Abstract
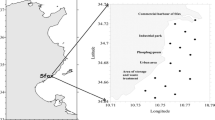
Heavy metal residues in sediment and Oreochromis niloticus fish muscles, collected from a Nile River Canal (Bahr Shebeen Canal), Egypt, were investigated from September 2014 to December 2015. The spatial and seasonal distributions of Cd, Cu, Fe, Pb, and Zn are described and discussed. Relative abundance of these metals in sediment was found as follows: Fe > Zn > Cu > Pb > Cd. Indices of pollution were used to detect the degree of sediment contamination and indicated elevated concentrations likely to adversely affect benthic and benthic-associated organisms. Anthropogenic activities strongly influenced metal occurrence in sediments. Accumulation of heavy metals in fish muscular tissue was found to be nearly comparable to the sediment. Relative abundance of metals in fish tissue followed the trend of Fe > Zn > Pb > Cu > Cd. Fish can be used as a surrogate for heavy metals pollution. The bioaccumulation factor (BAF) in fish muscle showed the following trend: Pb > Zn > Cu > Fe > Cd. Levels of most selected heavy metals detected in muscular tissue of fish were below admissible limits set by different organizations. However, HI (hazard index) showed that the cumulative risk effects are of considerable concern, especially where fish consumption is high. Consequently, it is recommended that discharged water containing pollutants should be prioritized to include continuous monitoring, and adequate public awareness.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Satar AM (2005) Quality of River Nile sediments from Idfo to Cairo. Egypt J Aquat Res 31:182–199
AbouelFadl KY, Aly W, Abd El-Reheem AE, Mahmoud UM, Hamed HS, Moustafa MA, Osman AGM (2016) Heavy metals levels in the blood of Oreochromis niloticus niloticus and Clarias gariepinus as biomarkers of metal pollution in the River Nile. Int J Ecotoxicol Ecobiol 1:1–12
Al-Alimi AKAA, Alhudify NS (2016) Assessment of heavy metals contamination and its ecological risk in the surface sediments of Al-Mukalla coast, Yemen. J Sci Eng Res 3:13–23
Al-Nenaei AA (2003) Contamination of irrigation and drainage canals and ponds in the Nile delta by heavy metals and its association with human health risks. Egypt. J Zool 4l:47–60
Al-Nenaei AA (2004) Storage of illegally cultured fishes in the Nile streams—a possible gateway for contamination of aquatic environment and wild fishes. Egypt. J Zool 42:133–153
Alne-na-ei AA, Rady MI (1998) Ecological studies on the catfish, Chrysichthys rueppelli (Siluroidei, Bagridae) in a Nile tributary with notes on the factors influencing the ratio of ovarian atresia. J Union Arab Biol, Cairo 10(A):467–488
Alomary AA, Belhadj S (2007) Determination of heavy metals (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Ni, Pb, Zn) by ICP-OES and their speciation in Algerian Mediterranean sea sediments after a five-stage sequential extraction procedure. Environ Monit Assess 135:265–280
Asuquo FE, Ewa-Oboho I, Asuquo EF, Udoh PJ (2004) Fish species used as biomarker for heavy metal and hydrocarbon contamination for Cross River, Nigeria. Environmentalist 24:29–37
Authman MMN, Abbas WT, Gaafar AY (2012) Metals concentrations in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) from illegal fish farm in Al-Minufiya Province, Egypt, and their effects on some tissues structures. Ecotox Environ Safe 84:163–172
Authman MMN, Zaki MS, Khallaf EA, Abbas HH (2015) Use of fish as bio-indicator of the effects of heavy metals pollution. J Aquacult Res Develop 6:328, 13p
Bayomy HM, Rozan MA, Ziena HM (2015) Lead and cadmium contents in Nile water, tilapia and catfish from Rosetta branch, River Nile, Egypt. J Food and Dairy Sci, Mansoura Univ, Egypt 6:253–262
Bishai HM, Khalil MT (1997) Freshwater fishes of Egypt. Egyptian Environmental Affairs Agency (EEAA), Cabinet of Ministers, Egypt, Department of Nature Protection. Publication of National Biodiversity Unit No. 9: 229p
CCME (Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment) (2012) Sediment Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life, Canadian environmental quality guidelines summary table. Dec–2012, 9p.
EC (Commission Regulation) (2006) 1881/2006 Setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Off J Eur Union L 364:20p
El Bouraie MM, El Barbary AA, Yehia MM, Motawea EA (2010) Heavy metal concentrations in surface river water and bed sediments at Nile Delta in Egypt. Suoseura-Finnish Peatland Society 61:1–12
Elias MdS, Hamzah MS, Ab Rahman S, Salim NAA, Siong WB, Sanuri E (2014) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metal in surface sediment collected from Tuanku Abdul Rahman National Park, Sabah. AIP Conference Proceedings 1584(1):196–206
Elkady AA, Sweet ST, Wade TL, Klein AG (2015) Distribution and assessment of heavy metals in the aquatic environment of Lake Manzala, Egypt. Ecol Indic 58:445–457
El-Sayed SA, Moussa EMM, El-Sabagh MEI (2015) Evaluation of heavy metal content in Qaroun Lake, El-Fayoum, Egypt. Part I: bottom sediments. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 8:276–285
EOSQC (Egyptian Organization for Standardization and Quality Control) (1993) Maximum Residue Limits for Heavy Metals in Food. Ministry of Industry No. 2360/1993, 5p
FAO (1992) Committee for Inland Fisheries of Africa. Report of the third Session of the Working Party on Pollution and Fisheries, Accra, Ghana, 25–29 November 1991, FAO Fisheries Report, No. 471, Rome, 43p
FAO/WHO (2006) A model for establishing upper levels of intake for nutrients and related substances. Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Technical Workshop on Nutrient Risk Assessment, WHO Headquarters, Geneva, Switzerland 2–6 May 2005, WHO Headquarters, Geneva, Switzerland
Gati G, Pop C, Brudaşcă F, Gurzău AE, Spînu M (2016) The ecological risk of heavy metals in sediment from the Danube Delta. Ecotoxicology 25:688–696
Ghanem MH, Ghanem EH, Shehata SM, Zaahkouk SA, El-Amawy AB (2016) Influences of some pollutants on water quality of El-Bagouria Canal at Kafr El-Zayat Region, El-Gharbia Governorate, Egypt. Egypt J Aquat Biol Fish 20:89–111
Giesy JP, Hoke RA (1990) Freshwater sediment quality criteria: toxicity bioassessment. In: Baudo R, Giesy JP, Muntao M (eds) Sediments: Chemistry and toxicity of in-place pollutants. Lewis Publishers, Ann Arbor, MI, pp 265–348
Goher ME, Farhat HI, Abdo MH, Salem SG (2014) Metal pollution assessment in the surface sediment of Lake Nasser, Egypt. Egypt J Aquat Res 40:213–224
Goodwin TH, Young AR, Holmes MGR, Old GH, Hewitt N, Leeks GJL, Packman JC, Smith BPG (2003) The temporal and spatial variability of sediment transport and yields within the Bradford Beck catchment, West Yorkshire. Sci Total Environ 314-316:475–494
Gu J, Salem A, Chen Z (2013) Lagoons of the Nile delta, Egypt, heavy metal sink: with a special reference to the Yangtze estuary of China. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 117:282–292
Håkanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Hayat S, Javed M, Razzaq S (2007) Growth performance of metal stressed major carps viz. Catla Catla, Labeo Rohita and Cirrhina Mrigala reared under semi-intensive culture system. Pak Vet J 27:8–12
Ibrahim AThA, Omar HM (2013) Seasonal variation of heavy metals accumulation in muscles of the African catfish Clarias gariepinus and in River Nile water and sediments at Assiut governorate, Egypt. J Biol Earth Sci 3:B236–B248
Ibrahim AThA, Wassif ET, Alfons MS (2016) Heavy metals assessment in water, sediments and some organs of Oreochromis niloticus under the impact of sewage water. J Heavy Metal Toxicity Dis 1(1):4, 7p
Jain CK, Gupta H, Chakrapani GJ (2008) Enrichment and fractionation of heavy metals in bed sediments of River Narmada, India. Environ Monit Assess 141:35–47
Javed M (2005) Heavy metal contamination of freshwater fish and bed sediments in the River Ravi stretch and related tributaries. Pak J Biol Sci 8:1337–1341
Jones DS, Suter GW, Hull RN (1997) Toxicological benchmarks for screening contaminants of potential concern for effects on sediment-associated biota: 1997 revision. ES/ER/TM-95/R4, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, US Dept. of Energy, Oak Ridge, TN
Khallaf EA (2002) An ecological assessment of Bahr Shebeen Nilotic Canal (a review paper). J Union Arab Biol, Cairo, Egypt 17(A):65–75
Khallaf EA, Authman MN (1992) Changes in diet, prey size and feeding habit in Bagrus bayad, and possible interactions with B. docmac in a Nile canal. Environ Biol Fish 34:425–431
Khallaf EA, Authman MMN, Alne-na-ei AA (2017) Evaluation of organochlorine and organophosphorus pesticides residues in the sediment and muscles of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) fish from a River Nile Canal, Egypt. Int J Environ Stud, https://doi.org/10.1080/00207233.2017.1378019, 23p
Klavins M, Briede A, Parele E, Rodinov V, Klavina I (1998) Metal accumulation in sediments and benthic invertebrates in Lakes of Latvia. Chemosphere 36:3043–3053
Korium MA, Toufeek MEF, El-Haty EY (2006) Distribution of Al, Ag, Cr, Mn, Ni, Zn and some physicochemical characteristics of River Nile water and sediment at Aswan. Egypt J Aquat Res 32:208–225
Kouadio I, Trefry JH (1987) Sediment trace metal contamination in the Ivory Coast, West Africa. Water Air Soil Pollut 32:145–154
Lasheen MR, Ammar NS (2009) Speciation of some heavy metals in River Nile sediments, Cairo, Egypt. Environmentalist 29:8–16
Maanan M, Saddik M, Maanan M, Chaibi M, Assobhei O, Zourarah B (2014) Environmental and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Nador lagoon, Morocco. Ecol Indic 48:616–626
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Malhat FMM (2010) Organochlorines and organophosphours pesticides, petroleum hydrocarbons, polychlorinated biphenyls and trace metal monitoring of Nile River in Egypt. Ph D Dissertation, Faculty of Science, Benha University, Benha, Egypt, 186p
Malhat F (2011) Distribution of heavy metal residues in fish from the River Nile tributaries in Egypt. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 87:163–165
Mansour SA, Sidky MM (2002) Ecotoxicological studies. 3. Heavy metals contaminating water and fish from Fayoum governorate, Egypt. Food Chem 78:15–22
Mekkawy IAA, Mahmoud UM, Ibrahim ATA (2008) Heavy metal distribution in some organs of Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) collected from three localities at Assiut, Egypt and the corresponding tissue damage. J Egypt Ger Soc Zool 55(B):97–127
Morgan AM, Shin H-C, Abd El Aty AM (2008) Characterization of the heavy metals contaminating the River Nile at El-Giza Governorate, Egypt and their relative bioaccumulations in Tilapia nilotica. Toxicol Res 24:297–305
Mulligan CN, Yong RN, Gibbs BF (2001) An evaluation of technologies for the heavy metal remediation of dredged sediments. J Hazard Mater 85:145–163
Nauen CE (1983) Compilation of legal limits for hazardous substances in fish and fishery products. FAO Fish Circ 764:102p
Omar WA, Zaghloul KH, Abdel-Khalek AA, Abo-Hegab S (2013) Risk assessment and toxic effects of metal pollution in two cultured and wild fish species from highly degraded aquatic habitats. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 65:753–764
Omar WA, Mikhail WZA, Abdo HM, Abou El Defan TA, Poraas MM (2015) Ecological risk assessment of metal pollution along Greater Cairo Sector of the River Nile, Egypt, using Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, as bioindicator. Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Toxicology Volume 2015, Article ID 167319, 11p
Osman AGM (2012) Biomarkers in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) to assess the impacts of River Nile pollution: bioaccumulation, biochemical and tissues biomarkers. J Environ Prot 3:966–977
Osman AGM, Kloas W (2010) Water quality and heavy metal monitoring in water, sediments, and tissues of the African catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822) from the River Nile, Egypt. J Environ Prot 1:389–400
Osman AGM, Abd El Reheem AEBM, AbuelFadl KY, GadEl-Rab AG (2010) Enzymatic and histopathologic biomarkers as indicators of aquatic pollution in fishes. Nat Sci 2:1302–1311
Osman GY, Radwan NA, Khalil AI, Abo Msalam AM (2008) Helminth communities of Bagrus docmac and Malepterurus electricus in three water bodies at Menoufiya governorate, Egypt. Egypt J Exp Biol (Zool) 4:177–192
Peña-Mendoza B, Gómez-Márquez JL, Salgado-Ugarte IH, Ramírez-Noguera D (2005) Reproductive biology of Oreochromis niloticus (Perciformes: Cichlidae) at Emiliano Zapata dam, Morelos, Mexico. Rev Biol Trop 53:515–522
Persaud D, Jaagumagi R, Hayton A (1993) Guidelines for the protection and management of aquatic sediment quality in Ontario. Ministry of Environment and Energy, Ontario, Canada, 39p
Phillips DJH (1980) Quantitative aquatic biological indicators: their use to monitor trace metal and organochlorine pollution. Applied Science Publishers Ltd., London, 488p
Raeisi S, Rad JS, Rad MS, Zakariaei H (2014) Analysis of heavy metals content in water, sediments and fish from the Gorgan bay, southeastern Caspian sea, Iran. Int J Adv Biol Biomed Res 2:2162–2172
Rashed MN (2001) Monitoring of environmental heavy metals in fish from Nasser Lake. Environ Int 27:27–33
Redwan M, Elhaddad E (2016) Seasonal variation and enrichment of metals in sediments of Rosetta branch, Nile River, Egypt. Environ Monit Assess 188:354, 12p
Schuller PL, Coles LE (1979) The determination of copper in foodstuffs. (IUPAC, International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Applied Chemistry Division, Commission on Food Contaminants). Pure Appl Chem 51:385–392
Soltan ME, Moalla SMN, Rashed MN, Fawzy EM (2005) Physicochemical characteristics and distribution of some metals in the ecosystem of Lake Nasser, Egypt. Toxicol Environ Chem 87:167–197
Sondag F, Guyot J-L, Moquet JS, Laraque A, Adéle G, Cochonneau G, Dodou J-C, Lagane C, Vauchel P (2010) Suspended sediment and dissolved load budgets of two Amazonian rivers from the Guiana Shield: Maroni River at Langa Tabiki and Oyapock River at Saut Maripa (French Guiana). Hydrol Process 24:1433–1445
Taylor SR (1964) Abundance of chemical elements in the continental crust: a new table. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 28:1273–1285
Tomlinson DL, Wilson JG, Harris CR, Jeffery DW (1980) Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen 33:566–575
Turekian KK, Wedepohl KH (1961) Distribution of the elements in some major units of the Earth’s crust. Geol Soc Am Bull 72:175–192
Uluturhan E, Kucuksezgin F (2007) Heavy metal contaminations in Red Pandora (Pagellus erythrinus) tissues from the Eastern Aegean Sea, Turkey. Water Res 41:1185–1192
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (2000) Guidance for assessing chemical contaminant data for use in fish advisories. Volume 2: risk assessment and fish consumption limits (3rd ed.). EPA 823-B-00-008, Office of Science and Technology, Office of Water, Washington, DC, 383p
Usero J, González-Regalado E, Gracia I (1997) Trace metals in bivalve molluscs Ruditapes decussatus and Ruditapes philippinarum from the Atlantic Coast of southern Spain. Environ Int 23:291–298
Weber P, Behr ER, Knorr CDL, Vendruscolo DS, Flores EMM, Dressler VL, Baldisserotto B (2013) Metals in the water, sediment, and tissues of two fish species from different trophic levels in a subtropical Brazilian river. Microchem J 106:61–66
WHO (World Health Organization) (2008) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, Volume 1: Recommendations. Third ed. WHO, Geneva, Switzerland, 668p
Yacoub AM, Gad NS (2012) Accumulation of some heavy metals and biochemical alterations in muscles of Oreochromis niloticus from the River Nile in Upper Egypt. Int J Environ Sci Eng 3:1–10
Yehia HM, Sebaee ESh (2012) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in water, sediment and fish (Oreochromis niloticus and Clarias anguillaris), in Rosetta branch of the River Nile, Egypt. Afr J Biotec 11:14204–14216
Yi Y, Wang Z, Zhang K, Yu G, Duan X (2008) Sediment pollution and its effect on fish through food chain in the Yangtze River. Int J Sedim Res 23:338–347
Yi Y, Yang Z, Zhang S (2011) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin. Environ Pollut 159:2575–2585
Zhai M, Kampunzu HAB, Modisi MP, Totolo O (2003) Distribution of heavy metals in Gaborone urban soils (Botswana) and its relationship to soil pollution and bedrock composition. Environ Geol 45:171–180
Zhao S, Feng C, Quan W, Chen X, Niu J, Shen Z (2012) Role of living environments in the accumulation characteristics of heavy metals in fishes and crabs in the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Mar Pollut Bull 64:1163–1171
Funding
This research is funded, for the first author of this article, by the University of Minoufia Research Projects Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Only caught fish by fishermen are used.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khallaf, E.A., Authman, M.M. & Alne-na-ei, A.A. Contamination and Ecological Hazard Assessment of Heavy Metals in Freshwater Sediments and Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) Fish Muscles in a Nile River Canal in Egypt. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 13796–13812 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1521-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1521-5