Abstract
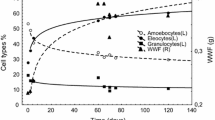
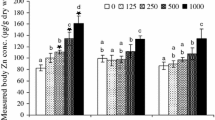
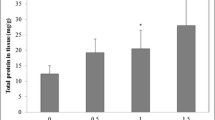
Sewage sludge (SS) is a complex organic by-product of wastewater treatment plants. Deposition of large amounts of SS can increase the risk of soil contamination. Therefore, there is an increasing need for fast and accurate assessment of SS toxic potential. Toxic effects of SS were tested on earthworm Eisenia fetida tissue, at the subcellular and biochemical level. Earthworms were exposed to depot sludge (DS) concentration ratio of 30 or 70 %, to undiluted and to 100 and 10 times diluted active sludge (AS). The exposure to DS lasted for 24/48 h (acute exposure), 96 h (semi-acute exposure) and 7/14/28 days (sub-chronic exposure) and 48 h for AS. Toxic effects were tested by the measurements of multixenobiotic resistance mechanism (MXR) activity and lipid peroxidation levels, as well as the observation of morphological alterations and behavioural changes. Biochemical markers confirmed the presence of MXR inhibitors in the tested AS and DS and highlighted the presence of SS-induced oxidative stress. The MXR inhibition and thiobarbituric acid reactive substance (TBARS) concentration in the whole earthworm’s body were higher after the exposition to lower concentration of the DS. Furthermore, histopathological changes revealed damage to earthworm body wall tissue layers as well as to the epithelial and chloragogen cells in the typhlosole region. These changes were proportional to SS concentration in tested soils and to exposure duration. Obtained results may contribute to the understanding of SS-induced toxic effects on terrestrial invertebrates exposed through soil contact and to identify defence mechanisms of earthworms.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achard M, Baudrimont M, Boudou A, Bourdineaud JP (2004) Induction of a multixenobiotic resistance protein (MXR) in the Asiatic clam Corbicula fluminea after heavy metals exposure. Aquat Toxicol 67(4):347–357
Amorim MJB, Novais S, Römbke J, Soares AMVM (2008) Enchytraeus albidus (Enchytraeidae): a test organism in a standardised avoidance test? Effects of different chemical substances. Environ Int 34:363–371
Antolin MC, Pascual I, Garcia C, Polo A, Sanchez-Diaz M (2005) Growth, yield and solute content of barley in soils treated with sewage sludge under semiarid Mediterranean conditions. Field Crops Res 94:224–237
Artuso N, Kennedy TF, Connery J, Grant J, Schmidt O (2011) Effects of biosolids at varying rates on earthworms (Eisenia fetida) and springtails (Folsomia candida). Appl Environ Soil Sci. doi: 10.1155/2011/519485
Aydoğan Kılıç G (2011) Histopathological and biochemical alterations of the earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris) as biomarker of soil pollution along Porsuk River Basin (Turkey). Chemosphere 83:1175–1180
Babić S, Dragun Z, Sauerborn Klobučar R, Bačić N, Fiket Ž, Barišić J, Krasnići N, Strunjak-Perović I, Topić Popović N, Čož-Rakovac R (2015) Different patterns of concentration variability of various metals and metalloids in the soluble tissue fractions of earthworm Eisenia fetida after exposure to active sludge. Sci Total Environ 526:127–135
Baynes RE, Hodgson E (2004) Absorption and distribution of toxicants. In: Hodgson E (ed) A textbook of modern toxicology, 3rd edn. Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 77–110
Bošnjak I, Bielen A, Babić S, Šver L, Popović NT, Strunjak-Perović I, Čož-Rakovac R, Sauerborn Klobučar R (2014) First evidence of the P-glycoprotein gene expression (P-gp/Abcb1) and MXR activity modulation in earthworm Eisenia fetida, Savigny. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol 65(1):67–74
Braguglia CM, Coors A, Gallipoli A, Gianico A, Guillon E, Kunkel U, Mascolo G, Richter E, Ternes TA, Tomei MC, Mininni G (2014) Quality assessment of digested sludges produced by advanced stabilization processes. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3090-6
Caminada D, Žaja R, Smital T, Fent K (2008) Human pharmaceuticals modulate P-gp1 (ABCB1) transport activity in the fish cell line PLHC-1. Aquat Toxicol 90:214–222
Carpené E, Andreani G, Monari M, Castellani G, Isani G (2006) Distribution of Cd, Zn, Cu and Fe among selected tissues of the earthworm (Allolobophora caliginosa) and Eurasian woodcock (Scolopax rusticola). Sci Total Environ 363:126–135
Chen C, Zhou Q, Liu S, Xiu Z (2011) Acute toxicity, biochemical and gene expression responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to polycyclic musks. Chemosphere 83(8):1147–1154
Christofoletti C, Francisco A, Fontanetti CS (2012) Biosolid soil application: toxicity tests under laboratory conditions. Appl Environ Soil Sci. doi: 10.1155/2012/518206.
Clauss W (2001) Epithelial transport and osmoregulation in annelids. Can J Zool 79:192–203
Contreras-Ramos SM, Escamilla–Silva EM, Dendooven L (2005) Vermicomposting of biosolids with cow dung and oat straw. Biol Fertil Soils 41:190–198
Creamer RE, Rimmer DL, Black HIJ (2008) Do elevated soil concentrations of metals affect the diversity and activity of soil invertebrates in the long-term? Soil Use Manage 24:37–46
Del Rio D, Stewart AJ, Pellegrini N (2005) A review of recent studies on malondialdehyde as toxic molecule and biological markers of oxidative stress. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 15(4):316–328
Directive 86/278/EEC (1986) On the protection of the environment, and in particular of the soil, when sewage sludge is used in agriculture. Official Journal of the European Communities No. 181:6–12
Directive 91/271/EEC (1991) Concerning urban wastewater treatment. Official Journal of the European Communities No. L 135:40–52
Domene X, Solà L, Ramírez W, Alcañiz JM, Andrés P (2011) Soil bioassays as tools for sludge compost quality assessment. Waste Manag 31(3):512–522
Domínguez-Crespo MA, Sánchez-Hernández ZE, Torres-Huerta AM, Negrete-Rodríguez MX, Conde-Barajas E, Flores-Vela A (2012) Effect of the heavy metals Cu, Ni, Cd and Zn on the growth and reproduction of epigeic earthworms (E. fetida) during the vermistabilization of municipal sewage sludge. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:915–931
Egiarte G, Pinto M, Ruíz-Romera E, Camps Arbestain M (2008) Monitoring heavy metal concentrations in leachates from a forest soil subjected to repeated applications of sewage sludge. Environ Pollut 156:840–848
EPA (2012) 850.3100 ecological effects test guidelines—earthworm subchronic toxicity test. Environmental Protection Agency (Office of Chemical Safety and Pollution Prevention), US
Epel D, Luckenbach T, Stevenson CN, Macmanus-Spencer LA, Hamdoun A, Smital T (2008) Efflux transporters: newly appreciated roles in protection against pollutants. Environ Sci Technol 42:3914–3920
Fuentes A, Lloréns M, Sáez J, Soler A, Aguilar M, Ortuño F (2004) Phytotoxicity and heavy metals speciation of stabilized sewage sludges. J Hazard Mater 108:161–169
García-Gómez C, Fernández MD, Babin M (2014) Ecotoxicological evaluation of sewage sludge contaminated with zinc oxide nanoparticles. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 67(4):494–506
Hait S, Tare V (2012) Transformation and availability of nutrients and heavy metals during integrated composting–vermicomposting of sewage sludges. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 79:214–224
Han Y, Zhu L, Wang J, Wang J, Xie H, Zhang S (2014) Integrated assessment of oxidative stress and DNA damage in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) exposed to azoxystrobin. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 107:214–219
He C, Chen CL, Giannis A, Yang Y, Wang JY (2014) Hydrothermal gasification of sewage sludge and model compounds for renewable hydrogen production: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 39:1127–1142
Huang K, Li F, Fu X, Chen X (2013) Feasibility of a novel vermitechnology using vermicast as substrate for activated sludge disposal by two epigeic earthworm species. Agr Sci 4(10):529–535
ISO (1993) Soil quality—effects of pollutants on earthworms (Eisenia fetida). 11268–1 determination of acute toxicity using artificial soil substrate. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva
ISO (1998) Soil quality—effects of pollutants on earthworms (Eisenia fetida). 11268–2 determination of effects on reproduction. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva
Kinney CA, Furlong ET, Koplin DW, Burkhardt MR, Zaugg SD, Werner SL, Bossio JP, Benotti MJ (2008) Bioaccumulation of pharmaceuticals and other anthropogenic waste indicators in earthworms from agricultural soil amended with biosolid or swine manure. Environ Sci Technol 42(6):1863–1870
Kinney CA, Campbell BR, Thompson R, Furlong ET, Kolpin DW, Burkhardt MR, Zaugg SD, Werner SL, Hay AG (2012) Earthworm bioassays and seedling emergence for monitoring toxicity, aging and bioaccumulation of anthropogenic waste indicator compounds in biosolids-amended soil. Sci Total Environ 433:507–515
Kizilkaya R, Hepşen Türkay FŞ (2014) Vermicomposting of anaerobically digested sewage sludge with hazelnut husk and cow manure by earthworm Eisenia foetida. Compost Sci Util 22:68–82
Kotowska U, Kapelewska J, Sturgulewska J (2014) Determination of phenols and pharmaceuticals in municipal wastewaters from Polish treatment plants by ultrasound-assisted emulsification-microextraction followed by GC-MS. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:660–673
Kurelec B (1997) A new type of hazardous chemicals: the chemosensitizers of multixenobiotic resistance. Environ Health Perspect 105:855–860
Latare AM, Kumar O, Singh SK, Gupta A (2014) Direct and residual effect of sewage sludge on yield, heavy metals content and soil fertility under rice-wheat system. Ecol Eng 69:17–24
LeBlanc RJ, Matthews P, Roland PR (2008) Global atlas of excreta wastewater sludge, and biosolids management: moving forward the sustainable and welcome uses of a global resource. Kenya, United Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-HABITAT)
Li X, Xing M, Yang J, Dai X (2014) Earthworm eco-physiological characteristics and quantification of earthworm feeding in vermifiltration system for sewage sludge stabilization using stable isotopic natural abundance. J Hazard Mater 276:353–361
Litman T, Druley TE, Stein WD, Bates SE (2001) From MDR to MXR: new understanding of multidrug resistance systems, their properties and clinical significance. Cell Mol Life Sci 58(7):931–959
Liu J, Lu Z, Yang J, Xing M, Yu F, Guo M (2012) Effect of earthworms on the performance and microbial communities of excess sludge treatment process in vermifilter. Bioresour Technol 117:214–221
Liu F, Zhu P, Sheng W, Xue JJ (2013) Sludge earthworm composting technology by Eisenia fetida. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 15:482–488
Lourenço J, Silva A, Carvalho F, Oliveira J, Malta M, Mendo S, Gonçalves F, Pereira R (2011) Histopathological changes in the earthworm Eisenia andrei associated with the exposure to metals and radionuclides. Chemosphere 85(10):1630–1634
Ludibeth SM, Marina IE, Vicenta EM (2012) Vermicomposting of sewage sludge: earthworm population and agronomic advantages. Compost Sci Util 20(1):11–17
Malara A, Oleszczuk P (2013) Application of a battery of biotests for the determination of leachate toxicity to bacteria and invertebrates from sewage sludge-amended soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:3435–3446
Mann KH (1961) Leeches (Hirudinea): their structure, physiology, ecology and embryology. Pergamon, Oxford
McBride MB (2003) Toxic metals in sewage sludge-amended soils: has promotion of beneficial use discounted the risks? Adv Environ Res 8:5–19
Mininni G, Blanch AR, Lucena F, Berselli S (2015) EU policy on sewage sludge utilization and perspectives on new approaches of sludge management. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:7361–7374
Ministry of Environmental Protection, Physical Planning and Construction (2008) Directive on management of sludge from wastewater treatment plants when the sludge is intended for agricultural use. Official Gazette No. 38/08
Molina MJ, Soriano MD, Ingelmo F, Llinares J (2013) Stabilisation of sewage sludge and vinasse bio-wastes by vermicomposting with rabbit manure using Eisenia fetida. Biresour Technol 137:88–97
Nahmani J, Hodson ME, Black S (2007) A review of studies performed to assess metal uptake by earthworms. Environ Pollut 145:402–424
Nogarol LR, Fontanetti CS (2010) Acute and subchronic exposure of diplopods to substrate containing sewage mud: tissular responses of the midgut. Micron 41:239–246
OECD (1984) Guidelines for testing of chemicals—section 2. Effects on biotic systems. Earthworm, acute toxicity tests (filter paper test and artificial soil test). Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris
OECD (2004) Guideline for testing of chemicals. Earthworm reproduction test (Eisenia fetida/Eisenia andrei). Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris
Pathak A, Dastidar MG, Sreekrishnan TR (2009) Bioleaching of heavy metals from sewage sludge: a review. J Environ Manage 90:2343–2353
Perez DGP, Fontanetti CS (2010) Assessment of the toxic potential of sewage sludge in the midgut of the diplopod Rhinocricus padbergi. Water Air Soil Pollut 218:437–444
Poleksić V, Lenhardt M, Jarić I, Djordjević D, Gačić Z, Cvijanović G, Rašković B (2010) Liver, gills, and skin histopathology and heavy metal content of the Danube sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus Linnaeus, 1758). Environ Toxicol Chem 29(3):515–521
Reinecke AJ, Reinecke SA (2004) Earthworm as test organisms in ecotoxicological assessment of toxicant impacts on ecosystems. In: Edwards CA (ed) Earthworm Ecology, 2nd edn. CRC, USA, pp 299–320
Ribera D, Narbonne JF, Arnaud C, Saint-Denis M (2001) Biochemical responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida andrei exposed to contaminated artificial soil, effects of carbaryl. Soil Biol Biochem 33:1123–1130
Sauerborn Klobučar R, Žaja R, Franjević D, Brozović A, Smital T (2010) Presence of ecotoxicologically relevant P-gp and MRP transcripts and proteins in cyprinid fish. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol 61:175–182
Schaefer M (2003) Behavioral endpoints in earthworm ecotoxicology: evaluation of different test systems in soil toxicity assessment. J Soil Sediment 3(2):79–84
Schreck E, Geret F, Gontier L, Treilhou M (2008) Neurotoxic effect and metabolic responses induced by a mixture of six pesticides on the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa nocturna. Chemosphere 71(10):1832–1839
Shaheen SM, Shams MS, Ibrahim SM, Elbehiry FA, Antoniadis V, Hooda PS (2014) Stabilization of sewage sludge by using various by-products: effects on soil properties, biomass production, and bioavailability of copper and zinc. Water Air Soil Pollut 225. doi: 10.1007/s11270-014-2014-x
Sharma VJ, Satyanarayan S (2011) Effect of selected heavy metals on the histopathology of different tissues of earthworm Eudrillus eugeniae. Environ Monit Assess 180(1–4):257–267
Silveira MLA, Alleoni LRF, Guilherme LRG (2003) Review: biosolids and heavy metals in soils. Sci Agric 60:793–806
Singh RP, Agrawal M (2008) Potential benefits and risks of land application of sewage sludge. Waste Manag 28:347–358
Smital T, Sauerborn R, Hackenberger BK (2003) Inducibility of the P-glycoprotein transport activity in the marine mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis and the freshwater mussel Dreissena polymorpha. Aquat Toxicol 65:443–465
Sohal RS, Mockett RJ, Orr WC (2002) Mechanisms of aging: an appraisal of the oxidative stress hypothesis. Free Radic Biol Med 33:575–586
Topić Popović N, Strunjak-Perović I, Sauerborn Klobučar R, Barišić J, Babić S, Jadan M, Kepec S, Kazazić SP, Matijatko V, Beer Ljubić B, Car I, Klobučar GV, Čož-Rakovac R (2015) Impact of treated wastewater effluent on fish and toxicity biosensors. Sci Total Environ 538:23–37
Wang Y, Wu S, Chen L, Wu C, Yu R, Wang Q, Zhao X (2012) Toxicity assessment of 45 pesticides to the epigeic earthworm Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere 88:484–491
Xing M, Yang J, Wang Y, Liu J, Yu F (2011) A comparative study of synchronous treatment of sewage and sludge by two vermifiltrations using an epigeic earthworm Eisenia fetida. J Hazard Mater 185:881–888
Xing M, Li X, Yang J, Lv B, Lu Y (2012) Performance and mechanism of vermifiltration system for liquid-state sewage sludge treatment using molecular and stable isotopic techniques. Chem Eng J 197:143–150
Xing M, Lv B, Zhao C, Yang J (2014) Towards understanding the effects of additives on the vermicomposting of sewage sludge. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:4644–4653
Yadav A, Garg VK (2011) Recycling of organic wastes by employing Eisenia fetida. Bioresour Technol 102:2874–2880
Žaja R, Klobučar GIV, Sauerborn Klobučar R, Hackenberger BH, Smital T (2006) Haemolymph as compartment for efficient and non-destructive determination of P-glycoprotein (Pgp) mediated MXR activity in bivalves. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 143(1):103–112
Žaja R, Terzić S, Senta I, Lončar J, Popović M, Ahel M, Smital T (2013) Identification of P-glycoprotein inhibitors in contaminated freshwater sediments. Environ Sci Technol 47(9):4813–4821
Zhang Q, Zhang B, Wang C (2014) Ecotoxicological effects on the earthworm Eisenia fetida following exposure to soil contaminated with imidacloprid. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:12345–12353
Acknowledgments
The financial support by the Ministry of Science, Education and Sport of the Republic of Croatia (project No. 098-1782739-2749) is acknowledged. The sampling was carried out as a part of doctoral thesis titled “Ecotoxicological and microbiological characterization of purified wastewater of the city Virovitica”. Special thanks are due to the PhD student Slavko Kepec.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Thomas Braunbeck
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babić, S., Barišić, J., Malev, O. et al. Sewage sludge toxicity assessment using earthworm Eisenia fetida: can biochemical and histopathological analysis provide fast and accurate insight?. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 12150–12163 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6097-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6097-3