Abstract
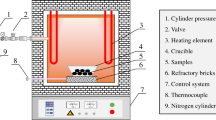
A SSW/Al-Cu formed from an industrial solid waste and Al-Cu Nps are utilized for the removal of fluoride from aqueous solutions. The SSW/Al-Cu was obtained by a chemical reduction method. The SSW/Al-Cu was characterized by TEM, SEM, FT-IR, XRD, BET, and pHzpc techniques. The Nps were formed as bimetallic oxides and deposited in the form of spheroidal particles forming agglomerations. The sizes of these particles range from 1 to 3 nm. The surface area and average pore width of SSW/Al-Cu were 2.99 m2/g and 17.09 nm, respectively. The adsorption kinetics were better described using the second-order model, pointing to chemical adsorption with an equilibrium time of 540 min. The thermodynamic parameters obtained here confirm the spontaneous and endothermic nature of the process. The percentage of fluoride removal was 89.5% using the four-bladed disk turbine, and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling demonstrated that using the four-bladed disk turbine helped improve the fluoride removal process. The maximum adsorption capacity was 3.99 mg/g. The Langmuir-Freundlich model best describes the adsorption process, which occurred by a combination of mechanisms, such as electrostatic interactions between the ions involved in the process. This study proves that the chemical modification of this waste solid created an efficient bimetallic nanomaterial for fluoride removal. Furthermore, the method of preparation of these nanocomposites is quite scalable.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah D, Usamah A, Tahar L, Rached B, Al-Marri MJ, Almanassra IW, Abdala A, Muataz A (2016) Heat transfer enhancement of nanofluids using iron nanoparticles decorated carbon nanotubes. Appl Therm Eng 107:1008–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.07.026
Abo A, Alonso A, Sánchez A, Font X (2017) Adsorption process of fluoride from drinking water with magnetic core-shell Ce-Ti@Fe3O4 and Ce-Ti oxide nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ 598:949–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.191
Aguirre JM, Gutiérrez A, Giraldo O (2011) Simple route for the synthesis of copper hydroxy salts. J Braz Chem Soc 22(3):546–551. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-50532011000300019
Alarcón-Herrera MT, Bundschuh J, Bibhash N, Nicolli HB, Gutierrez M, Reyes-Gomez VM, Nuñez D, Martín-Dominguez IR, Sracek O (2013) Co-occurrence of arsenic and fluoride in groundwater of semi-arid regions in Latin America: genesis, mobility and remediation. J Hazard Mater 262:960–969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.08.005
Amalraj A, Pius A (2013) Health risk from fluoride exposure of a population in selected areas of Tamil Nadu South India. Food Sci Hum Wellness 2(2):75–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2013.03.005.AP
Bayazit Ş, Yildiz M, Asçi YS, Bener M, Eğlence S, Salam MA (2017) Rapid adsorptive removal of naphthalene from water using graphene nanoplatelet/MIL-101 (Cr) nanocomposite. J Alloy Compd 701:740–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.01.111
Blanco-Flores A, Colín-Cruz A, Gutiérrez-Segura E, Sánchez-Mendieta V, Solís-Casados DA, Garrudo-Guirado MA, Batista-González R (2014) Efficient removal of crystal violet dye from aqueous solutions by vitreous tuff mineral. Environ Technol 35(12):1508–1519. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2013.871352
Blanco-Flores A, Sánchez-Mendieta V, Gutiérrez-Segura E, Vilchis-Néstor AR, Morales-Luckie RA (2016) Novel tuffite/Fe-Cu oxides nanocomposite with functionality for dye removal in aqueous solution. J Environ Chem Eng 4(4):4472–4484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.10.007
Clifford DM, Castano CE, Rojas JV (2017) Supported transition metal nanomaterials: nanocomposites synthesized by ionizing radiation. Radiat Phys Chem 132:52–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2016.12.001
García-Cortés D, Jáuregui-Haza U (2006) Hidrodinámica en tanques agitados con turbinas de disco con paletas planas. Revis Fac Ing 38:97–113
González IM (2013) Síntesis de materiales compuestos a partir de escoria de acería. Universidad de Oviedo, España
Hafshejani L, Nasab S, Gholami R, Moradzadeh M, Izadpanah Z, Hafshejani S, Bhatnagar A (2015) Removal of zinc and lead from aqueous solution by nanostructured cedar leaf ash as biosorbent. J Mol Liq 211:448–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.07.044
Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi SA, Pournajaf R, Moradi-Faradonbeh A, Sadeghinejad S (2016) Nanostructured CuAl2O4: co-precipitation synthesis, optical and photocatalytic properties. Cem Int 42(12):14121–14125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.06.026
Huang X, Wang Z, Liu Y, Hu W, Ni W (2016) On the use of blast furnace slag and steel slag in the preparation of green artificial reef concrete. Constr Build Mater 112:241–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.02.088
Ioana A, Constantin N, Moldovan P (2015) About EAF and environment. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng 85. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/85/1/012015, 012015
Khalid H, Shamaila S, Zafar N, Shahzadi S (2015) Synthesis of copper nanoparticles by chemical reduction method. Sci Int (Lahore) 27:3085–3088. 10.13140/RG.2.1.1085.0643
Kumar JP, Ramacharyulu PVRK, Prasad GK, Singh B (2015) Montmorillonites supported with metal oxide nanoparticles for decontamination of sulfur mustard. Appl Clay Sci 116-117:263–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.04.007
Largitte L, Brudey T, Tant T, Couespel Dumesnil P, Lodewyckx P (2016) Comparison of the adsorption of lead by activated carbons from three lignocellulosic precursors. Microporous Mesoporous Mat 219:265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.07.005
Leofanti G, Padovan M, Tozzola G, Venturelli B (1998) Surface area and pore texture of catalysts. Catal Today 41(1-3):207–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-5861(98)00050-9
Li X, Liu W, Ma J, Wen Y, Wu Z (2015) High catalytic activity of magnetic FeOx/NiOy/SBA-15: the role of Ni in the bimetallic oxides at the nanometer level. Appl Catal B-Environ 179:239–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.05.034
Liang S, Guo X, Feng N, Tian Q (2010) Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic studies of adsorption of Cu2+ from aqueous solutions by Mg2+/K+ type orange peel adsorbents. J Hazard Mater 174(1-3):756–762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.116
López-Téllez G, Morales-Luckie RA, Olea-Mejía OF, Sánchez-Mendieta V, Trujillo-Reyes J, Varela-Guerrero V, Vilchis-Néstor AR (2013) Nanoestructuras Metálicas: Síntesis. Caracterización Y Aplicaciones, DF
Lyu H, Tang J, Huang Y, Gai L, Zeng EY, Liber K, Gong Y (2017) Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by a novel biochar supported nanoscale iron sulfide composite. Chem Eng J 322:516–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.058
Mahboob S, Haghighi M, Rahmani F (2017) Sonochemically preparation and characterization of bimetallic Ni-Co/Al2O3-ZrO2 nanocatalyst: effects of ultrasound irradiation time and power on catalytic properties and activity in dry reforming of CH4. Ultrason Sonochem 38:38–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.02.039
Martínez-Acuña MI, Mercado-Reyes M, Alegría-Torres JA, Mejía-Saavedra JJ (2016) Preliminary human health risk assessment of arsenic and fluoride in tap water from Zacatecas, México. Environ Monit Asses 188:476–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5453-6
Minaei S, Haghighi M, Jodeiri N, Ajamein H, Abdollahifar M (2017) Urea-nitrates combustion preparation of CeO2-promoted CuO/ZnO/Al2O3 nanocatalyst for fuel cell grade hydrogen production via methanol steam reforming. Adv Powder Technol 28(3):842–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2016.12.010
Navarro C, Díaz M, Villa-Garcia MA (2010) Physico-chemical characterization of steel slag. Study of its behavior under simulated environmental conditions. Environ Sci Technol 44(14):5383–5388. https://doi.org/10.1021/es100690b
Nilforoushan M, Sasan O (2015) The Study of ion adsorption by amorphous blast furnace slag. Iran J Chem Chem Eng 34:57–64
Ortiz N, Pires MAF, Bressiani JC (2001) Use of steel converter slag as nickel adsorber to wastewater treatment. Waste Manag 21(7):631–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-053X(00)00123-9
Pornsawai P, Medhat M, Kulyakorn K, Panomchai W, Trung TN, Surapol P (2017) Enhanced defluoridation using reusable strong acid cation exchangers in Al3+ form (SAC-Al) containing hydrated Al(III) oxide nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 314:192–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.122
Rađenović A, Jadranka M, Sofilić T (2013) Characterization of ladle furnace slag from carbon steel production as a potential adsorbent. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2013:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/198240
Rathore VK, Mondal P (2017) Stabilization of arsenic and fluoride bearing spent adsorbent in clay bricks: preparation, characterization and leaching studies. J Environ Manag 200:160–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.05.081
Repo E, Warchol JK, Westholm L, Sillanpää M (2015) Steel slag as a low-cost sorbent for metal removal in the presence of chelating agents. J Ind Eng Chem 27:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.12.025
Ribeiro D (2015) An analysis of access to improved drinking water and sanitation and distance to the water source in a newly independent country. Assessing Geographical and Socioeconomic Disparities. Assessing Geographical and Socioeconomic Disparities. Thesis, Georgia State University, Timor-Leste http://scholarworks.gsu.edu/iph_theses/391
Sarkar C, Kumar J, Amar S (2017) Removal of Ni2+ ion from wastewater by geopolymeric adsorbent derived from LD slag. J Water Process Eng 17:237–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2017.04.012
Sheng-Yu L, Gao J, Yang Y, Yang YG, Ye ZX (2010) Adsorption intrinsic kinetics and isotherms of lead ions on steel slag. J Hazard Mater 173(1-3):558–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.08.122
Soto O, Soto I (2009) Caracterización de las escorias de acería de la empresa metalúrgica antillana de acero “José Martí” de la Habana para su empleo como árido y adición de morteros, hormigones y productos de la construcción. Minerva 7:53–60
Trujillo-Reyes J, Sánchez-Mendieta V, Colín-Cruz A, Morales-Luckie RA (2008) Obtención y caracterización de un composito de carbón activado y una nanoaleación de Fe/Cu como adsorbente. Rev Latin Rec Natur 4:116–121
Wang M, Yu X, Yang Chongling Yang X, Lin M, Ge M (2017) Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution by Mg-Al-Zr triple-metal composite. Chem Eng J 322:246–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.03.155
Wu FC, Liu BL, KT W, Tseng RL (2010) A new linear form analysis of Redlich–Peterson isotherm equation for the adsorption of dyes. Chem Eng J 162(1):21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.03.006
Wu FC, Tseng RL, Juang RS (2009) Characteristics of Elovich equation used for the analysis of adsorption kinetics in dye-chitosan systems. Chem Eng J 150(2-3):366–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.01.014
Xu L, Chen G, Peng C, Qiao H, Ke F, Li D, Cai H, Wan X, Hou R (2017a) Adsorptive removal of fluoride from drinking water using porous starch loaded with common metalions. Carbohydr Polym 160:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.12.052
Xu Y, Li T, Musser J, Liu X, Xu G, Rogers WA (2017b) CFD-DEM modeling the effect of column size and bed height on minimum fluidization velocity in micro fluidized beds with Geldart B particles. Powder Technol 318:321–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2017.06.020
Yan Q, Yu N, Yang R, Cui Y, De O’H, Wang Q (2017b) Highly dispersed CuyAlOx mixed oxides as superior low-temperature alkali metal and SO2 resistant NH3-SCR catalysts. Appl Catal A-Gen 538:37–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2017.03.021
Yan Z, Xu Z, Yu J, Jaroniec M (2017a) Effect of microstructure and surface hydroxyls on the catalytic activity of Au/AlOOH for formaldehyde removal at room temperature. J Colloid Interface Sci 501:164–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.04.050
Yedra A, Fernández Barquín L, Gómez Sal JC, Pankhurst QA (2003) Nanoscale alloys prepared by sodium borohydride reduction of aqueous Fe-Cu and Co-Cu solutions. J Magn Magn Mater 254-255:14–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(02)00735-7
Yusuf M, Chuah L, Khan MA, Choong T (2014) Adsorption of nickel on electric arc furnace slag: batch and column studies. Sep Sci Technol 49(3):388–397. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2013.843099
Zhang J, Chen N, Su P, Li M, Feng C (2017) Fluoride removal from aqueous solution by zirconium-chitosan/graphene oxide membrane. React Funct Polym 114:127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2017.03.008
Zhao J, Huang Q, Liu M, Dai Y, Chen J, Huang H, Wen Y, Zhu X, Zhang X, Wei Y (2017) Synthesis of functionalized MgAl-layered double hydroxides via modified mussel inspired chemistry and their application in organic dye adsorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 505:168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.05.087
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from PRODEP-SEP, Scholarship Grant reference DSA/103.5/16/14528 for Alien Blanco Flores. Financial support of this work by the Universidad Autónoma de San Luis Potosí is gratefully acknowledged. We are indebted to Rosa Lina Tovar and Claudia Hernández (XRD analyses), Izanami López (chemical composition analyses), Martha Alejandra Lomelí (FT-IR analyses), and Claudia Guadalupe Elias (Transmission Electron Microscopy analyses), who are all at Instituto de Metalurgia, Universidad Autónoma de San Luis Potosí, for their technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Guilherme L. Dotto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blanco-Flores, A., Arteaga-Larios, N., Pérez-García, V. et al. Efficient fluoride removal using Al-Cu oxide nanoparticles supported on steel slag industrial waste solid. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 6414–6428 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0849-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0849-6