Abstract
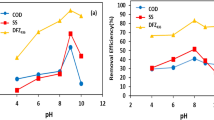
The reclamation of graywater for non-potable purposes has attained utmost importance, particularly in developing nations. The present research aimed to evaluate the optimal condition of electro-coagulation system in treatment of graywater and its reuse. Moreover, the study also evaluates the impact of major operating parameters on pollutant removal and anode dissolution. To achieve this, two-factor (voltage potential and time) and 5-level (− 1, − 0.5, 0, + 0.5, and + 1) full factorial design, based on response surface methodology (RSM) has been executed for the actual design. The data were acquired after conducting 20 experiments, as suggested by RSM (response surface methodology). Design Expert 12.0.8.0 software has been used to design mathematical model to obtain optimum condition (14 V and 47 min) at pH of 7.35, which provides experimental removal efficiency (75.6% chemical oxygen demand, 78.7% total dissolved solids, 93.4% turbidity, and 63.2% chloride) with minimal electrode consumption of 1.38 mg L−1. Adequacy of the model developed has been verified by ANOVA. The operating cost of treating graywater at the optimized condition obtained as 0.7 US$/kg COD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Gheethi AA, Radin Mohamed RMS, Efaq AN, Amir Hashim MK (2016) Reduction of microbial risk associated with greywater by disinfection processes for irrigation. J Water Health 14:379–398. https://doi.org/10.2166/wh.2015.220
Al-Qodah Z, Al-Qudah Y, Omar W (2019) On the performance of electrocoagulation-assisted biological treatment processes: a review on the state of the art. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:28689–28713. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06053-6
APHA, AWWA W (2012) Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater. 22nd Ed®
Arden S, Ma X (2018) Constructed wetlands for greywater recycle and reuse: a review. Sci Total Environ 630:587–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.218
Asaithambi P, Aziz ARA, Daud WMABW (2016) Integrated ozone—electrocoagulation process for the removal of pollutant from industrial effluent: optimization through response surface methodology. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 105:92–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2016.03.013
Bajpai M, Katoch SS (2020) Techno-economical optimization using Box-Behnken (BB) design for COD and chloride reduction from Hospital wastewater by electro-coagulation. Water Environ Res Wer:1387. https://doi.org/10.1002/wer.1387
Bajpai M, Katoch SS, Chaturvedi NK (2019) Comparative study on decentralized treatment technologies for sewage and graywater reuse – a review. Water Sci Technol 80:2091–2106. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.039
Benazzi TL, Di Luccio M, Dallago RM et al (2016) Continuous flow electrocoagulation in the treatment of wastewater from dairy industries. Water Sci Technol 73:1418–1425. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2015.620
Boyer TH (2015) Removal of dissolved organic matter by magnetic ion exchange resin. Curr Pollut Reports 1:142–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-015-0012-2
Bracher GH, Carissimi E, Wolff DB, Graepin C, Hubner AP (2020) Optimization of an electrocoagulation-flotation system for domestic wastewater treatment and reuse. Environ Technol 0:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2019.1709905
Cardoso M, Antunes M (2016) Greywater treatment using a moving bed bio film reactor at a university campus in Brazil. J Clean Prod:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.07.162
Cecconet D, Callegari A, Hlavínek P, Capodaglio AG (2019) Membrane bioreactors for sustainable, fit-for-purpose greywater treatment: a critical review. Clean Technol Environ Policy 21:745–762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-019-01679-z
Dargahi A, Mohammadi M, Amirian F, Karami A, Almasi A (2017) Phenol removal from oil refinery wastewater using anaerobic stabilization pond modeling and process optimization using response surface methodology (RSM). Desalin Water Treat 87:199–208. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.21064
Drennan DM, Koshy RE, Gent DB, Schaefer CE (2019) Electrochemical treatment for greywater reuse: effects of cell configuration on COD reduction and disinfection byproduct formation and removal. Water Sci Technol Water Supply 19:891–898. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2018.138
Etchepare R, van der Hoek JP (2015) Health risk assessment of organic micropollutants in greywater for potable reuse. Water Res 72:186–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.10.048
Fernandes A, Pacheco MJ, Ciríaco L, Lopes A (2015) Review on the electrochemical processes for the treatment of sanitary landfill leachates: present and future. Appl Catal B Environ 176–177:183–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.03.052
Fountoulakis MS, Markakis N, Petousi I, Manios T (2016) Science of the total environment single house on-site grey water treatment using a submerged membrane bioreactor for toilet flushing. Sci Total Environ 551–552:706–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.02.057
Gassie LW, Englehardt JD (2017) Advanced oxidation and disinfection processes for onsite net-zero greywater reuse: a review. Water Res 125:384–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.08.062
Gatsios E, Hahladakis JN, Gidarakos E (2015) Optimization of electrocoagulation (EC) process for the purification of a real industrial wastewater from toxic metals. J Environ Manage 154:117–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.02.018
Ghahremani H, Bagheri S, Hassani SM, Khoshchehreh MR (2012) Treatment of dairy industry wastewater using an electrocoagulation process. Adv Environ Biol 6:1897–1901
Ghaitidak DM, Yadav KD (2013) Characteristics and treatment of greywater—a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2795–2809. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1533-0
Ghunmi LA, Zeeman G, Fayyad M, van Lier JB (2011) Grey water treatment systems: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 41:657–698. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380903048443
Gilhotra V, Das L, Sharma A, Kang TS, Singh P, Dhuria RS, Bhatti MS (2018) Electrocoagulation technology for high strength arsenic wastewater: process optimization and mechanistic study. J Clean Prod 198:693–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.023
Hey T, Väänänen J, Heinen N, la Cour Jansen J, Jönsson K (2017) Potential of combining mechanical and physicochemical municipal wastewater pre-treatment with direct membrane filtration. Environ Technol (United Kingdom) 38:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2016.1186746
Karichappan T, Venkatachalam S, Jeganathan PM (2014) Optimization of electrocoagulation process to treat grey wastewater in batch mode using response surface methodology. J Environ Heal Sci Eng 12:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/2052-336X-12-29
Khandegar V, Saroh AK (2014) Treatment of distillery spentwash by electrocoagulation. J Clean Energy Technol 2:244–247. https://doi.org/10.7763/jocet.2014.v2.133
Kobya M, Gengec E, Demirbas E (2016) Operating parameters and costs assessments of a real dyehouse wastewater effluent treated by a continuous electrocoagulation process. Chem Eng Process - Process Intensif 101:87–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2015.11.012
Li F, Wichmann K, Otterpohl R (2009) Review of the technological approaches for grey water treatment and reuses. Sci Total Environ 407:3439–3449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.02.004
Mansoorian HJ, Mahvi AH, Jafari AJ (2014) Removal of lead and zinc from battery industry wastewater using electrocoagulation process: influence of direct and alternating current by using iron and stainless steel rod electrodes. Sep Purif Technol 135:165–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2014.08.012
Molla Mahmoudi M, Khaghani R, Dargahi A, Monazami Tehrani G (2020) Electrochemical degradation of diazinon from aqueous media using graphite anode: effect of parameters, mineralisation, reaction kinetic, degradation pathway and optimisation using central composite design. Int J Environ Anal Chem 00:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1742893
Moussa DT, El-Naas MH, Nasser M, Al-Marri MJ (2017) A comprehensive review of electrocoagulation for water treatment: potentials and challenges. J Environ Manage 186:24–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.10.032
Nguyen QH, Kawamura Y, Watari T et al (2020) Electrocoagulation with a nanosecond pulse power supply to remove COD from municipal wastewater using iron electrodes. Int J Electrochem Sci 15:493–504. https://doi.org/10.20964/2020.01.66
Norton-Brandão D, Scherrenberg SM, van Lier JB (2013) Reclamation of used urban waters for irrigation purposes – a review of treatment technologies. J Environ Manage 122:85–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.03.012
Ogedey A, Tanyol M (2017) Optimizing electrocoagulation process using experimental design for COD removal from unsanitary landfill leachate. Water Sci Technol 76:2907–2917. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.460
Oh KS, Yip J, Leong C et al (2017) A review of greywater recycling related issues: challenges and future prospects in Malaysia. J Clean Prod. 171:17–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.267
Ren X, Zhang Y, Chen H (2019) Graywater treatment technologies and reuse of reclaimed water for toilet flushing. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05154-6
Revitt DM, Eriksson E, Donner E (2011) The implications of household greywater treatment and reuse for municipal wastewater flows and micropollutant loads. Water Res 45:1549–1560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.11.027
Rodríguez-Gómez R, Renman G (2017) Phosphorus removal from UASB reactor effluent by reactive media filtration. Environ Technol (United Kingdom) 38:2024–2031. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2016.1244570
Sahu O, Mazumdar B, Chaudhari PK (2014) Treatment of wastewater by electrocoagulation: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:2397–2413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2208-6
Saidi A, Masmoudi K, Nolde E, el Amrani B, Amraoui F (2017) Organic matter degradation in a greywater recycling system using a multistage moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR). Water Sci Technol 76:3328–3339. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.499
Tanyol M, Ogedey A, Oguz E (2018) COD removal from leachate by electrocoagulation process: treatment with monopolar electrodes in parallel connection. Water Sci Technol 77:177–186. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.528
Tezcan Un U, Kandemir A, Erginel N, Ocal SE (2014) Continuous electrocoagulation of cheese whey wastewater: an application of Response Surface Methodology. J Environ Manage 146:245–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.08.006
Tsioptsias C, Petridis D, Athanasakis N, Lemonidis I, Deligiannis A, Samaras P (2015) Post-treatment of molasses wastewater by electrocoagulation and process optimization through response surface analysis. J Environ Manage 164:104–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.09.007
Tsoumachidou S, Velegraki T, Antoniadis A, Poulios I (2017) Greywater as a sustainable water source: a photocatalytic treatment technology under artificial and solar illumination. J Environ Manage 195:232–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.08.025
Veli S, Arslan A, Bingöl D (2016) Application of response surface methodology to electrocoagulation treatment of hospital wastewater. Clean - Soil, Air, Water 44:1516–1522. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201500729
Vuppaladadiyam AK, Merayo N, Blanco A, Hou J, Dionysiou DD, Zhao M (2018) Simulation study on comparison of algal treatment to conventional biological processes for greywater treatment. Algal Res 35:106–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2018.08.021
Vuppaladadiyam AK, Merayo N, Prinsen P, Luque R, Blanco A, Zhao M (2019) A review on greywater reuse: quality, risks, barriers and global scenarios. Rev Environ Sci Bio/Technology 18:77–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-018-9487-9
Wu B (2019) Membrane-based technology in greywater reclamation: a review. Sci Total Environ 656:184–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.347
Ziembińska-Buczyńska A, Ciesielski S, Żabczyński S, Cema G (2019) Bacterial community structure in rotating biological contactor treating coke wastewater in relation to medium composition. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:19171–19179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05087-0
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Environmental Engineering Laboratory, National Institute of Technology Hamirpur (India) for providing experimental facilities related to study. The authors would also like to thank the anonymous reviewers and editor for their positive criticism and valuable suggestions that have contributed to an improved manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Using iron electrode in EC process results maximum 76.4% COD and 90.6% turbidity removal at optimum conditions.
• The optimal operating conditions for graywater treatment were 14 voltage, 7.35 pH, and 47 min of electro-coagulation.
• The ANOVA demonstrates the model F-value within the range, which points out that the considered model is statistically fit.
• The values of the chosen responses were deemed significant, because the experimental results are below 5% of the predicted results.
• The operating cost of treating graywater at the optimized condition was 0.7 US$/kg COD and can be reused for non-potable purposes.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bajpai, M., Singh Katoch, S. & Singh, M. Optimization and economical study of electro-coagulation unit using CCD to treat real graywater and its reuse potential. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 42040–42050 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10171-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10171-x