Abstract
Introduction
Advances in high-resolution mass spectrometry have created renewed interest for studying global lipid biochemistry in disease and biological systems.
Objectives
Here, we present an untargeted 30 min. LC-MS/MS platform that utilizes positive/negative polarity switching to perform unbiased data dependent acquisitions (DDA) via higher energy collisional dissociation (HCD) fragmentation to profile more than 1000–1500 lipid ions mainly from methyl-tert-butyl ether (MTBE) or chloroform:methanol extractions.
Methods
The platform uses C18 reversed-phase chromatography coupled to a hybrid QExactive Plus/HF Orbitrap mass spectrometer and the entire procedure takes ~10 h from lipid extraction to identification/quantification for a data set containing 12 samples (~4 h for a single sample). Lipids are identified by both accurate precursor ion mass and fragmentation features and quantified using LipidSearch and Elements software.
Results
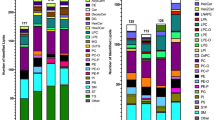
Using this approach, we are able to profile intact lipid ions from up to 18 different main lipid classes and 66 subclasses. We show several studies from different biological sources, including cultured cancer cells, resected tissues from mice such as lung and breast tumors and biological fluids such as plasma and urine.
Conclusions
Using mouse embryonic fibroblasts, we showed that TSC2−/− KD significantly abrogates lipid biosynthesis and that rapamycin can rescue triglyceride (TG) lipids and we show that SREBP−/− shuts down lipid biosynthesis significantly via mTORC1 signaling pathways. We show that in mouse EGFR driven lung tumors, a large number of TGs and phosphatidylmethanol (PMe) lipids are elevated while some phospholipids (PLs) show some of the largest decrease in lipid levels from ~ 2000 identified lipid ions. In addition, we identified more than 1500 unique lipid species from human blood plasma.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
AHMED, Z., MAYR, M., ZEESHAN, S., DANDEKAR, T., MUELLER, M. J., & FEKETE, A. (2015). Lipid-Pro: A computational lipid identification solution for untargeted lipidomics on data-independent acquisition tandem mass spectrometry platforms. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 31, 1150–1153.
Asara, J. M., Xu, Y., Breitkopf, S. B., Yuan, M., Ricoult, S. J. & Manning, B. D. (2016). Preparing Biological Samples for Metabolomics and Lipidomics, Can We Start with Just One Sample? Association of Biomolecular Resource Facilities. Ft. Lauderdale.
Ben-Sahra, I., Howell, J. J., Asara, J. M., & Manning, B. D. (2013). Stimulation of de novo pyrimidine synthesis by growth signaling through mTOR and S6K1. Science, 339, 1323–1328.
Bilgin, M., Born, P., Fezza, F., Heimes, M., Mastrangelo, N., Wagner, N., Schultz, C., Maccarrone, M., Eaton, S., Nadler, A., Wilm, M., & Shevchenko, A. (2016). Lipid Discovery by Combinatorial Screening and Untargeted LC-MS/MS. Scientific Reports, 6, 27920.
Bird, S. S., Marur, V. R., Sniatynski, M. J., Greenberg, H. K., & Kristal, B. S. (2011). Serum lipidomics profiling using LC-MS and high-energy collisional dissociation fragmentation: focus on triglyceride detection and characterization. Analytical Chemistry, 83, 6648–6657.
Breitkopf, S. B., Yuan, M., Helenius, K. P., Lyssiotis, C. A., & Asara, J. M. (2015). Triomics analysis of imatinib-treated myeloma cells connects kinase inhibition to RNA processing and decreased lipid biosynthesis. Analytical Chemistry, 87(21), 10995–11006
Breitkopf, S. B., Yuan, M., XU, Y., & Asara, J. M. 2016. A quantitative positive/negative ion switching method for shotgun lipidomics via high resolution LC-MS/MS from any biological source. San Antonio: American Society for Mass Spectrometry
Cajka, T., & Fiehn, O. (2014). Comprehensive analysis of lipids in biological systems by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Trends In Analytical Chemistry, 61, 192–206.
Chou, C. H., Chang, W. C., Chiu, C. M., Huang, C. C., & Huang, H. D. (2009). FMM: A web server for metabolic pathway reconstruction and comparative analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 37, W129–W134.
Collins, J. R., Edwards, B. R., Fredricks, H. F., & van MOOY, B. A. (2016). LOBSTAHS: An adduct-based lipidomics strategy for discovery and identification of oxidative stress biomarkers. Analytical Chemistry, 88, 7154–7162.
COOMBS, K. M. (2011). Quantitative proteomics of complex mixtures. Expert Review of Proteomics, 8, 659–677.
COX, J., & MANN, M (2011). Quantitative, high-resolution proteomics for data-driven systems biology. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 80, 273–299.
Duvel, K., Yecies, J. L., Menon, S., Raman, P., Lipovsky, A. I., Souza, A. L., Triantafellow, E., Ma, Q., Gorski, R., Cleaver, S., Vander Heiden, M. G., Mackeigan, J. P., Finan, P. M., Clish, C. B., Murphy, L. O., & Manning, B. D. (2010). Activation of a metabolic gene regulatory network downstream of mTOR complex 1. Molecular Cell, 39, 171–183.
Fahy, E., Sud, M., Cotter, D., & Subramaniam, S. (2007). LIPID MAPS online tools for lipid research. Nucleic Acids Research, 35, W606–W612.
Fauland, A., Kofeler, H., Trotzmuller, M., Knopf, A., Hartler, J., Eberl, A., Chitraju, C., Lankmayr, E., & Spener, F. (2011). A comprehensive method for lipid profiling by liquid chromatography-ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Journal of Lipid Research, 52, 2314–2322.
Folch, J., Lees, M., & Sloane Stanley, G. H. (1957). A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 226, 497–509.
Godzien, J., Ciborowski, M., Martinez-Alcazar, M. P., Samczuk, P., Kretowski, A., & Barbas, C. (2015). Rapid and reliable identification of phospholipids for untargeted metabolomics with LC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS. Journal of Proteome Research, 14, 3204–3216.
Han, X., Yang, K., & Gross, R. W. (2012). Multi-dimensional mass spectrometry-based shotgun lipidomics and novel strategies for lipidomic analyses. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 31, 134–178.
Hara, H., Uchimura, T., Akashi, N., Naganuma, T., Aizawa, T., Nagae, Y., & Masuda, N. (2004). Simultaneous analytical method for the determination of TCH346 and its four metabolites in human plasma by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 18, 377–384.
Hartler, J., Trotzmuller, M., Chitraju, C., Spener, F., Kofeler, H. C., & Thallinger, G. G. (2011). Lipid data analyzer: Unattended identification and quantitation of lipids in LC-MS data. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 27, 572–577.
Hein, E. M., Bodeker, B., Nolte, J., & Hayen, H. (2010). Software tool for mining liquid chromatography/multi-stage mass spectrometry data for comprehensive glycerophospholipid profiling. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 24, 2083–2092.
Hopperton, K. E., Duncan, R. E., Bazinet, R. P., & Archer, M. C. (2014). Fatty acid synthase plays a role in cancer metabolism beyond providing fatty acids for phospholipid synthesis or sustaining elevations in glycolytic activity. Experimental Cell Research, 320, 302–310.
Horton, J. D., Goldstein, J. L., & Brown, M. S. (2002). SREBPs: Activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 109, 1125–1131.
Hou, W., Zhou, H., Bou Khalil, M., Seebun, D., Bennett, S. A., & Figeys, D. (2011). Lyso-form fragment ions facilitate the determination of stereospecificity of diacyl glycerophospholipids. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 25, 205–217.
Houjou, T., Yamatani, K., Imagawa, M., Shimizu, T., & Taguchi, R. (2005). A shotgun tandem mass spectrometric analysis of phospholipids with normal-phase and/or reverse-phase liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 19, 654–666.
Junot, C., Fenaille, F., Colsch, B., & Becher, F. (2014). High resolution mass spectrometry based techniques at the crossroads of metabolic pathways. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 33, 471–500.
Kasiske, B. L., De Mattos, A., Flechner, S. M., Gallon, L., Meier-Kriesche, H. U., Weir, M. R., & Wilkinson, A. (2008). Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor dyslipidemia in kidney transplant recipients. American Journal of Transplantation, 8, 1384–1392.
Kluger, B., Bueschl, C., Neumann, N., Stuckler, R., Doppler, M., Chassy, A. W., Waterhouse, A. L., Rechthaler, J., Kampleitner, N., Thallinger, G. G., Adam, G., Krska, R., & Schuhmacher, R. (2014). Untargeted profiling of tracer-derived metabolites using stable isotopic labeling and fast polarity-switching LC-ESI-HRMS. Analytical Chemistry, 86, 11533–11537.
Kofeler, H. C., FAULAND, A., RECHBERGER, G. N., & TROTZMULLER, M. (2012). Mass spectrometry based lipidomics: an overview of technological platforms. Metabolites, 2, 19–38.
Koyama, J., Taga, S., Shimizu, K., Shimizu, M., Morita, I., & Takeuchi, A. (2011). Simultaneous determination of histamine and prostaglandin D2 using an LC–ESI–MS/MS method with positive/negative ion-switching ionization modes: Application to the study of anti-allergic flavonoids on the degranulation of KU812 cells. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 401, 1385–1392.
Kwiatkowski, D. J., & Manning, B. D. (2014). Molecular basis of giant cells in tuberous sclerosis complex. The New England Journal of Medicine, 371, 778–780.
Lam, S. M., & Shui, G (2013). Lipidomics as a principal tool for advancing biomedical research. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 40, 375–390.
Li, M., Yang, L., Bai, Y., & Liu, H. (2014). Analytical methods in lipidomics and their applications. Analytical Chemistry, 86, 161–175.
Linden, M. A., Lopez, K. T., Fletcher, J. A., Morris, E. M., Meers, G. M., Siddique, S., Laughlin, M. H., Sowers, J. R., Thyfault, J. P., Ibdah, J. A., & Rector, R. S. (2015). Combining metformin therapy with caloric restriction for the management of type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese rats. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, 40, 1038–1047.
Ma, S., & Chowdhury, S. K. (2013). Data acquisition and data mining techniques for metabolite identification using LC coupled to high-resolution MS. Bioanalysis, 5, 1285–1297.
Matyash, V., Liebisch, G., Kurzchalia, T. V., Shevchenko, A., & Schwudke, D. (2008). Lipid extraction by methyl-tert-butyl ether for high-throughput lipidomics. Journal of Lipid Research, 49, 1137–1146.
Menendez, J. A., & Lupu, R (2007). Fatty acid synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nature Reviews, 7, 763–777.
Min, H. K., Lim, S., Chung, B. C., & Moon, M. H. (2011). Shotgun lipidomics for candidate biomarkers of urinary phospholipids in prostate cancer. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 399, 823–830.
Morrisett, J. D., Abdel-Fattah, G., Hoogeveen, R., Mitchell, E., Ballantyne, C. M., Pownall, H. J., Opekun, A. R., Jaffe, J. S., Oppermann, S., & Kahan, B. D. (2002). Effects of sirolimus on plasma lipids, lipoprotein levels, and fatty acid metabolism in renal transplant patients. Journal of Lipid Research, 43, 1170–1180.
Narvaez-Rivas, M., & Zhang, Q (2016). Comprehensive untargeted lipidomic analysis using core–shell C30 particle column and high field orbitrap mass spectrometer. Journal of Chromatography A, 1440, 123–134.
Nicolay, B. N., Gameiro, P. A., Tschop, K., Korenjak, M., Heilmann, A. M., Asara, J. M., Stephanopoulos, G., Iliopoulos, O., & Dyson, N. J. (2013). Loss of RBF1 changes glutamine catabolism. Genes and Development, 27, 182–196.
Peake, D. A., Yokoi, Y., Wang, J. & Huang, Y. (2013). A New Lipid Software Workflow for Processing Orbitrap-based Global Lipidomics Data in Translational and Systems Biology Research. http://www.thermoscientific.com.
Porstmann, T., Santos, C. R., Griffiths, B., Cully, M., Wu, M., Leevers, S., Griffiths, J. R., Chung, Y. L., & Schulze, A. (2008). SREBP activity is regulated by mTORC1 and contributes to Akt-dependent cell growth. Cell Metabolism, 8, 224–236.
Ricoult, S. J., & Manning, B. D. (2013). The multifaceted role of mTORC1 in the control of lipid metabolism. EMBO Reports, 14, 242–251.
Ricoult, S. J., Yecies, J. L., Ben-Sahra, I., & Manning, B. D. (2015). Oncogenic PI3K and K-Ras stimulate de novo lipid synthesis through mTORC1 and SREBP. Oncogene, 35(10), 1250–1260
Rodamer, M., Elsinghorst, P. W., Kinzig, M., Gutschow, M., & Sorgel, F. (2011). Development and validation of a liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry procedure for the quantification of sunitinib (SU11248) and its active metabolite, N-desethyl sunitinib (SU12662), in human plasma: Application to an explorative study. Journal of Chromatography B, 879, 695–706.
Rolim, A. E., Henrique-Araujo, R., Ferraz, E. G., Dultra, F. K. D. A. A., & Fernandez, L. G. (2015). Lipidomics in the study of lipid metabolism: Current perspectives in the omic sciences. Gene, 554, 131–139.
Sajic, T., Liu, Y., & Aebersold, R. (2015). Using data-independent, high-resolution mass spectrometry in protein biomarker research: perspectives and clinical applications. Proteomics Clinical Applications, 9, 307–321.
Schwudke, D., Schuhmann, K., Herzog, R., Bornstein, S. R., & Shevchenko, A. (2011). Shotgun lipidomics on high resolution mass spectrometers. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 3, a004614.
Tate, S., Larsen, B., Bonner, R., & Gingras, A. C. (2013). Label-free quantitative proteomics trends for protein–protein interactions. Journal of Proteomics, 81, 91–101.
Theodoridis, G. A., Gika, H. G., Want, E. J., & Wilson, I. D. (2012). Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry based global metabolite profiling: A review. Analytica Chimica Acta, 711, 7–16.
Tyurina, Y. Y., Domingues, R. M., Tyurin, V. A., Maciel, E., Domingues, P., Amoscato, A. A., Bayir, H., & Kagan, V. E. (2014). Characterization of cardiolipins and their oxidation products by LC-MS analysis. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids, 179, 3–10.
van der Kloet, F. M., Hendriks, M., Hankemeier, T., & Reijmers, T. (2013). A new approach to untargeted integration of high resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry data. Analytica Chimica Acta, 801, 34–42.
Vaz, F. M., Pras-Raves, M., Bootsma, A. H., & van Kampen, A. H. (2015). Principles and practice of lipidomics. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease, 38, 41–52.
Wang, C., Wang, M., & HAN, X. (2015). Applications of mass spectrometry for cellular lipid analysis. Molecular Biosystems, 11, 698–713.
Wishart, D. S., Knox, C., Guo, A. C., Eisner, R., Young, N., Gautam, B., Hau, D. D., Psychogios, N., Dong, E., Bouatra, S., Mandal, R., Sinelnikov, I., XIA, J., Jia, L., Cruz, J. A., Lim, E., Sobsey, C. A., Shrivastava, S., Huang, P., Liu, P., Fang, L., Peng, J., Fradette, R., Cheng, D., Tzur, D., Clements, M., Lewis, A., de Souza, A., Zuniga, A., Dawe, M., Xiong, Y., Clive, D., Greiner, R., Nazyrova, A., Shaykhutdinov, R., LI, L., VOGEL, H. J., & FORSYTHE, I. (2009). HMDB: a knowledgebase for the human metabolome. Nucleic Acids Research, 37, D603–D610.
Xia, J., Psychogios, N., Young, N., & Wishart, D. S. (2009). MetaboAnalyst: a web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Research, 37, W652–W660.
Xia, J., & Wishart, D. S. (2011). Web-based inference of biological patterns, functions and pathways from metabolomic data using MetaboAnalyst. Nature Protocols, 6, 743–760.
Xiao, J. F., Zhou, B., & Ressom, H. W. (2012). Metabolite identification and quantitation in LC-MS/MS-based metabolomics. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 32, 1–14.
Yamada, T., Uchikata, T., Sakamoto, S., Yokoi, Y., Fukusaki, E., & Bamba, T. (2013a). Development of a lipid profiling system using reverse-phase liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry with rapid polarity switching and an automated lipid identification software. Journal of Chromatography A, 1292, 211–218.
Yamada, T., Uchikata, T., Sakamoto, S., Yokoi, Y., Nishiumi, S., Yoshida, M., Fukusaki, E., & Bamba, T. (2013b). Supercritical fluid chromatography/Orbitrap mass spectrometry based lipidomics platform coupled with automated lipid identification software for accurate lipid profiling. Journal of Chromatography A, 1301, 237–242.
Yang, K., Jenkins, C. M., Dilthey, B., & Gross, R. W. (2015). Multidimensional mass spectrometry-based shotgun lipidomics analysis of vinyl ether diglycerides. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 407, 5199–5210.
Yecies, J. L., Zhang, H. H., Menon, S., Liu, S., Yecies, D., Lipovsky, A. I., Gorgun, C., Kwiatkowski, D. J., Hotamisligil, G. S., Lee, C. H., & Manning, B. D. (2011). Akt stimulates hepatic SREBP1c and lipogenesis through parallel mTORC1-dependent and independent pathways. Cell Metabolism, 14, 21–32.
Ying, H., Kimmelman, A. C., Lyssiotis, C. A., Hua, S., Chu, G. C., Fletcher-Sananikone, E., Locasale, J. W., Son, J., Zhang, H., Coloff, J. L., Yan, H., Wang, W., Chen, S., Viale, A., Zheng, H., PAIK, J. H., LIM, C., Guimaraes, A. R., Martin, E. S., Chang, J., Hezel, A. F., Perry, S. R., Hu, J., Gan, B., Xiao, Y., Asara, J. M., Weissleder, R., Wang, Y. A., Chin, L., Cantley, L. C., & Depinho, R. A. (2012). Oncogenic Kras maintains pancreatic tumors through regulation of anabolic glucose metabolism. Cell, 149, 656–670.
Yuan, M., Breitkopf, S. B., Yang, X., & Asara, J. M. (2012). A positive/negative ion-switching, targeted mass spectrometry-based metabolomics platform for bodily fluids, cells, and fresh and fixed tissue. Nature Protocols, 7, 872–881.
Zhang, Y., Ren, Y., Jiao, J., & Li, D. (2011). Ultra high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the simultaneous analysis of asparagine, sugars, and acrylamide in Maillard reactions. Anal Chem, 83, 3297–3304.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Daniel Tenen lab at BIDMC for providing frozen lung tissue. We also thank Simon Dillon and Towia Libermann at BIDMC for providing human plasma samples. This study was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health 5P01CA120964 (B.D.M. and J.M.A.), 5P30CA006516 (J.M.A.), and R35CA197459 (B.D.M.), from the National Science Foundation DGE-1144152 (S.R.), and the BIDMC Research Capital Fund for funding the mass spectrometry instrumentation (J.M.A.).
Author Contributions
J.M.A., Y.X., S.B.B., S.R. and D.P. developed the platform. J.M.A., MY., S.R. and S.B.B. wrote the protocol. D.P. and B.M. edited the protocol and provided insight. Y.X, S.R., S.B.B. and M.Y. prepared biological samples for testing the protocol. J.M.A., M.Y., S.B. and S.R. analyzed data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing financial interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Mouse tissue and human plasma samples were previously acquired and stored frozen by other laboratories.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Breitkopf, S.B., Ricoult, S.J.H., Yuan, M. et al. A relative quantitative positive/negative ion switching method for untargeted lipidomics via high resolution LC-MS/MS from any biological source. Metabolomics 13, 30 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1157-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1157-8