner C, Hodzic E, Ferguson PL, Gunsch CK, Wiesner MR (2019) Chlorpyrifos degradation via photoreactive TiO2 nanoparticles: assessing the impact of a multi-component degradation scenario. J Hazard Mater 372:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.12.028
Burakov A, Galunin EV, Burakova IV, Kucherova AE, Agarwal S, Tkachev AG, Gupta VK (2018) Adsorption of heavy metals on conventional and nanostructured materials for wastewater treatment purposes: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:702–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.034
Chen Y, Wu Q, Jin Q, Liu K (2017) A facile sol-gel method for the fabrication of nitrogen doped TiO2/NiFe2O4/diatomite composite with enhanced photoactivity. Adv Powder Technol 28:2225–2231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2017.06.003
Cheng K, Cao D, Yang F, Zhang L, Xu Y, Wang G (2012) Electrodeposition of Pd nanoparticles on C@ TiO2 nanoarrays: 3D electrode for the direct oxidation of NaBH4. J Mater Chem 22:850–855. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1JM13560K
Cochran RC (2002) Appraisal of risks from nonoccupational exposure to chlorpyrifos. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 35:105–121. https://doi.org/10.1006/rtph.2001.1512
Devara M, Saravanan R, Deivasigamani R, Gupta VK, Gracia F, Jayadevan S (2016) Fabrication of novel shape Cu and Cu/Cu2O nanoparticles modified electrode for the determination of dopamine and paracetamol. J Mol Liq 221:930–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.06.028
Dil E, Alipanahpour M, Ghaedi AM, Ghaedi A, Asfaram A, Goudarzi S, Hajati M, Soylak M, Agarwal S, Gupta VK (2016) Modeling of quaternary dyes adsorption onto ZnO–NR–AC artificial neural network: analysis by derivative spectrophotometry. J Ind Eng Chem 34:186–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2015.11.010
Đorđević TM, Đurović-Pejčev RD (2015) Dissipation of chlorpyrifos-methyl by Saccharomyces cerevisiae during wheat fermentation. LWT-Food Sci Technol 61:516–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.12.044
Ghaedi M, Hajjati S, Mahmudi Z, Tyagi I, Agarwal S, Maity A, Gupta VK (2015) Modeling of competitive ultrasonic assisted removal of the dyes–methylene blue and Safranin-O using Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 268:28–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.12.090
Gupta VK, Saleh TA (2013) Sorption of pollutants by porous carbon, carbon nanotubes and fullerene-an overview. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2828–2843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1524-1
Gupta VK, Rastogi A, Dwivedi MK, Mohan D (1997) Process development for the removal of zinc and cadmium from wastewater using slag—a blast furnace waste material. Sep Sci Technol 32:2883–2912. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496399708002227
Gupta VK, Jain CK, Ali I, Chandra S, Agarwal SJWR (2002) Removal of lindane and malathion from wastewater using bagasse fly ash—a sugar industry waste. Water Res 36(10):2483–2490. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00474-2
Gupta VK, Jain R, Nayak A, Agarwal S, Shrivastava M (2011) Removal of the hazardous dye—tartrazine by photodegradation on titanium dioxide surface. Mater Sci Eng C 31:1062–1067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2011.03.006
Gupta VK, Ali I, Saleh TA, Siddiqui MN, Agarwal S (2013) Chromium removal from water by activated carbon developed from waste rubber tires. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:1261–1268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0950-9
Gupta VK, Atar N, Yola ML, Üstündağ Z, Uzun L (2014) A novel magnetic Fe@ Au core–shell nanoparticles anchored graphene oxide recyclable nanocatalyst for the reduction of nitrophenol compounds. Water Res 48:210–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.09.027
Gupta VK, Nayak A, Agarwal S, Gupta VK, Nayak A, Agarwal S (2015) Bioadsorbents for remediation of heavy metals: current status and their future prospects. Environ Eng Res 20:1–18. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2015.018
Gupta VK, Carrott PJM, Singh R, Chaudhary M, Kushwaha S (2016a) Cellulose: a review as natural, modified and activated carbon adsorbent. Bioresour Technol 216:1066–1076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.05.106
Gupta VK, Tyagi I, Agarwal S, Singh R, Chaudhary M, Harit A, Kushwaha S (2016b) Column operation studies for the removal of dyes and phenols using a low cost adsorbent. Glob J Environ Sci Manag 2:1–10. https://doi.org/10.7508/GJESM.2016.01.001
Hoffmann MR, Martin ST, Choi W, Bahnemann DW (1995) Environmental applications of semiconductor photocatalysis. Chem Rev 95:69–96. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00033a004
Karafas ES, Romanias MN, Stefanopoulos V, Binas V, Zachopoulos A, Kiriakidis G, Papagiannakopoulos P (2019) Effect of metal doped and co-doped TiO2 photocatalysts oriented to degrade indoor/outdoor pollutants for air quality improvement. A kinetic and product study using acetaldehyde as probe molecule. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 371:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.11.023
Kim SG, Dhandole LK, Seo YS, Chung HS, Chae WS, Cho M, Jang JS (2018) Active composite photocatalyst synthesized from inactive Rh & Sb doped TiO2 nanorods: enhanced degradation of organic pollutants & antibacterial activity under visible light irradiation. Appl Catal A Gen 564:43–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2018.07.016
Linsebigler AL, Lu G, Yates JT Jr (1995) Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces: principles, mechanisms, and selected results. Chem Rev 95:735–758. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00035a013
Matthews RW (1987) Photooxidation of organic impurities in water using thin films of titanium dioxide. J Phys Chem 91:3328–3333. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100296a044
Mittal A, Mittal J, Malviya A, Gupta VK (2010) Removal and recovery of Chrysoidine Y from aqueous solutions by waste materials. J Colloid Interface Sci 344:497–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2010.01.007
Mohammadi N, Khani H, Gupta VK, Amereh E, Agarwal S (2011) Adsorption process of methyl orange dye onto mesoporous carbon material–kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Colloid Interface Sci 362:457–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.06.067
Mosleh S, Rahimi MR, Ghaedi M, Dashtian K (2016) Sonophotocatalytic degradation of trypan blue and vesuvine dyes in the presence of blue light active photocatalyst of Ag3PO4/Bi2S3-HKUST-1-MOF: central composite optimization and synergistic effect study. Ultrason Sonochem 32:387–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.04.007
Mosleh S, Rahimi MR, Ghaedi M, Dashtian K, Hajati S (2018) Sonochemical-assisted synthesis of CuO/Cu2O/Cu nanoparticles as efficient photocatalyst for simultaneous degradation of pollutant dyes in rotating packed bed reactor: LED illumination and central composite design optimization. Ultrason Sonochem 40:601–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.08.007
Nekouei F, Nekouei S, Tyagi I, Gupta VK (2015) Kinetic, thermodynamic and isotherm studies for acid blue 129 removal from liquids using copper oxide nanoparticle-modified activated carbon as a novel adsorbent. J Mol Liq 201:124–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2014.09.027
Nodeh HR, Ibrahim WAW, Ali I, Sanagi MM (2016) Development of magnetic graphene oxide adsorbent for the removal and preconcentration of As (III) and As (V) species from environmental water samples. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:9759–9773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6137-z
Priya B, Gupta VK, Pathania D, Singha AS (2014) Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of biodegradable starch/PVA composite films reinforced with cellulosic fibre. Carbohydr Polym 109:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.03.044
Rajendran S, Khan MM, Gracia F, Qin J, Gupta VK, Arumainathan S (2016) Ce 3+-ion-induced visible-light photocatalytic degradation and electrochemical activity of ZnO/CeO2 nanocomposite. Sci Rep 6:31641. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31641
Saini R, Kumar P (2016) Optimization of chlorpyrifos degradation by Fenton oxidation using CCD and ANFIS computing technique. J Environ Chem Eng 4:2952–2963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.06.003
Saleh TA, Gupta VK (2011) Functionalization of tungsten oxide into MWCNT and its application for sunlight-induced degradation of rhodamine B. J Colloid Interface Sci 362:337–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.06.081
Saleh TA, Gupta VK (2012) Photo-catalyzed degradation of hazardous dye methyl orange by use of a composite catalyst consisting of multi-walled carbon nanotubes and titanium dioxide. J Colloid Interface Sci 371:101–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.12.038
Saleh TA, Gupta VK (2014) Processing methods, characteristics and adsorption behavior of tire derived carbons: a review. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 211:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2014.06.006
Saravanan R, Joicy S, Gupta VK, Narayanan V, Stephen AJMS (2013a) Visible light induced degradation of methylene blue using CeO2/V2O5 and CeO2/CuO catalysts. Mater Sci Eng C 33:4725–4731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2013.07.034
Saravanan R, Karthikeyan S, Gupta VK, Sekaran G, Narayanan V, Stephen AJMS (2013b) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of ZnO/CuO nanocomposite for the degradation of textile dye on visible light illumination. Mater Sci Eng C 33:91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2012.08.011
Saravanan R, Gupta VK, Prakash T, Narayanan V, Stephen A (2013c) Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of novel Hg doped ZnO nanorods prepared by thermal decomposition method. J Mol Liq 178:88–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2012.11.012
Saravanan R, Thirumal E, Gupta VK, Narayanan V, Stephen A (2013d) The photocatalytic activity of ZnO prepared by simple thermal decomposition method at various temperatures. J Mol Liq 177:394–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2012.10.018
Saravanan R, Karthikeyan N, Gupta VK, Thirumal E, Thangadurai P, Narayanan V, Stephen AJMS (2013e) ZnO/Ag nanocomposite: an efficient catalyst for degradation studies of textile effluents under visible light. Mater Sci Eng C 33:2235–2244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2013.01.046
Saravanan R, Gupta VK, Narayanan V, Stephen A (2013f) Comparative study on photocatalytic activity of ZnO prepared by different methods. J Mol Liq 181:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2013.02.023
Saravanan R, Gupta VK, Narayanan V, Stephen A (2014a) Visible light degradation of textile effluent using novel catalyst ZnO/γ-Mn2O3. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 45:1910–1917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2013.12.021
Saravanan R, Gupta VK, Mosquera E, Gracia F (2014b) Preparation and characterization of V2O5/ZnO nanocomposite system for photocatalytic application. J Mol Liq 198:409–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2014.07.030
Saravanan R, Khan MM, Gupta VK, Mosquera E, Gracia F, Narayanan V, Stephen AJJOC (2015a) ZnO/Ag/CdO nanocomposite for visible light-induced photocatalytic degradation of industrial textile effluents. J Colloid Interface Sci 452:126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.04.035
Saravanan R, Khan MM, Gupta VK, Mosquera E, Gracia F, Narayanan V, Stephen AJRA (2015b) ZnO/Ag/Mn 2 O 3 nanocomposite for visible light-induced industrial textile effluent degradation, uric acid and ascorbic acid sensing and antimicrobial activity. RSC Adv 5:34645–34651. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA02557E
Saravanan R, Sacari E, Gracia F, Khan MM, Mosquera E, Gupta VK (2016) Conducting PANI stimulated ZnO system for visible light photocatalytic degradation of coloured dyes. J Mol Liq 221:1029–1033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.06.074
Serpone N, Maruthamuthu P, Pichat P, Pelizzetti E, Hidaka H (1995) Exploiting the interparticle electron transfer process in the photocatalysed oxidation of phenol, 2-chlorophenol and pentachlorophenol: chemical evidence for electron and hole transfer between coupled semiconductors. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 85:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/1010-6030(94)03906-B
Sun JH, Dong SY, Feng JL, Yin XJ, Zhao XC (2011) Enhanced sunlight photocatalytic performance of Sn-doped ZnO for methylene blue degradation. J Mol Catal A Chem 335:145–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2010.11.026
Sun F, Qiao X, Tan F, Wang W, Qiu X (2012) One-step microwave synthesis of Ag/ZnO nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic performance. J Mater Sci 47:7262–7268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6676-8
Sun Q, Hong Y, Liu Q, Dong L (2018) Synergistic operation of photocatalytic degradation and Fenton process by magnetic Fe3O4 loaded TiO2. Appl Surf Sci 430:399–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.08.085
Veisi H, Pirhayati M, Kakanejadifard A, Mohammadi P, Abdi MR, Gholami J, Hemmati S (2018) In situ green synthesis of Pd nanoparticles on tannic acid-modified magnetite nanoparticles as a green reductant and stabilizer agent: its application as a recyclable nanocatalyst (Fe3O4@ TA/Pd) for reduction of 4-nitrophenol and Suzuki reactions. ChemistrySelect 3:1820–1826. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201702869
Vigneshwaran S, Preethi J, Meenakshi S (2019) Removal of chlorpyrifos, an insecticide using metal free heterogeneous graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) incorporated chitosan as catalyst: Photocatalytic and adsorption studies. Int J Biol Macromol 132:289–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.071
Villaseñor J, Reyes P, Pecchi G (1998) Photodegradation of pentachlorophenol on ZnO. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 72:105–110. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4660(199806)72:2<105::AID-JCTB883>3.0.CO;2-0
Wang P, Yin Y, Guo Y, Wang C (2015) Removal of chlorpyrifos from waste water by wheat straw-derived biochar synthesized through oxygen-limited method. RSC Adv 5:72572–72578. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA10487D
Wilcoxon JP (2000) Catalytic photooxidation of pentachlorophenol using semiconductor nanoclusters. J Phys Chem B 104:7334–7343. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0012653
Yeber MC, Rodríguez J, Freer J, Durán N, Mansilla HD (2000) Photocatalytic degradation of cellulose bleaching effluent by supported TiO2 and ZnO. Chemosphere 41:1193–1197. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00551-2
Zhang H, He X, Zhao W, Peng Y, Sun D, Li H, Wang X (2017) Preparation of Fe3O4/TiO2 magnetic mesoporous composites for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Water Sci Technol 75:1523–1528. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.002
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere appreciation to the founders of Kerman University, Mr. Alireza Afzalipour, and his wife, Mrs. Fakhereh Saba, for their foresight and generosity in training future generations of doctors, engineers, and scientists. Also, the authors would like to acknowledge and thank Dr. Parviz Dabiri for his generous support for the research activities of the chemistry laboratories at Kerman University.
Availability of data and materials
Available.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A. Saljooqi carried out the experiment and wrote the manuscript with support from T. Shamspur and A. Mostafavi.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sami Rtimi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saljooqi, A., Shamspur, T. & Mostafavi, A. Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of porous ZnO stabilized by TiO2 and Fe3O4 nanoparticles: investigation of pesticide degradation reaction in water treatment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 9146–9156 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11122-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11122-2