Abstract
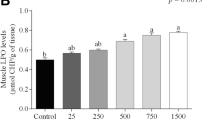
Repeated deposition of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO-NPs) into aquatic systems makes them a global threat since the NPs accumulate in various organs of the fish particularly skeletal muscle. In the present study, adult zebrafish were exposed to different concentrations of CuO-NPs (1 and 3 mg/L) for a period of 30 days. The status of functional markers (acetylcholinesterase, creatine kinase-MB, and lactate dehydrogenase) and oxidative stress markers (oxidants and antioxidants) were analyzed. The histological changes in muscle were studied followed by the immunohistochemistry expression for catalase. Further, the expression of myoD, myogenin, pax7, β-actin, and desmin was examined by semi-quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. The results indicated that chronic exposure to CuO-NPs causes muscular damage as evidenced by elevated levels of functional markers. There was a significant increase in the oxidants with reduction in the antioxidant levels, implying that the antioxidant enzymes were unable to scavenge the free radicals induced by the CuO-NPs. The histopathological analysis showed degeneration and atrophy in the treated groups confirming muscle damage. The immunohistochemical catalase expression in the muscle was reduced in the treated groups further supporting the evidence that the antioxidant has suffered a decline. The altered gene expression indicates skeletal muscle damage due to the CuO-NPs exposure. Overall, the data suggest that chronic exposure to CuO-NPs caused muscular toxicity which may lead to muscle degeneration in adult zebrafish.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Ahamed M, Siddiqui MA, Akhtar MJ, Ahmad I, Pant AB, Alhadlaq HA (2010) Genotoxic potential of copper oxide nanoparticles in human lung epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 396(2):578–583
Akhtar MJ, Ahamed M, Kumar S, Khan MM, Ahamad J, Alrokayan SA (2012) Zinc oxide nanoparticles selectively induce apoptosis in human cancer cells through reactive oxygen species. Int J Nanomedicine 7:845–857
Al-Bairuty GA, Shaw BJ, Handy RD, Henry TB (2013) Histopathological effects of waterborne copper nanoparticles and copper sulphate on the organs of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat Toxicol 126:104–115
Ates M, Arslan Z, Demir V, Daniels J, Farah IO (2015) Accumulation and toxicity of CuO and ZnO nanoparticles through waterborne and dietary exposure of goldfish (Carassius auratus). Environ Toxicol 30(1):119–128
Ates M, Dugo MA, Demir V, Arslan Z, Tchounwou PB (2014) Effect of copper oxide nanoparticles to sheepshead minnow (Cyprinodon variegatus) at different salinities. Dig J Nanomater Biostruct 9(1):369–377
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44(1):276–287
Bhatt I, Tripathi BN (2011) Interaction of engineered nanoparticles with various components of the environment and possible strategies for their risk assessment. Chemosphere 82(3):308–317
Chang YN, Zhang M, Xia L, Zhang J, Xing G (2012) The toxic effects and mechanisms of CuO and ZnO nanoparticles. Materials 5(12):2850–2871
Choi JE, Kim S, Ahn JH, Youn P, Kang JS, Park K, Yi J, Ryu DY (2010) Induction of oxidative stress and apoptosis by silver nanoparticles in the liver of adult zebrafish. Aquat Toxicol 2:151–159
Cole LK, Ross LS (2001) Apoptosis in the developing zebrafish embryo. Dev Biol 240(1):123–142
Dalle-Donne I, Rossi R, Giustarini D, Milzani A, Colombo R (2003) Protein carbonyl groups as biomarkers of oxidative stress. Clin Chim Acta 329(1-2):23–38
Devasagayam TP, Tarachand U (1987) Decreased lipid peroxidation in the rat kidney during gestation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 145(1):134–138
Dubey P, Matai I, Kumar SU, Sachdev A, Bhushan B, Gopinath P (2015) Perturbation of cellular mechanistic system by silver nanoparticle toxicity: cytotoxic, genotoxic and epigenetic potentials. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 221:4–21
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82(1):70–77
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7(2):88–95
Elsaesser A, Howard CV (2012) Toxicology of nanoparticles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64(2):129–137
Fard JK, Jafari S, Eghbal MA (2015) A review of molecular mechanisms involved in toxicity of nanoparticles. Adv Pharm Bull 5(4):447–454
Flonta ML, De Beir-Simaels J, Mesotten D, Van Driessche W (1986) Cu2+ reveals different binding sites of amiloride and CDPC on the apical Na channel of frog skin. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1370(1):169–174
Ganesan S, Anaimalai Thirumurthi N, Raghunath A, Vijayakumar S, Perumal E (2016) Acute and sub-lethal exposure to copper oxide nanoparticles causes oxidative stress and teratogenicity in zebrafish embryos. J Appl Toxicol 36(4):554–567
Gebicka L, Didik J (2010) Oxidative stress induced by peroxynitrite. Postepy Biochem 56(2):103–106
Ghobadian M, Nabiuni M, Parivar K, Fathi M, Pazooki J (2015) Toxic effects of magnesium oxide nanoparticles on early developmental and larval stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 122:260–267
Gomes T, Pinheiro JP, Cancio I, Pereira CG, Cardoso C, Bebianno MJ (2011) Effects of copper nanoparticles exposure in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Environ Sci Technol 45(21):9356–9362
González C, Salazar-García S, Palestino G, Martínez-Cuevas PP, Ramírez-Lee MA, Jurado-Manzano BB, Rosas-Hernández H, Gaytán-Pacheco N, Martel G, Espinosa-Tanguma R, Biris AS (2011) Effect of 45 nm silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) upon the smooth muscle of rat trachea: role of nitric oxide. Toxicol Lett 207(3):306–313
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N] nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126(1):131–138
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JM (2015) Free radicals in biology and medicine. Oxford University Press, USA
Ispas C, Andreescu D, Patel A, Goia DV, Andreescu S, Wallace KN (2009) Toxicity and developmental defects of different sizes and shape nickel nanoparticles in zebrafish. Environ Sci Technol 43(16):6349–6356
Kablar B, Krastel K, Tajbakhsh S, Rudnicki MA (2003) Myf5 and MyoD activation define independent myogenic compartments during embryonic development. Dev Biol 258(2):307–318
Keller AA, Lazareva A (2013) Predicted releases of engineered nanomaterials: from global to regional to local. Environ Sci Technol Lett 1(1):65–70
Khalaj M, Kamali M, Khodaparast Z, Jahanshahi A (2018) Copper-based nanomaterials for environmental decontamination–an overview on technical and toxicological aspects. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:813–824
Khan KM, Taha M, Naz F, Siddiqui S, Ali S, Rahim F, Perveen S, Choudhary MI (2012) Acylhydrazide Schiff bases: DPPH radical and superoxide anion scavengers. Med Chem 8(4):705–10
Knight JA (1995) Diseases related to oxygen-derived free radicals. Ann Clin Lab Sci 25(2):111–121
Kono Y, Fridovich I (1982) Superoxide radical inhibits catalase. J Biol Chem 257(10):5751–5754
Korani M, Rezayat SM, Bidgoli SA (2013) Sub-chronic dermal toxicity of silver nanoparticles in guinea pig: special emphasis to heart, bone and kidney toxicities. Iran J Pharm Res 12(3):511
Lai X, Zhao H, Zhang Y, Guo K, Xu Y, Chen S, Zhang J (2018) Intranasal delivery of copper oxide nanoparticles induces pulmonary toxicity and fibrosis in C57BL/6 mice. Sci Rep 8(1):4499
Lazarides E (1980) Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature 283(5744):249–255
Levine RL, Garland D, Oliver CN, Amici A, Climent I, Lenz AG, Ahn BW, Shaltiel S, Stadtman ER (1990) Determination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol 186:464–478 Academic Press
Li M, Andersson-Lendahl M, Sejersen T, Arner A (2013) Knockdown of desmin in zebrafish larvae affects interfilament spacing and mechanical properties of skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol 141(3):335–345
Li X, Nie F, Yin Z, He J (2011) Enhanced hyperplasia in muscles of transgenic zebrafish expressing Follistatin1. Sci China Life Sci 54(2):159–165
Li Z, Mericskay M, Agbulut O, Butler-Browne G, Carlsson L, Thornell LE, Babinet C, Paulin D (1997) Desmin is essential for the tensile strength and integrity of myofibrils but not for myogenic commitment, differentiation, and fusion of skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol 139(1):129–144
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Lushchak VI (2012) Glutathione homeostasis and functions: potential targets for medical interventions. J Amino Acids 2012:1–26
Ma X, Geiser-Lee J, Deng Y, Kolmakov A (2010) Interactions between engineered nanoparticles (ENPs) and plants: phytotoxicity, uptake and accumulation. Sci Total Environ 408(16):3053–3061
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47(3):469–474
Maves L, Waskiewicz AJ, Paul B, Cao Y, Tyler A, Moens CB, Tapscott SJ (2007) Pbx homeodomain proteins direct Myod activity to promote fast-muscle differentiation. Development. 134(18):3371–3382
Melegari SP, Perreault F, Moukha S, Popovic R, Creppy EE, Matias WG (2012) Induction to oxidative stress by saxitoxin investigated through lipid peroxidation in Neuro 2A cells and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii alga. Chemosphere 89(1):38–43
Monserrat JM, Martínez PE, Geracitano LA, Amado LL, Martins CM, Pinho GL, Chaves IS, Ferreira-Cravo M, Ventura-Lima J, Bianchini A (2007) Pollution biomarkers in estuarine animals: critical review and new perspectives. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 146(1-2):221–234
Mwaanga P, Carraway ER, van den Hurk P (2014) The induction of biochemical changes in Daphnia magna by CuO and ZnO nanoparticles. Aquat Toxicol 150:201–209
Olson EN, Perry M, Schulz RA (1995) Regulation of muscle differentiation by the MEF2 family of MADS box transcription factors. Dev Biol 172(1):2–14
Olsvik PA, Lie KK, Jordal AE, Nilsen TO, Hordvik I (2005) Evaluation of potential reference genes in real-time RT-PCR studies of Atlantic salmon. BMC Mol Biol 6(1):21
Osborne OJ, Lin S, Chang CH, Ji Z, Yu X, Wang X, Lin S, Xia T, Nel AE (2015) Organ-specific and size-dependent Ag nanoparticle toxicity in gills and intestines of adult zebrafish. ACS Nano 9(10):9573–9584
Ozel RE, Alkasir RS, Ray K, Wallace KN, Andreescu S (2013) Comparative evaluation of intestinal nitric oxide in embryonic zebrafish exposed to metal oxide nanoparticles. Small 9(24):4250–4261
Pandey S, Parvez S, Sayeed I, Haque R, Bin-Hafeez B, Raisuddin S (2003) Biomarkers of oxidative stress: a comparative study of river Yamuna fish Wallago attu (Bl. & Schn.). Sci Total Environ 309(1-3):105–115
Peng C, Shen C, Zheng S, Yang W, Hu H, Liu J, Shi J (2017) Transformation of CuO nanoparticles in the aquatic environment: influence of ph, electrolytes and natural organic matter. Nanomaterials 7(10):326
Radu M, Din IM, Hermenean A, Cinteză OL, Burlacu R, Ardelean A, Dinischiotu A (2015) Exposure to iron oxide nanoparticles coated with phospholipid-based polymeric micelles induces biochemical and histopathological pulmonary changes in mice. Int J Mol Sci 16(12):29417–29435
Radi R (2013) Peroxynitrite, a stealthy biological oxidant. J Biol Chem 288(37):26464–72
Raghunath A, Perumal E (2017) Metal oxide nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: a promise for the future. Int J Antimicrob Agents 49(2):137–152
Roe JH, Kuether CA (1943) The determination of ascorbic acid in whole blood and urine through the 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine derivative of dehydroascorbic acid. J Biol Chem 147:399–407
Rotruck JT, Pope AL, Ganther HE, Swanson AB, Hafeman DG, Hoekstra W (1973) Selenium: biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase. Science 179(4073):588–590
Rowlerson A, Veggetti A (2004) Cellular mechanisms of post-embryonic muscle growth in aquaculture species. Fish Physiol 18:103–140
Ruan W, Lai M (2007) Actin, a reliable marker of internal control? Clin Chim Acta 385(1-2):1–5
Sarkar A, Das J, Manna P, Sil PC (2011) Nano-copper induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in kidney via both extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. Toxicology 290(2-3):208–217
Schnapp E, Pistocchi AS, Karampetsou E, Foglia E, Lamia CL, Cotelli F, Cossu G (2009) Induced early expression of mrf4 but not myog rescues myogenesis in the myod/myf5 double-morphant zebrafish embryo. J Cell Sci 122(Pt 4):481–488
Seger C, Hargrave M, Wang X, Chai RJ, Elworthy S, Ingham PW (2011) Analysis of Pax7 expressing myogenic cells in zebrafish muscle development, injury, and models of disease. Dev Dyn 240(11):2440–2451
Shi J, Abid AD, Kennedy IM, Hristova KR, Silk WK (2011) To duckweeds (Landoltia punctata), nanoparticulate copper oxide is more inhibitory than the soluble copper in the bulk solution. Environ Pollut 159(5):1277–1282
Siddiqui MA, Alhadlaq HA, Ahmad J, Al-Khedhairy AA, Musarrat J, Ahamed M (2013) Copper oxide nanoparticles induced mitochondria mediated apoptosis in human hepatocarcinoma cells. PLoS One 8(8):e69534
Stadtman ER, Berlett BS (1997) Reactive oxygen-mediated protein oxidation in aging and disease. Chem Res Toxicol 10(5):485–94
Sun D, Zhang Y, Wang C, Hua X, Zhang XA, Yan J (2013) Sox9-related signaling controls zebrafish juvenile ovary–testis transformation. Cell Death Dis 4(11):e930
Sun Y, Zhang G, He Z, Wang Y, Cui J, Li Y (2016) Effects of copper oxide nanoparticles on developing zebrafish embryos and larvae. Int J Nanomedicine 11:905
Tang R, Dodd A, Lai D, McNabb WC, Love DR (2007) Validation of zebrafish (Danio rerio) reference genes for quantitative real-time RT-PCR normalization. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 39(5):384–390
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT, Mazur M, Telser J (2007) Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39(1):44–84
Vogel FS (1959) The deposition of exogenous copper under experimental conditions with observations on its neurotoxic and nephrotoxic properties in relation to Wilson’s disease. J Exp Med 110(5):801–810
Wang HF, Zhong XH, Shi WY, Guo B (2011) Study of malondialdehyde (MDA) content, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) activities in chickens infected with avian infectious bronchitis virus. Afr J Biotechnol 10(45):9213–9217
Wang T, Long X, Cheng Y, Liu Z, Yan S (2014) The potential toxicity of copper nanoparticles and copper sulphate on juvenile Epinephelus coioides. Aquat Toxicol 152:96–104
Wang Y, Yang F, Zhang HX, Zi XY, Pan XH, Chen F, Luo WD, Li JX, Zhu HY, Hu YP (2013b) Cuprous oxide nanoparticles inhibit the growth and metastasis of melanoma by targeting mitochondria. Cell Death Dis 4(8):e783
Wang Z, Von Dem Bussche A, Kabadi PK, Kane AB, Hurt RH (2013a) Biological and environmental transformations of copper-based nanomaterials. ACS Nano 7(10):8715–8727
Wei T, Chen C, Hou J, Xin W, Mori A (2000) Nitric oxide induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in neuronal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta, Mol Cell Res 1498(1):72–79
Weintraub H (1993) The MyoD family and myogenesis: redundancy, networks, and thresholds. Cell 75(7):1241–1244
Wu B, Torres-Duarte C, Cole BJ, Cherr GN (2015) Copper oxide and zinc oxide nanomaterials act as inhibitors of multidrug resistance transport in sea urchin embryos: their role as chemosensitizers. Environ Sci Technol 49(9):5760–5770
Wu Y, Zhou Q (2012) Dose-and time-related changes in aerobic metabolism, chorionic disruption, and oxidative stress in embryonic medaka (Oryzias latipes): underlying mechanisms for silver nanoparticle developmental toxicity. Aquat Toxicol 124:238–246
Xiang Q, Xu B, Ding Y, Liu X, Zhou Y, Ahmad F (2018) Oxidative stress response induced by butachlor in zebrafish embryo/larvae: the protective effect of vitamin C. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 100(2):208–215
Xiao Y, Vijver MG, Chen G, Peijnenburg WJ (2015) Toxicity and accumulation of Cu and ZnO nanoparticles in Daphnia magna. Environ Sci Technol 49(7):4657–4664
Xiong D, Fang T, Yu L, Sima X, Zhu W (2011) Effects of nano-scale TiO2, ZnO and their bulk counterparts on zebrafish: acute toxicity, oxidative stress and oxidative damage. Sci Total Environ 409(8):1444–1452
Xu J, Zhang Q, Li X, Zhan S, Wang L, Chen D (2017) The effects of copper oxide nanoparticles on dorsoventral patterning, convergent extension, and neural and cardiac development of zebrafish. Aquat Toxicol 188:130–137
Yamakoshi Y, Umezawa N, Ryu A, Arakane K, Miyata N, Goda Y, Masumizu T, Nagano T (2003) Active oxygen species generated from photoexcited fullerene (C60) as potential medicines: O2-• versus 1O2. J Am Chem Soc 125(42):12803–12809
Zhang J, Shen H, Wang X, Wu J, Xue Y (2004) Effects of chronic exposure of 2, 4-dichlorophenol on the antioxidant system in liver of freshwater fish Carassius auratus. Chemosphere 55(2):167–174
Zhang M, An C, Gao Y, Leak RK, Chen J, Zhang F (2013) Emerging roles of Nrf2 and phase II antioxidant enzymes in neuroprotection. Prog Neurobiol 100:30–47
Zhao CM, Wang WX (2011) Comparison of acute and chronic toxicity of silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate to Daphnia magna. Environ Toxicol Chem 30(4):885–892
Zhao CM, Wang WX (2012) Importance of surface coatings and soluble silver in silver nanoparticles toxicity to Daphnia magna. Nanotoxicology 6(4):361–370
Zhao J, Liu Y, Pan B, Gao G, Liu Y, Liu S, Liang N, Zhou D, Vijver MG, Peijnenburg WJ (2017) Tannic acid promotes ion release of copper oxide nanoparticles: impacts from solution pH change and complexation reactions. Water Res 127:59–67
Zhu X, Zhu L, Duan Z, Qi R, Li Y, Lang Y (2008) Comparative toxicity of several metal oxide nanoparticle aqueous suspensions to Zebrafish (Danio rerio) early developmental stage. J Environ Sci Health A 43(3):278–284
Acknowledgments
Satheeswaran Balasubramanian acknowledges the URF fellowship (C2/29000/2018) funded by Bharathiar University, Tamil Nadu, India. Azhwar Raghunath acknowledges the UGC-BSR Senior Research Fellowship (UGC-BSR No. F7-25/2007), UGC-BSR, New Delhi, India. The authors thank the Department of Science and Technology, Science and Engineering Research Board (EEQ/2018/000633).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mani, R., Balasubramanian, S., Raghunath, A. et al. Chronic exposure to copper oxide nanoparticles causes muscle toxicity in adult zebrafish. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 27358–27369 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06095-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06095-w