Abstract
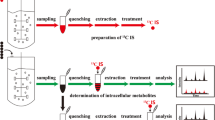
This study describes metabolite profiles of Ralstonia eutropha H16 focusing on biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), bacterial polyesters attracted as biodegradable bio-based plastics. As CoA-thioesters are important intermediates in PHA biosynthesis, four kinds of acyl-CoAs with medium chain length were prepared and used to establish analytical conditions for capillary electrophoresis-electron spray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry (CE–ESI-MS/MS). Metabolites were extracted from R. eutropha cells in growth, PHA production, and stationary phases on fructose and PHA production phase on octanoate, and subjected to stable isotope dilution-based comparative quantification by multiple reaction monitoring using CE–ESI-MS/MS and 13C-labeled metabolites prepared by extraction from R. eutropha mutant grown on U-13C6-glucose. This procedure allowed to quantify relative changes of 94 ionic metabolites including CoA-thioesters. Hexose-phosphates except for glucose 1-phosphate were decreased in the PHA production phase than in the growth phase, suggesting reduced flux of sugar degradation after the cell growth. Several intermediates in TCA cycle and gluconeogenesis were increased in the PHA production phase on octanoate. Interestingly, ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate were detected in all the samples examined, raising possibilities of CO2 fixation by Calvin–Benson–Bassham cycle in this bacterium even under heterotrophic growth conditions. Turnover of acyl moieties through β-oxidation was suggested to be active on fructose, as CoA-thioesters of C6 and C8 were detected in the fructose-grown cells. In addition, major metabolic pools in R. eutropha cells were estimated from the signal intensities. The results of the present study provided new insights into global metabolisms in PHA-producing R. eutropha.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armando, J. W., Boghigian, B. A., & Pfeifer, B. A. (2012). LC-MS/MS quantification of short-chain acyl-CoA’s in Escherichia coli demonstrates versatile propionyl-CoA synthetase substrate specificity. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 54, 140–148.
Bowien, B., & Kusian, B. (2002). Genetics and control of CO2 assimilation in the chemoautotroph Ralstonia eutropha. Archives of Microbiology, 178, 85–93.
Brigham, C. J., Budde, C. F., Holder, J. W., Zeng, Q., Mahan, A. E., Rha, C., et al. (2010). Elucidation of β-oxidation pathways in Ralstonia eutropha H16 by examination of global gene expression. Journal of Bacteriology, 192, 5454–5464.
Brigham, C. J., Speth, D. R., Rha, C., & Sinskey, A. J. (2012). Whole-genome microarray and gene deletion studies reveal regulation of the polyhydroxyalkanoate production cycle by the stringent response in Ralstonia eutropha H16. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78, 8033–8044.
Budde, C. F., Mahan, A. E., Lu, J., Rha, C., & Sinskey, A. J. (2010). Roles of multiple acetoacetyl coenzyme A reductases in polyhydroxybutyrate biosynthesis in Ralstonia eutropha H16. Journal of Bacteriology, 192, 5319–5328.
Budde, C. F., Riedel, S. L., Willis, L. B., Rha, C., & Sinskey, A. J. (2011). Production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) from plant oil by engineered Ralstonia eutropha strains. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 77, 2847–2854.
Cramm, R. (2009). Genomic view of energy metabolism in Ralstonia eutropha H16. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 16, 38–52.
Dalluge, J. J., Gort, S., Hobson, R., Selifonova, O., Amore, F., & Gokarn, R. (2002). Separation and identification of organic acid-coenzyme A thioesters using liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 374, 835–840.
Dube, G., Henrion, A., Ohlendorf, R., & Vidal, C. (2001). Application of the combination of isotope ratio monitoring with isotope dilution mass spectrometry to the determination of glucose in serum. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 15, 1322–1326.
Fong, J. C., & Schulz, H. (1981). Short-chain and long-chain enoyl-CoA hydratases from pig heart muscle. Methods in Enzymology, 71, 390–398.
Friedrich, C. G., Friedrich, B., & Bowien, B. (1981). Formation of enzymes of autotrophic metabolism during heterotrophic growth of Alcaligenes eutrophus. Journal of General Microbiology, 16, 69–78.
Fukui, T., & Doi, Y. (1997). Cloning and analysis of the poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) biosynthesis genes of Aeromonas caviae. Journal of Bacteriology, 179, 4821–4830.
Fukui, T., & Doi, Y. (1998). Efficient production of polyhydroxyalkanoates from plant oils by Alcaligenes eutrophus and its recombinant strain. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 49, 333–336.
Fukui, T., Shiomi, N., & Doi, Y. (1998). Expression and characterization of (R)-specific enoyl coenzyme A hydratase involved in polyhydroxyalkanoate biosynthesis by Aeromonas caviae. Journal of Bacteriology, 180, 667–673.
Fukusaki, E., Harada, K., Bamba, T., & Kobayashi, A. (2005). An isotope effect on the comparative quantification of flavonoids by means of methylation-based stable isotope dilution coupled with capillary liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 99, 75–77.
Harada, K., Fukusaki, E., & Kobayashi, A. (2006). Pressure-assisted capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry using combination of polarity reversion and electroosmotic flow for metabolomics anion analysis. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 101, 403–409.
Harada, K., Ohyama, Y., Tabushi, T., Kobayashi, A., & Fukusaki, E. (2008). Quantitative analysis of anionic metabolites for Catharanthus roseus by capillary electrophoresis using sulfonated capillary coupled with electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 105, 249–260.
Haywood, G. W., Anderson, A. J., Chu, L., & Daws, E. A. (1988). The role of NADH- and NADPH-linked acetoacetyl-CoA reductases in the poly-3-hydroxybutyrate synthesizing organism Alcaligenes eutrophus. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 52, 259–264.
Kaddor, C., & Steinbüchel, A. (2011). Effects of homologous phosphoenolpyruvate-carbohydrate phosphotransferase system proteins on carbohydrate uptake and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) accumulation in Ralstonia eutropha H16. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 77, 3582–3590.
Kahar, P., Tsuge, T., Taguchi, K., & Doi, Y. (2004). High yield production of polyhydroxyalkanoates from soybean oil by Ralstonia eutropha and its recombinant strain. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 83, 79–86.
Kawashima, Y., Cheng, W., Mifune, J., Orita, I., Nakamura, S., & Fukui, T. (2012). Characterization and functional analyses of R-specific enoyl coenzyme A hydratases in polyhydroxyalkanoate-producing Ralstonia eutropha. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78, 493–502.
Kim, J. K., Harada, K., Bamba, T., Fukusaki, E., & Kobayashi, A. (2005). Stable isotope dilution-based accurate comparative quantification of nitrogen-containing metabolites in Arabidopsis thaliana T87 cells using in vivo 15N-isotope enrichment. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 69, 1331–1340.
King, R., Bonfiglio, R., Fernandez-Metzler, C., Miller-Stein, C., & Olah, T. (2000). Mechanistic investigation of ionization suppression in electrospray ionization. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 11, 942–950.
Lenz, O., Ludwig, M., Schubert, T., Burstel, I., Ganskow, S., Goris, T., et al. (2010). H2 conversion in the presence of O2 as performed by the membrane-bound [NiFe]-hydrogenase of Ralstonia eutropha. ChemPhysChem, 11, 1107–1119.
Lindenkamp, N., Peplinski, K., Volodina, E., Ehrenreich, A., & Steinbüchel, A. (2010). Impact of multiple β-ketothiolase deletion mutations in Ralstonia eutropha H16 on the composition of 3-mercaptopropionic acid-containing copolymers. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76, 5373–5382.
Madison, L. L., & Huisman, G. W. (1999). Metabolic engineering of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates): from DNA to plastic. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 63, 21–53.
Magnes, C., Sinner, F. M., Regittnig, W., & Pieber, T. R. (2005). LC/MS/MS method for quantitative determination of long-chain fatty acyl-CoAs. Analytical Chemistry, 77, 2889–2894.
Magnes, C., Suppan, M., Pieber, T. R., Moustafa, T., Trauner, M., Haemmerle, G., et al. (2008). Validated comprehensive analytical method for quantification of coenzyme A activated compounds in biological tissues by online solid-phase extraction LC/MS/MS. Analytical Chemistry, 80, 5736–5742.
Matsusaki, H., Abe, H., Taguchi, K., Fukui, T., & Doi, Y. (2000). Biosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyalkanoates) by recombinant bacteria expressing the PHA synthase gene phaC1 from Pseudomonas sp. 61-3. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 53, 401–419.
Mifune, J., Nakamura, S., & Fukui, T. (2008). Targeted engineering of Cupriavidus necator chromosome for biosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) from vegetable oil. Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 86, 621–627.
Mifune, J., Nakamura, S., & Fukui, T. (2010). Engineering of pha operon on Cupriavidus necator chromosome for efficient biosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) from vegetable oil. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 95, 1305–1312.
Mooney, B. P. (2009). The second green revolution? Production of plant-based biodegradable plastics. The Biochemical Journal, 418, 219–232.
Müller, C., Schäfer, P., Störtzel, M., Vogt, S., & Weinmann, W. (2002). Ion suppression effects in liquid chromatography-electrospray-ionisation transport-region collision induced dissociation mass spectrometry with different serum extraction methods for systematic toxicological analysis with mass spectra libraries. Journal of Chromatography B, 773, 47–52.
Nomura, C. T., et al. (2005). Expression of 3-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein reductase (fabG) genes enhances production of polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer from glucose in recombinant Escherichia coli JM109. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 4297–4306.
Peplinski, K., Ehrenreich, A., Döring, C., Bömeke, M., Reinecke, F., Hutmacher, C., et al. (2010). Genome-wide transcriptome analyses of the ‘Knallgas’ bacterium Ralstonia eutropha H16 with regard to polyhydroxyalkanoate metabolism. Microbiology, 156, 2136–2152.
Pohlmann, A., Fricke, W. F., Reinecke, F., Kusian, B., Liesegang, H., Cramm, R., et al. (2006). Genome sequence of the bioplastic-producing “Knallgas” bacterium Ralstonia eutropha H16. Nature Biotechnology, 24, 1257–1262.
Putri, S. P., Nakayama, Y., Matsuda, F., Uchikata, T., Kobayashi, S., Matsubara, A., et al. (2013a). Current metabolomics: Practical applications. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 115, 579–589.
Putri, S. P., Yamamoto, S., Tsugawa, H., & Fukusaki, E. (2013b). Current metabolomics: Technological advances. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 116, 9–16.
Rehm, B. H. (2003). Polyester synthases: natural catalysts for plastics. The Biochemical Journal, 376, 15–33.
Riedel, S. L., Bader, J., Brigham, C. J., Budde, C. F., Yusof, Z. A., Rha, C., et al. (2012). Production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) by Ralstonia eutropha in high cell density palm oil fermentations. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 109, 74–83.
Shimizu, R., Chou, K., Orita, I., Suzuki, Y., Nakamura, S., & Fukui, T. (2013). Detection of phase-dependent transcriptomic changes and Rubisco-mediated CO2 fixation into poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) under heterotrophic condition in Ralstonia eutropha H16 based on RNA-seq and gene deletion analyses. BMC microbiology, in press.
Soga, T., Ohashi, Y., Ueno, Y., Naraoka, H., Tomita, M., & Nishioka, T. (2003). Quantitative metabolome analysis using capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry. Journal of Proteome Research, 2, 488–494.
Soga, T., Ueno, Y., Naraoka, H., Matsuda, K., Tomita, M., & Nishioka, T. (2002a). Pressure-assisted capillary electrophoresis electrospray ionization mass spectrometry for analysis of multivalent anions. Analytical Chemistry, 74, 6224–6229.
Soga, T., Ueno, Y., Naraoka, H., Ohashi, Y., Tomita, M., & Nishioka, T. (2002b). Simultaneous determination of anionic intermediates for Bacillus subtilis metabolic pathways by capillary electrophoresis electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 74, 2233–2239.
Steinbüchel, A., & Lütke-Eversloh, T. (2003). Metabolic engineering and pathway construction for biotechnological production of relevant polyhydroxyalkanoates in microorganisms. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 16, 81–96.
Stitt, M., & Fernie, A. R. (2003). From measurements of metabolites to metabolomics: an ‘on the fly’ perspective illustrated by recent studies of carbon-nitrogen interactions. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 14, 136–144.
Sudesh, K., Abe, H., & Doi, Y. (2000). Synthesis, structure and properties of polyhydroxyalkanoates: biological polyesters. Progress in Polymer Science, 25, 1503–1555.
Sudesh, K., Bhubalan, K., Chuah, J. A., Kek, Y. K., Kamilah, H., Sridewi, N., et al. (2011). Synthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoate from palm oil and some new applications. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 89, 1373–1786.
Sumner, L. W., Amberg, A., Barrett, D., Beale, M. H., Beger, R., Daykin, C. A., et al. (2007). Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. Metabolomics, 3, 211–221.
Timm, A., & Steinbuchel, A. (1992). Cloning and molecular analysis of the poly(3-hydroxyalkanoic acid) gene locus of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. European Journal of Biochemistry, 209, 15–30.
Tsuge, T., Taguchi, K., Seiichi, T., & Doi, Y. (2003). Molecular characterization and properties of (R)-specific enoyl-CoA hydratases from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: metabolic tools for synthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates via fatty acid β-oxidation. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 31, 195–205.
Valentin, H. E., & Steinbüchel, A. (1994). Application of enzymatically synthesized short-chain-length hydroxy fatty-acid coenzyme-A thioesters for assay of polyhydroxyalkanoic acid synthases. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 40, 699–709.
Yang, S., Sadilek, M., Synovec, R. E., & Lidstrom, M. E. (2009). Liquid chromatography-tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry and comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry measurement of targeted metabolites of Methylobacterium extorquens AM1 grown on two different carbon sources. Journal of Chromatography A, 1216, 3280–3289.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by KAKENHI (Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research) on Priority Areas “Applied Genomics” from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukui, T., Chou, K., Harada, K. et al. Metabolite profiles of polyhydroxyalkanoate-producing Ralstonia eutropha H16. Metabolomics 10, 190–202 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-013-0567-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-013-0567-0