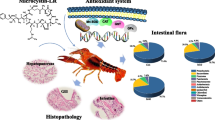
Abstract
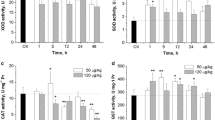
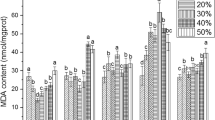
Glutathione (GSH) plays crucial roles in antioxidant defense and detoxification metabolism of microcystin-LR (MC-LR). However, the detoxification process of MC-LR in mammals remains largely unknown. This paper, for the first time, quantitatively analyzes MC-LR and its GSH pathway metabolites (MC-LR-GSH and MC-LR-Cys) in the liver of Sprague–Dawley (SD) rat after MC-LR exposure. Rats received intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of 0.25 and 0.5 lethal dose 50 (LD50) of MC-LR with or without pretreatment of buthionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine (BSO), an inhibitor of GSH synthesis. The contents of MC-LR-GSH were relatively low during the experiment; however, the ratio of MC-LR-Cys to MC-LR reached as high as 6.65 in 0.5 LD50 group. These results demonstrated that MC-LR-GSH could be converted to MC-LR-Cys efficiently, and this metabolic rule was in agreement with the data of aquatic animals previously reported. MC-LR contents were much higher in BSO + MC-LR-treated groups than in the single MC-LR-treated groups. Moreover, the ratio of MC-LR-Cys to MC-LR decreased significantly after BSO pretreatment, suggesting that the depletion of GSH induced by BSO reduced the detoxification of MCs. Moreover, MC-LR remarkably induced liver damage, and the effects were more pronounced in BSO pretreatment groups. In conclusion, this study verifies the role of GSH in the detoxification of MC-LR and furthers our understanding of the biochemical mechanism for SD rats to counteract toxic cyanobacteria.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anders MW (1980) Metabolism of drugs by kidney. Kidney Int 18:636–647
Azevedo SMFO, Carmichael WW, Jochimsen EM, Rinehart KL, Lau S, Shaw GR, Eaglesham GK (2002) Human intoxication by microcystins during renal dialysis treatment in Caruaru-Brazil. Toxicology 181:441–446
Bláha L, Kopp R, Šimkova K, Mareš J (2004) Oxidative stress biomarkers are modulated in silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix Val.) exposed to microcystin-producing cyanobacterial water bloom. Acta Vet Brno 73:477–482
Botes D, Tuinman A, Wessels P, Viljoen C, Kruger H, Williams D, Santikarn S, Smith R, Hammond S (1984) The structure of cyanoginosin-LA, a cyclic heptapeptide toxin from the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 1:2311–2318
Buratti FM, Testai E (2015) Species- and congener-differences in microcystin-LR and -RR GSH conjugation in human, rat, and mouse hepatic cytosol. Toxicol Lett 232:133–140
Carmichael WW, Beasley V, Bunner DL, Eloff JN, Falconer I, Gorham P, Harada K, Krishnamurthy T, Yu MJ, Moore RE (1988) Naming of cyclic heptapeptide toxins of cyanobacteria (blue-green algae). Toxicon Off J Int Soc Toxinol 26:971–973
Chen J, Xie P (2005) Seasonal dynamics of the hepatotoxic microcystins in various organs of four freshwater bivalves from the large eutrophic Lake Taihu of subtropical China and the risk to human consumption. Environ Toxicol 20:572–584
Chen J, Xie P, Li L, Xu J (2009) First identification of the hepatotoxic microcystins in the serum of a chronically exposed human population together with indication of hepatocellular damage. Toxicol Sci 108:81–89
Chen L, Li SC, Guo XC, Xie P, Chen J (2014) The role of GSH in microcystin-induced apoptosis in rat liver: involvement of oxidative stress and NF-κB. Environ Toxicol. doi:10.1002/tox.22068
Clark SP, Davis MA, Ryan TP, Searfoss GH, Hooser SB (2007) Hepatic gene expression changes in mice associated with prolonged sublethal microcystin exposure. Toxicol Pathol 35:594–605
Craig M, Luu HA, McCready TL, Williams D, Andersen RJ, Holmes CF (1996) Molecular mechanisms underlying the interaction of motuporin and microcystins with type-1 and type-2A protein phosphatases. Biochem Cell Biol 74:569–578
Dai M, Xie P, Liang GD, Chen J, Lei HH (2008) Simultaneous determination of microcystin-LR and its glutathione conjugate in fish tissues by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 862:43–50
Dawson RM (1998) The toxicology of microcystins. Toxicon 36:953–962
Ding WX, Shen HM, Shen Y, Zhu HG, Ong CN (1998) Microcystic cyanobacteria causes mitochondrial membrane potential alteration and reactive oxygen species formation in primary cultured rat hepatocytes. Environ Health Perspect 106:409–413
Ding WX, Shen HM, Ong CN (2000) Microcystic cyanobacteria extract induces cytoskeletal disruption and intracellular glutathione alteration in hepatocytes. Environ Health Perspect 108:605–609
Fischer A, Hoeger SJ, Stemmer K, Feurstein DJ, Knobeloch D, Nussler A, Dietrich DR (2010) The role of organic anion transporting polypeptides (OATPs/SLCOs) in the toxicity of different microcystin congeners in vitro: a comparison of primary human hepatocytes and OATP-transfected HEK293 cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 245:9–20
Fu BD, He SP (2012) Transcriptome analysis of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) by paired-end RNA sequencing. DNA Res 19:131–142
Gehringer MM, Shephard EG, Downing TG, Wiegand C, Neilan BA (2004) An investigation into the detoxification of microcystin-LR by the glutathione pathway in Balb/c mice. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:931–941
Guo XC, Xie P, Chen J, Tuo X, Deng XW, Li SC, Yu DZ, Zeng C (2014) Simultaneous quantitative determination of microcystin-LR and its glutathione metabolites in rat liver by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 963:54–61
Gupta N, Pant SC, Vijayaraghavan R, Rao PV (2003) Comparative toxicity evaluation of cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin variants (LR, RR, YR) in mice. Toxicology 188:285–296
He J, Chen J, Xie P, Zhang DW, Li GY, Wu LY , Zhang W, Guo XC, Li SC (2012) Quantitatively evaluating detoxification of the hepatotoxic microcystins through the glutathione and cysteine pathway in the cyanobacteria-eating bighead carp. Aquat Toxicol 116:61–68
Ibelings B, Bruning K, De Jonge J, Wolfstein K, Pires L, Postma J, Burger T (2005) Distribution of microcystins in a lake foodweb: no evidence for biomagnification. Microb Ecol 49:487–500
Ito E, Takai A, Kondo F, Masui H, Imanishi S, K-i H (2002) Comparison of protein phosphatase inhibitory activity and apparent toxicity of microcystins and related compounds. Toxicon 40:1017–1025
Jayaraj R, Anand T, Lakshmana Rao PV (2006) Activity and gene expression profile of certain antioxidant enzymes to microcystin-LR induced oxidative stress in mice. Toxicology 220:136–146
Jiang JL, Gu XY, Song R, Zhang Q, Geng JJ, Wang XR, Yang LY (2011) Time-dependent oxidative stress and histopathological changes in Cyprinus carpio L. exposed to microcystin-LR. Ecotoxicology 20:1000–1009
Ketterer B, Coles B, Meyer DJ (1983) The role of glutathione in detoxication. Environ Health Perspect 49:59–69
Kondo F, Ikai Y, Oka H, Okumura M, Ishikawa N, Harada K, Matsuura K, Murata H, Suzuki M (1992) Formation, characterization, and toxicity of the glutathione and cysteine conjugates of toxic heptapeptide microcystins. Chem Res Toxicol 5:591–596
Kondo F, Matsumoto H, Yamada S, Ishikawa N, Ito E, Nagata S, Ueno Y, Suzuki M, Harada K (1996) Detection and identification of metabolites of microcystins formed in vivo in mouse and rat livers. Chem Res Toxicol 9:1355–1359
Kotak B, Zurawell R, Prepas E, Holmes C (1996) Microcystin-LR concentration in aquatic food web compartments from lakes of varying trophic status. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 53:1974–1985
Li L, Xie P, Chen J (2007a) Biochemical and ultrastructural changes of the liver and kidney of the phytoplanktivorous silver carp feeding naturally on toxic Microcystis blooms in Taihu Lake, China. Toxicon 49:1042–1053
Li L, Xie P, Li SX, Qiu T, Guo LG (2007b) Sequential ultrastructural and biochemical changes induced in vivo by the hepatotoxic microcystins in liver of the phytoplanktivorous silver carp Hypophthalmichthys molitrix. Comp Biochem Physiol C 146:357–367
Li L, Xie P, Guo LG, Ke ZX, Zhou Q, Liu YQ, Qiu T (2008) Field and laboratory studies on pathological and biochemical characterization of microcystin-induced liver and kidney damage in the phytoplanktivorous bighead carp. Sci World J 8:121–137
Li SC, Chen J, Xie P, Guo X, Fan H, Yu D, Zeng C, Chen L (2014a) The role of glutathione detoxification pathway in MCLR-induced hepatotoxicity in SD rats. Environ Toxicol. doi:10.1002/tox.22017
Li W, Chen J, Xie P, He J, Guo XC, Tuo X, Zhang W, Wu LY (2014b) Rapid conversion and reversible conjugation of glutathione detoxification of microcystins in bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis). Aquat Toxicol 147:18–25
Lu SC (2013) Glutathione synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1830:3143–3153
MacKintosh C, Beattie KA, Klumpp S, Cohen P, Codd GA (1990) Cyanobacterial microcystin-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A from both mammals and higher plants. FEBS Lett 264:187–192
Malbrouck C, Kestemont P (2006) Effects of microcystins on fish. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:72–86
Malbrouck C, Trausch G, Devos P, Kestemont P (2004) Effect of microcystin-LR on protein phosphatase activity in fed and fasted juvenile goldfish Carassius auratus L. Toxicon 43:295–301
Malecot M, Marie A, Puiseux-Dao S, Edery M (2011) iTRAQ-based proteomic study of the effects of microcystin-LR on medaka fish liver. Proteomics 11:2071–2078
Miura GA, Robinson NA, Lawrence WB, Pace JG (1991) Hepatotoxicity of microcystin-LR in fed and fasted rats. Toxicon 29:337–346
Nishiwakimatsushima R, Ohta T, Nishiwaki S, Suganuma M, Kohyama K, Ishikawa T, Carmichael WW, Fujiki H (1992) Liver-tumor promotion by the cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin-LR. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 118:420–424
Pflugmacher S, Wiegand C, Oberemm A, Beattie KA, Krause E, Codd GA, Steinberg CE (1998) Identification of an enzymatically formed glutathione conjugate of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin-LR: the first step of detoxication. Biochim Biophys Acta 1425:527–533
Pflugmacher S, Wiegand C, Beattie KA, Krause E, Steinberg CEW, Codd GA (2001) Uptake, effects, and metabolism of cyanobacterial toxins in the emergent reed plant Phragmites australis (cav.) trin. ex steud. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:846–852
Qiu T, Xie P, Ke ZX, Li L, Guo LG (2007) In situ studies on physiological and biochemical responses of four fishes with different trophic levels to toxic cyanobacterial blooms in a large Chinese lake. Toxicon 50:365–376
Råbergh CMI, Bylund G, Eriksson JE (1991) Histopathological effects of microcystin-LR, a cyclic peptide toxin from the cyanobacterium (blue-green alga) Microcystis aeruginosa on common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Aquat Toxicol 20:131–145
Ramanan S, Tang J, Velayudhan A (2000) Isolation and preparative purification of microcystin variants. J Chromatogr A 883:103–112
Soares RM, Yuan M, Servaites JC, Delgado A, Magalhaes VF, Hilborn ED, Carmichael WW, Azevedo SM (2006) Sublethal exposure from microcystins to renal insufficiency patients in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Environ Toxicol 21:95–103
Sun XY, Mi LX, Liu J, Song LR, Chung F-L, Gan NQ (2011) Sulforaphane prevents microcystin-LR-induced oxidative damage and apoptosis in BALB/c mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 255:9–17
Tencalla FG, Dietrich DR, Schlatter C (1994) Toxicity of Microcystis aeruginosa peptide toxin to yearling rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat Toxicol 30:215–224
Ufelmann H, Kruger T, Luckas B, Schrenk D (2012) Human and rat hepatocyte toxicity and protein phosphatase 1 and 2A inhibitory activity of naturally occurring desmethyl-microcystins and nodularins. Toxicology 293:59–67
Wang Q, Xie P, Chen J, Liang GD (2008) Distribution of microcystins in various organs (heart, liver, intestine, gonad, brain, kidney and lung) of Wistar rat via intravenous injection. Toxicon 52:721–727
Wolfgang D (2001) Chemical-induced nephrotoxicity mediated by glutathione S-conjugate formation. Toxicol Lett 124:21–36
Wu LY, Xie P, Chen J, Zhang DW, Liang GD (2010) Development and validation of a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry assay for the simultaneous quantitation of microcystin-RR and its metabolites in fish liver. J Chromatogr A 1217:1455–1462
Yuan M, Carmichael WW, Hilborn ED (2006) Microcystin analysis in human sera and liver from human fatalities in Caruaru, Brazil 1996. Toxicon 48:627–640
Žegura B, Lah TT, Filipič M (2006) Alteration of intracellular GSH levels and its role in microcystin-LR-induced DNA damage in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Mutat Res 611:25–33
Zhang DW, Xie P, Chen J, Dai M, Qiu T, Liu YQ, Liang GD (2009) Determination of microcystin-LR and its metabolites in snail (Bellamya aeruginosa), shrimp (Macrobrachium nipponensis) and silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) from Lake Taihu, China. Chemosphere 76:974–981
Zhang DW, Yang Q, Xie P, Deng XW, Chen J, Dai M (2012) The role of cysteine conjugation in the detoxification of microcystin-LR in liver of bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis): a field and laboratory study. Ecotoxicology 21:244–252
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank editor Philippe Garrigues and anonymous reviewers for their useful comments and suggestions on the manuscript. This study was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (grant number 31070457 and 31322013) and the State Key Laboratory of Freshwater Ecology and Biotechnology (grant number 2014FBZ02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Chen, L., Chen, J. et al. Quantitatively evaluating detoxification of the hepatotoxic microcystin-LR through the glutathione (GSH) pathway in SD rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 19273–19284 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5531-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5531-2