Abstract
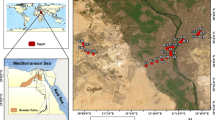
A total of 23 road-dust and 9 house-dust samples were collected from Alexandria and Kafr El-Sheikh cities, Egypt in 2016 to investigate heavy metal (Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn) contamination, spatial distribution, sources, and health risks. The mean concentrations (mg kg−1) of Cd (road-dust (RD) = 0.33, house-dust (HD) = 0.77), Cu (RD = 80, HD = 141), Pb (RD = 70, HD = 260), and Zn (RD = 169, HD = 771) in Alexandria and Zn (RD = 192, HD = 257) in Kafr El-Sheikh were higher than corresponding background (background refers to generic earth crust shale values given in the literature) levels. Whereas average concentrations (mg kg−1) of Co, Cr, Mn, and Ni (Alexandria: RD = 2.7, 24.3, 251, 14.4; HD = 3.2, 29.2, 237, 25.1 and Kafr El-Sheikh: RD = 6.6, 31.9, 343, 20.2; HD = 8.6, 33.4, 438, 23.2) in both cities were much lower than their background values. Spatially, for most heavy metals, the high concentrations were observed in areas characterized with increased anthropogenic activities, heavy traffic, and high population density. Contamination indices revealed moderate contamination (Cd and Cu) to high contamination (Pb: only house-dust from Alexandria), which posed low (most metals) to moderate ecological risk (Cd and Pb). Correlation analysis and factor analysis classified the studied metals in two groups as: natural input (Co, Cr, Mn, Ni, and Fe) and anthropogenic sources (Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn). The noncancerous risks posed by studied metals ranged from 0.0001 (Cd) to 0.15 (Pb) and were insignificant. The cancerous risk of Pb (1.4 × 10−4) for children on exposure to house-dust form Alexandria exceeded the guideline values and was considered unacceptable, whereas the cancerous risks of other studied metals were acceptable for both subpopulations. The results of health risk revealed that children are facing higher risk than adults.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiman U, Mahmood A, Waheed S, Malik RN (2016) Enrichment, geo accumulation and risk surveillance of toxic metals for different environmental compartments from Mehmood Booti dumping site, Lahore city, Pakistan. Chemosphere 144:2229–2237
Apeagyei E, Bank MS, Spengler JD (2011) Distribution of heavy metals in road dust along an urban-rural gradient in Massachusetts. Atmos Environ 45:2310–2323
Chattopadhyay G, Lin KCP, Feitz AJ (2003) Household dust metal levels in the Sydney metropolitan area. Environ Res 93:301–307
Chen M, Pi L, Luo Y, Geng M, Hu W, Li Z, Su S, Gan Z, Ding S (2016) Grain size distribution and health risk assessment of metals in outdoor dust in Chengdu, Southwestern China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 70:534–543
Cheng Z, Chen LH, Li HH, Lin JQ, Yang ZB, Yang YX, Xu XX, Xian JR, Shao JR, Zhu XM (2018) Characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals exposure via household dust from urban area in Chengdu, China. Sci Total Environ 619–620:621–629
Duong TTT, Lee BK (2011) Determining contamination level of heavy metals in road dust from busy traffic areas with different characteristics. J Environ Manag 92:554–562
Elsokkary IH, Lag J (1980) Status of some trace elements in Egyptian soils and in wheat grains. Beitrage Trop Landwirtsch Veterinarmed 18:35–47
Eqani SAMAS, Kanwal A, Bhowmik AK, Sohail M, Ullah R, Ali SM, Alamdar A, Ali N, Fasola M, Shen H (2016) Spatial distribution of dust–bound trace elements in Pakistan and their implications for human exposure. Environ Pollut 213:213–222
Ferreira-Baptista L, De Miguel E (2005) Geochemistry and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: a tropical urban environment. Atmos Environ 39:4501–4512
Harb MK, Ebqa’ai M, Al-rashid A, Alaziqi BH, Al Rashdi MS, Ibrahim B (2015) Investigation of selected heavy metals in street and house dust from Al-Qunfudah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Environ Earth Sci 74:1755–1763
Hassan SKM (2012) Metal concentrations and distribution in the household, stairs and entryway dust of some Egyptian homes. Atmos Environ 54:207–215
Hu X, Zhang Y, Ding Z, Wang T, Lian H, Sun Y, Wu J (2012) Bioaccessibility and health risk of arsenic and heavy metals (Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn and Mn) in TSP and PM2.5 in Nanjing, China. Atmos Environ 57:146–152
Hu Y, Liu X, Bai J, Shih K, Zeng EY, Cheng H (2013) Assessing heavy metal pollution in the surface soils of a region that had undergone three decades of intense industrialization and urbanization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:6150–6159
Jabeen N, Ahmed S, Hassan ST, Alam NM (2001) Levels and sources of heavy metals in house dust. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 247:145–149
Jadoon WA, Khpalwak W, Chidya RCG, Abdel-Dayem SMMA, Takeda K, Makhdoom MA, Sakugawa H (2018) Evaluation of levels, sources and health hazards of road-dust associated toxic metals in Jalalabad and Kabul cities, Afghanistan. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 74:32–45
Kelepertzis E (2014) Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Mediterranean: insights from Argolida basin, Peloponnese, Greece. Geoderma 221–222:82–90
Komarnicki GJK (2005) Lead and cadmium in indoor air and the urban environment. Environ Pollut 136:47–61
Kong S, Lu B, Bai Z, Zhao X, Chen L, Han B, Li Z, Ji Y, Xu Y, Liu Y, Jiang H (2011) Potential threat of heavy metals in re-suspended dusts on building surfaces in oilfield city. Atmos Environ 25:4192–4204
Lorenzi D, Entwistle JA, Cave M, Dean JR (2011) Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban street dust: implications for human health. Chemosphere 83:970–977
Mahmoud EK, Ghoneim AM (2016) Effect of polluted water on soil and plant contamination by heavy metals in El-Mahla El-Kobra, Egypt. Solid Earth 7:703–711
Malik RN, Jadoon WA, Hussain SZ (2010) Metal contamination of surface soils of industrial city Sialkot, Pakistan: a multivariate and GIS approach. Environ Geochem Health 32:179–191
Men C, Liu R, Xu F, Wang Q, Guo L, Shen Z (2018) Pollution characteristics, risk assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. Sci Total Environ 612:138–147
Mohmand J, Eqani SAMAS, Fasola M, Alamdar A, Mustafa I, Ali N, Liu L, Peng S, Shen H (2015) Human exposure to toxic metals via contaminated dust: bio-accumulation trends and their potential risk estimation. Chemosphere 132:142–151
Naggar YA, Naiem E, Mona M, Giesy JP, Seif A (2014) Metal in agricultural soils and plants in Egypt. Toxicol Environ Chem 96:730–742
Pan H, Lu X, Lei K (2017) A comprehensive analysis of heavy metals in urban road dust of Xi'an, China: contamination, source apportionment and spatial distribution. Sci Total Environ 609:1361–1369
Praveena SM, Mutalib NSA, Aris AZ (2015) Determination of heavy metals in indoor dust from primary school (Sri Serdang, Malaysia): estimation of the health risks. Environ Forensic 16:257–263
Rasmussen PE, Levesque C, Chenier M, Gardner HD, Jones-Otazo H, Petrovic S (2013) Canadian house dust study: population-based concentrations, loads and loading rates of arsenic, cadmium, chromium, copper, nickel, lead, and zinc inside urban homes. Sci Total Environ 443:520–529
Saeedi M, Li LY, Salmanzadeh M (2012) Heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: pollution and ecological risk assessment in street dust of Tehran. J Hazard Mater 227–228:9–17
Shah MH, Shaheen N (2007) Statistical analysis of atmospheric trace metals and particulate fractions in Islamabad, Pakistan. J Hazard Mater 147:759–767
Soltani N, Keshavarzi B, Moore F, Tavakol T, Lahijanzadeh RA, Jaafarzadeh N, Kermani M (2015) Ecological and human health hazards of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in road dust of Isfahan metropolis, Iran. Sci Total Environ 505:712–723
Srithawirat T, Latif MT (2015) Concentration of selected heavy metals in the surface dust of residential buildings in Phitsanulok, Thailand. Environ Earth Sci 74:2701–2706
Tang Z, Chai M, Cheng J, Jin J, Yang Y, Nie Z, Huang Q, Li Y (2017) Contamination and health risks of heavy metals in street dust from a coal mining city in eastern China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 138:83–91
Tong STY, Lam KC (2000) Home sweet home? A case study of household dust contamination in Hong Kong. Sci Total Environ 256:115–123
Torghabeh AK, Jahandari A, Jamasb R (2018) Concentration, contamination level, source identification of selective trace elements in Shiraz atmospheric dust sediments (Fars Province, SW Iran). Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(7):6424–6435
Turekian KK, Wedepohl KH (1961) Distribution of the Elements in Some Major Units of the Earth's Crust. GSA Bulletin 72(2):175–192
Yoshinaga J, Yamasaki K, Yonemura A, Ishibashi Y, Kaido T, Mizuno K, Takagi M, Tanaka A (2014) Lead and other elements in house dust of Japanese residences–source of lead and health risks due to metal exposure. Environ Pollut 189:223–228
Yousif M, El-Abd E, Baraka A (2013) Assessment of water resources in some drainage basins, northwestern coast, Egypt. Appl Water Sci 3(2):439–452
Zhang J, Wu J, Hua P, Zhao Z, Wu L, Fan G, Bai Y, Kaeseberg T, Krebs P (2017) The influence of land use on source apportionment and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in road-deposited sediment. Environ Pollut 229:705–714
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to Mr. Mohamed Ali Abdel-Dayem for road- and house-dust sample collection. The anonymous reviewers should be appreciated for their constructive comments that improved this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2155 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jadoon, W.A., Abdel-Dayem, S.M.M.A., Saqib, Z. et al. Heavy metals in urban dusts from Alexandria and Kafr El-Sheikh, Egypt: implications for human health. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 2007–2018 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08786-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08786-1