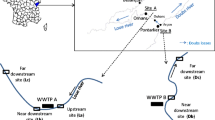
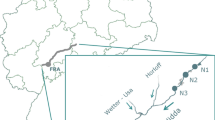
Abstract
There is a consensus within the scientific community that sediments act as a long-term sink for a variety of organic and inorganic pollutants, which, however, can re-enter the water column upon resuspension of deposited material under certain hydraulic conditions such as flood events. Within the implementation of the European Water Framework Directive, it is important to understand the potential short- and long-term impact of suspended particulate matter (SPM)-associated contaminants on aquatic organisms as well as the related uptake mechanisms for a sound risk assessment. To elucidate the effects of sediment-bound organic pollutants, such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) were exposed to three resuspended natural sediments with different contamination levels. Physicochemical parameters including dissolved oxygen concentration, pH and temperature, total PAH concentration in sediments and SPM as well as different biomarkers of exposure in fish (7-ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase activity, biliary PAH metabolites, micronuclei, and lipid peroxidation) were measured following seven days of exposure within an annular flume, a device to assess erosion and deposition processes of cohesive sediment. Concentrations of PAHs in SPM remained constant and represented the different contamination levels in the un-suspended sediments. Significant differences in bile metabolite concentrations as well as in 7-ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase induction compared to control experiments (untreated animals and animals that were exposed in the annular flume without sediment) were observed for all exposure scenarios. The ratio between 1-hydroxypyrene in bile from fish exposed to the three different contamination levels was 1.0:3.6:10.7 and correlated well with (1) the ratio of pyrene concentrations in corresponding sediments which was 1.0:3.1:12.7 and (2) with the ratio of particle-bound pyrene in SPM which was 1.0:2.7:11.7. In contrast, hepatic lipid peroxidation and micronuclei formation represented the different contamination levels less conclusive. The results of this study clearly demonstrate that firmly bound PAH from aged sediments can become bioaccessible upon resuspension under flood-like conditions and are readily absorbed by aquatic organisms such as rainbow trout. Associated short-term effects were clearly documented and possible adverse long-term impacts due to genotoxicity are likely to follow.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addison R, Willis D, Zinck M (1994) Liver microsomal mono-oxygenase induction in winter flounder (Pseudopleuronectes americanus) from a gradient of sediment PAH concentrations at Sydney Harbour, Nova Scotia. Mar Environ Res 37(3):283–296
Ahlf W, Hollert H, Neumann-Hensel H, Ricking M (2002) A guidance for the assessment and evaluation of sediment quality—a German approach based on ecotoxicological and chemical measurements. J Soils Sediments 2:37–42
Al-Sabti K, Metcalfe CD (1995) Fish micronuclei for assessing genotoxicity in water. Mutat Res-Genet Tox 343(2):121–135
Balk L, Meijer J, DePierre JW, Appelgren L-E (1984) The uptake and distribution of [3H]benzo[a]pyrene in the Northern pike (Esox lucius). Examination by whole-body autoradiography and scintillation counting. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 74(3):430–449
Bear EA, McMahon TE, Zale AV (2007) Comparative thermal requirements of westslope cutthroat trout and rainbow trout: implications for species interactions and development of thermal protection standards. Trans Am Fish Soc 136(4):1113–1121
Benner BA, Gordon GE, Wise SA (1989) Mobile sources of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: a roadway tunnel study. Environ Sci Technol 23(10):1269–1278
BFG (2008) WSV-Sedimentmanagement Tideelbe. Strategien und Potenziale—eine Systemstudie. Ökologische Auswirkungen der Umlagerung von Wedeler Baggergut. Bundesanstalt für Gewässerkunde, Koblenz
Blumer M, Youngblood WW (1975) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils and recent sediments. Science 188(4183):53–55
Brinkmann M, Hudjetz S, Cofalla C, Roger S, Kammann U, Giesy JP, Hecker M, Wiseman S, Zhang XW, Wolz J, Schuttrumpf H, Hollert H (2010a) A combined hydraulic and toxicological approach to assess re-suspended sediments during simulated flood events. Part I—multiple biomarkers in rainbow trout. J Soils Sediments 10(7):1347–1361
Brinkmann M, Hudjetz S, Keiter S, Seiler TB, Wölz J, Hallare AV, Hollert H, Cofalla C, Roger S, Schüttrumpf H, Gerbersdorf SU (2010b) Toxizität und Risk Assessment fluvialer Sedimente und Schwebstoffe: Eine kurze Übersicht bisheriger und neuerer Entwicklungen. Umweltwiss Schadst-Forsch 22(6):651–655
Brinkmann M, Hudjetz S, Kammann U, Hennig M, Kuckelkorn J, Chinoraks M, Cofalla C, Wiseman S, Giesy JP, Schaffer A, Hecker M, Wolz J, Schuttrumpf H, Hollert H (2013) How flood events affect rainbow trout: evidence of a biomarker cascade in rainbow trout after exposure to PAH contaminated sediment suspensions. Aquat Toxicol 128:13–24
Carney Almroth B, Sturve J, Förlin L (2008) Oxidative damage in rainbow trout caged in a polluted river. Mar Environ Res 66(1):90–91
Chapman PM, Hollert H (2006) Should the sediment triad become a tetrad, pentad or possibly even a hexad? J Soils Sediments 6:4–8
Christie GC, Regier HA (1988) Measures of optimal thermal habitat and their relationship to yields for four commercial fish species. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 45(2):301–314
Cofalla C, Hudjetz S, Roger S, Brinkmann M, Frings R, Wölz J, Schmidt B, Schäffer A, Kammann U, Hecker M, Hollert H, Schüttrumpf H (2012) A combined hydraulic and toxicological approach to assess re-suspended sediments during simulated flood events—part II: an interdisciplinary experimental methodology. J Soils Sediments 12(3):429–442
Commission of the European Communities (2000) Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Brussels
Commission of the European Communities (2008) Directive 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on environmental quality standards in the field of water policy, amending and subsequently repealing Council Directives 82/176/EEC, 83/513/EEC, 84/156/EEC, 84/491/EEC, 86/280/EEC and amending Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council. Brussels
Commission of the European Communities (2009) Guidance Document 19, Common Implementation Strategy for the Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC), Guidance on Surface Water Chemical Monitoring Under The Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC). Brussels
Commission of the European Communities (2012) Proposal 2011/0429 (COD) for a Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council amending Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/105/EC as regards priority substances in the field of water policy. Brussels
Das R, Nanda N (1986) Induction of micronuclei in peripheral erythrocytes of fish Heteropneustes fossilis by mitomycin C and paper mill effluent. Mutat Res Lett 175(2):67–71
De Flora S, Vigano L, D’agostini F, Camoirano A, Bagnasco M, Bennicelli C, Melodia F, Arillo A (1993) Multiple genotoxicity biomarkers in fish exposed in situ to polluted river water. Mutat Res-Genet Tox 319(3):167–177
Diekmann M, Waldmann P, Schnurstein A, Grummt T, Braunbeck T, Nagel R (2004) On the relevance of genotoxicity for fish populations II: genotoxic effects in zebrafish (Danio rerio) exposed to 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide in a complete life-cycle test. Aquat Toxicol 68(1):27–37
EPA Method 610 (1984) EPA Method 610: Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati, OH
Eyrolle F, Radakovitch O, Raimbault P, Charmasson S, Antonelli C, Ferrand E, Aubert D, Raccasi G, Jacquet S, Gurriaran R (2012) Consequences of hydrological events on the delivery of suspended sediment and associated radionuclides from the Rhône River to the Mediterranean Sea. J Soils Sediments 12(9):1479–1495
Feiler U, Ahlf W, Fahnenstich C, Gilberg D, Hammers-Wirtz M, Höss S, Hollert H, Melbye K, Meller M, Neumann-Hensel H, Ratte H-T, Seiler T-B, Spira D, Weber J, Heininger P (2009) Definition von Referenzbedingungen, Kontrollsedimenten und Toxizitätsschwellenwerten für limnische Sedimentkontakttests—SeKT. Bundesanstalt für Gewässerkunde, Koblenz
Feiler U, Höss S, Ahlf W, Gilberg D, Hammers Wirtz M, Hollert H, Meller M, Neumann Hensel H, Ottermanns R, Seiler TB (2013) Sediment contact tests as a tool for the assessment of sediment quality in German waters. Environ Toxicol Chem 32(1):144–155
Förstner U, Heise S, Schwartz R, Westrich B, Ahlf W (2004) Historical contaminated sediments and soils at the river basin scale. J Soils Sediments 4(4):247–260
Gerbersdorf S, Hollert H, Brinkmann M, Wieprecht S, Schüttrumpf H, Manz W (2011) Anthropogenic pollutants affect ecosystem services of freshwater sediments: the need for a “triad plus x” approach. J Soils Sediments 11:1099–1114
Goossens H, Zwolsman JJ (1996) An evaluation of the behaviour of pollutants during dredging activities. Terra et Aqua 62:20–28
Grung M, Holth TF, Jacobsen MR, Hylland K (2009) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) metabolites in Atlantic cod exposed via water or diet to a synthetic produced water. J Toxicol Environ Health A 72(3–4):254–265
Gustafsson O, Haghseta F, Chan C, MacFarlane J, Gschwend PM (1997) Quantification of the dilute sedimentary soot phase: implications for PAH speciation and bioavailability. Environ Sci Technol 31(1):203–209
Haritash AK, Kaushik CP (2009) Biodegradation aspects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): a review. J Hazard Mater 169(1–3):1–15
Heddle J, Cimino M, Hayashi M, Romagna F, Shelby M, Tucker J, Vanparys P, MacGregor J (1991) Micronuclei as an index of cytogenetic damage: past, present, and future. Environ Mol Mutag 18(4):277–291
Hermes-Lima M, Zenteno-Savın T (2002) Animal response to drastic changes in oxygen availability and physiological oxidative stress. Comp Biochem Physiol C 133(4):537–556
Hilscherova K, Dusek L, Kubik V, Cupr P, Hofman J, Klanova J, Holoubek I (2007) Redistribution of organic pollutants in river sediments and alluvial soils related to major floods. J Soils Sediments 7(3):167–177
Hokanson KEF, Kleiner CF, Thorslund TW (1977) Effects of constant temperatures and diel temperature fluctuations on specific growth and mortality rates and yield of juvenile rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. J Fish Res Board Can 34(5):639–648
Hollert H, Haag I, Dürr M, Wetterauer B, Holtey-Weber R, Kern U, Westrich B, Färber H, Erdinger L, Braunbeck T (2003) Investigations of the ecotoxicological hazard potential and risk of erosion of contaminated sediments in lock-regulated rivers. UWSF—Z Umweltchem Ökotox 15:5–12
Hollert H, Dürr M, Haag I, Wölz J, Hilscherova K, Blaha L, Gerbersdorf SU (2008) Influence of hydrodynamics on sediment ecotoxicity. In: Westrich B, Förster U (eds) Sediment dynamics and pollutant mobility in rivers. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 401–416
Höss S, Ahlf W, Fahnenstich C, Gilberg D, Hollert H, Melbye K, Meller M, Hammers-Wirtz M, Heininger P, Neumann-Hensel H, Ottermanns R, Ratte HT, Seiler TB, Spira D, Weber J, Feiler U (2010) Variability of sediment-contact tests in freshwater sediments with low-level anthropogenic contamination—determination of toxicity thresholds. Environ Pollut 158(9):2999–3010
IKSO (1999) Odereinzugsgebiet. Das Hochwasser 1997. Internationale Kommission zum Schutz der Oder gegen Verunreinigung, Wroclaw
Jiang B, Zheng H-l, Huang G-q, Ding H, X-g L, Suo H-t, Li R (2007) Characterization and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in sediments of Haihe River, Tianjin, China. J Environ Sci 19(3):306–311
Johnson-Restrepo B, Olivero-Verbel J, Lu S, Guette-Fernández J, Baldiris-Avila R, O’Byrne-Hoyos I, Aldous KM, Addink R, Kannan K (2008) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their hydroxylated metabolites in fish bile and sediments from coastal waters of Colombia. Environ Pollut 151(3):452–459
Jung J-H, Kim M, Yim UH, Ha SY, An JG, Won JH, Han GM, Kim NS, Addison RF, Shim WJ (2011) Biomarker responses in pelagic and benthic fish over 1 year following the Hebei Spirit oil spill (Taean, Korea). Mar Pollut Bull 62(8):1859–1866
Kammann U (2007) PAH metabolites in bile fluids of dab (Limanda limanda) and flounder (Platichthys flesus)—spatial distribution and seasonal changes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 14(2):102–108
Karickhoff SW, Brown DS, Scott TA (1979) Sorption of hydrophobic pollutants on natural sediments. Water Res 13(3):241–248
Kennedy CJ, Law FC (1990) Toxicokinetics of selected polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rainbow trout following different routes of exposure. Environ Toxicol Chem 9(2):133–139
Krahn MM, Rhodes LD, Myers MS, Moore LK, Macleod WD, Malins DC (1986) Associations between metabolites of aromatic compounds in bile and the occurrence of hepatic lesions in English sole (Parophrys vetulus) from Puget Sound, Washington. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 15(1):61–67
Latimer J, Davis W, Keith D (1999) Mobilization of PAHs and PCBs from in-place contaminated marine sediments during simulated resuspension events. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 49(4):577–595
Lima ALC, Farrington JW, Reddy CM (2005) Combustion-derived polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the environment—a review. Environ Forensics 6(2):109–131
McElroy A, Farrington J, Teal J (1989) Bioavailability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the aquatic environment. Metabolism of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the aquatic environment. CRC, Boca Raton, Florida, pp. 1–39, 14 fig, 9 tab, 159 ref NOAA Contract 83-ABD-00012
McKim JM, Goeden HM (1982) A direct measure of the uptake efficiency of a xenobiotic chemical across the gills of brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. Comp Biochem Physiol C 72(1):65–74
Means JC, Wood SG, Hassett JJ, Banwart WL (1980) Sorption of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons by sediments and soils. Environ Sci Technol 14(12):1524–1528
Mehta AJ, Partheniades E. Resuspension of deposited cohesive sediment beds. In: Edge BL (ed) Eighteenth Coastal Engineering Conference, Cape Town, Republic of South Africa, 1982. ASCE, pp 1569–1588
Meybeck M, Laroche L, Dürr H, Syvitski J (2003) Global variability of daily total suspended solids and their fluxes in rivers. Global Planet Change 39(1):65–93
Moermond CT, Roozen FC, Zwolsman JJ, Koelmans AA (2004) Uptake of sediment-bound bioavailable polychlorobiphenyls by benthivorous carp (Cyprinus carpio). Environ Sci Technol 38(17):4503–4509
Nagel F, Kammann U, Wagner C, Hanel R (2012) Metabolites of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in bile as biomarkers of pollution in European eel (Anguilla anguilla) from German rivers. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 62(2):254–263
Neff JM (1979) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the aquatic environment: sources, fates and biological effects. Applied Science, London
Neff J (1985) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Fundamentals of aquatic toxicology: methods and applications. Hemisphere, Washington DC, pp. 416–454, 2 fig, 7 tab, 140 ref
Neff JM, Stout SA, Gunster DG (2005) Ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments: identifying sources and ecological hazard. Integr Environ Assess Manage 1(1):22–33
Power EAC, Chapman PM (1992) Assessing sediment quality. In: Burton GA (ed) Sediment toxicity assessment. Lewis, Boca Raton, pp. 1–18
Qiao P, Gobas F, Farrell A (2000) Relative contributions of aqueous and dietary uptake of hydrophobic chemicals to the body burden in juvenile rainbow trout. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39(3):369–377
Quick I, Schöl A, Mäueler J, Gehres N, Schriever S (2011) Auswirkungen der Wasserinjektionsbaggerung im Unteren Vorhafen der Schleuse Herbrum auf den Sedimenthaushalt und die Sauerstoffverhältnisse der Tideems. WSV-Workshop am 21./22. Juni 2010 in Bremerhaven., vol BfG-Veranstaltungen 2/2011. Bundesanstalt für Gewässerkunde, Koblenz
Randall D, Connell D, Yang R, Wu S (1998) Concentrations of persistent lipophilic compounds in fish are determined by exchange across the gills, not through the food chain. Chemosphere 37(7):1263–1270
Ravikrishna R, Valsaraj KT, Yost S, Price CB, Brannon JM (1998) Air emissions from exposed, contaminated sediment and dredged materials: 2. Diffusion from laboratory-spiked and aged field sediments. J Hazard Mater 60(1):89–104
Roberts DA (2012) Causes and ecological effects of resuspended contaminated sediments (RCS) in marine environments. Environ Int 40:230–243
Ruddock PJ, Bird DJ, McEvoy J, Peters LD (2003) Bile metabolites of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in European eels Anguilla anguilla from United Kingdom estuaries. Sci Total Environ 301(1–3):105–117
Ryan PA (1991) Environmental effects of sediment on New Zealand streams: a review. N Z J Mar Freshwat Res 25(2):207–221
Schrap SM, Opperhuizen A (1990) Relationship between bioavailability and hydrophobicity: reduction of the uptake of organic chemicals by fish due to the sorption on particles. Environ Toxicol Chem 9(6):715–724
Schubert B, Heininger P, Keller M, Claus E, Ricking M (2012) Monitoring of contaminants in suspended particulate matter as an alternative to sediments. Trends Anal Chem 36:58–70
Schüttrumpf H, Brinkmann M, Cofalla C, Frings RM, Gerbersdorf SU, Hecker M, Hudjetz S, Kammann U, Lennartz G, Roger S (2011) A new approach to investigate the interactions between sediment transport and ecotoxicological processes during flood events. Environ Sci Eur 23(1):1–5
Spork V, Ruland P, Schneider B, Köngeter J (1995) Das Kreisgerinne, ein Gerät zur Untersuchung der Transportvorgänge feiner Sedimente. Wasserwirtschaft 85:480–484
Stevens ED, Randall DJ (1967) Changes of gas concentrations in blood and water during moderate swimming activity in rainbow trout. J Exp Biol 46(2):329–337
Tuvikene A (1995) Responses of fish to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Ann Zool Fenn 32:295–309
van der Oost R, Beyer J, Vermeulen NPE (2003) Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 13(2):57–149
Van Veld PA, Westbrook DJ, Woodin BR, Hale RC, Smith CL, Huggett RJ, Stegeman JJ (1990) Induced cytochrome P-450 in intestine and liver of spot (Leiostomus xanthurus) from a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated environment. Aquat Toxicol 17(2):119–131
Varanasi U, Stein JE, Nishimoto M, Reichert WL, Collier TK (1987) Chemical carcinogenesis in feral fish: uptake, activation, and detoxification of organic xenobiotics. Environ Health Perspect 71:155
Vigano L, Arillo A, Bagnasco M, Bennicelli C, Melodia F (1993) Xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes in uninduced and induced rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): effects of diets and food deprivation. Comp Biochem Physiol C 104(1):51–55
Wassenberg DM, Swails EE, Di Giulio RT (2002) Effects of single and combined exposures to benzo (a) pyrene and 3, 3′ 4, 4′ 5-pentachlorobiphenyl on EROD activity and development in Fundulus heteroclitus. Mar Environ Res 54(3):279–283
Werres F, Balsaa P, Schmidt TC (2009) Total concentration analysis of polycylic aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous samples with high suspended particulate matter content. J Chromatogr 1216(12):2235–2240
White PA, Robitaille S, Rasmussen JB (1999) Heritable reproductive effects of benzo [a] pyrene on the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Environ Toxicol Chem 18(8):1843–1847
Whyte JJ, Jung R, Schmitt C, Tillitt D (2000) Ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase (EROD) activity in fish as a biomarker of chemical exposure. Crit Rev Toxicol 30(4):347–570
Wilby RL, Orr HG, Hedger M, Forrow D, Blackmore M (2006) Risks posed by climate change to the delivery of Water Framework Directive objectives in the UK. Environ Int 32(8):1043–1055
Willett KL, Wassenberg D, Lienesch L, Reichert W, Di Giulio RT (2001) In vivo and in vitro inhibition of CYP1A-dependent activity in Fundulus heteroclitus by the polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon fluoranthene. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 177(3):264–271
Witt G, Gründler P (2005) The consequences of the Oder flood in 1997 on the distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Oder River. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 33(4):301–314
Wölz J, Cofalla C, Hudjetz S, Roger S, Brinkmann M, Schmidt B, Schäffer A, Kammann U, Lennartz G, Hecker M, Schüttrumpf H, Hollert H (2009) In search for the ecological and toxicological relevance of sediment re-mobilisation and transport during flood events. J Soils Sediments 9(1):1–5
Wölz J, Brack W, Moehlenkamp C, Claus E, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2010a) Effect-directed analysis of Ah receptor-mediated activities caused by PAHs in suspended particulate matter sampled in flood events. Sci Total Environ 408:3327–3333
Wölz J, Fleig M, Schulze T, Maletz S, Lübcke-von Varel U, Reifferscheid G, Kühlers D, Braunbeck T, Brack W, Hollert H (2010b) Impact of contaminants bound to suspended particulate matter in the context of flood events. J Soils Sediments 10(6):1174–1185
Wood C, Munger R (1994) Carbonic anhydrase injection provides evidence for the role of blood acid–base status in stimulating ventilation after exhaustive exercise in rainbow trout. J Exp Biol 194(1):225–253
Xia X, Yu H, Yang Z, Huang G (2006) Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the natural waters of the Yellow River: effects of high sediment content on biodegradation. Chemosphere 65(3):457–466
Yang R, Brauner C, Thurston V, Neuman J, Randall DJ (2000) Relationship between toxicant transfer kinetic processes and fish oxygen consumption. Aquat Toxicol 48(2):95–108
Acknowledgments
This study has been supported by a Boost-Funds project of the Exploratory Research Space (ERS) at the RWTH Aachen University, as part of the German Excellence Initiative. We would like to thank the German Federal Institute of Hydrology (Bundesanstalt für Gewässerkunde, BfG), especially Denise Spira and Dr. Georg Reifferscheid, for assistance and support during sampling of the sediments. Furthermore, we would like to thank the Hans Böckler Foundation (Düsseldorf, Germany) who supported Henning Hermann with a scholarship during his studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 492 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hudjetz, S., Herrmann, H., Cofalla, C. et al. An attempt to assess the relevance of flood events—biomarker response of rainbow trout exposed to resuspended natural sediments in an annular flume. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 13744–13757 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2414-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2414-2