Abstract
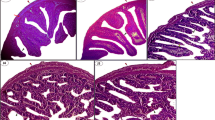
The present study was conducted to investigate the effect of graded levels of dietary bentonite supplementation on growth performance, carcass traits, nutrient digestibility, and histopathology of certain organs in rabbits fed a diet naturally contaminated with aflatoxin. In total, 125 weanling New Zealand White male rabbits were randomly assigned to five treatment groups each of five replicates. Treatments were as follows: T1, basal diet with no aflatoxin and no additives (positive control diet, PCD); T2, basal diet naturally contaminated with 150 ppb aflatoxin and no additives (negative control diet, NCD); T3, NCD plus 0.5% Egyptian bentonite; T4, NCD plus 1% Egyptian bentonite; and T5, NCD plus 1% Egyptian bentonite. The experiment lasted for 8 weeks. Results showed a significant decrease (P < 0.05) in the body weight and the body weight gain in the NCD, while they were improved (P < 0.05) in groups fed diets supplemented with different levels of bentonite. The relative weight of the liver and kidneys were higher in the NCD, while the liver weight was relatively high in the group fed NCD supplemented with 0.5% bentonite, and it was not significant in other bentonite-supplemented groups. Bentonite supplementation improved the digestibility coefficients of various nutrients. Bentonite addition decreased the histopathological lesions in liver, kidney, and intestine caused by aflatoxin-infected diets. In conclusion, bentonite supplementation overcame the negative effect of aflatoxin, enhanced growth performance traits, decreased the relative weights of the liver and the kidney which are usually increased by aflatoxin, caused significant improvement in nutrients’ digestibility, and decreased the histopathological lesions caused by aflatoxin-infected diets. The level of 2% bentonite is recommended for ameliorating the aflatoxin effects.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Wahhab MA, Nada SA, Khalil FA (2002) Physiological and toxicological responses in rats fed aflatoxin-contaminated diet with or without sorbent materials. Anim Feed Sci Tech 97:4209–4219
Abdl-Rahman MA, Sohair YS, Amal AZ (2011) Growth performance, cecal fermentation and blood biochemistry of rabbits fed diet supplemented with urea–bentonite combination. J Agri Sci 3:1
AOAC, Association of Official Analytical Chemists (2002) Official methods of analysis of AOAC international, 17th edn. AOAC, Gaithersburg. Chapt 4, pp 20–27
Azizpour A, Moghadam N (2015) Effects of yeast glucomannan and sodium bentonite on the toxicity of aflatoxin in broilers. Brazilian Journal of Poultry Science 17:7–13
Bailey RH, Kubena LF, Harvey RB, Buckley SA, Rottinghous GE (1998) Efficacy of various inorganic sorbents to barley. J Assoc Off Anal Chem 57:1104–1110
Blasco A, Ouhayoun J, Masoero G (1993) Harmonization of criteria and terminology in rabbit meat research. World Rabbit Sci 1:3–10
Brody S (1968) Bioenergetics and growth. Hafner Publ com, New York
CAST (1989) Mycotoxins. Economic and health risks. Task force rep. No. 116. November. Council for Agricultural Science and Technology, Ames, p 1989
Çelik İ, Oğuz H, Demet Ö, Boydak M, Dönmez HH, Sur E, Nizamlioğlu F (2000) Embryotoxicity assay of aflatoxin produced by Aspergillus parasiticus NRRL 2999. B. Poult Sci 41:401–409
Damiri H, Chaji M, Bojarpour M, Eslami M, Mamoei M (2010) The effect of sodium betonites on economic value of broiler chickens diet. J Anim Vet Adv 9:2668–26670
Dos Anjos FR, Ledoux DR, Rottinghaus GE, Chimonyo M (2015) Efficacy of Mozambican bentonite and diatomaceous earth in reducing the toxic effects of aflatoxins in chicks. World Mycotoxin J 9:63–72
Edrington TS, Kubena LF, Harvey RB, Rottinghous GE (1997) Influence of a super activated charcoal on the toxic effectiveness of cholestyramine as a binding agent for fumonisins. Mycopathologia 151:14753
Eraslan G, Liman BC, Güçlü BK, Atasever A, Koç AN, Beyaz L (2004) Evaluation of aflatoxin toxicity in Japanese quails given various doses of hydrated sodium calcium aluminosilicate. Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 48:511–517
Harvey RB, Phillips TD, Ellis JA, Kubena LF, Huff WE, Petersen HD (1991) Effects on aflatoxin M1 residues in milk by addition of hydrated sodium calcium aluminosilicate to aflatoxin-contaminated diets of dairy cows. Am J Vet Res 52:1556–1559
Hassan MS, Abdel-Khalek NA (1998) Beneficiation and applications of an Egyptian bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 13:99–115
Hu XR, Lu GL, Chen LS, Gu JM, Zhang Y (2002) Study on the mechanism of the interaction between montmorillonite and bacterium. Acta Pharm Sin 37:718–720
Huff WE, Kubena LF, Harvey RB, Phillips TD (1992) Efficacy of hydrated sodium calcium aluminosilicate to reduce human and animal health. Pathotox Publications, Park Forest South
Kubena LF, Edrington TS, Harvey RB, Buckley SA, Phillips TD, Rottinghaus GE, Caspers HH (1998) Individual and combined effects of fumonsin B1 present in Fusarium moniliforme culture material and T-2 toxin or deoxynivalenol in broiler chicks. Poult Sci 76:1239–1247
Lindemann MD, Blodgett DJ, Kornegay ET, Schurig GG (1993) Potential ameliorators of aflatoxicosis in weanling/growing swine. J Anim Sci 71:171–178
Lopes JM, Rutz F, Mallmann CA, Toledo GSP (2006) Adição de bentonita sódica como adsorvente de aflatoxinas em rações de frangos de corte. Cienc Rural 36:1594–1599
Ma YL, Guo T (2008) Intestinal morphology, brush border and digesta enzyme activities of broilers fed on a diet containing Cu2+loaded montmorillonite. Br Poult Sci 49:65–73
Magnoli AP, Teixeira M, Rosa CAR, Magnoli CE, Dalcero AM, Chiacchiera SM (2011) Sodium bentonite and monensin under chronic aflatoxicosis in broiler chickens. Poul Sci 90:352–357
Mc Donald P, Edwards RA, Green Halgh JFD (1987) Animal nutrition, 4th edn. Longman Group (FE) Ltd., Hong Kong
Miazzo R, Peralta MF, Magnoli C, Salvano M, Ferrero S, Chiacchiera SM, Carvalho EC, Rosa CA, Dalcero A (2005) Efficacy of sodium bentonite as a detoxifier of broiler feed contaminated with aflatoxin and fumonisin. Poult Sci 84:1–8
Miles RD, Henry PR (2007) Safety of improved Milbond-TX® when fed in broiler diets at greater than recommended levels. Anim Feed Sci Tec 138:309–317
Neeff DV, Ledoux DR, Rottinghaus GE, Bermudez AJ, Dakovic A, Murarolli RA, Oliveira CAF (2013) In vitro and in vivo efficacy of a hydrated sodium calcium aluminosilicate to bind and reduce aflatoxin residues in tissues of broiler chicks fed aflatoxin B1. Poult Sci 92:131–137
Pasha TN, Mahmood A, Khattak FM, Jabbar MA, Khan AD (2008) The effect of feed supplemented with different sodium bentonite treatments on broiler performance. Turkish. J Vet Anim Sci 32:245–248
Phillips TD, Kubena LF, Harvey RB, Taylor DR, Heidelbaugh ND (1988) Hydrated sodium calcium aluminosilicate. A high affinity sorbent for aflatoxin. Poult Sci 67:243–247
Phillips TD, Sarr AB, Clement BA, Kubena LF, Harvey RB (1990) Prevention of aflatoxicosis in farm animals via selective chemisorption of aflatoxins. In: Bray GA, Ryan DH (eds) Pennington Center Nutrition Series. In: Mycotoxins, cancer, and health, vol 1. Louisiana State University Press, Baton Rouge, pp 223–237
Ramos AJ, Fink-Gremmels J, Hernandez E (1996) Prevention of toxic effects of mycotoxins by means of nonnutritive adsorbent compounds. J Food Prot 59:631–641
Romer RT (1975) Screening methods for the detection of aflatoxins in mixed feeds and other agricultural commodities with subsequent confirmation and quantitative measurement of aflatoxins in positive samples. J Assoc Off Analyt Chem 58:500–506
Rosa CA, Miazzo R, Magnoli C, Salvano M, Hiacchiera SM, Ferrero S, Saenz M, Carvalho EC, Dalcero A (2001) Evaluation of the efficacy of bentonite from the south of Argentina to ameliorate the toxic effects of aflatoxin in broilers. Poult Sci 80:139–144
Safaeikatouli M, Boldaji F, Dastar B, Hassani S (2012) The effect of dietary silicate mineral supplementation on apparent ileal digestibility of energy and protein in broiler chickens. Int J Agric Biol 14:299–302
Santurio JM, Mallmann CA, Rosa AP, Appel G, Heer A, Dageforde S, Bottcher M (1999) Effect of sodium bentonite on the performance and blood variables of broiler chickens intoxicated with aflatoxin. Br Poult Sci 40:115–119
Shehata SA (2002) Detoxification of mycotoxin contaminated animal feedstuffs. PhD thesis, Zagazig Univ, Fac Agric, Egypt
Shehata SA, Abd El-Shafi S (2011) Effect of copper bearing Egyptian bentonite on the growth performance and intestinal microflora of rabbits. J Am Sci 7:72–78
Tatar A, Boldaji F, Dastar B, Yaghobfar A (2008) Comparison of different levels of zeolite on serum characteristics, gut pH, apparent digestibility of crude protein and performance of broiler chickens, p: 235. International Zeolite Conference, Tehran, Iran
Tauqir NA, Nawaz H (2001) Performance and economics of broiler chicks fed on rations supplemented with different levels of sodium bentonite. Int J Agri Biol 3:149–150
Tauqir NA, Sultan GI, Nawaz H (2001) Effect of different levels of bentonite with varying energy levels on the performance of broilers. Int J Agric Biol 3:85–88
Van Rensburg CJ, Van Rensburg CEJ, Van Ryssen JBJ, Casey NH, Rottinghaus GE (2006) In vitro and in vivo assessment of humic acid as an aflatoxin binder in broiler chickens. Poult Sci 85:1576–1583
Veniale F, Bettero A, Jobstraibizer PG, Setti M (2007) Thermal muds: perspectives of innovations. Appl Clay Sci 36:141–147
Wagner DD, Furrow RD, Bradly BD (1983) Subchronic toxicity of growth promoters in broiler chickens. Vet Pathol 20:253–359
Xia MS, Hu CH, Xu ZR (2005) Effects of copper bearing montmorillonite on the growth performance, intestinal microflora and morphology of weanling pigs. Anim Feed Sci Technol 118:307–317
Yang F, Bai FK, Bai S, Peng X, Ding X, Li Y, Zhang J, Zhao J (2012) Effects of feeding corn naturally contaminated with aflatoxin B1 and B2 on hepatic functions of broilers. Poult Sci 91:2792–2801
Ye Y, Zhou YH, Xia MS, Hu CH (2003) A new type of inorganic antibacterial material: Cu-bearing montmorillonite and discussion on its mechanism. J Inorg Mat 18:569–574
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Department of Nutrition and Clinical Nutrition, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Zagazig University (Egypt) for their cooperation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The current study was conducted at the Rabbit Research Unit, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Zagazig University, Egypt. All the experimental procedures were carried out according to the Local Experimental Animal Care Committee and approved by the ethics of the institutional committee. Animals were cared for using husbandry guidelines derived from Zagazig University standard operating procedures.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amer, S.A., Kishawy, A.T.Y., ELseddawy, N.M. et al. Impacts of bentonite supplementation on growth, carcass traits, nutrient digestibility, and histopathology of certain organs of rabbits fed diet naturally contaminated with aflatoxin. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 1340–1349 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0578-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0578-x