Abstract
Purpose
The oxone process for azo dye decolorization has drawbacks such as difficulties with reuse, risks of secondary pollution, and high costs associated with UV irradiation. This study aims to explore the use of oxone for decolorization in the absence of catalyst and under natural sunlight conditions (i.e., oxone/natural sunlight system) and evaluate the impacts of operating parameters (reagent dosage, initial methyl orange (MO) concentration, and initial pH) and coexisting substances (humic acid, NO −3 , metal ions) on the system’s decolorization efficiency.
Methods
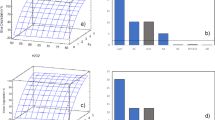
Four levels of operating parameters were configured under a Taguchi L16 orthogonal array design to examine their effects on decolorization efficiency. Fractional factional design was then used to derive the optimal combination of operating parameters, under which the effects of coexisting substances at various concentrations were examined. In addition, H2O2, CH3OH, and (CH3)3COH were used to derive the possible reaction mechanisms in the oxone/sunlight system, while ultrasonic power was used to shorten the reaction time.
Results
In the oxone/sunlight system, (1) the MO decolorization efficiency reaches 96.4% under the optimal operating conditions: initial concentration, 100 mg L−1; initial pH 6.04; dosage of reagent, 3 mmol L−1; and reaction time, 30 min. (2) Coexisting substances do not affect the overall decolorization efficiency. (3) The decolorization of MO in the oxone/sunlight system takes place mainly via oxidation by SO ⋅−4 . (4) Ultrasonic irradiation could remarkably accelerate the MO decolorization process.
Conclusion
Effective for MO decolorization, the oxone/sunlight system improves over the traditional oxone process with advantages of lower costs and avoiding secondary pollution by catalyst.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anipsitakis GP, Dionysiou DD (2003) Degradation of organic contaminants in water with sulfate radicals generated by the conjunction of peroxymonosulfate with cobalt. Environ Sci Technol 37:4790–4797
Bokare AD, Chikate RC, Rode CV, Paknikar KM (2008) Iron–nickel bimetallic nanoparticles for reductive degradation of azo dye Orange G in aqueous solution. Appl Catal B—Environ 79:270–278
Brezonik PL, Fulkerson-Brekken J (1998) Nitrate-induced photolysis in natural waters: controls on concentrations of hydroxyl radical photo-intermediates by natural scavenging agents. Environ Sci Technol 32:3004–3010
Chen JX, Zhu LZ (2007) Heterogeneous UV-Fenton catalytic degradation of dyestuff in water with hydroxyl-Fe pillared bentonite. Catal Today 126:463–470
Chen XY, Qiao XL, Wang DG, Lin J, Chen JW (2007) Kinetics of oxidative decolorization and mineralization of Acid Orange 7 by dark and photoassisted Co2+-catalyzed peroxymonosulfate system. Chemosphere 67:802–808
Daud NK, Hameed BH (2010) Decolorization of Acid Red 1 by Fenton-like process using rice husk ash-based catalyst. J Hazard Mater 176:938–944
Enayatzamir K, Alikhani HA, Yakhchali B, Tabandeh F, Rodríguez-Couto S (2010) Decolouration of azo dyes by Phanerochaete chrysosporium immobilised into alginate beads. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17:145–153
Fernandez J, Maruthamuthu P, Renken A, Kiwi J (2004a) Bleaching and photobleaching of Orange II within seconds by the oxone/Co2+ reagent in Fenton-like process. Appl Catal B—Environ 49:207–215
Fernandez J, Maruthamuthu P, Renken A, Kiwi J (2004b) Photobleaching and mineralization of Orange II by oxone and metal-ions involving Fenton-like chemistry under visible light. J Photoch Photobio A 161:185–192
Fersi C, Dhahbi M (2008) Treatment of textile plant effluent by ultrafiltration and/or nanofiltration for water reuse. Desalination 222:263–271
Golob V, Vinder A, Simonic M (2005) Efficiency of the coagulation/flocculation method for the treatment of dyebath effluents. Dye Pigment 67:93–97
Guivarch E, Trevin S, Lahitte C, Oturan MA (2003) Degradation of azo dyes in water by electro-Fenton process. Environ Chem Lett 1:38–44
He HY, Huang JF, Cao LY, Wu JP (2010) Photodegradation of methyl orange aqueous on MnWO4 powder under different light resources and initial pH. Desalination 252:66–70
Huang YH, Huang YF, Huang CI, Chen CY (2009) Efficient decolorization of azo dye Reactive Black B involving aromatic fragment degradation in buffered Co2+/PMS oxidative processes with a ppb level dosage of Co2+-catalyst. J Hazard Mater 170:1110–1118
Li Y, Xi DL (2004) Decolorization and biodegradation of dye wastewaters by a facultative-aerobic process. Environ Sci Pollut Res 16:372–377
Ling SK, Wang SB, Peng YL (2010) Oxidative degradation of dyes in water using Co2+/H2O2 and Co2+/peroxymonosulfate. J Hazard Mater 178:385–389
Liu HN, Li GT, Qu JH, Liu HJ (2007) Degradation of azo dye Acid Orange 7 in water by Fe0/granular activated carbon system in the presence of ultrasound. J Hazard Mater 144:180–186
Liu Q, Luo XZ, Zheng Z, Zheng BG, Zhang JB, Zhao YJ, Yang XY, Wang JQ, Wang LH (2011) Factors that have an effect on degradation of diclofenac in aqueous solution by gamma ray irradiation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:1243–1252. doi:10.1007/s11356-011-0457-9
Lu K, Zhang XL, Zhao YL, Wu ZL (2010) Removal of color from textile dyeing wastewater by foam separation. J Hazard Mater 182:928–932
Madhavan J, Maruthamuthu P, Murugesan S, Ashokkumar M (2009) Kinetics of degradation of acid red 88 in the presence of Co2+-ion/peroxomonosulphate reagent. Appl Catal A—Gen 368:35–39
Park H, Choi W (2003) Visible light and Fe(III)-mediated degradation of acid Orange 7 in the absence of H2O2. J Photoch Photobiol A 159:241–247
Sandvik SLH, Bilski P, Pakulski JD, Chignell CF, Coffin RB (2000) Photogeneration of singlet oxygen and free radicals in dissolved organic matter isolated from the Mississippi and Atchafalaya River plumes. Mar Chem 69:139–152
Sun JH, Li XY, Feng JL, Tian XK (2009) Oxone/Co2+ oxidation as an advanced oxidation process: comparison with traditional Fenton oxidation for treatment of landfill leachate. Water Res 43:4363–4369
Ugurlu M, Karaoglu MH (2009) Removal of AOX, total nitrogen and chlorinated lignin from bleached Kraft mill effluents by UV oxidation in the presence of hydrogen peroxide utilizing TiO2 as photocatalyst. Environ Sci Pollut Res 16:265–273
Yu ZY, Kiwi-Minsker L, Renken A, Kiwi J (2006) Detoxification of diluted azo-dyes at biocompatible pH with the oxone/Co2+ reagent in dark and light processes. J Mol Catal A—Chem 252:113–119
Zahrim AY, Tizaoui C, Hilal N (2010) Evaluation of several commercial synthetic polymers as flocculant aids for removal of highly concentrated C.I. Acid Black 210 dye. J Hazard Mater 182:624–630
Zhan MJ, Yang X, Xian QM, Kong LG (2006) Photosensitized degradation of bisphenol A involving reactive oxygen species in the presence of humic substances. Chemosphere 63:378–386
Zhang H, Duan LJ, Zhang DB (2006) Decolorization of methyl orange by ozonation in combination with ultrasonic irradiation. J Hazard Mater B 138:53–59
Acknowledgments
Zheng Zheng gratefully acknowledges support from the Natural Science Foundation of China (Foundation item no. 10475040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hailong Wang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Zheng, Z., Yang, X. et al. Effect of factors on decolorization of azo dye methyl orange by oxone/natural sunlight in aqueous solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19, 577–584 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0591-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0591-4