Abstract
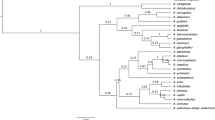
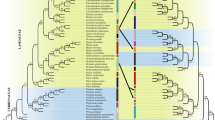
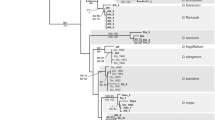
Given the difficulties for rapid biodiversity assessments in understudied regions, DNA barcoding appears as a suitable alternative. Still, this approach relies heavily on accurate reference sequence databases for correct taxonomic assignments. In this study, we evaluated the effectiveness of matK, rbcL, and ITS regions for the identification of Myrtaceae species with emphasis on the megadiverse genus Syzygium from Sumatra, Indonesia; and analyzed the applicability of species-tree inference for species assignment using barcode markers. ITS was the most variable barcode region (42.6% of variable sites), followed by matK (25.7%), and rbcL (14.9%). In terms of assignments of sequences using the BLAST algorithm, all markers were effective for genus-level attribution. For assignments at species rank, rbcL was able to attribute 30.15% of the samples at the species level, followed by matK (26.47%), and ITS (17.21%). These results are largely related to the availability of reference sequences for Myrtaceae in the databases since for the 27 species analyzed in this study, only 8 species had reference sequences for all three barcode regions available in GenBank. The species-tree inference based on the combination of matK, rbcL, and ITS markers recovered 41% of the species as monophyletic clades with strong node support. Due to its high level of differentiation, we recommend the ITS region as the most efficient barcode marker for the identification of Syzygium, and the traditional core-barcodes (matK + rbcL) as add-on barcodes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
22 July 2022
Handling editor name correction.
References
Álvarez I (2003) Ribosomal ITS sequences and plant phylogenetic inference. Mol Phylogenet Evol 29(3):417–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1055-7903(03)00208-2
Amandita FY, Rembold K, Vornam B, Rahayu S, Siregar IZ, Kreft H, Finkeldey R (2019) DNA barcoding of flowering plants in Sumatra. Indonesia Ecol Evol 9(4):1858–1868. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.4875
Barbosa LCA, Silva CJ, Teixeira RR, Meira RMSA, Pinheiro AL (2013) Chemistry and biological activities of essential oils from Melalueca L. species. Agric Conspec Sci 78(1):11–13
Barthlott W, Rafiqpoor D, Kier G, Kreft H (2005) Global centers of vascular plant diversity. Nova Acta Leopold 92(342):61–83
Bello A, Daru BH, Stirton CH, Chimphango SBM, van der Bank M, Maurin O, Muasya AM (2015) DNA barcodes reveal microevolutionary signals in fire response trait in two legume genera. AoB Plants 7:plv124. https://doi.org/10.1093/aobpla/plv124
Besse P (2021) Molecular plant taxonomy: Methods and protocols (Vol. 2222). Springer, US. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0997-2
Biffin E, Lucas EJ, Craven LA, Ribeiro da Costa I, Harrington MG, Crisp MD (2010) Evolution of exceptional species richness among lineages of fleshy-fruited Myrtaceae. Ann Bot 106(1):79–93. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcq088
Binghong X, Chunyan L, Xinlan X, Zhifang X, Liyun Z, Haibo T, Shengxiang Q, Caixia A, Shiquan L, Xiongyao H, Jian C, Lian L, Li T, Shujun Y (2019) Collection and utilization of germplasm resources of Myrtaceae wild plants in China. J Plant Sci 7(6):151–157. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.jps.20190706.14
Bozzuto C, Blackenhorn WU (2017) Taxonomic resolution and treatment effects – alone and combined – can mask significant biodiversity reductions. Int J Biodivers Sci Ecosyst Serv Manag 13(1):86–99. https://doi.org/10.1080/21513732.2016.1260638
Brambach F, Byng JW, Culmsee H (2017) Five new species of Syzygium (Myrtaceae) from Sulawesi, Indonesia. PhytoKeys 81:47–78. https://doi.org/10.3897/phytokeys.81.13488
CBOL Plant Working Group (2009) A DNA barcode for land plants. PNAS 106(31):12794–12797. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0905845106
Chandra R, Mishra M (2007) Biotechnological interventions for improvement of guava (Psidium guajava L.). Acta Hortic. 735:117–125. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2007.735.15
Chase MW, Fay MF (2009) Barcoding of plants and fungi. Science 325(5941):682–683. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1176906
Chen S, Yao H, Han J, Liu C, Song J, Shi L, Zhu Y, Ma X, Gao T, Pang X, Luo K, Li Y, Li X, Jia X, Lin Y, Leon C (2010) Validation of the ITS2 region as a novel DNA barcode for identifying medicinal plant species. PLoS ONE 5(1):e8613. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0008613
Chen Q, Wu X, Zhang D (2020) Comparison of the abilities of universal, super, and specific DNA barcodes to discriminate among the original species of Fritillariae cirrhosae bulbus and its adulterants. PLoS ONE 15(2):e0229181. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0229181
China Plant BOL Group, Li DZ, Gao LM, Li HT, Wang H, Ge XJ, Liu JQ, Chen ZD, Zhou SL, Chen SL et al (2011) Comparative analysis of a large dataset indicates that internal transcribed spacer (ITS) should be incorporated into the core barcode for seed plants. PNAS 108(49):19641–19646. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1104551108
Colpaert N, Cavers S, Bandou E, Caron H, Gheysen G, Lowe AJ (2005) Sampling tissue for DNA analysis of trees: trunk cambium as an alternative to canopy leaves. Silvae Genet 54(1–6):265–269. https://doi.org/10.1515/sg-2005-0038
Cribb R, Ford M (2009) Indonesia as an Archipelago: managing islands, managing the seas. In Indonesia beyond the water’s edge (pp. 1–27). ISEAS Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1355/9789812309815-005
Culmsee H, Pitopang R, Mangopo H, Sabir S (2011) Tree diversity and phytogeographical patterns of tropical high mountain rain forests in Central Sulawesi, Indonesia. Biodivers Conserv 20(5):1103–1123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-011-0019-y
de Vere N, Rich TCG, Ford CR, Trinder SA, Long C, Moore CW, Satterthwaite D, Davies H, Allainguillaume J, Ronca S, Tatarinova T, Garbett H, Walker K, Wilkinson MJ (2012) DNA barcoding the native flowering plants and conifers of wales. PLoS ONE 7(6):e37945. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0037945
DeSalle R, Goldstein P (2019) Review and interpretation of trends in DNA barcoding. Front Ecol Evol 7:302. https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2019.00302
Drummond AJ, Suchard MA, Xie D, Rambaut A (2012) Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol Biol Evol 29(8):1969–1973. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mss075
El-Saber Batiha G, Alkazmi LM, Wasef LG, Beshbishy AM, Nadwa EH, Rashwan EK (2020) Syzygium aromaticum L. (Myrtaceae): Traditional uses, bioactive chemical constituents, pharmacological and toxicological activities. Biomolecules 10(2):202. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020202
Ely VC, de Loreto Bordignon SA, Trevisan R, Boldrini II (2017) Implications of poor taxonomy in conservation. J Nat Conserv 36:10–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnc.2017.01.003
Farooq Q, Shakir M, Ejaz F, Zafar T, Durrani K, Ullah A (2020) Role of DNA Barcoding in plant biodiversity conservation. Sch Int J Biochem 03(03):48–52. https://doi.org/10.36348/sijb.2020.v03i03.002
Feng S, Jiang M, Shi Y, Jiao K, Shen C, Lu J, Ying Q, Wang H (2016) Application of the Ribosomal DNA ITS2 region of Physalis (Solanaceae): DNA barcoding and phylogenetic study. Front Plant Sci 7:1047. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01047
Forest Watch Indonesia (FWI) (2002) The state of forest: Indonesia. World Resources Institute. https://fwi.or.id/publikasi/. Accessed 6 Feb 2021
Forest Watch Indonesia (FWI) (2020) Deforestation journey of Indonesia "A critical note on natural forest loss in Indonesia" (in Bahasa); (Ministry of Environment and Forestry's presentation at the 9th West Merdeka Forum discussion). Forest Watch Indonesia (FWI) website. https://fwi.or.id/publikasi/. Accessed 6 Feb 2021
Francis CM, Borisenko AV, Ivanova NV, Eger JL, Lim BK, Guillén-Servent A, Kruskop SV, Mackie I, Hebert PDN (2010) The Role of DNA barcodes in understanding and conservation of mammal diversity in Southeast Asia. PLoS ONE 5(9):e12575. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0012575
Gamage DT, de Silva MP, Inomata N, Yamazaki T, Szmidt AE (2006) Comprehensive molecular phylogeny of the sub-family Dipterocarpoideae (Dipterocarpaceae) based on chloroplast DNA sequences. Genes Genet Syst 81(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1266/ggs.81.1
Gómez-Rubio V (2017) ggplot2—Elegant graphics for data analysis (2nd Edition). J. Stat. Softw. 77(Book Review 2) https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v077.b02
Gonzalez MA, Baraloto C, Engel J, Mori SA, Pétronelli P, Riéra B, Roger A, Thébaud C, Chave J (2009) Identification of Amazonian trees with DNA barcodes. PLoS ONE 4(10):e7483. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0007483
Govaerts, R Sobral M, Ashton P, Barrie F, Holst BK, Landrum LL, Matsumoto K, Fernanda Mazine F, Nic Lughadha E, Proenca C, Soares-Silva LH, Wilson PG, Lucas, E (2021) World Checklist of Myrtaceae. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Published on the Internet; http://wcsp.science.kew.org/. Retrieved 28 March 2021
Government of Indonesia (2003) Tropical rainforest heritage of Sumatra. Published on Internet; https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1167/. Retrieved 01 July 2021
Hajibabaei M, Singer GAC, Hebert PDN, Hickey DA (2007) DNA barcoding: how it complements taxonomy, molecular phylogenetics and population genetics. Trends Genet 23(4):167–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2007.02.001
Hartvig I, Czako M, Kjær ED, Nielsen LR, Theilade I (2015) The use of DNA barcoding in identification and conservation of Rosewood (Dalbergia spp.). PLoS ONE 10(9):e0138231. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138231
Hollingsworth ML, Andra CA, Forrest LL, Richardson J, Pennington RT, Long DG, Cowan R, Chase MW, Gaudeul M, Hollingsworth PM (2009) Selecting barcoding loci for plants: evaluation of seven candidate loci with species-level sampling in three divergent groups of land plants: DNA barcoding. Mol Ecol Resour 9(2):439–457. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2008.02439.x
Hollingsworth PM, Graham SW, Little DP (2011) Choosing and using a plant DNA barcode. PLoS ONE 6(5):e19254. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019254
Hosseinzadeh-Colagar A, Haghighatnia MJ, Amiri Z, Mohadjerani M, Tafrihi M (2016) Microsatellite (SSR) amplification by PCR usually led to polymorphic bands: Evidence which shows replication slippage occurs in extend or nascent DNA strands. Mol Biol Res Commun 5(3):167–174. https://doi.org/10.22099/MBRC.2016.3789
Jaén-Molina R, Marrero-Rodríguez Á, Reyes-Betancort JA, Santos-Guerra A, Naranjo-Suárez J, Caujapé-Castells J (2015) Molecular taxonomic identification in the absence of a ‘barcoding gap’: A test with the endemic flora of the Canarian oceanic hotspot. Mol Ecol Resour 15(1):42–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12292
Jansson R, Davies TJ (2007) Global variation in diversification rates of flowering plants: Energy vs. climate change: Diversification rates of flowering plants. Ecol Lett 11(2):173–183. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01138.x
Kang Y, Deng Z, Zang R, Long W (2017) DNA barcoding analysis and phylogenetic relationships of tree species in tropical cloud forests. Sci Rep 7(1):12564. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13057-0
Kesharwani V, Gupta S, Kushwaha N, Kesharwani R, Patel DKM (2018) A review on therapeutics application of Eucalyptus oil. Int J Herb Med 6(6):110–115
Kress WJ, Erickson DL (2007) A two-locus global DNA barcode for landplants: the coding rbcL gene complements the non-coding trnH-psbA spacer region. PLoS ONE 2(6):e508. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0000508
Kress WJ, Wurdack KJ, Zimmer EA, Weigt LA, Janzen DH (2005) Use of DNA barcodes to identify flowering plants. PNAS 102(23):8369–8374. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0503123102
Kress WJ, Erickson DL, Jones FA, Swenson NG, Perez R, Sanjur O, Bermingham E (2009) Plant DNA barcodes and a community phylogeny of a tropical forest dynamics plot in Panama. PNAS 106(44):18621–18626. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0909820106
Kress WJ, García-Robledo C, Uriarte M, Erickson DL (2015) DNA barcodes for ecology, evolution, and conservation. Trends Ecol Evol 30(1):25–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2014.10.008
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Lahaye R, van der Bank M, Bogarin D, Warner J, Pupulin F, Gigot G, Maurin O, Duthoit S, Barraclough TG, Savolainen V (2008) DNA barcoding the floras of biodiversity hotspots. PNAS 105(8):2923–2928. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0709936105
Laumonier Y, Uryu Y, Stüwe M, Budiman A, Setiabudi B, Hadian O (2010) Eco-floristic sectors and deforestation threats in Sumatra: identifying new conservation area network priorities for ecosystem-based land use planning. Biodivers Conserv 19(4):1153–1174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-010-9784-2
Leigh EG Jr, Davidar P, Dick CW, Puyravaud JP, Terborgh J, Steege H, Wright SJ (2004) Why do some tropical forests have so many species of trees? Biotropica 36(4):447–473. https://doi.org/10.1646/1607
Li FW, Kuo LY, Rothfels CJ, Ebihara A, Chiou WL, Windham MD, Pryer KM (2011) rbcL and matK earn two thumbs up as the core DNA barcode for ferns. PLoS ONE 6(10):e26597. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0026597
Li X, Yang Y, Henry RJ, Rossetto M, Wang Y, Chen S (2015) Plant DNA barcoding: from gene to genome: plant identification using DNA barcodes. Biol Rev 90(1):157–166. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12104
Lis JA, Lis B, Ziaja DJ (2016) In BOLD we trust? A commentary on the reliability of specimen identification for DNA barcoding: a case study on burrower bugs (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Cydnidae). Zootaxa 4114(1):83. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4114.1.6
Liu J, Yan HF, Newmaster SG, Pei N, Ragupathy S, Ge XJ (2015) The use of DNA barcoding as a tool for the conservation biogeography of subtropical forests in China. Divers Distrib 21(2):188–199. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddi.12276
Low YW, Rajaraman S, Tomlin CM, Ahmad JA, Ardi WH, Armstrong K, Athen P, Berhaman A, Bone RE, Cheek M, Cho NRW, Choo LM, Cowie ID, Crayn D, Fleck S et al (2021) Genomic insights into rapid speciation within the world’s largest tree genus. Res Sq. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-969304/v1
Luo K, Chen S, Chen K, Song J, Yao H, Ma X, Zhu Y, Pang X, Yu H, Li X, Liu Z (2010) Assessment of candidate plant DNA barcodes using the Rutaceae family. Sci China Life Sci 53(6):701–708. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-010-4009-1
Maimunah S, Capilla B, Armadiyanto Harrison M (2019) Tree diversity and forest composition of a Bornean heath forest, Indonesia. IOP Conf Ser.: Earth Environ Sci 270:012028. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/270/1/012028
Margono BA, Potapov PV, Turubanova S, Stolle F, Hansen MC (2014) Primary forest cover loss in Indonesia over 2000–2012. Nat Clim Change 4:730–735. https://doi.org/10.1038/NCLIMATE2277
Martin PR, McKay JK (2004) Latitudinal variation in genetic divergence of populations and the potential for future speciation. Evol 58(5):938–945. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0014-3820.2004.tb00428.x
Massante JC, Götzenberger L, Takkis K, Hallikma T, Kaasik A, Laanisto L, Hutchings MJ, Gerhold P (2019) Contrasting latitudinal patterns in phylogenetic diversity between woody and herbaceous communities. Sci Rep 9(1):6443. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42827-1
Meiklejohn KA, Damaso N, Robertson JM (2019) Assessment of BOLD and GenBank – their accuracy and reliability for the identification of biological materials. PLoS ONE 14(6):e0217084. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0217084
Meyer CP, Paulay G (2005) DNA barcoding: Error rates based on comprehensive sampling. PLoS Biol 3(12):e422. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0030422
Miller MA, Pfeiffer W, Schwartz T (2010) Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. 2010 Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/GCE.2010.5676129
Mishra P, Kumar A, Nagireddy A, Shukla AK, Sundaresan V (2017) Evaluation of single and multilocus DNA barcodes towards species delineation in complex tree genus Terminalia. PLoS ONE 12(8):e0182836. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0182836
Mittelbach GG, Schemske DW, Cornell HV, Allen AP, Brown JM, Bush MB, Harrison SP, Hurlbert AH, Knowlton N, Lessios HA, McCain CM, McCune AR, McDade LA, McPeek MA, Near TJ, Price TD, Ricklefs RE, Roy K, Sax DF, Schluter D, Sobel JM, Turelli M (2007) Evolution and the latitudinal diversity gradient: Speciation, extinction and biogeography. Ecol Lett 10(4):315–331. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01020.x
Moura CCM, Brambach F, Jair Hernandez Bado K, Krutovsky KV, Kreft H, Tjitrosoedirdjo SS, Siregar IZ, Gailing O (2019) Integrating DNA barcoding and traditional taxonomy for the identification of Dipterocarps in remnant lowland forests of Sumatra. Plants 8(11):461. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8110461
Mudiana D (2016) Syzygium diversity in Gunung Baung, East Java, Indonesia. Biodiversitas 17(2):733–740. https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d170248
Musthafa KS, Sianglum W, Saising J, Lethongkam S, Voravuthikunchai SP (2017) Evaluation of phytochemicals from medicinal plants of Myrtaceae family on virulence factor production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. APMIS 125(5):482–490. https://doi.org/10.1111/apm.12672
Newmaster SG, Fazekas AJ, Steeves RAD, Janovec J (2008) Testing candidate plant barcode regions in the Myristicaceae. Mol Ecol Resour 8(3):480–490. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.02002.x
Packer L, Gibbs J, Sheffield C, Hanner R (2009) DNA barcoding and the mediocrity of morphology. Mol Ecol Resour 9:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2009.02631.x
Parmentier I, Duminil J, Kuzmina M, Philippe M, Thomas DW, Kenfack D, Chuyong GB, Cruaud C, Hardy OJ (2013) How effective are DNA barcodes in the identification of african rainforest trees? PLoS ONE 8(4):e54921. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0054921
Pentinsaari M, Ratnasingham S, Miller SE, Hebert PDN (2020) BOLD and GenBank revisited – do identification errors arise in the lab or in the sequence libraries? PLoS ONE 15(4):e0231814. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0231814
Piredda R, Simeone MC, Attimonelli M, Bellarosa R, Schirone B (2011) Prospects of barcoding the Italian wild dendroflora: Oaks reveal severe limitations to tracking species identity. Mol Ecol Resour 11(1):72–83. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2010.02900.x
Porter TM, Hajibabaei M (2018) Over 2.5 million COI sequences in GenBank and growing. PLoS ONE 13(9):e0200177. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0200177
Purwaningsih, Kartawinata K (2018) Species composition and structure of forests in the Muara Kendawangan nature reserve, West-Kalimantan, Indonesia. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 166:012005. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/166/1/012005
Raven PH, Axelrod DI (1974) Angiosperm biogeography and past continental movements. Ann Missouri Bot Gard 61(3):539. https://doi.org/10.2307/2395021
Ray R, Chattopadhyay B, Garg KM, Ramachandra T, Ray A (2020) Western Ghats Myrtaceae are not Gondwana elements but likely dispersed from South-east Asia. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.12.037960
Rembold K, Mangopo H, Tjitrosoedirdjo SS, Kreft H (2017) Plant diversity, forest dependency, and alien plant invasions in tropical agricultural landscapes. Biol Conserv 213:234–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2017.07.020
Rosleine D, Choesin DN, Sulistyawati E (2006) The contribution of dominant tree species to nutrient cycling in a mixed forest ecosystem on mount Tangkubanperahu, West Java, Indonesia. ICMNS. Published on Internet; https://sith.itb.ac.id/ Retrieved 25 June 2021
Rye BL (1979) Chromosome number variation in the Myrtaceae and its taxonomic implications. Aust J Bot 27(5):547. https://doi.org/10.1071/BT9790547
Sass C, Little DP, Stevenson DWm, Specht CD (2007) DNA barcoding in the Cycadales: testing the potential of proposed barcoding markers for species identification of Cycads. PLoS ONE 2(11):e1154. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001154
Schmitz-Linneweber C, Maier RM, Alcaraz JP, Cottet A, Herrmann RG, Mache R (2001) The plastid chromosome of spinach (Spinacia oleracea): Complete nucleotide sequence and gene organization. Plant Mol Biol 45:307–315
Selvaraj D, Park JI, Chung MY, Cho YG, Ramalingam S, Nou IS (2013) Utility of DNA Barcoding for plant biodiversity conservation. Plant Breed Biotechnol 1(4):320–332. https://doi.org/10.9787/PBB.2013.1.4.320
Singh N, Meena B, Pal AK, Roy RK, Tewari SK, Tamta S, Rana TS (2017) Nucleotide diversity and phylogenetic relationships among Gladiolus cultivars and related taxa of family Iridaceae. J Genet 96(1):135–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-017-0755-1
Soberon J, Medellín RA (2007) Categorization systems of threatened species. Conserv Biol 21(5):1366–1367. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1739.2007.00784.x
Stace CA (2005) Plant taxonomy and biosystematics—Does DNA provide all the answers? Taxon 54(4):999–1007. https://doi.org/10.2307/25065484
Syzygium Working Group (SYZWG), Ahmad B, Baider C, Bernardini B, Biffin E, Brambach F, Burslem D, Byng JW, Christenhusz M, Florens FBV, Lucas E, Ray A, Ray R, Smets E, Snow N, Strijk JS, Wilson PG (2016) Syzygium (Myrtaceae): Monographing a taxonomic giant via 22 coordinated regional revisions. PeerJ Prepr 4:e1930v1. https://doi.org/10.7287/peerj.preprints.1930v1
Taberlet P, Gielly L, Pautou G, Bouvet J (1991) Universal primers for amplification of three non-coding regions of chloroplast DNA. Plant Mol Biol 17(5):1105–1109. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00037152
Tamura K (1992) Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions when there are strong transition-transversion and G+C-content biases. Mol Biol Evol. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040752
Thornhill AH, Ho SYW, Külheim C, Crisp MD (2015) Interpreting the modern distribution of Myrtaceae using a dated molecular phylogeny. Mol Phylogenetics Evol 93:29–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2015.07.007
Tripathi AM, Tyagi A, Kumar A, Singh A, Singh S, Chaudhary LB, Roy S (2013) The internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region and trnhH-psbA are suitable candidate loci for DNA barcoding of tropical tree species of India. PLoS ONE 8(2):e57934. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0057934
Vasconcelos TNC, Proença CEB, Ahmad B, Aguilar DS, Aguilar R, Amorim BS, Campbell K, Costa IR, De-Carvalho PS, Faria JEQ, Giaretta A, Kooij PW, Lima DF, Mazine FF, Peguero B, Prenner G, Santos MF, Soewarto J, Wingler A, Lucas EJ (2017) Myrteae phylogeny, calibration, biogeography and diversification patterns: Increased understanding in the most species rich tribe of Myrtaceae. Mol Phylogenet Evol 109:113–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2017.01.002
Waugh J (2007) DNA barcoding in animal species: progress, potential and pitfalls. BioEssays 29(2):188–197. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.20529
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols (pp. 315–322). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-372180-8.50042-1
Widodo P (2007) Speciation in the myrtle family (Myrtaceae): rapid and slow models. Biodiversitas 8(01):79–82
Widodo P, Chikmawati T (2016) Six new species of Syzygium (Myrtaceae) from Sumatra. Edinb J Bot 73(3):277–289. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0960428616000111
Widodo P, Lucas E (2018) Two new species of Syzygium (Myrtaceae) from north and west Sumatra. Kew Bull 73(4):47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12225-018-9770-5
Williamson DF (1989) The box plot: A simple visual method to interpret data. Ann Intern Med 110(11):916. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-110-11-916
Wilson PG (2011) Myrtaceae. In: Kubitzki K (ed) The families and genera of vascular plants, vol X. Flowering plants Eudicots: Sapindales, Cucurbitales. Myrtaceae. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, pp 212–271
Wilson PG, O’Brien MM, Heslewood MM, Quinn CJ (2005) Relationships within Myrtaceae sensu lato based on a matK phylogeny. Plant Syst Evol 251(1):3–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-004-0162-y
Wright JS (2002) Plant diversity in tropical forests: A review of mechanisms of species coexistence. Oecologia 130(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420100809
Wu CT, Hsieh CC, Lin WC, Tang CY, Yang CH, Huang YC, Ko YJ (2013) Internal transcribed spacer sequence-based identification and phylogenic relationship of I-Tiao-Gung originating from Flemingia and Glycine (Leguminosae) in Taiwan. J Food Drug Anal 21(4):356–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2013.08.002
Yang Z (1994) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic estimation from DNA sequences with variable rates over sites: Approximate methods. J Mol Evol 39(3):306–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00160154
Yang HQ, Dong YR, Gu ZJ, Liang N, Yang JB (2012) A preliminary assessment of matK, rbcL and trnH-psbA as DNA barcodes for Calamus (Arecaceae) species in China with a note on ITS. Ann Bot Fenn 49(5–6):319–330. https://doi.org/10.5735/085.049.0603
Yulisma A, Thomy Z, Harnelly E (2018) phylogenetic relationships within families Myrtaceae in Tripa peat swamp forest using internal transcribed spacer (ITS). Natural 18(2):65–71. https://doi.org/10.24815/jn.v18i2.10105
Zhang J, An M, Wu H, Stanton R, Lemerle D (2010) Chemistry and bioactivity of Eucalyptus essential oils. Allelopathy J 25(2):313–330
Zhang CY, Wang FY, Yan HF, Hao G, Hu CM, Ge XJ (2012) Testing DNA barcoding in closely related groups of Lysimachia L. (Myrsinaceae): DNA barcoding of Lysimachia. Mol Ecol Resour 12(1):98–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2011.03076.x
Acknowledgements
We thank Katja Rembold and the EFForTS B06/B14 field and herbarium teams for sampling and management of Myrtaceae specimens. Furthermore, we acknowledge our technicians Gudrun Diederich, Larissa Kunz, and Oleksandra Dolynska for their assistance with DNA isolation, amplification, and sequencing. Moreover, we appreciate the Ministry of Research and, Technology (RISTEK)/Agency for Research and Innovation (BRIN) of the Republic of Indonesia (RISTEKDIKTI) for permitting us to perform the research in Indonesia, and recognize the support of the German Research Foundation. We thank the two anonymous reviewers for contributing with valuable comments to our manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the German Research Foundation (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, DFG) as part of the EFForTS project (Collaborative Research Centre 990, https://www.uni-goettingen.de/efforts), project number 192626868.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Development of concept, all authors; Sampling preparation and specimen processing, F.Y.A., I.Z.S, C.C.M.M. and F.B; Bioinformatics analysis, R.W., F.Y.A., and C.C.M.M.; Data curation, R.W., F.Y.A., C.C.M.M. and F.B.; Original draft preparation, R.W. and C.C.M.M.; Review and editing, all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Data Archiving Statement
All sequences used in this study have been submitted to GenBank (NCBI), accession numbers are MT864746 to MW854235 (details in Table S1).
Additional information
Communicated by G.G. Vendramin
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wati, R., Amandita, F.Y., Brambach, F. et al. Filling gaps of reference DNA barcodes in Syzygium from rainforest fragments in Sumatra. Tree Genetics & Genomes 18, 6 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-022-01536-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-022-01536-z