Abstract
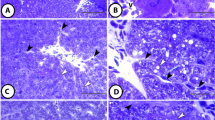
Liver lesions in wild fish have been associated with xenobiotic exposure. Facing reports of pollution in the Douro River estuary (north of Portugal), we have been making field surveys using fishes and targeting histopathological biomarkers of exposure and effect. Herein, we intended to better characterize and report the rate of one poorly understood lesion—hepatocellular fibrillar inclusions (HFI)—found in European flounder (Platichthys flesus). With this report, we aimed to establish sound baseline data that could be viewed as a starting point for future biomonitoring, while offering the world's second only pool of field data on such a liver toxicopathic lesion, which could be compared with data available from the UK estuaries. Sampling was done in the Douro River estuary over 1 year. A total of 72 animals were fished with nets, in spring–summer (SS) and autumn–winter (AW) campaigns. Livers were processed for histopathology and both routine and special staining procedures (alcian blue, periodic acid Schiff (PAS), tetrazonium coupling reaction). Immunohistochemistry targeted AE1/AE3 (pan cytokeratins). The severity of the HFI extent was graded using a system with four levels, varying from 0 (absence of HFI) to 3 (high relative density of cells with HFI). Cells (isolated/groups) with HFI appeared in 35 % or more of the fish, in the total samples of each season, and over 40 % in more homogeneous sub-samples. There were no significant differences when comparing samples versus sub-samples or SS versus AW. When merging the data sets from the two seasons, the frequency of fish with HFI was ≈36 % for the total sample and ≈49 % for the sub-sample. The extreme group (biggest and smallest fish) revealed a HFI frequency of only 16 %, which differed significantly from the total and sub-sampled groups. Immunostaining and PAS were negative for the HFI, and alcian blue could, at times, faintly stain the inclusions. These were positive with the tetrazonium reaction. We showed the presence of HFI in European flounder from the Douro River estuary, proving that they are essentially protein in nature, that no seasonal changes existed in the HFI frequency, and that it was rarer in the smallest and biggest fish groups. Within the ranges of weight/size of our total sample, we estimate that the frequency of HFI in the local flounder is ≈35 %. That rate stands as a baseline value for future assessments, namely for biomonitoring purposes targeting correlations with the estuary pollution status.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams SM, Shepard KL, Greeley MS Jr, Jimenez BD, Ryon MG, Shugart LR, McCarthy JF, Hinton DE (1989) The use of bioindicators for assessing the effects of pollutant stress on fish. Mar Environ Res 28:459–464
Allan IJ, Vrana B, Greenwood R, Mills GA, Roig B, Gonzalez C (2006) A “toolbox” for biological and chemical monitoring requirements for the European Union's Water Framework Directive. Talanta 69:302–322
Andrade VM, Silva J, Silva FR, Heuser VD, Dias JF, Yoneama ML, Freitas TR (2004) Fish as bioindicators to assess the effects of pollution in two southern Brazilian rivers using the Comet assay and micronucleus test. Environ Mol Mutagen 44:459–468
Anon (1999) Work package 6: external fish diseases and liver histopathology. Biological effects quality assurance in monitoring programmes (BEQUALM), CEFAS Weymouth laboratory, UK
Au DW (2004) The application of histo-cytopathological biomarkers in marine pollution monitoring: a review. Mar Poll Bull 48:817–834
Bateman AC, Hübscher SG (2010) Cytokeratin expression as an aid to diagnosis in medical liver biopsies. Histopathology 56:415–425
Braunbeck T, Appelbaum S (1999) Ultrastructural alterations in the liver and intestine of carp Cyprinus carpio induced orally by ultra-low doses of endosulfan. Dis Aquat Org 36:183–200
Broeg K, Westernhagen H, Zander S, Körting W, Koehler A (2005) The “bioeffect assessment index” (BAI): a concept for the quantification of effects of marine pollution by an integrated biomarker approach. Mar Poll Bull 50:495–503
Bucke D, Feist SW (1993) Histopathological changes in the livers of dab (Limanda limanda L.). J Fish Dis 16:281–296
Cajaraville MP (2000) Towards an integrative approach in environmental contamination and toxicology. Sci Total Environ 247:95–97
Cajaraville MP, Bebianno MJ, Blasco J, Porte C, Sarasquete C, Viarengo A (2000) The use of biomarkers to assess the impact of pollution in coastal environments of the Iberian Peninsula: a practical approach. Sci Total Environ 247:295–311
Carrola J (2011) Light microscopic studies of toxicopathic changes in fishes from the Tinhela and Vizela Rivers, and from the Mondego, Douro and Ave estuaries. Dissertation, University of Trás-os-Montes and Alto Douro (UTAD), Vila Real, Portugal
Carrola J, Fontainhas-Fernandes A, Matos P, Rocha E (2009) Liver histopathology in brown trout (Salmo trutta f. fario) from the Tinhela River, subjected to mine drainage from the abandoned Jales Mine (Portugal). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 83:35–41
Chovanec A, Hofer R, Schiemer F (2003) Chapter 18 Fish as bioindicators. In: B.A. Markert AMB, Zechmeister HG (eds), Trace metals and other contaminants in the environment. Elsevier, Amsterdam pp. 639–676
Corsi I, Mariottini M, Sensini C, Lancini L, Focardi S (2003) Fish as bioindicators of brackish ecosystem health: integrating biomarker responses and target pollutant concentrations. Oceanol Acta 26:129–138
Fernandes C, Fontainhas-Fernandes A, Monteiro SM, Salgado MA (2007) Changes in plasma electrolytes and gill histopathology in wild Liza saliens from the Esmoriz-Paramos coastal lagoon, Portugal. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:301–305
Fernandes C, Fontainhas-Fernandes A, Rocha E, Salgado MA (2008) Monitoring pollution in Esmoriz-Paramos lagoon, Portugal: liver histological and biochemical effects in Liza saliens. Environ Monit Assess 145:315–322
Hinton DE, Laurén DJ (1990) Liver structural alterations accompanying chronic toxicity in fishes: potential biomarkers of exposure. In: McCarty F, Shugart LR (eds) Biomarkers of environmental contaminations. JLewis Publishers, Florida, pp 17–57
Koehler A (2004) The gender-specific risk to liver toxicity and cancer of flounder (Platichthys flesus (L.)) at the German Wadden Sea coast. Aquat Toxicol 70:257–276
Köhler A (1990) Identification of contaminant-induced cellular and subcellular lesions in the liver of flounder (Platichthys flesus L.) caught at differently polluted estuaries. Aquat Toxicol 16:271–293
Kohler A, Ellesat K (2008) Nuclear changes in blood, early liver anomalies and hepatocellular cancers in flounder (Platichthys flesus L.) as prognostic indicator for a higher cancer risk? Mar Environ Res 66:149–150
Kohler HR, Sandu C, Scheil V, Nagy-Petrica EM, Segner H, Telcean I, Stan G, Triebskorn R (2007) Monitoring pollution in river Mures, Romania, Part III: biochemical effect markers in fish and integrative reflection. Environ Monit Assess 127:47–54
Lang T, Wosniok W, Barsiene J, Broeg K, Kopecka J, Parkkonen J (2006) Liver histopathology in Baltic flounder (Platichthys flesus) as indicator of biological effects of contaminants. Mar Pollut Bull 53:488–496
Lyons BP, Stentiford GD, Green M, Bignell J, Bateman K, Feist SW, Goodsir F, Reynolds WJ, Thain JE (2004) DNA adduct analysis and histopathological biomarkers in European flounder (Platichthys flesus) sampled from UK estuaries. Mutat Res Fundam Mol Mech Mutag 552:177–186
Maceda-Veiga A, Monroy M, Viscor G, De Sostoa A (2010) Changes in non-specific biomarkers in the Mediterranean barbel (Barbus meridionalis) exposed to sewage effluents in a Mediterranean stream (Catalonia, NE Spain). Aquat Toxicol 100:229–237
Madureira TV, Barreiro JC, Rocha MJ, Cass QB, Tiritan ME (2009) Pharmaceutical trace analysis in aqueous environmental matrices by liquid chromatography-ion trap tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1216:7033–7042
Madureira TV, Barreiro JC, Rocha MJ, Rocha E, Cass QB, Tiritan ME (2010) Spatiotemporal distribution of pharmaceuticals in the Douro River estuary (Portugal). Sci Total Environ 408:5513–5520
Madureira TV, Rocha MJ, Cruzeiro C, Rodrigues I, Monteiro RAF, Rocha E (2012) The toxicity potential of pharmaceuticals found in the Douro River estuary (Portugal): evaluation of impacts on fish liver, by histopathology, stereology, vitellogenin and CYP1A immunohistochemistry, after sub-acute exposures of the zebrafish model. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 34:34–45
Marigomez I, Soto M, Cancio I, Orbea A, Garmendia L, Cajaraville MP (2006) Cell and tissue biomarkers in mussel, and histopathology in hake and anchovy from Bay of Biscay after the Prestige oil spill (Monitoring Campaign 2003). Mar Pollut Bull 53:287–304
Myers MS, French BL, Reichert WL, Willis ML, Anulacion BF, Collier TK, Stein JE (1998a) Reductions in CYP1A expression and hydrophobic DNA adducts in liver neoplasms of English sole (Pleuronectes vetulus): further support for the ‘resistant hepatocyte’ model of hepatocarcinogenesis. Mar Environ Res 46:197–202
Myers MS, Johnson LL, Hom T, Collier TK, Stein JE, Varanasi U (1998b) Toxicopathic hepatic lesions in subadult English sole (Pleuronectes vetulus) from Puget Sound, Washington, USA: relationships with other biomarkers of contaminant exposure. Mar Environ Res 45:47–67
Niimi AJ (1990) Review of biochemical methods and other indicators to assess fish health in aquatic ecosystems containing toxic chemicals. J Great Lakes Res 16:529–541
Pal S, Kokushi E, Cheikyula JO, Koyama J, Uno S (2011) Histopathological effects and EROD induction in common carp exposed to dietary heavy oil. Ecotox Environ Safe 74:307–314
Pinto AL, Varandas S, Coimbra AM, Carrola J, Fontainhas-Fernandes A (2010) Mullet and gudgeon liver histopathology and macroinvertebrate indexes and metrics upstream and downstream from a wastewater treatment plant (Febros River-Portugal). Environ Monit Assess 169:569–585
Ribeiro C, Tiritan ME, Rocha E, Rocha MJ (2009a) Seasonal and spatial distribution of several endocrine-disrupting compounds in the Douro River estuary, Portugal. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 56:1–11
Ribeiro C, Pardal MA, Martinho F, Margalho R, Tiritan ME, Rocha E, Rocha MJ (2009b) Distribution of endocrine disruptors in the Mondego River estuary, Portugal. Environ Monit Assess 149:183–193
Rocha E, Ferreira M, Lopes C, Reis-Henriques MA (2004) Liver pathology in grey mullets (Mugil chepalus) and flounder (Platichthys flesus) from the Douro river estuary, Portugal. Mar Environ Res 58:324
Rocha MJ, Ferreira P, Reis A, Cruzeiro C, Rocha E (2011a) Development and validation of a MAE-SPE-GC-MS method for the evaluation of sixteen priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in marine and estuarine sediments—applications to the Porto coastal region (Portugal). J Chromatogr Sci 9:695–701
Rocha MJ, Ribeiro MFT, Cruzeiro C, Figueiredo F, Rocha E (2011b) Development and validation of a GC-MS method for determination of thirty nine common pesticides in estuarine water—targeting hazardous amounts in the Douro River estuary. Int J Environ Anal Chem 92:1587–1608
Rocha MJ, Ferreira PC, Reis PA, Cruzeiro C, Rocha E (2011c) Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in coastal sediments from Porto region (Portugal) by microwave-assisted extraction followed by solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr Sci 49:695–701
Rocha MJ, Cruzeiro C, Ferreira C, Rocha E (2012) Occurrence of endocrine disruptor compounds in the estuary of the Iberian Douro River and nearby Porto Coast (NW Portugal). Toxicol Environ Chem 94:252–261
Schlacher TA, Mondon JA, Connolly RM (2007) Estuarine fish health assessment: evidence of wastewater impacts based on nitrogen isotopes and histopathology. Mar Pollut Bull 54:1762–1776
Silva P, Rocha MJ, Cruzeiro C, Malhão F, Reis B, Urbatzka R, Monteiro RAF, Rocha E (2012) Testing the effects of ethinylestradiol and of an environmentally relevant mixture of xenoestrogens as found in the Douro River (Portugal) on the maturation of fish gonads—a stereological study using the zebrafish (Danio rerio) as model. Aquat Toxicol 124–125:1–10
Slooff W (1983) A study on the usefulness of feral fish as indicators for the presence of chemical carcinogens in Dutch surface waters. Aquat Toxicol 3:127–139
Stein JE, Collier TK, Reichert WL, Casillas E, Hom T, Varanasi U (1993) Bioindicators of contaminant exposure and sublethal effects in benthic fish from Puget Sound, WA, USA. Mar Environ Res 35:95–100
Stentiford GD, Longshaw M, Lyons BP, Jones G, Green M, Feist SW (2003) Histopathological biomarkers in estuarine fish species for the assessment of biological effects of contaminants. Mar Environ Res 55:137–159
Triebskorn R, Adam S, Behrens A, Beier S, Böhmer J, Braunbeck T, Casper H, Dietze U, Gernhöfer M, Honnen W, Köhler H-R, Körner W, Konradt J, Lehmanni R, Luckenbach T, Oberemm A, Schwaiger J, Segner H, Strmac M, Schüürmann G, Siligato S, Traunspurger W (2003) Establishing causality between pollution and effects at different levels of biological organization: the VALIMAR project. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 9:171–194
Urbatzka R, Rocha E, Reis B, Cruzeiro C, Monteiro RAF, Rocha MJ (2012) Effects of ethinylestradiol and of an environmentally relevant mixture of xenoestrogens on steroidogenic gene expression and specific transcription factors in zebrafish. Environ Pollut 164:28–35
van der Oost R, Beyer J, Vermeulen NPE (2003) Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 13:57–149
Van Eyken P, Sciot R, Desmet VJ (1989) A cytokeratin immunohistochemical study of cholestatic liver disease: evidence that hepatocytes can express “bile duct-type” cytokeratins. Histopathology 15:125–135
Vethaak AD, Wester PW (1996) Diseases of flounder Platichthys flesus in Dutch coastal and estuarine waters, with particular reference to environmental stress factors. II. Liver histopathology. Dis Aquat Org 26:99–116
Viarengo A, Lowe D, Bolognesi C, Fabbri E, Koehler A (2007) The use of biomarkers in biomonitoring: a 2-tier approach assessing the level of pollutant-induced stress syndrome in sentinel organisms. Comp Biochem Physiol C: Toxicol Pharmacol 146:281–300
Zimmerli S, Bernet D, Burkhardt-Holm P, Schmidt-Posthaus H, Vonlanthen P, Wahli T, Segner H (2007) Assessment of fish health status in four Swiss rivers showing a decline of brown trout catches. Aquat Sci 69:11–25
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) through the Competitiveness and Trade Expansion Program (COMPETE) and by National Funds provided by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT) via the research projects PTDC/MAR/70436/2006 and PEst-C/MAR/LA0015/2011, and the PhD grant SFRH/BD/25746/2005. We are grateful to Mrs. Nádia S. Santos for performing the histochemistry and immunohistochemistry procedures in selected liver sections.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Thomas Braunbeck
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carrola, J., Fontaínhas-Fernandes, A., Pires, M.J. et al. Frequency of hepatocellular fibrillar inclusions in European flounder (Platichthys flesus) from the Douro River estuary, Portugal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 3116–3125 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2248-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2248-y