Abstract
Purpose
The power push-up test can reveal significant differences in evaluating upper extremity strength. The aim of this study was to investigate the test–retest reliability of the parameters produced from the force platform of the power push-up test in young swimmers.
Methods
A total of 35 swimmers (age: 15.8 ± 2.6 years) participated in this study. Flight time (FT), peak force (PF), mean force (MF), rate of force development (RFD), and impulse were analyzed from the force platform.
Results
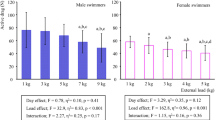
There was no difference between the two measurements for all parameters (p > 0.05). Intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and coefficient of variation (CV %) showed that some parameters from the force platform were highly reliable (ICC: RFD (0.94) FT, (0.96), PF (0.98), MF (0.97), impulse (0.97), CV%: RFD (50%), FT (20%), PF (17%), MF (18%), impulse (25%).
Conclusion
The results of this study showed that the parameters obtained from the power push-up test performed on the force platform are a reliable tool for swimmers and can be used by practitioners by carefully interpreting them.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Taylor JB, Wright AA, Smoliga JM, DePew JT, Hegedus EJ (2016) Upper-extremity physical-performance tests in college athletes. J Sport Rehabil 25(2):146–154
Sander A, Keiner M, Wirth K, Schmidtbleicher D (2013) Influence of a 2-year strength training programme on power performance in elite youth soccer players. Eur J Sport Sci 13(5):445–451
Keiner M, Wirth K, Fuhrmann S, Kunz M, Hartmann H, Haff GG (2021) The influence of upper- and lower-body maximum strength on swim block start, turn, and overall swim performance in sprint swimming. J Strength Cond Res 35(10):2839–2845
Wang R, Hoffman JR, Sadres E, Bartolomei S, Muddle TW, Fukuda DH et al (2017) Evaluating upper-body strength and power from a single test: The ballistic push-up. J Strength Cond Res 31(5):1338–1345
Parry GN, Herrington LC, Horsley IG, Gatt I (2021) The test–retest reliability of bilateral and unilateral force plate–derived parameters of the countermovement push-up in elite boxers. J Sport Rehab 1:1–5
Suchomel TJ, Sands WA, McNeal JR (2016) Comparison of static, countermovement, and drop jumps of the upper and lower extremities in us junior national team male gymnasts. Sci Gymn J. 8(1):78
Stockbrugger BA, Haennel RG (2001) Validity and reliability of a medicine ball explosive power test. J Stren Condit Res 15(4):431–438
Koch J, Riemann BL, Davies GJ (2012) Ground reaction force patterns in plyometric push-ups. J Stren Condit Res 26(8):2220–2227
Morais JE, Marques MC, Rodríguez-Rosell D, Barbosa TM, Marinho DA (2020) Relationship between thrust, anthropometrics, and dry-land strength in a national junior swimming team. Phys Sportsmed 48(3):304–311
Morais JE, Silva AJ, Marinho DA, Marques MC, Batalha N, Barbosa TM (2016) Modelling the relationship between biomechanics and performance of young sprinting swimmers. Eur J Sport Sci 16(6):661–668
McLellan CP, Lovell DI, Gass GC (2011) The role of rate of force development on vertical jump performance. J Stren Condit Res 25(2):379–385
Hogarth L, Deakin G, Sinclair W (2013) Are plyometric push-ups a reliable power assessment tool? J Aust Stren Condit 21:67–69
Dai B, Layer J, Vertz C, Hinshaw T, Cook R, Li Y et al (2019) Baseline assessments of strength and balance performance and bilateral asymmetries in collegiate athletes. J Stren Condit Res 33(11):3015–3029
Bohannon NA, Gillen ZM, Shoemaker ME, McKay BD, Gibson SM, Cramer JT (2020) Test–retest reliability of static and countermovement power push-up tests in young male athletes. J Stren Condit Res 34(9):2456–2464
Parry GN, Herrington LC, Horsley IG (2020) The test–retest reliability of force plate–derived parameters of the countermovement push-up as a power assessment tool. J Sport Rehabil 29(3):381–383
Deschodt V, Arsac L, Rouard A (1999) Relative contribution of arms and legs in humans to propulsion in 25-m sprint front-crawl swimming. Eur J Appl Physiol 80:192–199
Bartolomeu RF, Costa MJ, Barbosa TM (2018) Contribution of limbs’ actions to the four competitive swimming strokes: a nonlinear approach. J Sports Sci 36(16):1836–1845
McKay AK, Stellingwerff T, Smith ES, Martin DT, Mujika I, Goosey-Tolfrey VL et al (2021) Defining training and performance caliber: a participant classification framework. Int J Sports Physiol Perform 17(2):317–331
Bland JM, Altman DG (1999) Measuring agreement in method comparison studies. Stat Methods Med Res 8(2):135–160
Cormack SJ, Newton RU, McGuigan MR, Doyle TL (2008) Reliability of measures obtained during single and repeated countermovement jumps. Int J Sports Physiol Perform 3(2):131–144
Zalleg D, Dhahbi AB, Dhahbi W, Sellami M, Padulo J, Souaifi M et al (2020) Explosive push-ups: from popular simple exercises to valid tests for upper-body power. J Stren Condit Res 34(10):2877–2885
Gillen ZM, Miramonti AA, McKay BD, Jenkins ND, Leutzinger TJ, Cramer JT (2018) Reliability and sensitivity of the power push-up test for upper-body strength and power in 6–15-year-old male athletes. J Stren Condit Res 32(1):83–96
Hrysomallis C, Kidgell D (2001) Effect of heavy dynamic resistive exercise on acute upper-body power. J Stren Condit Res 15(4):426–430
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study's conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by F.Ö., E.Ü., and A.Ö. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Ş.A.C., G.İ.K., and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare(s) that there is no conflict of interest. The authors declare they have no financial interests.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by Hacettepe University Non-Invasive Clinical Research Ethics Committee (GO 21/1151).
Human and animal rights
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all swimmers and their legal guardians.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Öztürk, F., Ünver, E., Özçadırcı, A. et al. Test–retest reliability of the power push-up test in adolescent swimmers: force plate-derived parameters’ reliability of power push-up test in adolescent swimmers. Sport Sci Health (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11332-023-01144-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11332-023-01144-x